The onion began to turn yellow what to do. When to harvest onions. Fungal diseases and control methods
Onion is a widely popular plant that is grown by all gardeners. Even if the plot is very small or it's just a flower bed, onion lovers will still find a place for a couple of rows of onions. And in this case, it is especially important to get a quality crop. After all, quite often the onions in the garden begin to turn yellow and do not grow, so you need to know what to do if this happens even before the harvest season.
Reasons why onions turn yellow
- onion moth;
- nematode;
- onion fly;
- secretive proboscis;
- thrips.
To prevent onion damage by these insects, it is recommended to plant it every year in a new place. You can return to the first bed only after four years.
In order not to breed an onion fly, onions should be planted as early as possible and not far from the carrots. Feed the onion beds with a mixture of pepper and tobacco dust. Top dressing is carried out at a time when the dandelion blooms. To combat the flies that have already settled, pour the bulbs (but not feathers and beds) with a salt solution at the rate of 200 g per bucket of water.
They get rid of the appeared onion moth and the secretive proboscis by completely removing the remnants of the upper shoots of the onion from the site and deep digging the site immediately before frost.
So that the onion does not turn yellow due to damage by nematodes and thrips, before planting, lower it for 10 minutes in hot water.
Calendula and marigolds planted between the rows of onions repel pests with their aroma.
Prevention of onion diseases leading to yellowing
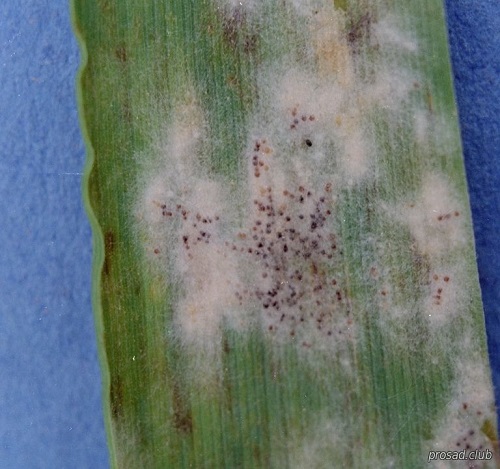
To prevent fungal diseases that cause yellowing of the onion, before planting it is laid out for 12 hours under direct sunlight for heating. Planted bulbs must be watered with a solution using copper oxychloride (1 tablespoon) and laundry soap(1 tablespoon) per bucket of water.
So that onion plantings are not damaged by bottom rot, onion beds cannot be made in a lowland.
Correction of errors in the care of onions that caused them to turn yellow

To prevent yellowing of the onion as a result of care errors, it should be provided proper watering. For irrigation, use only warm, settled water, water strictly under the root, preventing the soil from washing out on the bulb. Mineral fertilizers can be added to water for irrigation.
One month before the start of harvesting, watering must be stopped.
What to do if the onion turns yellow due to weather conditions?
With a lack of precipitation in a dry summer, onion beds should be watered more often. And during the period of prolonged rains, it is better to cover the plantings in the greenhouse.
How to prevent yellowing of the pen from a lack of nitrogen?

In cases where the watering is correct, and there are no diseases with pests, and the onion still turns yellow, the cause may be a deficiency. In this case, the onion must be fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizer (special complexes or humus).
Why onions turn yellow and how to deal with it - video
Diseases of onions and garlic
1. The main thing for onions is healthy planting material, pre-sowing treatment and well-fertilized, loose soils, do not forget about regular weeding from weeds.
2. Powdery mildew, onion fly, onion secretive proboscis
· The feather turns yellow, a grayish-purple hue appears on the leaves. Treated with a 1% solution of Bordeaux liquid.
· There is a fairly effective folk method - 2 times, at intervals of a week, shed a solution under the root of the bulbs - 1 cup of ordinary table salt per 10 liters of water with the addition of potassium permanganate until pink.
· If onions begin to turn yellow, vegetable growers take different measures. For example, watering the beds with water and kerosene, two tablespoons of kerosene per bucket of water. It is advisable to water under the root of onion plants. You can spray plantings with a cool saline solution. A sharp, as often happens in Siberia, the onset of heat provokes activity onion fly and onion hoverfly. The larvae are introduced into the bulbs. They might even rot leaves turn yellow and dry up. It is necessary to mulch onion crops with peat. Introduce along the rows substances that have strong smell repelling flies: tobacco or shag dust in its pure form or in half with lime or ash (1-2 kg per 10 sq. m). You can fill the aisles with a mixture of naphthalene and sand (1 part of naphthalene to 20 parts of sand).
In order for a full-fledged bulb to grow, it is necessary to form a good leaf apparatus. After all, scales form from the bottom of each leaf. How more leaves, the more scales, the larger the bulb. Therefore, you should not cut off green leaves on crops intended for turnips.
Water onions - as needed, no more than 4-6 times a month. It is better less often, but plentifully, in order to wet the soil layer to a depth of 15-20 cm. Before watering and after it, when the top layer dries out a little, loosening is necessary. If the plant develops poorly when planted with bulbs, it can be fed with mullein or bird droppings, diluted 10-12 times with water. 30-40 g of ammonium nitrate are added to a bucket of such a solution. At the end of June, you can make a second top dressing. To do this, take 30 g of superphosphate and potassium salt per 10 liters of water.
If the soils in the plots are fertile, there is a lot of humus, then organic and nitrogen mineral fertilizers do not need to be applied. You can achieve leaf growth, but delay the formation of bulbs. It is necessary to periodically inspect plantings and completely remove plants damaged by fly larvae. They are burned or buried to a depth of at least 50 cm.
- The tips of the pen turn yellow in onions and garlic
In a favorable summer, this is the result of a lack of watering in hot weather. Today (2000) this is no longer the case. So, two reasons: either a lack nutrients, or the onion fly commands the parade. The first reason can be eliminated by feeding the plants with a complete complex fertilizer. I, for example, use "Crystalline". Worse, of course, if the onion fly harms the onion and garlic. This must be checked. If the plant has turned yellow, do not regret pulling it out. At worst, dig the ground near the bulb. If you see a small worm, then the onion fly dominates. In this case, there are two options for getting rid of it. We take a glass of table salt in a bucket of water, dilute it, make grooves between the rows of onions, garlic, and water the ground well. If this does not help, then take two tablespoons ammonia on a bucket of water and using the same technology we cultivate the land around the plants.
If you are not satisfied with either option, then use urea.
|
Peronosporosis, or downy mildew of onions and garlic
. The causative agent of the disease is a fungus Peronospora destructor (Berk) Casp.The disease affects all types of onions: batun, shallots, chives, leeks and garlic. The disease manifests itself in the spring with the growth of perennial onions and onion seed plants. In the middle of summer (late June - early July), downy mildew appears on turnip and onion sets. |
|
Control measures. The main measure in the fight against downy mildew of onions and garlic is to obtain healthy planting material. To do this, crops of nigella and garlic must be placed in fields with the greatest isolation from perennial onions, turnips and seed plants. Positive results are obtained by autumn warming of small bulbs before the end of drying at a temperature of 40 ° for 8 hours and large bulbs - 24 hours and spring warming no later than 1.5 months before planting. A necessary condition for obtaining healthy material is a systematic inspection and cleaning of crops from diseased plants, starting from the 3rd-4th week after planting. |
Onion and garlic rust . The causative agents of the disease are fungi Puccinia porri Wint. and Puccinia allii Rud. It affects all types of onions and garlic. The main damage to plants is caused by the uredospore stage, so the rust on the leaves of onions and garlic appears as light yellow, slightly convex pads. Later, when telitospores develop, the pads turn black. With a strong development of rust, the leaves dry prematurely. Rust fungi overwinter as telitospores on affected plant debris, as well as on perennial species Luke.
|
Bacterial bulb rot
. The causative agents of the disease are bacteria Erwinia carotovora (Jones) Holland., Erwinia aroideae (Town.)Holland. The disease manifests itself during the growing season of onion sets and on the testes. The leaves turn yellow, areas of dying weeping tissue appear. On the testicles, the arrows turn yellow, fade. On bulbs, signs of bacterial rot can only be detected on a longitudinal section. Under healthy outer scales, dirty-brown, softened and mucilaginous scales are found. After 2-3 months, such bulbs completely rot and emit bad smell. |
|
Control measures |
|
onion stemfiliasis. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Stemphylium allii Oud. It affects onions, garlic, leeks. Especially dangerous for testes. On the leaves, as well as on the arrows of the testes, mainly on plants affected by false powdery mildew, clearly visible brown-violet spots appear, covered with abundant pinkish-purple at first, later brown bloom of the fungus, consisting of colorless conidiophores and oblong, packet-shaped, brown-violet, smoky-brown spores 20-50 X 12-25 microns in size. Leaves and arrows break in places of defeat. Seeds do not have time to form or are formed feeble. |
|
Control measures the same as with peronosporosis |
|
Onion smut. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Urocystis cepulae Frost. The disease appears only on onions of the first year in the form of dark, slightly swollen stripes, translucent through the skin on the cotyledon leaf, as soon as it comes to the soil surface. Over time, the skin cracks and a mass of black spores of the fungus is found. Most of the affected seedlings die at the age of 3-4 weeks. In those plants that do form bulbs, dark stripes also form at the base of their scales. When the skin cracks, a mass of black spores is found, which enter the soil and can remain viable in it for 5-6 years. Onion seedlings are most susceptible to smut starting from the second day after seed germination and ending with the formation of the first leaf, i.e. within 12-15 days after germination. |
|
Control measures with smut are reduced to observing the correct crop rotation with a 4-5-year break for sowing black onions in one area. Onion sets and turnips can be grown on contaminated soils. Early sowing or sowing with germinated seeds is recommended, as well as growing onion seedlings on uninfected soil and planting it in the ground |
|
Neck rot of onion and garlic
. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Botrytis allii Munn. The most common and harmful disease of onions and garlic. The primary infection of plants occurs in the field even before harvesting when the leaves are lodging, which is a favorable substrate for the development of the fungus. The causative agent of cervical rot penetrates into tissues through a loosely closed neck and mechanical damage. Infection in the initial period is not detected, so the affected bulbs, along with the healthy ones, fall into the storage. The first symptoms of the disease become noticeable already at the beginning of storage (September-October). Neck rot develops as a result of infection in the field and rot of the lateral parts or bottom due to re-infection from nearby diseased bulbs. The bulb softens in the affected areas, the tissue becomes watery, yellow-pink in color, with bad smell. If all scales are affected, the bulbs become mummified. On the surface of the affected scales, a dense gray mold is formed, which is a mass of conidiophores of the fungus and colorless, oval, unicellular conidia 7-16x4-9 microns in size. Later, sclerotia of the fungus appear among the mold, often merging into a solid black crust. |
|
Control measures. To reduce onion losses from neck rot, it is first necessary to obtain healthy planting material. To do this, black onion should be sown in separate areas remote from fields occupied by turnips and seed plants. Harvesting of the bulbs should be carried out during the period of their full maturation, followed by drying of the bulbs in sunny weather in an open place in one layer, in wet weather - first under a canopy, and then for 7-10 days indoors when the air is heated to 26 - 35 °. When cutting onions, leave a neck 3-6 cm long. It is recommended to store onions at optimal conditions: food - at a temperature of 1-3 ° and a relative humidity of 75-80%, uterine bulbs - at 2-5 ° and 70-80%, sets - at 18-20 ° and 60-70%. |
|
gray onion mold
. The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Botrytis cinerea Pers. It affects onion testicles in the phase of seed filling and bulbs during storage. Unlike cervical rot, the disease does not affect the neck, but develops on the lateral and bottom parts of the bulb. Gray mold infection can occur both in the field and in storage in the same ways as neck rot infection. The affected tissues are weeping, with an unpleasant odor, yellowish in color, covered with a gray fluffy coating of the fungus, consisting of conidiophores and unicellular, colorless, oval conidia 9-17x6-10 microns in size. Later, numerous sclerotia are formed in the plaque. |
|
Control measures with mushrooms and bacterial rots onions and garlic include the same tricks as with neck rot. |
|
Green mold onions and garlic, or penicillosis
. The causative agents of the disease are fungi from the genus Penicillium (Penicillium glaucum Link.). One of the most common diseases of garlic during storage. Less common on onions. On the bulbs, first on the bottom or outer scales, brown watery spots appear. In garlic, individual cloves become sluggish, depressed light yellow spots are visible on the juicy tissue. In the future, the affected tissues soften and become covered at first with a light, whitish, and then with a green moldy coating. The spores of the fungus are elliptical or spherical, small, with a diameter of 3-3.5 microns. When the scales break, they spill out in large quantities. The disease also spreads to the internal teeth. They shrivel, darken and crumble. The bulbs feel empty to the touch. |
|
Control measures with fungal and bacterial rots of onions and garlic include the same techniques as with neck rot. |
|
Black mold onion and garlic, or aspergillosis . The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Aspergillus niger Tiegh. The disease develops when onions and garlic are stored at a high temperature (18-25 °). The greatest damage is caused by onion sets and onion selection. Black mold affects the upper juicy scales. Sick bulbs soften, a black, dusty mass of small, up to 2-5 microns in diameter, spherical spores is formed between the scales. Unripened, poorly dried onions are more susceptible to the disease. During storage, re-infection of the bulbs can occur through direct contact, as well as with the help of spores that spread through the air. |
|
Control measures with fungal and bacterial rots of onions and garlic include the same techniques as with neck rot. |
|
White rot of onions and garlic . The causative agent of the disease is the fungus Sclerotium cepivorum Berk. It affects plants of any age during the growing season, as well as during storage. When infected in the field in young plants, the leaves turn yellow, starting from the top, and die off. Plants quickly wither and die. A white fluffy mycelium forms on the roots and scales of the bulbs, the garlic cloves become watery and rot. Small, poppy-seed-sized sclerotia appear on the affected tissue. The fungus develops well at a temperature of 10-20 °. It overwinters as sclerotia in the soil and in storage on infected bulbs. |
|
Control measures with fungal and bacterial rots of onions and garlic include the same techniques as with neck rot. |
|
Fusarium, or root rot of onions and garlic
. The causative agents of the disease are fungi from the genus Rizagsht. The first signs of the disease appear even in the field, during the ripening of onions and garlic. In affected plants, the leaves die off quickly, starting from the top. Most of the roots rot. On the bulbs in the area of the bottom, a pink, yellow, often white mycelium bloom with clearly visible pads, consisting of elongated, crescent-shaped, with 3-5 partitions, colorless spores 30-50x3-4 microns in size, is always noticeable. Accumulations of mycelium and spores are also clearly visible between the scales. The affected tissues dry out, and by the end of storage, the bulbs are mummified. The disease is promoted by pest damage. Unlike white rot, Fusarium rot develops more often in years when onions and garlic ripen at high soil temperatures. During storage at elevated temperatures, the disease also progresses rapidly. |
|
Control measures with fungal and bacterial rots of onions and garlic include the same techniques as with neck rot. |
|
Bacteriosis of garlic
. The causative agents of the disease are the bacteria Erwinia carotovora (Jones) Holland., Pseudomonas xanthochlora (Schuster) Stapp. During storage, deep sores or stripes appear on the cloves of garlic, going up from the bottom. Fabrics acquire a pearly yellow color. In places of defeat, fungi from the genus Penicillium usually settle. Affected bulbs during planting in most cases germinate and develop normally. |
|
Control measures with fungal and bacterial rots of onions and garlic include the same techniques as with neck rot. |
|
yellow dwarfism
. The causative agent of the disease is the Onion yellow dwarf virus. The disease is more pronounced on the testes and is detected shortly after the planting of the queen cells. Plants have a depressed appearance: the leaves turn yellow, often become folded or corrugated, fall to the ground due to the loss of turgor, and become flat. Peduncles also turn yellow, curl and give the plant a dwarf appearance. Flower heads and seeds are smaller than those healthy plants. Onions, which have been propagated vegetatively for a long time, are more susceptible to dwarfism. |
|
Control measures. The main measures to combat viral diseases of onions and garlic are obtaining healthy planting material by isolating (up to 1.5 km) black onion crops from crops of other crop years, perennial onions and garlic, protecting against virus vectors, selecting uterine bulbs from healthy plants, removal of diseased onion sets. |
|
Onion and garlic mosaic . The causative agent is Allium virus I Smith. Leaves and inflorescences are affected. On leaves, the disease appears as small, more or less elongated speckles or wide light green or cream stripes. Sometimes the leaves become corrugated, stunted and lodging. The arrows are bent, longitudinal mosaic stripes are visible on them. The inflorescences of the affected plant are loose, the flowers are sterile or produce very few seeds. Instead of stamens and pistils, long leaves often develop, and bulbs instead of flowers. Germination of seeds from diseased plants is reduced. Bulbs from infected plants often have an elongated shape and, before reaching maturity, germinate. The disease is carried by the four-legged garlic mite. The infection persists in onion sets, mother onions and perennial onions, on which the disease manifests itself in the form of a weak leaf mosaic. |
|
Control measures. The main measures to combat viral diseases of onions and garlic are obtaining healthy planting material by isolating (up to 1.5 km) black onion crops from crops of other crop years, perennial onions and garlic, protecting against virus vectors, selecting uterine bulbs from healthy plants, removal of diseased onion sets |
|
OnionflyDelia (Hylemia) antigua Meig
.
Widespread dangerous pest(especially in wet years). More harmful on sandy and loamy soils, less on peat. More damage to bows household plots with permanent cultivation of culture, less - garlic. |
|
Control measures. Spatial isolation of onion crops from last year's crops. Arrangement (or alternation) of onion and carrot rows, onion crops next to carrot crops. Phytoncides secreted by carrot leaves repel the onion fly. Early sowing of onions contributes to resistance to onion fly damage, since by the time the flies emerge, the plants will get stronger, coarsen and less damaged by the pest. There is an opinion that mulching with peat between rows helps to scare away the onion fly, since the pest avoids peaty soils. The use of drugs with a strong odor such as naphthalene mixed with sand in a ratio of 1: 1, tobacco dust in its pure form or in half with lime or ash (1-2 kg per 10 m2). Processing is carried out in the initial period of laying eggs. Subsequent - in 7-8 days. It is necessary to periodically inspect crops, remove and destroy damaged bulbs. At the end of the growing season, remove the tops, the remaining damaged bulbs, followed by digging the soil. Good results are obtained by treatment with an infusion or decoction of a volatile plant - tobacco. Leaves and stems are used. For infusion, take 400 g of crushed raw materials or dust, insist two days in 10 liters of water. The infusion is filtered. To the resulting solution add 40 g of soap. For a decoction, take 400 g of dried raw materials per 10 liters of water, insist for a day, then boil for 2 hours. After cooling, another 10 liters of water are added and for every 10 liters of solution, 40 g of soap are added. |
|
Onionhoverfly(Eurnerus strigatus Fall).Moisture-loving insect. Widespread. Damages all kinds of onions, garlic, gladioli, tulips, daffodils and other plants. The larvae that have penetrated the bulbs destroy them and cause decay. |
|
Control measures. The same as against the onion fly, as well as the use of healthy planting material. |
|
Onionmole(Acrolepia assectella Zeil.). Distributed everywhere. More harmful in hot, dry years. Damages leeks, onions, garlic. Caterpillars penetrate inside the tubular leaves of onions, eat away the parenchyma in the form of irregular stripes,. leaving the epidermis intact. Damaged leaves turn yellow and dry, starting from the apical part. On onion sets, caterpillars often penetrate the neck and even inside the bulb, causing the complete death of the plant. On leeks and garlic, the caterpillars mine the leaves, on the seed plants they feed in buds, eat out the rudiments of flowers, gnaw the pedicels, which leads to a decrease in seed yield. The onion moth is a small butterfly, with a wingspan of 8-10 mm, dark brown in color. Forewings with small white spots. In the middle of the front wings there is White spot almost triangular in shape. The hindwings are lead gray with a long fringe. Eggs are milky white and bean-shaped. The caterpillar is yellow-green in color, with a dark head, spindle-shaped, with 8 pairs of legs. Body 10-11 mm long covered with brown warts. Pupae are dark brown in color, about 7 mm long, located in a grayish cobweb cocoon. Butterflies hibernate in various shelters, on plant remains. The emergence of moths is observed in mid-May and phenologically coincides with the flowering period of bird cherry. The female lives for about two weeks and during this period manages to lay up to 100 or more eggs. Their development lasts 5-8 days. In the conditions of Belarus it develops in two generations. |
|
Control measures. It is necessary to observe crop rotation and proper agricultural technology. Return the bow to its original place no earlier than after 3-6 years. Modern loosening and top dressing mineral fertilizers. Destruction of plant debris. spraying seed plantings insecticides during the summer of butterflies and the appearance of caterpillars. |
|
Onion secret proboscis (Ceuthorrhynchus suturalis Schul.).
Beetles and larvae damage onions, onions, chives, less often garlic. Beetles in tubular leaves eat out small cavities, as a result of which rounded white spots form on them. The larvae eat away the pulp inside the leaf, in longitudinal strips, without touching the outer skin. In damaged plants, the leaves turn yellow from the top and dry out. |
|
Control measures. Collection and destruction of post-harvest residues, autumn plowing, which destroys the wintering grounds of beetles. Additional loosening of row-spacings during the period of mass pupation of larvae, followed by watering and fertilizing with mineral fertilizers. Removal of damaged leaves with the destruction of larvae. Insecticide treatment. There is a fairly effective folk method - remove and destroy damaged feathers and pour a solution under the root of the bulbs - 1 cup of ordinary table salt per 10 liters of water with the addition of potassium permanganate until pink. |
|
Root (onion) mite (Rhyzoglyphus echinopus).
Distributed everywhere. Damages the onion, mainly during storage, but can also be harmful in the field, where it is brought with planting material. Penetrating inside the bulb, usually near the bottom, the mites feed on fleshy scales, causing them to rot. Severely damaged bulbs dry out during storage. In the field, mites prefer plants damaged by other pests. They harm garlic, hyacinths, daffodils and other crops. |
|
Control measures. 1.5-2 months before planting, dry heating of onion sets and uterine onions is carried out at a temperature of 40-45 ° for 16 hours or at 35-37 ° for 5-7 days. In the storages where the pest is found, gas disinfection is carried out with sulfur dioxide obtained by burning Gamma checkers (0.5-1 g per 1 m ^) or lump sulfur (50 g / m2). Exposure - 48 hours. A prerequisite for decontamination of premises is their tightness and compliance with safety regulations. |
|
Onion nematode, or onion and garlic stem nematode (Ditglenchus allii Belj.)
. Damages onions, especially garlic. Found on parsley, parsnips, tomatoes, radishes, cucumbers, thistle and other plants. Larvae and adult nematodes feed on plant sap, causing them to bend and stun. In bulbs damaged by the nematode, the internal tissues are loose, granular, grayish. Juicy scales do not fit tightly to each other, as a result of which the bulb feels soft to the touch, the bottom cracks. In garlic plants, growth retardation, thickening of the false stem, yellowing and dying of leaves, yellowing of cloves at the base are observed. Mecia nematode localization - bulb, then feather and arrow. |
|
Control measures. Thermal disinfection of seeds and sowing in heated water at a temperature of 45-50 ° for 10-15 minutes. Sowing only healthy seed material. Compliance with crop rotation with the return of onions, garlic to their original place no earlier than in 3-4 years. Before laying the onion for storage, it is mandatory to disinfect the onion stores, dry and warm the bulbs at a temperature of 35-37 ° for 5-7 days. Carry out fumigation with sulfur dioxide (50 g of sulfur per 1 m2 of the room, exposure 24 hours). In storage at positive temperatures (maintain air humidity not higher than 70%. |
|
Tobacco onion thrips (Trips tabaci Lind.).
A very common species in the republic. In recent years, damages onions, tobacco, cabbage, watermelon, cucumbers in greenhouses. It feeds on more than 100 plant species. Adults are light yellow or brown in color with narrow wings, fringed at the edges, about 1 mm long. The eggs are small, kidney-shaped, white. The larvae are outwardly similar to adult thrips, but are smaller in size, without wings, whitish at first, then greenish in color. Adult thrips overwinter on plant debris, in the upper soil layer, but the main amount is concentrated under the scales of the bulbs. In early spring they feed on weeds, then they switch to cultivated ones. When the onion is damaged, silver-white spots appear on the leaves. In places where thrips feed, the excrement of the phytophage is visible to the naked eye in the form of black dots. Damaged leaves turn yellow, die off, starting from the top of the plant. If the inflorescences of the testes are damaged, the latter turn yellow, then dry out, no seeds are formed or they are feeble, with low germination. |
|
Control measures. Same as against onion nematode and onion root mite. |
There is practically no such garden where the owners would not grow onions. Gardeners are often interested in the question: what factors contribute to the fact that the onion feather turns yellow? Why does the onion turn yellow in the garden? After all, land owners make every effort to care for it: they regularly water onions, feed them, get rid of weeds, and perform other activities.
Reasons why onions turn yellow
What could be the reasons for the yellowing of onions, and how to deal with them? Consider the main factors affecting the condition of the onion in the garden.
Reasons for yellowing include:
Insufficient nitrogen content in the soil
Most often, onion yellowing is caused by a lack of nitrogen in the soil. When it's hot in summer, onions are deficient in nutrients, especially nitrogen, since onion roots receive nitrogen only in dissolved form. Excessive watering or frequent rains also adversely affect onion roots. This is due to the fact that water can wash out all the useful nutrients from the soil, which the onion especially needs during June-July.
Influence of pests
What is dangerous onion moth
This is not very bright appearance, a butterfly, has a dark brown color and light gray wings. The length of her body reaches only 8 mm. May appear in late spring. It harms the bow, as a rule, at night. Then the females lay larvae, which after 7 days will turn into caterpillars. These green pests are small in size, but they do a lot of damage.
How to deal with onion moth
Effective action of the drug "Iskra": you need to take 1 tablet and dilute in 10 liters of water. A high result can also be achieved by using the preparations "Dachnik", "Metaphos".
You should start sowing onion sets as early as possible. This is necessary so that before the onset of this problem it is already possible to harvest.
Moth plantings will not be threatened if onions are planted next to carrots. The soil must be loosened. The soil is treated with decoctions of tobacco, tincture of garlic and ash.
Well "shows itself" mixture for feeding. Take: wood ash, pepper, tobacco dust. The procedure is carried out during the period when dandelions bloom.
 Onion moth harms leeks and onions in hot, dry weather
Onion moth harms leeks and onions in hot, dry weather It happens that one of the reasons for the yellowing of the onion feather is tobacco (onion) thrips. Along the length of its body, this pest is smaller than aphids. Despite its small size, the insect causes serious damage not only to onions, but also to other cultivated plants.
How to proceed in such a case? Start with preventive measures. In order for everything to be good on the beds, they will be protected by a simple procedure: the seed material must be lowered into hot water, the temperature of which is from 44 to 46 degrees, for 10 minutes. After that, it must be placed in cool water. Onion thrips dies from such a procedure.
When a small pest began to show its activity on the onion beds and the feather turns yellow, the special chemical preparation "Confidor" will come to the rescue. You can use Spark.
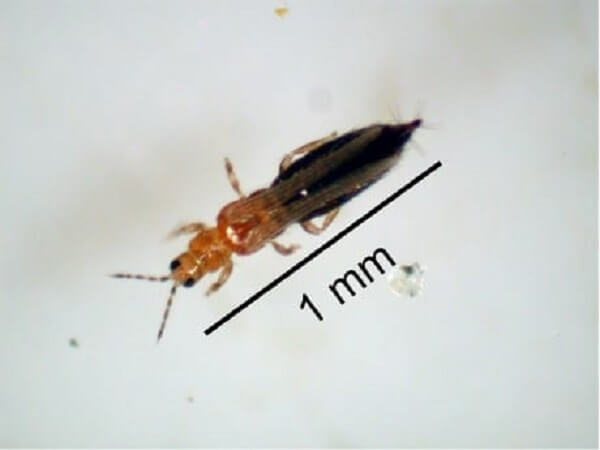 Onion (tobacco) thrips harms onion crops in beds in open field and onion sets during storage
Onion (tobacco) thrips harms onion crops in beds in open field and onion sets during storage Onion fly, and how to destroy it
This insect is difficult to distinguish from the common fly that we know and often see in the summer. This pest is about 8 mm in size, gray color(with shades of yellow and ash). In addition to the fact that the fly irritates all the inhabitants land plot that which is present among cultivated plants, it also seriously harms. In the garden - it's just a disaster. Females can lay their eggs both in the garden and directly on vegetables. The larvae, as soon as they hatch, will immediately begin to eat the vegetable, while the onion feathers turn yellow and dry out.
The pest is active from mid-spring to the end of summer. Over the entire period, there is a change of 2-3 generations of this insect. The onion fly lives in different corners of the world, and also poses a threat to crops such as: lettuce (all types), garlic, tulips and other types of flowers. It is important to carry out activities aimed at combating this pest.
Ways to deal with onion fly:
Effective is both the use of chemicals and folk methods. If you choose option 1, then there is a risk that the quality of the onion crop will not be high, since a certain part of the poisons remains in the turnip.
Using folk methods:
- Onion beds should be sprayed with tinctures: mint, wild rosemary, fir, tomato, pine needles, valerian.
- When planting, you need to alternate carrots and onions in the same row in the garden. It is carrots that with their smell will scare away not only onion, but also carrot flies.
- Onion beds should be watered with a solution of kitchen salt. For 1 bucket you need to take 300 grams of salt. Watering should be carried out only after the green onion sprouts reach a height of 5 cm. After 2 or 3 weeks, watering should be repeated, but this time for 10 liters. water take 450 grams of salt.
- Regularly planting should be sprinkled with wood ash. It will perform the functions of fertilizer and protection against pests.
- It is worth observing crop rotation.
In autumn, it is necessary to dig the garden as deep as possible.
- Before planting onions, they are soaked in diluted manganese.
- Effective chemicals are: "Flycat", "Aktara" or "Karate Zeon".
Preparations based on chemical compounds often used when seeding large areas. They are not used for processing garden plots.
 WE RECOMMEND!
WE RECOMMEND!
At the neighbor's better harvest? Increased yield in just 2-3 days. Even in an abnormally rainy summer, you will have an excellent harvest after applying the original bio-plant growth stimulator. The biofertilizer contains only natural ingredients.
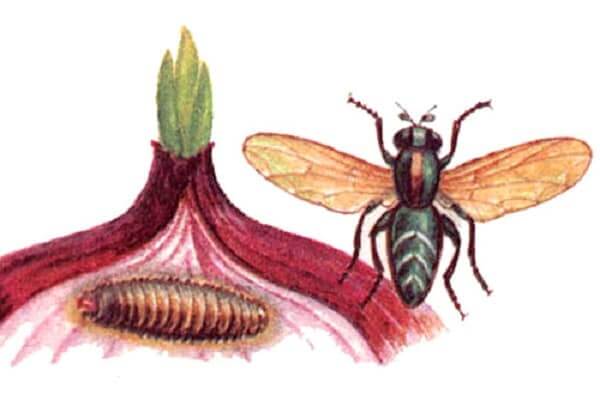 In appearance, the onion fly resembles a cabbage fly or housefly, only much smaller
In appearance, the onion fly resembles a cabbage fly or housefly, only much smaller stem nematode
Also, one of the reasons for the yellowing of onions may be a stem nematode. This is a worm small size. Due to its penetration, the bottom of the bulb cracks and begins to rot, and the onion feathers turn yellow. This pest, despite its size - 1.5 mm, can cause irreparable damage. The main problem is that the nematode can live in various parts of the garden, and it can live in the soil for many years.
This is a small beetle. The body is gray in color, has the shape of an oval, and is approximately 2.5 mm long. In winter, these pests hibernate. After they wake up in the spring, they immediately damage the onions. As a result: white spots appear on it. For them, new shoots are a delicacy.
After the weevils lay their eggs, and after 2.5 weeks, their offspring are already born. As soon as the babies - weevils are born, they immediately pounce on the vegetable. As a result, the leaves turn yellow and dry on the onion.
Onions, most often, are sick with rust. This disease is manifested by the appearance of yellow dots on the feathers, from which the leaves dry out and die. Methods of dealing with this disease are:

Bulb rot caused by bacteria
You can see this disease only when the onion is cut. Among the scales, which have a healthy appearance, dark layers of softened substance are visible. Infection of the bulb does not occur without the help of insects. There is no point in storing this bow, as it will quickly deteriorate. When such bulbs are planted, the culture, visually, looks unattractive. The feather of the bow will turn yellow, and the arrows will quickly dry out.
To prevent this type of disease, you must:
- carefully sort all the onions to be planted, separating the infected bulbs;
- before planting plants, the soil is treated with metronidazole (or other special preparations).
Fusarium (bottom rot)
This fungal disease can affect all existing varieties of onions and its types. The spores of these fungi live in the soil and can harm the bulb. Green onion feathers turn yellow, and then dry out and die.
Ways to deal with this type of disease:
- competent choice of a place where onions will grow;
- seeds should not be planted in the lowest part of the garden, as during heavy rains the water will flood the crop;
- it is necessary to change the landing sites of onion beds;
- onion seeds that are planned to be planted must be carefully processed and disinfected;
- it is worth planting seedlings strictly at the right time, and for this, the gardener's folk calendar is suitable;
- when the crop is harvested, to store it, you need to create good conditions with the required temperature and humidity.
In the event that these measures are carried out correctly, the bottom rot will not appear.
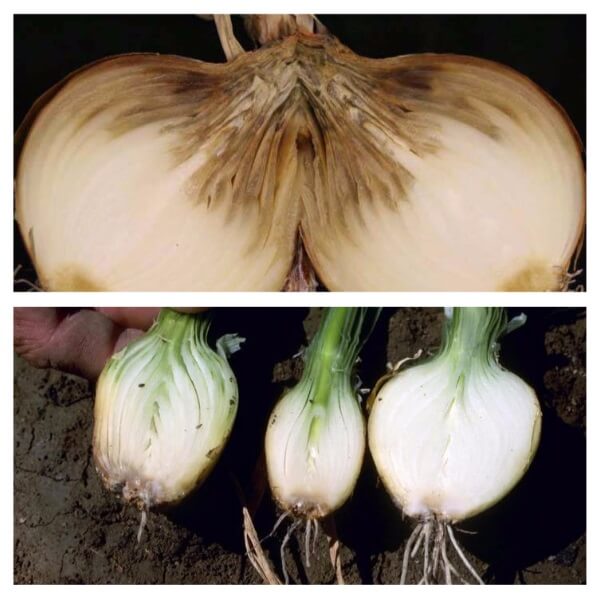 Rot affects onions in the soil, and especially during storage. The leaves of young plants begin to turn yellow and die.
Rot affects onions in the soil, and especially during storage. The leaves of young plants begin to turn yellow and die. Alternariosis
This disease manifests itself in the form of white spots on the feathers. The disease progresses in this way: the spots increase in size, and acquire a lilac (with brown) hue. It is already manifested, thus, the spores of the fungus. It happens that the spots have a white rim. The disease from the feather passes to the bulb, which becomes covered with brown or black mold.
 WE RECOMMEND!
WE RECOMMEND!
An effective remedy for alcohol addiction. Based on only natural ingredients. According to the results of the study, 25% of the tested volunteers noted a significant decrease in cravings for alcohol and an improvement in the state of the body, and 75% of the subjects stopped drinking completely!
The cause of the disease is too much nitrogen in the soil, or a high moisture content in the soil.
How to fight:
- monitor crop rotation;
- after the onion crop is harvested, all the husks should be removed from the beds.
In rainy weather, treatments are carried out for the purpose of prevention, using the following drugs:
- Shirlan 500 SC.
- "Consento";
- "Acrobat MC",
- "Cabrio Duo";
- "Polyram DF".
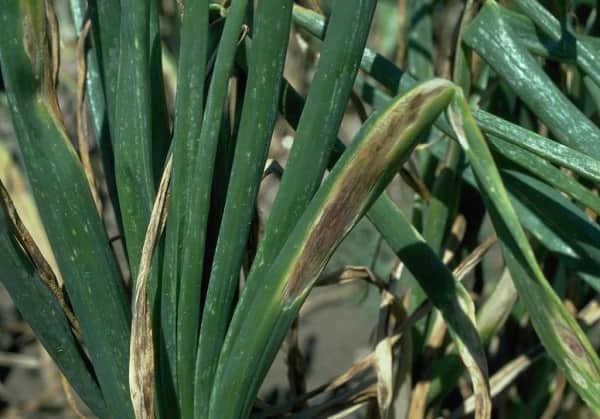 Alternariosis - onion disease photo. The disease affects onion scales, feathers break, the plant rots.
Alternariosis - onion disease photo. The disease affects onion scales, feathers break, the plant rots. Failure to follow the rules for onion care leads to yellowing of the onion
Plants most often get sick from the fact that the site owners do not properly care for them, do not carefully clean all the “traces” of vegetation after harvesting, and also did not take measures to disinfect the storage room.
Watering is not carried out according to the rules, or not in full
It is necessary to be informed about what means, and in what quantity, it is necessary to water the onion in order to avoid its yellowing. When it takes root, it is necessary to water it with water, which has a temperature of +18 to +25 degrees. The first half of the day for watering is the ideal time. When mulch is applied, watering should not be as frequent.
Feeding shortage
An important question is this: what to use as a top dressing so that the onion feather does not turn yellow. Fertilizers are combined with watering. The funds must be mixed by taking 50 g of ammonium nitrate, 20 g of potassium salt, 20 g of superphosphate, and dissolved in 10 liters of water.
The very first watering with this solution must be performed when the onion shoots rise 3 cm above the ground. The procedure is repeated after 7 days. Before harvesting (for 5-6 days) top dressing is stopped.
Video: Why does the onion turn yellow?
The above tips may turn out to be ineffective, since nature can make its own adjustments to this process. The season can be too dry, or very wet when it rains. This will cause the onion to turn yellow and disappear, no matter what the gardener tries to do. In order for a healthy crop to be harvested from onion beds, it is advisable to build a greenhouse on the site.
Pen yellowing on onion patch in July-August - this is a natural process that indicates the readiness of the onion for harvesting. But a fairly common problem for both professional gardeners and newcomers to suburban area- premature yellowing of the onion feather. If you pull such an onion out of the ground, you can find clear signs of its decay. And today about why the still growing onion turns yellow and rots, and how to deal with this scourge.
Before taking any action, you need to find out the likely cause of the problem. It is likely that the onion is dying due to a pest that has settled in it.
The most common insects that can harm the bulb are:
onion fly;
onion secretive proboscis;
thrips;
stem nematode;
onion moth.
If the onion at least once turned out to be damaged by one of the listed pests, then the minimum time period after which this crop can be planted on this bed again is four years. In general, onions on the same bed should not grow for several years in a row. This precaution significantly reduces the likelihood of contamination of planting material by pests remaining in the soil.
Onion fly: how to deal with a pest?
 The following tips will help you deal with a pest infestation:
The following tips will help you deal with a pest infestation:
1. It is necessary to plant onions as early as possible. In this case, by the time the pests appear, the young plants will get stronger enough, and the insects will no longer be able to cause irreparable damage to them.
2. Always plant a bed of onions next to carrot beds.
3. As soon as the dandelion begins to bloom, be sure to spray the onion with a mixture of tobacco dust, wood ash and pepper.
Onion Stalker

Thorough cleaning of the garden bed after the onion has already been pulled out will help get rid of the onion secretive trunk and onion moth. All remnants of the pen must be completely collected and destroyed.
In the autumn, just before the arrival of frost, the onion bed needs to be dug deep.
Stem nematode and thrips
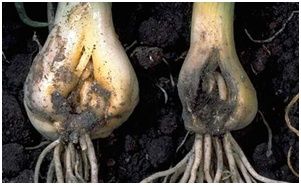
If the onion feather began to turn yellow because it was damaged by the stem nematode and thrips, then the following procedure will help to avoid this in the future:
soak the onion in hot water for about 10 minutes before planting. The water temperature should not exceed +45.
Calendula and marigolds planted in the aisles will help scare away the pest.
Onion diseases that cause yellowing of the feather and rotting of the bulb
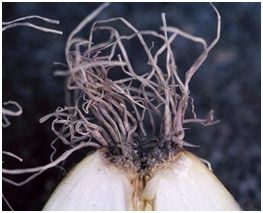
There are many diseases that can cause the death of the bulb, but the main reason is fungal diseases. To secure the future harvest, it is necessary to carry out pre-planting seed treatment. To do this, leave it under the sun for 12 hours, or soak in warm water(+30) for the same period.
As a prevention of fungal diseases, already planted onions can be watered with a solution of copper oxychloride. Norm: add a spoonful of the drug and the same volume of liquid soap to a bucket of water.
When choosing a place for a future bed, try to choose areas located on a hill. Most often, onions planted in a lowland suffer from bottom rot.
Improper care is another reason

Feather tips may begin to turn yellow due to improper planting care. There are certain rules that allow you to grow perfectly healthy onions:
1. Plants can only be watered with warm water. Cold tap water- one of the reasons for the death of the onion.
2. Watering should be carried out under the root. If you are watering the bed from above, then be sure to use a rain nozzle so as not to expose the bulbs.
3. Watering is recommended to be combined with mineral supplements.
4. About a month before harvest, watering must be completely stopped.
Weather
In hot weather, the bed should be watered as the top layer dries. The soil in the garden should always be moistened to a depth of one centimeter. 
To save the bed from heavy rains, and, accordingly, the decay of the crop, the construction of a greenhouse above it will help.
Lack of nitrogen in the soil
In certain situations, the onion begins to dry even with proper care and the absence of pests. What could be the reason in this case? Experienced gardeners It is recommended to check the soil for nitrogen content.
In case of its shortage, onions must be fed with nitrogen-containing fertilizers. As a top dressing, you can use chicken manure or mullein. If this is not possible, then it is recommended to purchase special complex mixtures.
Onions turn yellow than water and feedYellowing of onion leaves: causes and signs of their manifestation
With normal growth and development, onion stalks begin to wither in August and September, indicating that the bulbs are ready for harvest.
If the feathers turn yellow in spring or early summer, this is a sign of improper development of the culture. There may be several reasons for this phenomenon:
- lack of moisture;
- insufficient amount of nutrients;
- damage to plants by harmful insects;
- adverse weather conditions;
- fungal and bacterial diseases.
lack of moisture
Onions are very picky about the frequency and quality of watering. Without sufficient moisture, especially during a dry period, the edges of the leaves of plants turn yellow and die, and the roots dry out, which leads to loss of yield.
During the germination and leafing phases (in the first half of summer), onions should be watered at least 2 times a week. At the next stages of growth and development - 4-5 times a month. It is best to water before noon, and only at the root.
Use only soft water, the temperature of which is 18-25 degrees Celsius. Consumption rate per sq. m - 6-8 liters. After watering, when the topsoil dries out, loosening is sure to be carried out.
Inadequate Nutrients
A common cause of onion feather yellowing is a lack of nitrogen in the soil. With its deficiency, the leaves grow very slowly, they look short and thick, at first light green in color, and then turn yellow.
In this case, it is necessary to apply nitrogen-containing fertilizers under the plants. But, how to feed the onion so that it does not turn yellow? For this, a solution consisting of infused manure and urea is perfect. For 10 liters of water - 1 tbsp. organics (mullein or bird droppings) and 1 tbsp. l. urea.
Damage to plants by harmful insects
Among horticultural crops onions are most susceptible to insect damage. Pest damage causes feather yellowing and can result in the loss of the entire crop.
The onion fly is especially active during the development of onion greens - in April and May. She lays her eggs on the stem, under the leaves or in the loose soil of the beds near the plants. The larvae that appeared after 8-10 - white small worms climb into the bulb and feed on scales. Affected plants lag behind in growth, their leaves wither, and after a while become yellowish-gray and dry out.
Adverse weather conditions
One of the reasons for the instant yellowing of the leaves can also be climatic conditions, for example, too dry or rainy summers. A reliable protection of the crop from death will be a greenhouse or a ground greenhouse, where onion feathers will always be green and juicy.
Fungal and biological diseases
The most common diseases, a sign of which is the yellowness of the feather, are rust and bottom rot. On the leaves of plants affected by rust, light yellow, slightly convex spots form, after which the feathers dry and die. With bottom rot, the plants turn yellow completely, and then wither.
Onions turn yellow than water - folk remedies for diseases and pests
To get a bountiful onion crop, first of all, crop rotation, the timing of sowing and planting bulbs should be observed. To avoid infection of vegetables with pathogens, only healthy planting material should be used, well warmed up and dried before planting. The soil in the beds, just before sowing, disinfect with a solution blue vitriol: for 10 liters of water 1 tbsp. l. granules.
The onion turned yellow: how to pour from the onion fly
Excellent preventive measure from the onion fly is the placement of beds of onions and carrots in the neighborhood, as well as dusting the plantings with a mixture of ash and tobacco (taken in equal proportions). When worms are detected, vegetables should be watered with a solution consisting of tobacco dust, laundry soap and ground red pepper. For its preparation 200 gr. tobacco pour 2-3 liters hot water, insist three days. Then add water to 10 liters, add one spoonful of soap and pepper.
How to pour onions from worms
Plants affected by the stem nematode should be fed with a solution of ammonium sulfate in early June. Dilute 2 tbsp. l. the drug in a bucket of water and pour over the vegetables, at the rate of 4-5 liters per square meter. m. area. As a preventive measure, seeds, before sowing in the ground, need to be planted for 15-20 minutes. place in a solution of table salt (5 tablespoons per 5 liters of water).
Chemical methods and preparations for feeding onions
At home, especially if the onion is grown on a feather, it is not recommended to treat it with any pesticides. If necessary, it is better to use biological fungicides that will not harm the human body.
Application of Trichodermin
So that in the middle of the season the question does not arise: the onion sets turn yellow than to water - the bulbs should be treated with Trichodermin fungicide before planting. For soaking one kilogram of sevka, a solution is prepared from 30 g of suspension and 3 liters of water. During the growing season, plantings are additionally sprayed with Fitosporin-M or Gamair biological product (3-4 times).
Treatment of onions with metronidazole
One of the most effective means from yellowing of the pen, the antibacterial drug metronidazole, which can be bought at every pharmacy, is considered.
It will quickly and efficiently destroy pests and thereby save the crop. For the treatment of plants, 4 tablets are dissolved in 10 liters of water. The resulting solution is watered with beds at the rate of 4-6 liters per 1 sq. m.
Outcome
Every gardener who knows how and with what to water the onions so that the feather does not turn yellow can get a rich harvest of strong bulbs and healthy greenery. Use proven tools folk recipes to protect the crop from diseases and pests, follow the timely sowing and you can achieve the perfect result.


