Brief description of the lily. I. L. Zalivsky. Lilies. Brief botanical characteristics of lilies. General information. Description of white lily
We are starting to publish chapters from the book "Lilies" by Ippolit Leopoldovich Zalivsky. This is a wonderful book that has not ceased to be relevant at all. Moreover, it is very entertaining, written in good clear language. Thanks to her, the lilies will become closer and more understandable. And this is very important, because many are frightened by the modern classification, which only a specialist can understand. Zalivsky's book is for everyone.
Lily flowers are graceful additions to home garden or a lone vase on the kitchen counter. Whether grown outdoors or in an indoor pot, their vibrant colors and unusual locations add personality to any garden. The two main types of lilies are tropical and hardy. They are annuals in cold climates unless they enjoy winter protection in a greenhouse or home.
They are hardy varieties that survive in cold climates and tropical varieties that cannot tolerate frost. Their big leaves tend to be round and bloom with exotic flowers from individual stems. Although algae cannot survive under floating leaves that block sunlight, fish use them for shade, and tiny invertebrates sometimes live among the submerged sides of these plants. Growing from bulbs, lily flowers bloom between spring and autumn, with different varieties opening at different times.
Lilies are monocotyledonous and belong to the lily family, which includes tulips, hazel grouses, onions, asparagus, lilies of the valley. In the hostel, lilies are often incorrectly called amaryllis, clivia, krinum, belonging to the amaryllis family, for the most part are tropical plants widespread in indoor culture.
They are different colors including white, yellow, orange, red, pink, purple and blue. Some flowers are spotted or spotted. These flowers are often tube-shaped, with showy petals that curl outward and droop. Stamens and pistils protrude.
Lily flowers need well-drained soil with plenty of organic matter which enriches the soil with nutrients and keeps it moist. The sun is best in cooler climates, but lilies can tolerate partial shade in warm places. In addition to watering regularly, they also value a slow-release fertilizer rich in phosphorus, an ingredient that promotes flower and root growth.
It is also incorrect to call lilies a rhizome plant from the lily family known in soil culture - belladonna, or daylily (Hemerocallis). Water lilies are called water capsule(Nuphar) and water lily (Nymphaea) from the buttercup family.
Lily bulbs have a tiled, more or less loose structure and consist of scales, devoid of outer films, characteristic of tulip bulbs, onions, daffodils and others bulbous plants; only the coral lily bulbs are quite dense and sometimes covered with a yellowish brown coat.
Tropical lilies tend to bloom during the day - especially from early morning until early evening or at night, when they bloom in the late afternoon and remain open until early morning. Although you can plant lilies in the garden, they also stand out as houseplants in containers. However, if you have a cat, it is safer not to grow lilies in your home.
Can you tell me that the flower that is the "valley line" symbolically refers to Christ? After examining some of the roots of the holiday called "Easter", it is easy to understand that most of this "holiday" has nothing to do with the Resurrection of Christ.
Rice. 1. Types of lily bulbs. 1 - with a wintering rosette of leaves 2 - stem root, 3 - rhizome, 4 - stolon-bearing, 5 - false-columnar with a wandering stem (orig.)
The number of scales and the density of their adherence to each other, as well as their shape and the nature of the articulation, fluctuate at different types lilies. The scales of lily bulbs are white, yellow, pinkish-brown, purple-brown and pink. After dredging and after drying, the color of the lily bulbs often darkens, and White color changes to pink and yellowish.Could you tell me more about this color and is it really a biblical Easter holiday? We'll look at each question in turn. The Bible mentions lilies 15 times in 15 different verses. Of these 15 references, 8 of them are found in the Song of Solomon. Perhaps the most memorable poems.
Description of the medicinal properties of white lily
- Consider the lilies of the field as they grow; they do not work and they do not rotate.
- And why do you think about clothes?
Bulb sizes different types lilies in normally developed flowering specimens range from 1-1.5 to 20-30 cm in diameter; in Henry and Kesselring's lilies, bulbs reach 2 kg in weight. Bulbs of many species can tolerate rather strong freezing without losing vitality; for example, bulbs of Daurian, tiger and saffron lilies - up to minus 30 ° C, Tibetan lily - up to minus 15 ° C, provided that the bulbs are in the ground and more or less gradual freezing and thawing of the soil.
Many passages found in the Bible for lilies show that the lily is a common representation of a wide variety of flowers. It's like using a lily on English language... The dictionary says the lily is a large genus perennial plants a family of lilies, grown from a bulb and having typically tubular flowers, some white and some colored. Several plants that look like real lilies are also called lilies. Likewise, the biblical lily referred to the large range of flowering plants that usually grew in wild fields and covered valleys at certain times of the year.
Scales and fallen axillary bulbs (bulbs) of the most hardy lilies, namely tiger, dahurian and bulbous lilies, in our practice, were repeatedly transferred to the soil surface without snow cover, without losing vitality, frosts down to minus 35 ° С.
The lily bulb has a bottom-stem part, which is a convex, in many species, a cone-shaped or cylindrical formation, from which scales and roots extend and which carries a growth point located in the center. In adult bulbs, additional growth points are formed at the bottom, from which new bulbs are formed, called daughter ones, and the phenomenon itself is called bulb division. At first, in many species, daughter bulbs do not lose their connection with the mother bulb, since they have a common bottom with it and are enclosed in common outer scales. Gradually, the daughter bulbs move on to their own roots and form a nest or colony.
Benjamin Keach, in his type books, gives five comparisons between the valley line and The Lord Jesus Christ. Here is it summary... Will they not get up suddenly, that will bite you, and wake up, that will defile you, and you will be drinks for them? Because you have spoiled many nations, all the remnants of the people will carry you; because of the blood of people and for the violence on earth, in the city and on everyone living in it. According to ancient teachings, it could be used to restore a lost voice, help weakness, was good for the liver, and helped a fall. The Lord Jesus Christ is a great physician and is fully capable of healing all diseases and illnesses of the soul.
- Lily is a sweet and blatant flower with a strong scent.
- It has seven grains or seeds that are the color of gold.
- One root can expose fifty bulbs.
Many species, at least all stem-root ones, on the lower part of the stem, above the stem roots, form the so-called babies, bulbs that grow in the axils of the fallen off scales. Usually baby bulbs are formed in upper layers soil or on its surface. Thus, nests, or colonies of baby bulbs are formed on the soil surface.
The Easter Lily as we know it today is native to the southern islands of Japan. The United States replaces Japan, being the main source of Easter Lily during World War II. The Easter Lily requires three or four years of close attention and just the right blend of climate and soil to deliver the quality people expect today. Thus, the area on the California-Oregon border became known as the Easter Lily capital of the world. Easter Lily has become a traditional Easter flower and is considered a symbol of the resurrection.
For many, beautiful white lily flowers symbolize purity, life, goodness, innocence and hope. While we are free to establish a connection between Christ as the foliage of the valley and the Easter lily, those seeking support from historical traditions are likely to be disappointed. Poetry and mythology from around the world uses the beautiful white lily flowers in symbolic ways. Many ancient allegories associate the flower with motherhood. One fable tells us that the lily arose from the milk of Hera, the mythological Queen of Heaven.
In addition, many types of lilies on the stem, over its entire surface or only in its upper part, once or twice a summer in the axils of the leaves form stem bulbs, called air bulbs; on "ripening" the bulbs disappear, in some species they are able to germinate while still on the stem.
Only one stem, rosette, or one leaf emerges from each individual bulb. The appearance of two or more stems from the ground in the place where one bulb was planted indicates that this bulb has split or managed to give babies at the base of the stem that can germinate and sometimes bloom in the first year of its formation. Usually, the bulb does not die after discarding the stem.
This may explain why the lily is so closely associated with Mary in the Roman Catholic tradition. In early paintings, the angel Gabriel saw how to give a bouquet of white lilies to the Virgin Mary. In other paintings, the saints bring vessels full of lilies to Mary and the baby Jesus. In another legend, a visit to the tomb of Mary three days after her burial found nothing in the tomb, except for large bundles of beautiful lilies. Artists often used the lily to represent the Resurrection of Mary. The white petals of the lily are said to represent the flawless body of the Virgin Mary, and her golden anthers are said to glow with this heavenly light in her soul.
Lily roots in species with large bulbs reach 3 mm in diameter and up to 40-50 cm in length; in species with small bulbs - thinner and shorter; they are perennial and annual.
In some species, for example, the white lily (Fig. 1, item 1), the roots develop only from the base of the bottom of the bulb and are fully or partially perennial, which is why during transplantation and transportation they should not be broken off and dried out.
Clearly Easter Lily has a mixed history. It is also evident that the symbolism of the lily has a certain pagan origin. However, this does not change the fact that the lily was used as a type of Jesus Christ in the Bible. The typology is beautiful and powerful. As long as we can distinguish between them, the biblical type can make a big difference. When used, underline the biblical typology found in the lily of the valley and point people to Jesus Christ.
However, don't look at tradition as support. biblical meaning... Sources: Due to the factual nature of this article, I will have several wording that are very close to my sources. There are many colors, shapes and sizes. It is easy to find lilies in white, pink, red, yellow, purple or orange, striped or dotted. As for its size, the flower diameter ranges from 7 to 25 centimeters. They are orametal flowers, very much used in them, precisely because of their size, and because they are volumetric flowers that fill any corner with color.
In other species, for example, the tiger, Tibetan, Daurian lilies (Fig. 1, item 2), additional roots are formed, extending from the base of the stem above the bulb, these are the so-called stem-root lilies; these roots die off completely every year.
According to the structure of the underground parts, lilies are divided into three groups:
1. Species with an aerial stem only.
Depending on the variety, each stem can contain 3 to 5 flowers. Lilies are not only varied in color, shape and size, but also in their place of origin. Wild lilies can be found in Korea, Japan and parts of Russia, but also near Ecuador or India. In Europe, the lily grows in the Caucasus, the Balkans, Greece, Poland, the Alps or the Pyrenees. They can also be found in most of the United States, with the exception of the southwestern part. It is, indeed, the flower of the world.
Lilies are flowers filled with symbolism. These include the following values. Femininity: Greeks and Romans gave crowns of lilies to women with the intention of wishing them a hopeful and fruitful life. The moment of transition: The serene and pure aspect of the lily expresses the desire to overcome in moments of loss and mourning. 
- Love: In Victorian times, lovers gave lilies to women as a token of love.
- Purity: At weddings, white lilies take on a sense of purity.
2. Species with underground shoots - stolons, called stolon-bearing lilies. Such stolons are a modified bulb, the bottom of which is stretched into a shoot with sparse scales, ending in a bud capable of producing an aboveground plant. Stolons can branch and thus give several aerial stems. In some species, the stolons are shortened, densely seated with scales and represent an elongated bulb with an oblong bottom; the bulbs of such lilies are called rhizome. Under cultural conditions, stolon-bearing lilies often form a normal bulb structure. All stolon-bearing lilies, for example the proud lily, reproduce well with scales (Fig. 1, item 3.4).
If you want to send a bouquet of flowers with lilies, you will love what each one means according to the color. Sending a bouquet of white lilies is a common expression of good intentions and best wishes in relation to another person. Providing a bouquet of yellow lilies is also good option if you want to show loyalty. They also symbolize love and passion. Send a bouquet of orange lilies whenever you want to reward someone. Red lilies: They are a reflection of love and passion. This is a wonderful gift to send to your partner. Rose lilies: associated with kindness, naivety and tenderness, as well as with youth.
- White lilies: symbolize innocence and purity.
- Yellow lilies: associated with joy, happiness.
- Orange lilies: energy, creativity, encouragement and positivity.
3. Species in which the stem, emerging from the bulb, grows obliquely underground and emerges to the surface of the soil often 20-30 cm away from the planted bulb, while on the underground part of the stem, baby bulbs develop, as well as stem roots, usually in small quantities. Such lilies (Fig. 1, item 5) are called false lilies, and their stems are wandering; their bulbs, for example, Willmott's lily, are not very suitable for potting and tub culture.
Lilies are considered one of the most beautiful flowers in the garden. Most of the lilies grown today are garden varieties obtained by breeders from numerous crosses of botanical species. In natural areas, lilies are found only in the northern hemisphere - mainly in temperate climates... The condition for their flowering is periodic hypothermia of the bulbs, therefore, in warmer climates, they grow only in the mountains. A botanical species, found around 120, usually has relatively high cultivation requirements associated with the specifics of the habitat.
The stems of lilies are in most cases round, only in some species are they tetrahedral. Hybridization often produces forms with flat and ribbed stems (fasciations).
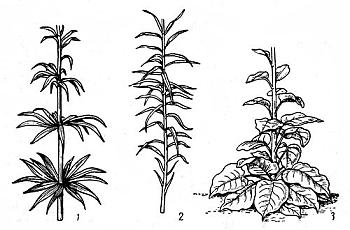 Rice. 2. The nature of the arrangement of leaves along the stem. 1 - whorled, 2 - alternate, 3 - alternate with a root rosette
Rice. 2. The nature of the arrangement of leaves along the stem. 1 - whorled, 2 - alternate, 3 - alternate with a root rosette
Golden lily has flowers up to 25 cm in diameter, sulfur lily flowers reach 22 cm in length; under the weight of such flowers, the stems bend and often break, therefore, despite the significant strength of the stems, multi-flowered and large-flowered species lilies need artificial support and a garter, even when grown in places protected from the wind.
And such a lily as the Tibetan lily, which, under good culture conditions, gives up to 30 heavy and large flowers per inflorescence on a 2-meter stem, despite the special strength of its thin stems, is not able to hold its inflorescences without support.
The height of the lily stems ranges from 5 cm in the mountain-alpine form of the Daurian lily to 4 m in the giant lily.
Lily leaves are usually more or less elongated, ellipsoid or lanceolate, less often ovoid and heart-shaped. The length of leaves in different species ranges from 1 to 15 cm, width - from 2 mm to 8 cm. Leaves are glabrous or pubescent, glossy or matte, always with more or less clearly expressed parallel venation.
In many species, for example, in the marchagon lily, the leaves form up to 5-9 whorls arranged in tiers (Fig. 2, item 1); in some species, for example, the oat lily, there is only one whorl, it is located slightly above the middle of the stem, and above it there are only single small leaves. In most species, the arrangement of leaves on the stem is alternate (Fig. 2, item 2). Some lilies, in addition to stem lilies, form basal leaves, collected in a rosette (Fig. 2, item 3).
Lily flowers consist of 6 large and brightly colored separate perianth lobes, 6 stamens with large brightly colored anthers and a pistil with an upper ovary. The pistil is formed by 6 carpels; the ovary has ovules located on the central placenta, the column is long, with a three-lobed, usually green, less often dark brown stigma. The fruit is a hexagonal capsule, pawing from above when ripe, filled with densely lying flat, translucent, somewhat winged seeds. The size and shape of the capsule varies from cylindrical to short-pear-shaped and clavate.
The shape of lily flowers is quite varied in different species (Fig. 3). Distinguish between cup-shaped, or cup-shaped flowers, directed upward (for example, in saffron and Daurian lilies); flowers of the classic type - funnel-shaped, usually half-ukly (for example, in Tibetan and white lilies); turban-shaped flowers with perianth lobes turned back (by the end of flowering, they are often turned away to the pedicel), usually drooping (for example, in the lily of Martagon and Willmott); bell-shaped flowers with curved tips of perianth lobes (for example, Kesselring's lily).
At present, through hybridization and selection, many hybrid forms of lilies have been obtained between species with drooping turban-shaped flowers, on the one hand, and species with open-up cup-shaped flowers, on the other. In these hybrids, for example, Michurin's violet lily, the flowers are directed with a bell to the side. By selection during sowing, varieties of lilies with flowers directed obliquely upward, instead of drooping, inherent in wild forms, were obtained.
In many species of lilies, double forms have long been known in culture, and the phenomenon of the doubleness of the lily flower, as usual, is due to the partial or complete transformation of the stamens and pistil into petal-shaped perianth lobes. Of these forms of lilies, the most common are: 1) the double form of the tiger lily, perhaps the most beautiful and noteworthy; 2) double, but rather ugly forms in umbrella lilies and Thunberg.
In our practice, Willmott and Daurian lilies often produced beautiful double flowers, as well as 8-, 10- and 12-petal forms, which were not retained either with seed or with vegetative propagation.
 Rice. 3. Types of flowers of lilies. 1 - funnel-shaped, 2 - wide-open, 3 - goblet, 4 - turban, 5 - tubular, 6 - bell-shaped
Rice. 3. Types of flowers of lilies. 1 - funnel-shaped, 2 - wide-open, 3 - goblet, 4 - turban, 5 - tubular, 6 - bell-shaped
Finally, the culture knows the "double" form of the white lily, which is the degeneration of all the organs of the flower into green perianth lobes, which has a spherical green "ovary" in the middle. This form is completely constant during vegetative propagation, and the plant itself is distinguished by its hardiness, but has no decorative value and does not produce seeds.
Lily flowers are usually collected in inflorescences; single flowers are observed only in weak or first-flowering plants.
Lily inflorescences are simple or complex brushes or umbrellas of different lengths, often collected in several tiers. The racemose inflorescences are usually pyramidal in shape and are observed in species with funnel-shaped and turban-shaped flowers. Umbellate and whorled inflorescences, characteristic of species with cup-shaped flowers, are usually chandelier in shape.
Currently, about 85 are known (Some guides on floriculture indicate that about 400 species of lilies are known. This is explained by the fact that the same types of lilies have been described several times by different researchers under different names, as a result of which the number of names known in the literature reaches up to 400, due to repeated names (synonyms)) of lily species common in the northern hemisphere, namely: in Europe, Asia Minor and the Caucasus 13 species, in Eastern and Central Asia 52, in North America 20. Of these, 18 species are found in the USSR: in the European part 1, in the Caucasus 9, in Siberia and the Far East 8. Garden forms about 250 are known of hybrid origin. Almost all species have been introduced into culture.
The most valuable lilies for ornamental gardening (golden, special, Tibetan, Sargent, Billmott, Daurian, coral, drooping, etc.) come from East and Central Asia.
Of the European and Middle Eastern lilies, it is worth noting the white lily, and especially the Caucasian lilies - Kesselringa, one-brother, Shovitsa, Pontic, Ledebour, Georgian, Armenian. These lilies have been studied relatively little in culture, but they are valuable for floriculture, especially as raw material for hybridization. Thus, these types of lilies are of great value and deserve widespread use in ornamental gardening.
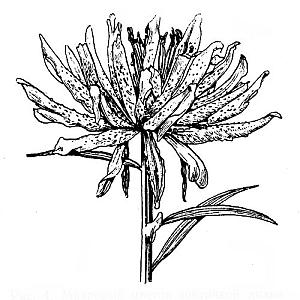 Rice. 4. Double flower umbrella lily (orig.)
Rice. 4. Double flower umbrella lily (orig.)
The natural conditions for the growth of lilies are extremely diverse. Most species of lilies grow in mountainous areas of the alpine and subalpine belts, on the slopes of hills and in the valleys of torny rivers and streams, under the forest canopy, among bushes, less often on open slopes, among a dense grassy cover; certain types grow on bare slopes. Dying grasses and fallen leaves of trees and shrubs provide a good cover for wintering bulbs. In addition, a layer of loose snow, even up to 10 cm thick, protects the soil from severe freezing and sharp temperature fluctuations.
In summer, shrubs and grasses provide good protection from the wind and support for the flower stems of the lilies. Thus, the soil near the base of the lily stems is usually considerably shaded. The upper part of the stems and inflorescences almost always use full sunshine except for a few species of lilies that bloom in some shade.
Lilies grow in different soils; Usually, the composition of the soils on which lilies grow, to a greater or lesser extent, include decomposed layers of dying grass sod and leaf humus, and along the river and stream valleys - alluvial silt impurities. Some species grow on humus-poor soils. Many species prefer acidic soils, others require lime. Most lily species require well-drained soil; wherever lilies grow in natural conditions, their bulbs during the dormant period are always located in permeable soil with a secure drain.
A genus of perennial bulbous herbs of the lily family. In beauty they compete with orchids, but they are far from being so capricious and demanding to care for.
Lily flowers have always amazed the imagination of people with their unusual beauty. The capital of ancient Persia was the city of Susa, which means the city of lilies (Susann or Shushun in the ancient language of the Persians called lily flowers). In France, before the revolution, lilies were a symbol of royal power. The lily flower is present on the coats of arms of many noble families in different countries.
White Lily- the lily of the Madonna among Christians is considered the flower of the Virgin Mary, as a symbol of purity and purity.
Among the Chinese, the most beautiful and attractive part of a woman's body was considered to be very small legs, which, with the help of bandages, were given an unusual pointed shape with an unnaturally curved instep and four toes bent inward. These legs were called "golden lotus" or "golden lily". Only the “golden lily” leg guaranteed in quite recent times a successful marriage to Chinese women.
Girls are named after Lily, implying that they will grow up as beautiful and delicate as this flower.
Bouquet of white lilies symbolizes beauty, purity of thoughts, loyalty and devotion.
Lily is a widespread flower in the Northern Hemisphere, where about 100 of its wild species... Numerous hybrid varieties, which are often named for their place of origin. Oriental hybrids derived from the wild-growing lilies of China and Japan, Asian hybrids are the largest and most unpretentious group of hybrids. Tubular hybrids , named for the shape of the flower. Hybrids derived from these hybrids - for example, Orientepes (the result of crossing Eastern and Tubular hybrids), etc.
The ground part of the lily consists of a stem, the height of which, depending on the variety, can be from 30cm to 200cm. Leaves are usually lanceolate, curved. Flowers from 5 to 25 cm in diameter consist of 6 perianth leaves, which can be in the form of a wide-open bowl, funnel, bell. The edges of the bracts can be straight or strongly curved outward. Usually several flowers bloom at once, which form a real bouquet of lilies on the stem. Inside the flower is sweet nectar that attracts pollinators. Stamens, on long legs, are located around the pistil with a thick three-lobed stigma. The fruit is a seed capsule with a lot of flat seeds.
The underground part of the lily consists of roots and a bulb, which is formed in the first year of planting from a seed, but until the bulb reaches sufficient size (after 3-4 years), the lily does not bloom or blooms weakly. After the bulb has reached the desired size, the lily blooms annually. Both the seeds and the bulbs of lilies are suitable for new plants, but most often the propagation of lilies is carried out by bulbs, because in this case, species differences are better preserved. Although lilies grown from seeds are less susceptible to viral diseases.

LILIES. VARIETIES.
Probably the most famous lily variety- tiger lily, or lanceolate lily. Abundantly flowering plant with flowers similar to a turban of bright orange color with numerous specks, but many do not even suspect that the tiger lily is white, pink, red, there are also yellow lilies of this variety.
Flower lovers are especially fond of the white lily - a symbol of nobility and purity. White lily otherwise they call the snow-white lily, the lily of the Madonna. It has long been grown in the Mediterranean countries. The oil of this lily is used for cosmetic purposes to soften and brighten the skin of the face.
In our area, a curly lily is found in the wild.
There are many more species of lilies known from time immemorial, but most of the lilies grown in modern gardens belong to one of the hybrid groups obtained through the efforts of breeders.
The largest group of garden lily hybrids is Asian hybrids. Lily varieties of Asian hybrids are distinguished by their unpretentiousness to soils and care, they hibernate (practically throughout the entire territory of the CIS) without shelter, rarely get sick, tolerate both bright sun and light shading well. Asian hybrids come from the wild-growing lilies of Transbaikalia, the northeastern provinces of China, Mongolia. These are Daurian lily, dwarf lily, David's lily, false tiger lily, etc. The flowers of these lilies are cup-shaped, turbid, drooping, directed to the sides. Lily varieties of Asian hybrids have a wide variety of colors from pure white (for example - Sorpressa), yellow (Val di Sole), pink (Elodie) to dark red (Black Out). Frequent and combinations different colors, dashes, stripes, etc. Of the old proven varieties of Asian lilies, we note the Inchantment - red-orange; Destin - lemon yellow Peprike - bright red lilies, etc.
Lily flowers of Oriental hybrids (Oriental) are very popular. Oriental lilies are distinguished by their exotic beauty, they were obtained by selection of Japanese and Chinese wild-growing lily flowers (Japanese lily, golden lily, beautiful lily, etc.). Orientals grow better in greenhouses. Oriental lilies in the garden, on open ground prefer partial shade, a place protected from drafts, require shelter in winter. Compared to Asian hybrids, they are more often affected by viral and fungal diseases. Representatives of this group: white lily - Siberia; pink lily - Mona Liza; lily lilac with white edges of petals - Tiber and many others.
American hybrids are obtained from North American species of lilies - leopard, Canadian, Philadelphia, proud. These are tall plants (up to 2 meters), drooping flowers, resembling a turban in shape, from golden yellow to crimson tones, with large dark spots. The best varieties: Afterglow, Del North, San Gabriel, Buttercup.
Tubular and Orleans hybrids originate from the Asiatic species of lilies with tubular flowers. These lilies are quite cold-resistant (although it is better to cover them with a layer of foliage for the winter) and are practically not affected by diseases. Popular varieties: Pink Perfection, Regale, Bright Star, Corona White, Golden Splendour ...
European wild curly lily became the basis of the Curly Hybrids group.
Breeders, crossing the above listed hybrids of lilies, received many new varieties: LO hybrids, LA hybrids, OA hybrids, OT hybrids, etc.

LANDING OF LILIES.
The main thing when planting lilies is to correctly determine the place in the garden where the lily flowers will feel best. So Asian hybrids grow well both in open and in slightly shaded areas. In partial shade, species of lilies grow well, having roots on the underground part of the stem (Canadian, curly, etc.). For these lilies, it is desirable that the lower part of the plants with roots be in the shade, so these lilies grow well among low shrubs and perennials.
Eastern hybrids grow better not in bright sun, but in light partial shade, but the lilies of Henry, David, Daurian, royal, leopard, drooping and their hybrids grow well in open sunny areas. It is not recommended to plant lilies on the north side.
Lily - the flower is not particularly demanding on the soil, but the vast majority of lilies do not tolerate stagnant water. For lilies, a light sandy-clay soil with the addition of leafy earth or peat is suitable. The soil should be neutral or slightly acidic.
Calcareous soils are preferred by the lilies of Henry, David, Royal, curly, lilies of the Caucasus and their hybrids, Dutch hybrids.
On peaty soils with the addition of leafy humus, American species and their hybrids develop well; oriental lilies.
Clay soils with the addition of lime are preferred by snow-white lily (Madonna's lily), as well as Taiwanese and Chalcedony.
The soil under the lilies should contain a sufficient amount of nutrients, primarily phosphorus and potassium. With a lack of phosphorus, the size of the flowers decreases, the color fades. Lack of potassium leads to poor development of babies and bulbs, which also affects appearance flowers and degrades the quality of planting material, therefore, the main fertilizer must be applied before digging the soil. Phosphate fertilizers applied to the soil at the rate of 100 gr. for 1 sq. m. Potash fertilizers - 40-60 gr. for 1 sq. m.
Humus is considered the best fertilizer for lilies. It must be made at the rate of 7-8 kg per 1 sq. M. Large quantity humus can be harmful - the plants will "fatten", which leads to stunted growth, reduced disease resistance, plants tolerate wintering worse.
Lily bulbs with large flowers are planted at a distance of 20 cm from each other and between the rows. Lilies with small flowers can be planted 10-15 cm apart. It is good to pour sand or gravel into the furrows between the rows, which will save the lilies from excessive accumulation of moisture. Before planting, it is advisable to soak the bulbs for half an hour in a disinfecting solution (manganese, foundation, etc.).
Lilies do not tolerate drying out of the roots. When planting and replanting lilies, the bulbs should not be kept in the sun. If the roots are dry, cover the bulbs with a damp cloth and allow time for them to absorb the water.
Large bulbs are planted to a depth of 25 cm, small bulbs are planted to a depth equal to three bulb diameters. Only snow-white lily bulbs, chalcedony and hybrid testaceum lily, the soil layer above the bulb should not exceed 2-3 cm, since these lilies form a root rosette of leaves.
In light sandy loam soils, lily bulbs are planted deeper, in heavy clay soils- smaller.

LILY TRANSFER.
Planted lilies grow in one place for 3-4 years. In the fourth - fifth year, the nest of bulbs grows strongly and must be divided and transplanted to a new place. Every year, digging and drying the bulbs, as is done with tulips, is not only unnecessary, but even harmful. Lily bulbs cannot stand drying out. When transplanting lilies, the nest must be divided. Plant the children separately and cover the planting with a 3-5 cm layer of humus or compost.
The most suitable time for planting and transplanting lilies is August - September, at the latest - early October. Only a very few lilies, such as the king lily, can be replanted in the spring.
When transplanting, you need to be careful about the roots. You should try to arrange them evenly in all directions from the bulb, without crushing or twisting.
LILIES. CARE.
How look after lilies? It is very important to follow the basic rules when planting lilies, then care will be easier, but without attention, you will not be able to get a full bouquet of lilies. So in the first year after planting, it is unlikely to get lily flowers, such as in a photo in a magazine or on an advertising brochure. The plant should gain strength, so in the first year after planting, it is better to remove all or most of the buds. In the future, the buds are plucked out only from weak plants.
Lily flowers need to be fed several times during the season. The first feeding with a full complex of fertilizers at the rate of 50 gr. for 1 sq. m. given in early spring before plant growth begins. This top dressing is applied to the ground. After 2-3 months, when the buds begin to form, a second top dressing is applied with full fertilizer in liquid form (40 grams per 10 liters of water, per 1 sq. M.) Or dry fertilizers, which are scattered on the ground before watering or before rain. The third top dressing, too, with full fertilizer is carried out after flowering, but no later than mid-August (50 grams per 1 sq. M. Dry or 40 grams per 10 liters per 1 sq. M. In liquid form). It is useful to add ash to the soil several times per season at the rate of 100 grams. for 1 sq. m. (Plants get sick less, and their flowers become larger and brighter).
During the season, the soil under the lilies must be loosened, mulched with leafy soil, humus, peat, and weeds must be removed. Lily is a flower that does not like excessive moisture, but in dry weather the plants must be watered, especially at the stage of bud formation. At the same time, you should try to moisturize the leaves less, because this contributes to the development of diseases.
Tall lilies with thin stems or large inflorescences are tied to pegs or strengthened in another way, preventing lodging and breaking off the stems.
If the lilies are not transplanted, then with the onset of frost at ground level, the peduncles are cut off. Previously, you should not do this, because until the very frost, the leaves and stems of the lily continue to supply the bulb nutrients... Cut leaves and flower stalks must be burned. This is a prophylaxis against various diseases.
For the winter garden lilies cover with leafy earth or humus, with a layer of up to 10 cm. The same layer of leaves is poured on top and covered with spruce branches of pine or spruce. Lilies of Asian hybrids, LA hybrids and some others do not require shelter for the winter.
In the spring the shelter is removed before sprouts appear, but young shoots must be protected from night frosts by covering with a film. You should be especially careful about planting baby bulbs. Their sprouts appear early and they are very fragile, so it is better to keep them under a film on a frame at night.
DISEASES OF LILIES. PESTS.
Unfortunately, many hybrids of lilies are affected by various viral and fungal diseases. Asian hybrids, LA hybrids, OT hybrids, Tubular and Orleans hybrids are relatively more resistant to diseases.
The occurrence of fungal diseases is often promoted by damp, cold, little sunny weather, as well as failure to comply with basic agrotechnical measures when growing lilies and storing bulbs.
The most common fungal disease of lilies is gray rot caused by the fungus Botrytis. Leaves, stems and buds are stained with gray downy mildew. If you do not take action, the whole plant is affected. At the first signs of the disease, all affected parts of the plant must be cut off and burned. Remove moldy soil, treat lily flowers with systemic fungicides. The best remedy against gray mold are preparations containing copper (for example, a 0.5% solution copper sulfate). In wet weather, these drugs are sprayed with plantings of lilies as a prophylaxis. During the season, 2-3 sprays are usually carried out.
Fusarium mushroom causes soft rot bulbs. On the scales of the bulbs, watery, rapidly blackening spots appear, the bulbs and roots under the bulbs become soft, moldy, the plants look depressed, sick. Control measures: dug out damaged bulbs (with a small lesion), powder with sulfur and coal in a 1: 1 ratio, pickle the bulbs in a 0.3% rocor solution for 40-50 minutes. In case of significant damage, dig up the plant and burn it.
Lily flowers are also affected by viral diseases that are spread by aphids. The most common viral disease of lilies is mosaic. First, light elongated spots appear on the leaves, then the entire leaf dries up. Lilies wither and do not bloom. Long-flowered, Taiwanese, golden, snow-white lilies are especially susceptible to this disease. Hybrids of Thunberg lilies, testaceum, sometimes tiger, are always amazed by the mosaic, but this is not particularly reflected in their growth, development and flowering. Brown, Hanson, curly, leopard lilies are not affected by viruses. King lilies, drooping lilies, sulfur lilies, as well as the lilies of Henry, Sargent, Willmott are strongly affected by viral diseases. These varieties of lilies are best grown from seed, because plants grown from seeds are not affected by viruses. As a prophylaxis for viral diseases, lilies should not be planted next to plants that are susceptible to viral diseases: cucumbers, dahlias, tobacco, etc. Diseased plants must be destroyed immediately. There are no other measures to combat.
Lily flowers are most often affected by pests when forcing them in greenhouses. Aphids, thrips settle on plants, spider mites... These pests suck out the sap from plants, which weakens, develops poorly and blooms. To combat pests, plants are sprayed with a solution of potash soap (200-300 gr.per 10 liters of water), a solution of anbazine sulfate (1 gr.per 1 liter of water) or nicotine sulfate (1 gr.per 1 liter of water) with green soap (4 grams per 1 liter of solution), or 0.2-0.3% karbofos solution.
Lily bulbs are damaged by root mites, onion fly larvae. To prevent damage to the bulbs, before planting, they are pickled with a 0.25% rocor solution for 40-50 minutes or disinfected in another way.
Various rodents, which eat bulbs, stems, and seeds, cause significant harm to the plantings of lilies. Laying their moves in the soil, moles destroy root system plants. Common rodent control measures are poison baits.

WATER LILY. ROOM LILY AND OTHER
It is not only garden lilies that are meant when they talk about lilies. There are other flowers belonging to different families called lilies. So a white water lily (Nymphaea Alba), many know how water lily... it beautiful flower an aquatic perennial with a thick rhizome extending into the bottom of the reservoir, rounded leaves and large white (sometimes, depending on the variety, pink) flowers that float on the surface. Water lily flowers bloom during the day, and at night they close and sink under the water. Blooming water lilies will decorate any body of water. White water lilies reproduce vegetatively (by rhizome) or by seeds, which in natural conditions are carried by waterfowl. White water lilies, also called nymphs, can be grown in decorative ponds, in barrels in the garden or even on the balconies of city apartments. To grow water lilies, you need a container of at least 45 cm in diameter and at least 50 cm in height. A heavy soil of turf, humus, clay and sand is placed at the bottom, which should cover the roots. It is advisable to sprinkle the soil on top with pebbles and sand. Water is poured so that the leaves float freely on the surface. As the plant grows, water must be added. In small containers, the water (partially, by 3/4) is changed once a month, while simultaneously cleaning the container from foreign algae and outdated old leaves and peduncles. To bloom, water lilies need at least 3 hours of direct sunlight, but in small containers in the hot sun, the water can overheat, which has a bad effect on the condition of water lilies, therefore, the container with flowers must either be surrounded tall plants, which will give the necessary shadow, or cover in some other way. Such plants hibernate at temperatures from 0 to +10 degrees. All large leaves are cut off, leaving the smallest leaves. The water is drained just to cover the leaves, covered and taken to a basement or other room with a suitable temperature. In the spring, when the threat of frost has passed, water is added to the container with lilies and moved to a permanent place.
Hybrid forms of nymphs propagate only vegetatively, the rest - by seeds or by dividing the rhizome. You can buy lilies in specialized stores. Planting material for breeding water lilies, they are sold only in containers, because these plants are very sensitive to moisture loss.
Due to the high starch content in the seeds and rhizomes of water lilies, they can be eaten. Flowers and roots of white water lilies contain a mixture of different alkaloids, therefore folk medicine they are used as a sedative, antihypertensive, sleeping pill. The crushed leaves and roots have anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects.
Lilies, like many bulbous plants, are suitable for forcing in indoor conditions... To obtain blooming lily in a pot, the bulbs are planted in the soil for bulbous plants at the end of October. A lily pot with a diameter of about 15 cm, must have good drainage... For 2.5 - 3 months, the planted bulbs are kept at a temperature of approximately + 5 degrees, after which they are mixed at a visit with a temperature of 15-16 degrees, but at the same time the night temperature should not exceed + 12 degrees. Rooting takes place within a month, after that you need to find the lightest place for the lily, and it is better to organize additional lighting with fluorescent lamps, water abundantly and sometimes spray, preventing water from getting on the opened flowers.
Flowering lasts about a month, if the flowering plant is kept at low temperatures (+5 - 7 degrees), then flowering can be extended.
After the lily has faded, the soil is kept in a slightly moist state until the leaves and stems die off, after which they are removed, the bulb is transplanted into new land and sent to rest. The cycle repeats itself.
As a room lily, the Amazonian lily or the Eucharis flower is often grown, which has nothing to do with lily flowers, belongs to another family - the amaryllis. it unpretentious plant... Doesn't require a lot of light. The most favorable temperature is + 15-18 degrees, but it also tolerates higher temperatures. Water abundantly, but not often. During the growing season, fertilizers are applied, transplanted every 5 years. Propagated by bulbs, which, when planting, must be completely covered with earth.
Another flower called " black Lily"And has nothing to do with the family of real lilies - this is a takka flower, originally from Africa and South-East Asia... This flower is a great exotic for our places. You can meet him in greenhouses and botanical gardens.


