Common potato. Dosage forms, method of using potatoes. The use of potatoes in medicine
Potato (lat. Solanum tuberosum)- a popular vegetable crop; perennial tuberous herbaceous plant.
Description
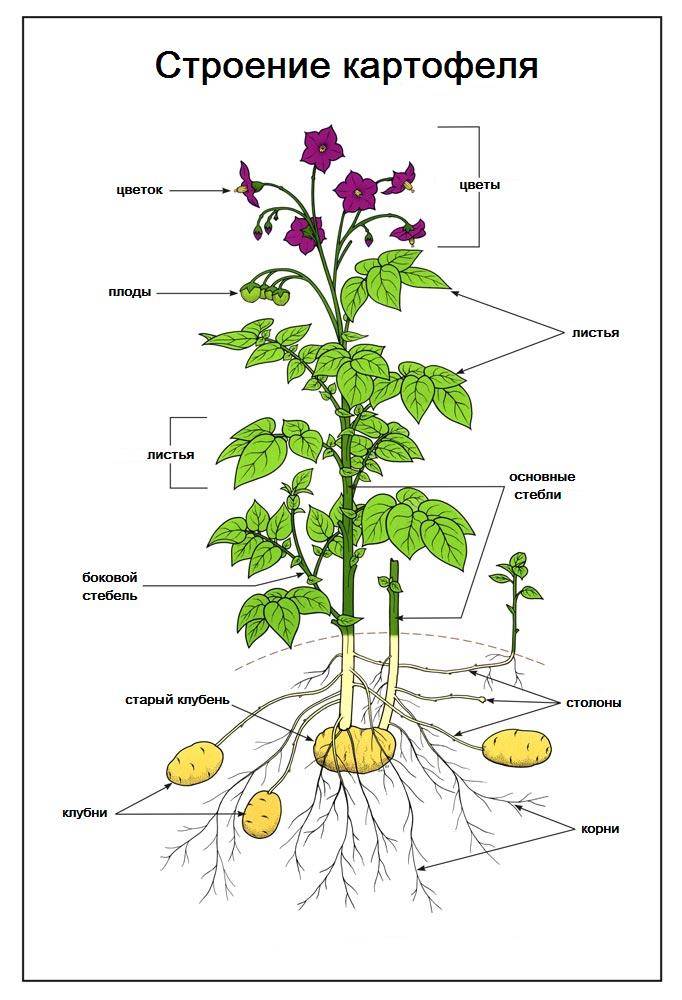
Potatoes are classified as perennial crops, but in Russian Federation it is cultivated as an annual low temperatures are extremely detrimental to tubers. The stem of the potato is ribbed, erect, branched, light green, no more than 150 cm high. The root system of the culture in question is branched, most of the roots go 60 cm deep.The leaves of the culture are pinnate, dissected, entire, dark green in color, equipped with petioles. Inflorescences are presented in the form of complex curls, they can be white-yellow, pure yellow, purple or purple-red, depending on the variety. The fruits are multi-seeded spherical or oval berries. A potato tuber is a thickened and short stem shoot, many eyes are formed on it. Tubers are round, oval or elongated; color - yellowish, brown, violet-blue or pale pink.
The subtleties of growing
Potato is a photophilous culture, it does not tolerate shaded areas well, as a result, plants develop slowly, and tubers are prone to rotting. Lack of sunlight leads to stretching of the stems and limited flowering, which threatens with a small crop of tubers. The normal temperature for cultivation is 20-22C. Temperatures above this limit result in slower tuber development.Positively, potatoes also relate to moisture, although they do not tolerate dampness and waterlogging. With a lack of moisture, the foliage quickly withers and dries up as a result. Soils for this crop are preferred loose, permeable, rich in potassium, nitrogen and phosphorus. An excess of minerals has a detrimental effect on the leaves as well. The second increases the green mass. Potatoes are negatively related to heavy clay, damp, strongly acidic and dense soils. The best forerunners of culture are vegetable crops. Many gardeners advise not to grow potatoes in one area for several years, although in practice no one uses this rule.
Soil preparation
The soil for potatoes is plowed to a depth of at least thirty centimeters, large lumps are broken up and organic fertilizers are applied. The introduction of fresh manure should be discarded, since it contributes to the development of pathogenic bacteria, plants are exposed to various diseases. Apart from organic fertilizers, the soil is also fed with mineral fertilizers, it can be superphosphate, ammonium nitrate and potassium salt.Landing
Potatoes are planted in late April - early May. For planting, I use pre-sprouted tubers weighing 50-80 g with thick sprouts 1-1.5 cm long. Tubers of unknown origin are treated in a 1% solution boric acid at least 20 minutes. The crop is planted in soil warmed up to 6-8C, according to the scheme 30 * 80 to a depth of 6-12 cm, in this case, the heating and germination of tubers is best ensured.Care
Until the appearance of potato sprouts, the soil is loosened at least twice every seven days. This procedure will prevent the emergence of weeds and fully aerate the soil. Plants that have gained a height of about 10-12 cm are spudded with a chopper. The second time spud about a month later.Watering the culture is carried out in a dry summer, for this you can use automated watering cans operating under the action of water pressure. Mineral fertilizers are applied when the first signs of potato wilting appear. In the phase of flower formation, plants are sprayed with organo-mineral fertilizers with a stimulating effect.
Harvest and storage
Potato harvesting is carried out in mid-September, it can be later, but in dry and sunny weather, otherwise the crop will not be stored well. A week before digging, the tops of plants are cut with a trimmer and raked.The tubers obtained by digging are sorted, left in the sun to dry and scattered under a canopy. After drying, the potato crop is placed in wooden containers or special bags. Store the potato harvest in the cellar, optimum temperature storage - 2-3C.
Photo of the flowers of the plant Common Potato
Potato - medicinal properties
Potato used as an enveloping, anti-inflammatory agent for gastrointestinal diseases, as a cosmetic.
Latin name: Solanum tuberosum.
English title: Potato.
Family: Solanaceae - Solanaceae.
Pharmacy name: starch, potato starch - Solani amylum (formerly: Amylum Solani).
Potato parts used: tubers, flowers.
Botanical description: potato is a herbaceous plant up to 50 cm in height. Leaves pinnate; the flowers are white, lilac or lilac, collected in half-umbrellas. From the axils of rudimentary leaves in the underground part of the stem, underground shoots grow - stolons, which, thickening at the tops, give rise to new tubers (modified shoots). At the ends of the stolons, tubers develop, which, in essence, are nothing more than swollen buds, the entire mass of which consists of thin-walled faceted cells filled with starch, and the outer part consists of a thin layer of cork tissue. The fruit of the potato is a multi-seeded, dark green, poisonous berry 2 cm in diameter. The tubers ripen in August - September.
Active ingredients: 1 kg of boiled peeled potatoes provides the body with 20% protein, 40% carbohydrates, 60% vitamins B1 (thiamine) and PP (nicotinic acid), 30% vitamin B2 (riboflavin), 200% vitamin C, and potassium (200%), magnesium and phosphorus (50%), iron (60%) and calcium (20%). Caloric content in this case is 800-900 kcal (30% of the daily requirement).
Nutritional table for 100 grams of potatoes in their skins
100 grams of skinless baked potato contains 4.29 grams of protein, 46.06 grams of carbohydrates, 7.9 grams, calories = 198 kcal.
Vitamins:
- - 10 IU
- - 0.122 mg
- - 0.106 mg
- - 3.065 mg
- - 0.857 mg
- - 0.614 mg
- - 22 mcg
- - 13.5 mg
- - 1.7 mcg
- Other vitamins in potatoes are absent or contained in the smallest amount.
Macro- and microelements:
- - 7.04 mg
- - 573 mg
- - 34 mg
- - 43 mg
- - 0.616 mg
- - 0.817 mg
- - 21 mg
- - 0.7 mcg
- - 101 mg
- - 0.49 mg
- Other macro-microelements are absent in potatoes or are contained in the smallest amount.

Potato - medicinal properties and uses
Potato juice has long been used to treat peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum. And potassium, which is rich in potatoes, is simply necessary for patients with heart and kidney diseases. Used for medicinal purposes and the starch of this wonderful natural gift. So, it is used as an enveloping, anti-inflammatory agent for gastrointestinal diseases. Even with severe forms of poisoning, you can eat boiled potatoes.
Recipes
- Infusion of flowers. Three tablespoons of flowers pour 1.5 cups of boiling water. Insist in a thermos or a warm place for three hours.
- Corned beef tincture. For more than 3 weeks, hold the potato tubers in the light - in the sun, until their surface turns dark green and the inner flesh turns bright green. Then the tubers should be washed with water and grated together with the peel (the peel and eyes contain the largest amount of solanine). Squeeze the juice from the resulting pulp, pour into a bottle, add vodka in a ratio of 2: 1 and let it brew for a week.
- flower tincture. 6 days after the potatoes bloom, collect potato flowers (color does not matter), tamp them tightly into a glass jar to the brim. Pour flowers with vodka or alcohol. At the same time, shake the jar periodically to release air. Close the jar with a lid and put in a dark place for 20-25 days.

photo of potato juice
ATTENTION!
Self-treatment is dangerous! Before treatment at home, consult with your doctor.
Potato treatment
- Abscess. Apply fresh grated potatoes.
- acne(acne). With phlegmonous acne, a compress of peeled and grated raw potatoes will help, change every 2 hours.
- Angina. With the onset of sore throat, a raw potato compress is very effective. 2-3 potatoes medium size wash, grate together with the peel, put on a strip of gauze folded in half, sprinkle lightly with table vinegar (not essence!). Fold the gauze and wrap the throat with this scarf. Top cover with polyethylene and wrap with a warm scarf or towel. Go to bed. Keep the compress for 4 hours, tightly pressed to the neck.
- Angina. Dry the potato flowers in the shade. Pour boiling water over 1 teaspoon of flowers in a clay pot - 1/4 cup. The pot can be placed on top of a freshly boiled kettle and allowed to cool. You can either gargle with a decoction or lubricate it with a cotton swab.
- Angina(inhalation). Washed, unpeeled potato tubers are put in a saucepan, poured with water and boiled until tender. The steam is inhaled, bending over a pot of potatoes and covering the head with a sheet or blanket.
- Arthritis. For those suffering from gout, arthritis, arthrosis, heel spurs, the following remedy will help: fill a jar of light glass with potato sprouts (choose the thickest and shortest, do not wash), lightly crush. Put an open jar on the windowsill for 2 weeks, after this period, fill the jar with medical alcohol (300 g of alcohol is needed for a half-liter jar), close tightly and place in a dark place for a month. Strain. Once a day, before going to bed, rub sore spots. One course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks according to well-being.
- Arthritis. 1 cup shoots of sprouted potatoes up to 1 cm long, rinse, dry slightly, pour 0.5 liters of vodka, leave for 21 days, rub sore joints with tincture.
- Arthritis of the hands. Take a raw, washed, but unpeeled potato, squeeze it into a fist. Put on a mitten on your hand (so as not to drop it in a dream), and so sleep. It is not necessary to change the potato each time, you can use it until it sprouts or shriveles.
- Myopia. Dry the potato flowers in the shade. Pour into a teaspoon clean, cold boiled water. Drown one dried flower in it. Hold the spoon over the candle until bubbles appear in the spoon (do not bring to a boil!). Cool to the temperature of fresh milk and use a pipette to instill two drops into each eye (no more!). There will be pain and tears in the eyes, but we must be patient. Dry your eyes with a clean handkerchief. The course of treatment is from 2 weeks to 1-2 months. It is better to do this procedure in the morning. After 2-3 weeks, check your vision with a doctor. This method cleanses the eyes, restores vision from -3-5 to normal. During treatment, you should not wear glasses and use a computer.
- Bowel disease. Drink 200 ml of potato juice every morning 30 minutes before meals. The course of treatment is 10 days, repeat after 10 days.
- Warts. Keep your hands in a decoction of potato peels. Then dry without wiping. Do the wart removal procedure at night.
- Warts. Lubricate the warts with potato juice. On half of the potato, on the cut, make two scratches, crosswise, make the same scratch on the wart, drip the juice. Warts will disappear in 1-1.5 months.
- Warts. For the night and for the whole day, make a compress with tincture of potato flowers. Place the flowers tightly in a medicine bottle, pour 70% medical alcohol to the top, leave for 10 days.
- Pain in the liver. With severe pain in the liver, potato applications will help. Mash 0.5 kg of boiled potatoes in their skins together with the skin and put on a linen or linen cloth. Apply a hot potato cake to the sore spot (at the same time, pleasant warmth should be felt) and wrap a warm scarf on top. Keep the application until it cools, then remove the potatoes, and wrap the place of application warm again. Such procedures should be done within 3-4 days.
- Joint pain. Wash 3 potatoes, dry and grate on a coarse grater. Wrap the resulting slurry in 3 layers of gauze and apply to the diseased joint. Top with polyethylene and wrap with a warm scarf. At the same time, take a warm potato decoction three times a day, 1 cup.
- Bronchial asthma. To get rid of suffocation allows a 15-minute inhalation over potatoes cooked in their skins with the addition of seeds (2-3 tablespoons) or greens (several twigs).
- Inflammation of the gastrointestinal tract. In the morning before eating, drink 1 glass of potato juice, then go to bed for 30 minutes, and after 1 hour you can have breakfast. The course of treatment is 10 days, repeat after 10 days.
- Gastritis. In the morning, before breakfast, cut out eyes from 4-5 potatoes (no need to peel), then grate them, squeeze the juice, add 2 teaspoons of honey, stir and drink the whole portion, lie down for half an hour. Then you can get up and eat. Course of treatment: 10 days to take juice, 10 days to rest, 10 days to take juice, 10 days to rest, 10 days to take juice. Exclude fish, meat, fish and meat products from the diet.
- Gastritis chronic(with normal and increased secretion). Potato juice - half a glass, honey - 1 tablespoon. Mix fresh juice with honey. Drink before meals 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10 days, after 10 days the course is repeated.
- Gastritis chronic(with normal and increased secretion). Drink 100 ml of fresh potato juice in the morning.
- Hepatitis. For pain in the right hypochondrium, make poultices from boiled potatoes with peel.
- Hypertension. Three times a day before meals, drink juice from one medium-sized potato. Just use 3 potatoes a day.
- Hypertension. Drink a decoction of potato peels three times a day for a third of a glass.
- Hypertension. In case of hypertension, potatoes of the "Sineglazka" variety are thoroughly washed, boiled in a peel without salt. Drain the decoction and drink 1 glass 3 times a day.
- Glossitis(inflammation of the tissues of the tongue). Rinse your mouth 2-3 times a day after meals with fresh potato juice.
- Dyspepsia. In the morning on an empty stomach, drink 1 glass of potato juice, then go to bed for 30 minutes, have breakfast after 1 hour. The course of treatment is 10 days.
- Wen(lipoma). 1 tablespoon of dried potato flowers pour 0.5 boiling water, insist in a thermos for 3 hours. Strain. Drink an infusion of 100 ml 3 times a day half an hour before meals. 10 days to drink, 5 days - a break. The course of treatment is 3-4 months.
- Malignant tumors of internal organs. Take half a glass of infusion of flowers half an hour before meals three times a day. The course of treatment is 14 days.
- Heartburn with high acidity. Potato juice drink 100 ml 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 10-12 days.
- Heartburn. In the morning, before breakfast, cut out eyes from 4-5 potatoes (no need to peel), then grate them, squeeze the juice, add 2 teaspoons of honey, stir and drink the whole portion, lie down for half an hour. Then you can get up and eat. Course of treatment: 10 days to take juice, 10 days to rest, 10 days to take juice, 10 days to rest, 10 days to take juice. Exclude fish, meat, fish and meat products from the diet.
- Heartburn. If you suffer from heartburn, you need to chew and swallow a piece of raw potatoes.
- Coronary artery disease. Rinse 1 cup of potato flowers (not chemically treated against pests) and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes, strain and add 2 tablespoons of honey. Drink an infusion of 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
- Cyst on the kidney. Chop the blue-eyed potato sprouts and put in a liter bottle, filling it 2/3, pour vodka and leave for 3 weeks in a dark place. Strain and take 1 time per day, starting with 1 drop in 50 ml of water one hour before meals. Gradually adding tincture drop by drop, bring the dose to 30 drops per 150 ml of water and start reducing again to 1 drop. After a week break, repeat the course of treatment, but bring the dose to 40 drops. The next course is up to 50 drops. If necessary, courses can be continued, increasing the dosage to 100 drops. At the same time, you can drink a decoction of burdock roots (1 tablespoon per 1 glass of water, boil for 5-10 minutes).
- Mastitis. Rub a few washed and dried potatoes on a fine grater, squeeze lightly and put the gruel on your chest. Top with a clean cotton cloth, compress paper and a warm handkerchief. Hold the compress for 2 hours. This treatment procedure is carried out 2-3 times a day for 2 days.
- Migraine. Potatoes are considered very effective tool against migraine. Our ancestors boiled potatoes in their uniforms and, with debilitating headaches, not only applied warm potatoes to their foreheads, but also drank freshly prepared potato juice in a quarter glass 3 times a day 30 minutes before meals for a week.
- uterine fibroids
- uterine fibroids. Every day for six months in the morning on an empty stomach, take 1/2 cup of potato juice, and it is better that the potatoes are pink varieties.
- calluses. Put potato flowers in a half-liter jar, pour vodka over it, leave for 10 days in a dark place. Make lotions of tincture on corns.
- frostbite. After restoring sensitivity, hold the sore spot in warm, unsalted potato broth 30 minutes.
- General cleansing of the body. To quickly and harmlessly cleanse the body of fungi and microbes, bacteria, viruses - take 5 drops of solanine tincture per 0.5 glass of water in the morning and evening 15-20 minutes before meals. After 5 days of admission, take a break for 5 days. Complete 4-5 such courses at once.
- burns. Apply potato pulp.
- Oncological diseases. 1 tablespoon of potato flowers pour 500 ml of boiling water, leave for 3 hours in a thermos, strain. Drink 1/2 cup 30 minutes before meals 1 time per day. Course of treatment: drink 4 liters of infusion!
- Acute dermatitis(due to sunburn). Put a compress of peeled and grated raw potatoes, change every 2 hours.
- Puffiness under the eyes. Grate thoroughly washed potatoes. Take two pieces of gauze, put 1 tablespoon of grated potato on each and attach to the eye bags for 10-15 minutes. After that, apply cream for the skin around the eyes to the places of edema in the direction from the bridge of the nose along the lower eyelid to the temples. After 15-20 minutes, remove the rest of the cream with cotton wool soaked in cold tea. The procedure should be done 2 times a day - in the morning and in the evening.
- Puffiness under the eyes. Cut the potatoes boiled in their uniforms in half and apply to closed eyes for 30-40 minutes. The temperature of the potatoes should not be too high, so as not to damage the skin.
- Salt deposits. 2 cups of potato flowers pour 0.5 liters of alcohol, bury in the ground, leave for 10 days, strain. Wipe the joints with tincture.
- Cleansing the body. Take 5 drops of solanine tincture in 0.5 cups of water in the morning and evening 15-20 minutes before meals. Drink for 5 days, break for 5 days. Pass 4-5 such purification courses.
- Swelling of the legs. Grate peeled potatoes and apply to the sore spot for 20-30 minutes, wrapping with a rough cloth.
- Otitis. Drip 2-3 drops of solanine tincture into the ear, cover with a piece of cotton. The pain will go away. Repeat a couple more times for prevention.
- pancreatitis. Drink 100-200 ml of freshly prepared potato juice every day in the morning and evening 2 hours before meals, and fresh kefir 5 minutes later. Potatoes are better Pink colour. Do not remove the skin. Potato juice should stand for no more than 10 minutes! The course of treatment is 15 days, then a break of 12 days. You need to spend 3-4 courses. You can not eat green tubers, they contain the poisonous substance solanine!
- Acidity. Take freshly prepared potato juice 3/4 cup three times a day on an empty stomach one hour before meals and at bedtime for 10 days, then take a 10-day break. Repeat the course of treatment. Attention! Juice can be made from July to January, while the solanine level in the potatoes is low.
- Gout. Fill a jar of light glass entirely with potato sprouts (choose the thickest and shortest, do not wash), lightly crush. Put an open jar on the windowsill for 2 weeks, after this period, fill the jar with medical alcohol (300 g of alcohol is needed for a half-liter jar), close tightly and place in a dark place for a month. Strain. Once a day, before going to bed, rub sore spots. One course of treatment lasts 2-3 weeks according to well-being.
- Sweating feet. Dust your feet with powdered dry potato starch.
- Cold. Do inhalations with a decoction of potato peel for 10 minutes.
- Rheumatism. Fill a half-liter glass jar with potato flowers, pour alcohol, bury in the ground for 10 days, strain. Lubricate sore spots at night.
- Rheumatism. Dry 10 g of potato sprouts, grind into powder, pour a glass of vodka in a dark glass dish, leave for 24 hours. Pour 0.5 cups of olive oil into the tincture, shake. Rub the sore spots with the prepared remedy 2-3 times a day, wrapping them with a woolen scarf after the procedure. The procedure is recommended for aching pains.
- Erysipelatous inflammation of the skin. Put the mashed raw potatoes on a cotton cloth and apply to the sore spot.
- bruises. To the site of the bruise, bandage the plates of chopped potatoes.
- Furuncles, pustular skin lesions. Put a compress of peeled and grated raw potatoes, change every 2 hours.
- fibroma of the uterus. Pour in a thermos 1 teaspoon of dried potato flowers with one glass of boiling water. Close the thermos after 5-10 minutes and infuse for 4-5 hours. Drink infusion 3-4 times a day 30 minutes before meals, 1/4 or 1/2 cup. The course of treatment is 1 month. Repeated course - in 1-2 months.
- fibroma of the uterus. Take 1/2 cup of raw potato juice daily on an empty stomach. (if the patient does not have swollen nodes and low acidity gastric juice). Treatment is carried out from June to January: drink juice for 1 month, then take a break for 7-10 days. It is necessary to conduct 3 such courses.
- fibroma of the uterus. Rinse 1 cup of potato flowers (not chemically treated against pests) and pour 0.5 liters of boiling water. Leave for 30 minutes, strain and add 2 tablespoons of honey. Drink 1 tablespoon 3 times a day before meals.
- Furuncle. Put the gruel from raw potatoes on a clean napkin and attach to the sore spot, fix. Keep the bandage on for 2 hours.
- Spurs on the heels. Grate the potatoes together with the peel, put on gauze, cover with wax paper and bandage to the sore spot. Do not remove such a compress for a day! If necessary, repeat every other day.
- Eczema. In case of acute dermatitis due to sunburn and pustular inflammation of the skin, a compress of peeled and grated raw potatoes is used, changed every 2 hours.
- Duodenal ulcer. Take 1/2-1/3 cup of freshly made potato juice before meals in the morning and in the afternoon.
- stomach ulcer. During the week, every morning, drink on an empty stomach 30-40 minutes before breakfast a mixture of half a glass of boiled warm water and half a glass of freshly squeezed pink potato juice.
- Ulcer of the stomach and duodenum. Dissolve 1 tablespoon of honey in fresh potato juice. Drink half a glass 3 times a day. The course of treatment is 12-14 days, repeat after 10 days.
Potatoes - traditional medicine recipes:
- analgesic effect has a compress of grated raw potatoes with honey for osteochondrosis. This compress is kept on the sore spot for at least an hour.
- With hypertension Eat a baked potato "in uniform" more often.
- With swelling of the hands or but d peel the potatoes, grate them, apply the resulting potato gruel to swollen areas and keep for 15-20 minutes, wrapping the “compress” tightly with a cotton or terry towel.
- Potato face mask recipe: prepare Potato Tenderness, for which you will need a couple of boiled tubers. Mash and mix them (hot) with one yolk, 1 tsp. honey, a little vegetable oil(preferably olive). Apply the resulting mass on the face, and then rinse boiled water. After this moisturizing and softening potato mask, lubricate your face with a nourishing cream. For lovers of natural cosmetics, I think this recipe will certainly come in handy: mix medium-sized boiled potatoes with 1 tbsp. l. fresh cottage cheese and add 0.5 tsp. honey and half a raw egg. Then apply the finished gruel on the skin of the face and neck. Top with a gauze cloth and hold the mask for 20 minutes, then rinse with warm water. It is useful to do such masks 1-2 times a week for 4-6 weeks. After 2 months, the course should be repeated.
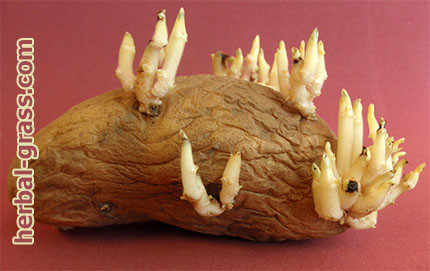
Sprouted potatoes - harm to health
Contraindications. Potato tubers, just dug out of the soil, do not contain the poisonous alkaloid solanine. But if the storage technology is violated, when light hits the tubers, a poison is formed in them that can cause symptoms of severe poisoning. Green potatoes are contraindicated for eating. People suffering from diabetes and other serious diseases should consult a doctor about the amount and appropriateness of eating potatoes.
Potato - Solanum tuberosum L.
4028mdk09" style="border-style:solid;border-width:6px;border-color:#ffcc66;" width="250" height="333">
style="border-style:solid;border-width:6px;border-color:#ffcc66;" width="300" height="202">
style="border-style:solid;border-width:6px;border-color:#ffcc66;" width="300" height="225">
Other names: Tuberous nightshade.
Diseases and effects: peptic ulcer, gastritis, arthritis, belching, heartburn, nausea, constipation, burns, eczema, polyarthritis, freckles, skin cracks, diseases of the cardiovascular system, acute respiratory diseases, dry skin, sunburn, colds, diabetes.
Active substances: starch, protein, sugar fructose, sucrose, fiber, fats, lemon acid, malic acid, oxalic acid, vitamins B 1 , B 2 , B 3 , B 6 , D, PP, K, E, H, U, ascorbic acid, folic acid, carotenoids, essential amino acids, calcium, potassium, phosphorus, iron , magnesium.
Plant collection and preparation time: September October.
Botanical description of potatoes
Potato- perennial herbaceous, tuberous plant of the family Solanaceae (Solanaceae).
Root rod, fibrous, highly developed.
A characteristic feature of potatoes is the formation of underground shoots - stolons, on which tubers develop (the scientific name of the plant just reflects this feature - tuberous nightshade). The tubers serve as a storage nutrients and body vegetative propagation. On their surface, depressions (“eyes”) are noticeable, in each of which there are 3 buds with rudiments of leaves and roots. Only the middle kidney starts growing. Above-ground shoots and roots grow from it. Potato tubers are round, round-oval, elongated-oval, long, flat and others. The main types of coloring are white, yellow, pink, red, purple.
stems potatoes are erect, juicy, ribbed, branched, fluffy, due to hairs pressed to the stem. The height of the stems is 30–150 cm. Outgrowths of green tissue, the so-called wings, are sometimes formed at the junction of the faces on the ribs of the stems. Each plant usually has 4–8 stems. More stems in plants developing from large tubers on fertile, sufficiently moist soils.
Leaves intermittently pinnately dissected, with 7-11 large and smaller leaflets, ovate, pointed, with an unequal base, glabrous above, downy below. Potato leaves are arranged in a spiral on the stems. Leaves have stipules where they branch off from the stem. Simple whole-edged leaves appear first, but they soon die off. The main leaves are pinnate with short petioles.
flowers five-membered are collected at the top in inflorescences-curls. They have a green calyx (consists of 5 sepals) and a cleft corolla (white, pink, blue, purple), against which orange or yellow stamens fused with anthers stand out. The pistil consists of a stigma, style and ovary. After fertilization, the ovary grows and turns into a fruit.
Fetus- globular green berry (which later turns dark purple) 1.5-2 cm in diameter. Fruit seeds (small, yellow) very often turn out to be sterile. When ripe, the berries first turn white and acquire a pleasant smell. The fruits are poisonous.
The plant blooms in June-July.
Distribution and habitat of the potato
The homeland of the potato is South America, where it was introduced into culture in ancient times.
At present, potatoes are grown everywhere in all countries. former USSR planting as a field crop.
Harvesting potatoes
Potatoes are grown as an annual crop. Harvest tubers of red varieties in autumn.
Usually, potatoes are propagated by tubers, less often by true seeds, as well as parts of a tuber with 1-2 eyes, tops, light and etiolated sprouts, layering and cuttings. When sown with seeds, the main root develops from the embryonic root and is, as it were, a continuation of the stem. The roots can penetrate to a depth of 1 m. However, their bulk is located in the arable soil layer.
The optimum soil temperature during seed germination is about 20 °C, tubers - 7-8 °C. Potato tubers are germinated before planting at a temperature of 12-15 °C. The higher the temperature at the same soil moisture, the faster the germination of tubers. Shoots at a temperature of 11-12 ° C appear on the 23rd day after planting, at a temperature of 14-15 ° C - on the 17-18th day, at 18-20 ° C - on the 12-13th day, and at 27-28 ° C - on the 6-7th day.
If in the spring after planting for a short time the soil temperature is in the range of 1-5 ° C, then the tubers do not develop sprouts, but immediately small tubers. This phenomenon is observed especially often in cases where the seed tubers were previously kept warm. The most favorable air and topsoil temperature for tuberization is 17-18°C during the day and 12-14°C at night. When the temperature rises to 29-30 °C or drops to 2 °C, the growth of tubers stops. Tubers freeze at -1.7-2 °C.
How more fertile soil and the more it water holding capacity, the less water is needed to obtain good harvest. Like all living things, potatoes breathe, consuming starch and sugar for breathing. Tubers breathe through small holes in the skin called lentils. Excess water in the soil prevents air from entering it, which adversely affects the growth of young tubers. In such tubers, lentils grow strongly in the form of fluffy white warts on the surface of the peel. This phenomenon is observed with excessive watering or in the event of a large amount of rain; tubers in these cases often rot.
Potato is a very photophilous plant. With a lack of light, it ceases to bloom, forms few tubers, and of poor quality, and with great shading, it dies. In areas that are well fertilized, but with a very thick planting, plants suffer from a lack of light, resulting in reduced yields.
For its growth and development, potatoes use many chemical substances- nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, magnesium, sulfur, boron, iron, copper and others entering it through root system from the soil. The need for nutrients increases with the growth of the tops and reaches a maximum in the flowering phase. Potassium and phosphorus potatoes consume especially a lot in July - during the formation of tubers. Most often, potatoes need additional nitrogen in the soil, especially in a humid climate and on light soils, or potassium on peat soils and where little organic fertilizer is applied - manure. However, the excess nitrogen fertilizer contributes to the accelerated growth of stems with a weak development of the root system. As a result, plants with excessively lush tops evaporate a lot of moisture and often suffer from a lack of it. With a lack of nutrients in the soil, signs appear on the leaves of potatoes that indicate a lack of one or another element: with a lack of potassium, the leaves become wrinkled, their edges bend down, acquire a bronze brown-green color and die prematurely. With a lack of nitrogen and phosphorus, the leaves have a lighter color than normal plants and stick up. With a lack of magnesium in the leaves, brown spots appear between the veins (along the midrib of the leaf lobes).
The introduction of organic fertilizers into the soil, as well as mulching the soil with humus, peat, compost, can almost double the amount of carbon dioxide released from the soil. And the more carbon dioxide in the air, the more it is absorbed and used by the plant to produce starch.
Potatoes develop best on loose, light-textured soils with a finely cloddy structure. For its cultivation, sandy loam, light loams and low-lying cultivated peatlands are preferable. It does not grow well in areas with high level ground water. Potatoes tolerate high acidity of the soil better than other plants, but slightly acidic soils are most suitable for it.
in gardens and household plots potatoes are often forced to grow continuously for more than a dozen years. Continuous cultivation of potatoes in one place contributes to the accumulation of diseases and pests, as well as some types of weeds.
For medicinal purposes, flowers, potato shoots, its peel and underground tubers are used, which are harvested during their ripening period. It should be remembered about one feature of potato tubers - they must be stored in a dark place. Otherwise (if the tubers lie in the light, especially in the sun), they take on a green color and become poisonous, unsuitable for food, much less for medicinal use.
It is known that freshly harvested tubers do not germinate even if they are placed in favorable conditions for this. This is due to the fact that after harvesting the tubers are in a state (period) of natural dormancy.
The chemical composition of potatoes
Potato tubers, depending on the variety and growing conditions, contain 14-22% starch, 1-2% protein (in potatoes it is called tuberin), 0.5-1% sugars (sucrose and sucrose) and about 1% mineral salts, as well as fiber, fats, organic acids (mainly citric, malic and oxalic) and other compounds.
Vitamins B 1 , B 2 (riboflavin), B 3 , B 6 , ascorbic (up to 50 mg%) and folic acids, carotenoids, vitamins D, PP, K, E, H, U, essential amino acids, salts were found in potato tubers calcium (8 mg%), potassium (426 mg%), phosphorus (38 mg%), iron (0.9 mg%), magnesium (17 mg%) and other substances important for human health. In total, tubers contain 32 trace elements. Potato proteins contain 14 of the 20 amino acids necessary for the construction of human body cells, including all 8 that are indispensable, i.e. they are not synthesized in the human or animal body and must be obtained from food.
Nitrogenous substances are concentrated in the core of the tuber and under its skin, that is, where there is less starch.
The biological value of potato proteins is one of the highest among plants (85% of the value of chicken egg proteins and 100% digestibility in humans and animals).
Potatoes are the main supplier of potassium to the body. There is no such amount of potassium in bread, meat, or fish. The potassium requirement of an adult is about 2 g per day, and this can be met by eating 400 g of potatoes per day. Sufficient provision of the body with potassium is especially important for people with diseases of the cardiovascular system, with atherosclerosis, as well as for the elderly.
Pharmacological properties of potatoes
In medical practice, potato tubers are used not only as a source of vitamins, but also for the prevention and treatment of a number of diseases. The tubers of the plant have anti-inflammatory, wound healing, antispasmodic and diuretic properties. Starch obtained from potatoes has an emollient, enveloping and anti-inflammatory effect.
Potato juice inhibits the secretion of the digestive glands. Due to the presence of acetylcholine in potato tubers, the constant use of potato juice helps to reduce blood pressure.
The use of potatoes in medicine
Potato tubers occupy a leading place in dietary nutrition. They are included in the diet of patients suffering from cardiovascular diseases, diseases of metabolism and gastrointestinal tact. Fresh juice is effective for gastritis and peptic ulcer, accompanied by increased secretion of gastric juice. Potato juice (1/2 cup) taken 30-40 minutes before a meal improves digestion and normalizes bowel function.
The use of potatoes in diseases of the cardiovascular system is due not only to the high content of potassium salts in it, but also to the diuretic and antispasmodic properties of the plant. A positive therapeutic effect of grated fresh tubers was noted when applied externally for the treatment of burns, eczema-like and other skin diseases. Acute and chronic respiratory diseases are treated by inhaling vapors containing a number of volatile medicinal substances while rubbing freshly boiled potatoes.
For cosmetic purposes, face masks are used, made from potatoes boiled in their uniforms, mixed with cream or sour cream. Such masks are especially effective for dry skin and the treatment of sunburn.
IN folk medicine fresh potato juice is given orally for high blood pressure, it also helps to reduce the secretion of acid from the digestive glands and scarring of ulcers on the mucous membrane of the digestive tract.
Potato starch is used as a base for powders and fillers in powders and tablets.
For colds of the upper respiratory tract, potato steam is inhaled (the therapeutic effectiveness of this procedure is doubtful, but the relief of the condition is undeniable).
Potatoes that have turned green in the light, containing solanine, are used for compresses for arthritis.
The use of potatoes causes the removal of toxins from the body and thereby contributes to the regulation of metabolic processes. Potassium, contained in large quantities in potatoes, plays a positive role in maintaining the normal function of the heart muscle and, according to the latest scientific data, can be classified as an anti-sclerotic agent. Due to potassium, potatoes have a diuretic effect. Therefore, it is included in the diet of patients suffering from diseases of the cardiovascular system and kidneys.
Potato juice lowers blood sugar levels, so it is useful in the initial stages of diabetes.
Dosage forms, method of using potatoes
Juice from potato tubers. Well washed and wiped dry tubers, together with the skin, are rubbed on a grater or ground in a meat grinder. Juice with starch is squeezed through 2 layers of gauze. Raw juice is taken 1/2-1/3 cup (about 100 ml) 3 times a day before meals, then before lunch and before dinner for 2-3 weeks. After a week break, the course is repeated.
In total, the course of treatment requires from 5 to 15 liters of raw juice. At the same time, they adhere to a sparing diet: drug treatment and physiotherapy procedures are suspended for this time.
Patients with peptic ulcer are recommended to prevent exacerbations of the disease in autumn and spring (from half of September to half of October and from half of March to half of April) to take raw potato juice for two weeks. At the same time, pain, belching, heartburn, nausea disappear, the acidity of gastric juice normalizes, patients gain weight, constipation and intestinal swelling disappear. Treatment with raw potato juice does not give side effects.
Also, juice with milk or sour cream is used to get rid of freckles and cracks from exposed parts of the skin.
Chopped raw potato tubers. They are considered a good healing agent for burns, eczema and various other skin lesions. The mass ground on a grater is simply applied to the affected areas of the skin.
Peel a medium-sized potato, cut into small pieces and slowly chew one by one for heartburn.
Boiled potatoes. Potato is an effective means of cleansing the joints of toxins and is considered a good remedy with polyarthritis. To do this, within 3 days you need to eat 2-3 kg of potatoes, boiled with peel in plenty of water. Potatoes are mashed in broth and eaten with the peel. Do not take any other food during this time. To eat potatoes with skin, you need to cook it for a long time.
Contraindications to the use of potatoes
We should not forget about the possibility of severe poisoning when eating poor-quality potatoes. Poisoning occurs due to the content in germinated tubers, especially in the peel and the so-called eyes, of a highly active glucoalkaloid - solanine. In small doses, this alkaloid has a cortisone-like anti-inflammatory effect, and in large doses it can have a toxic effect. With long-term storage and strong germination of potato tubers or their greening and decay, the content of solanine can increase sharply, which leads to different form poisoning. In large doses, solanine depresses the function of the central nervous system, damages blood cells.
Potato poisoning is characterized by nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, shortness of breath, palpitations, convulsions, severe cases brief loss of consciousness. With the provision of timely medical care, the symptoms of poisoning are stopped.
The use of potatoes in nutrition
In our countries, potato tubers are one of the most common food products. Due to the nutritional value and high content of vitamins, amino acids and minerals, potatoes should be given one of the leading places in terms of dietary and therapeutic and preventive value. Almost half of the daily requirement for ascorbic acid can be met through the use of potatoes in food, and 200 g of fresh potatoes contain almost the full daily dose of ascorbic acid.
During cooking, potatoes should not be exposed to high temperatures for a long time due to the possible destruction of vitamins.
Because potatoes are alkaline, they make a great addition to all vegetables, milk, and cheese.
Other information about potatoes
At the end of the 19th century, the area under potatoes on the planet was about 15 million hectares, after the first world war - already 21 million hectares, and after the second - about 24 million hectares. In recent decades, there has been a reduction in potato plantings: by the end of the 80s of the last century, the total area under potatoes did not exceed 18 million hectares. However, due to the increase in productivity, its gross yields did not decrease.
Now a significant part of the potato tuber crop goes to the production of starch and the production of alcohol.
Potatoes in history and mythology
Potatoes began to be cultivated about 14 thousand years ago by the Indians South America. In the burials and burial grounds of the Indians, vases were found in the form of interconnected potatoes, as well as the dried tubers themselves. There are about 200 wild and cultivated potato species, which grow mainly in South and Central America. There are two main cultural species: Indian (since ancient times grown in Colombia, Peru, Ecuador, Bolivia) and Chilean (homeland - Central Chile), which are widespread in countries with a temperate climate.
The potato was brought to Europe by the conquistadors. In 1553, the book Chronicle of Peru was published in the Spanish city of Seville. Its author, who visited this country, wrote: “Papas is a special kind of peanuts. When cooked, they become soft, like a roasted chestnut ... They are covered with a skin no thicker than a truffle skin. This was the first written mention of potatoes in Europe. Potatoes were originally called truffles. At first, this plant was grown only in botanical gardens and pharmaceutical gardens. As a delicacy, it was sometimes served on the table of kings and nobility.
From Spain, potatoes go to Italy, then to Belgium and other European countries. Initially, everywhere this plant was considered in more like a curiosity beautiful flowers and to a lesser extent as a source of food. Therefore, many fashionistas from high society pinned bouquets of potato flowers to their hair.
Ordinary people also reacted to potatoes in a peculiar way. Potato varieties cultivated at that time were too bitter (due to the excessive content of solanine) and therefore not everyone liked it. In addition, there were a lot of superstitions around the potato at that time. It was said that the fruits of this plant will be born with a head and eyes, like a person, so eating potatoes means eating human souls. There were also those who called the potato a "damn apple" that seduced the biblical progenitors of mankind - Adam and Eve - with their fruit. And, therefore, a person who eats potatoes was unequivocally recognized as a sinner. The notoriety was so firmly held among the people that they flatly refused to plant potatoes. It was in all European countries without exception. The rulers of some countries tried to force the people to grow potatoes, others - by cunning and bribery. For example, in Prussia, at first, peasants were forced to plant potatoes under the escort of dragoons, and in England they promised to give out gold medals for growing potatoes, etc.
In France, they went to the trick. Potatoes were planted in the fields owned by the state. As soon as it began to bloom, an armed guard was assigned to each bush, which was purposely removed at night. This aroused some interest among the surrounding peasants. “It can be seen that these“ damn apples ”are of great value to the state,” the amazed people reasoned. And we decided to plant potatoes too. And the peasants began to secretly dig up the tubers and plant them in their fields. Naturally, no one punished them for this. Having tasted the grown tubers, they were able to make sure that the potatoes are tasty, give a big harvest and make good money on it. So the potato "conquered" France. But it was only in the 18th century that potatoes received wide use in the fields of peasants of all countries of Europe, and even later - of Asia, Africa, Australia and North America.
Potatoes came to Russia thanks to Peter I, who sent a bag of tubers from Holland in 1698. And after the decree of the Senate of January 19, 1765, potatoes began to be planted purposefully. However, as a result of the violent tsarist measures to introduce potato crops in 1834-1844, there were unrest among the peasants of the Vyatka and Vladimir provinces, the regions of the Urals, the Lower and Middle Volga regions. The Old Believers turned out to be especially fierce opponents of it. They compiled a lesson that it is a sin for a Christian to eat potatoes. In the book Life of the Russian People, published in 1848, it is written: “There are counties where the peasants are even afraid to plant it, thinking they will bring God’s displeasure to their fields.”
Since the introduction of the potato into Europe, scurvy epidemics have ceased: the potato provided nearly 50% of the body's vitamin C requirement.
Potatoes in dreams

Potato, or tuberous nightshade, is a perennial tuberous plant from the flowering department, the dicotyledonous class, the solanaceous order, the nightshade family, the nightshade genus.
The name "potato" (lat. Solanum tuberosum), under which today's layman knows this plant (vegetable), was proposed by Kaspar Baugin in 1596. The Italians, because of the outward resemblance of the fruiting bodies to potato tubers, began to call them "tartuffolli" or "tartofel". From this word, the German version of the name of the underground fruits "Kartoffel" was formed, which gave the Russian name.
Potatoes - description and appearance. The structure of plants and vegetables.
The number of stems per plant ranges from 4 to 8-10. Their height, depending on the variety of potatoes, may not exceed 30 cm or reach 1.5 meters. On erect fleshy stems of green (sometimes with a brown tint) color, peculiar ribs are clearly distinguished. Dark green potato leaves on short petioles rise in a spiral form from the base to the top.
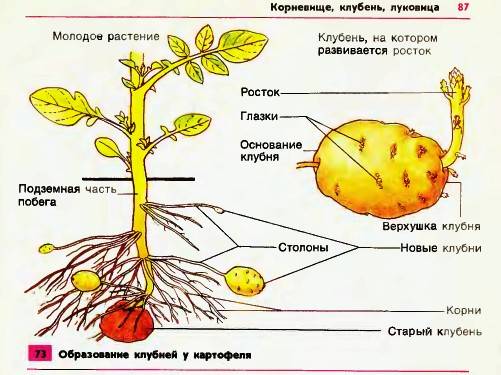

From the part of the potato stem immersed in the ground, shoots (stolons) diverge in different directions, the length of which can reach 0.5 m. Potato tubers are located at their ends, the thin outer shell of which is formed by cork tissue. On their surface there are depressions called eyes. They contain several buds, from which a new plant develops. The flowers of the plant, collected at the top of the stems, are usually white. However, there are varieties with pink, blue or purple flowers. Below you can see what a potato stalk looks like, as well as the detailed structure of a potato.
The above-ground fruit of the potato is a poisonous green berry shaped like a miniature tomato. As it matures, it acquires a whitish hue.


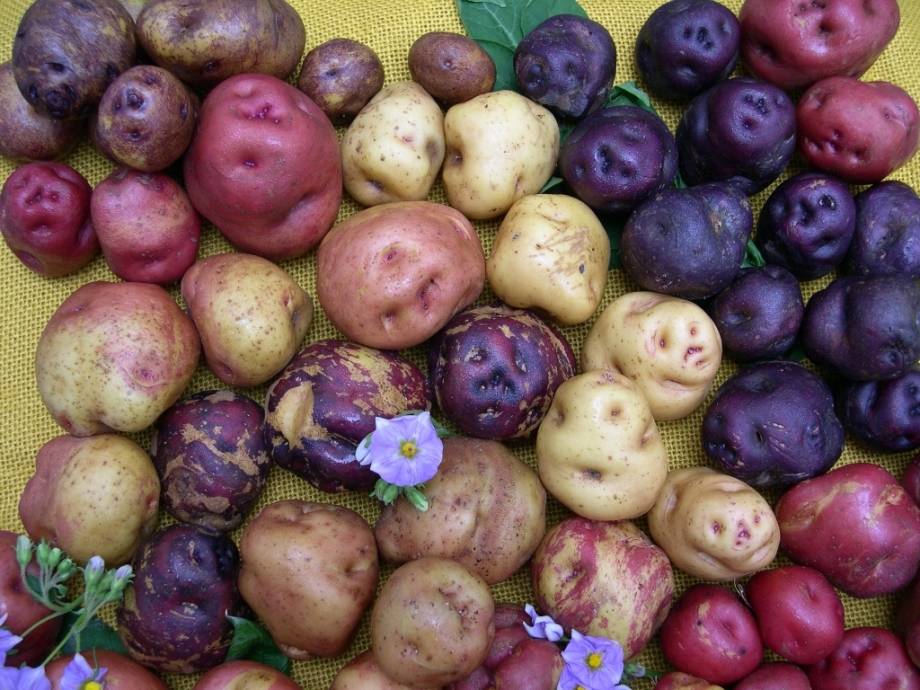
The appearance, weight, color of the top layer of the potato tuber and its pulp differ depending on the cultivar. The peel of the tuber can be colored in various shades of brown, yellow, pink or purple. Therefore, to the question of what color the potato is, it will not be possible to give a definite answer.

The flesh of a potato when cut is usually white, but there are varieties with a dark yellow, cream or even purple, blue and pink color.


The shape of potato tubers is round, oblong, spherical or abstract, with protrusions and irregularities, and the weight of individual specimens can reach 1 kg or more.
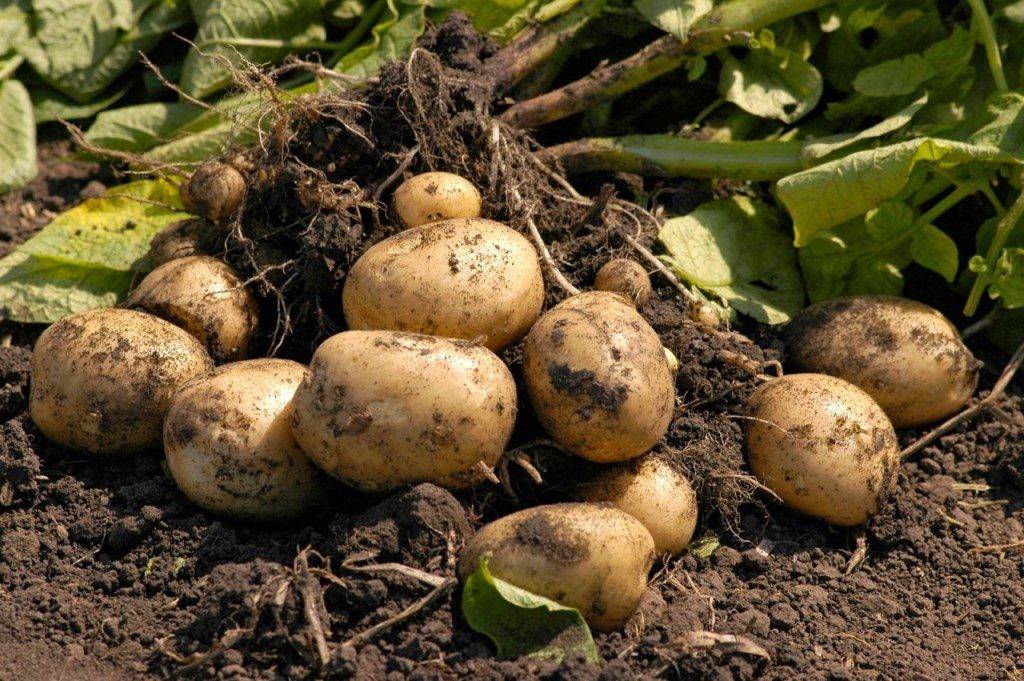

Potato varieties - photo and description.
Today, approximately 5,000 varieties of potatoes are known. Of these, 260 are recommended for breeding in large farms and for private use in Russia.
By practical application All varieties are divided into the following groups:
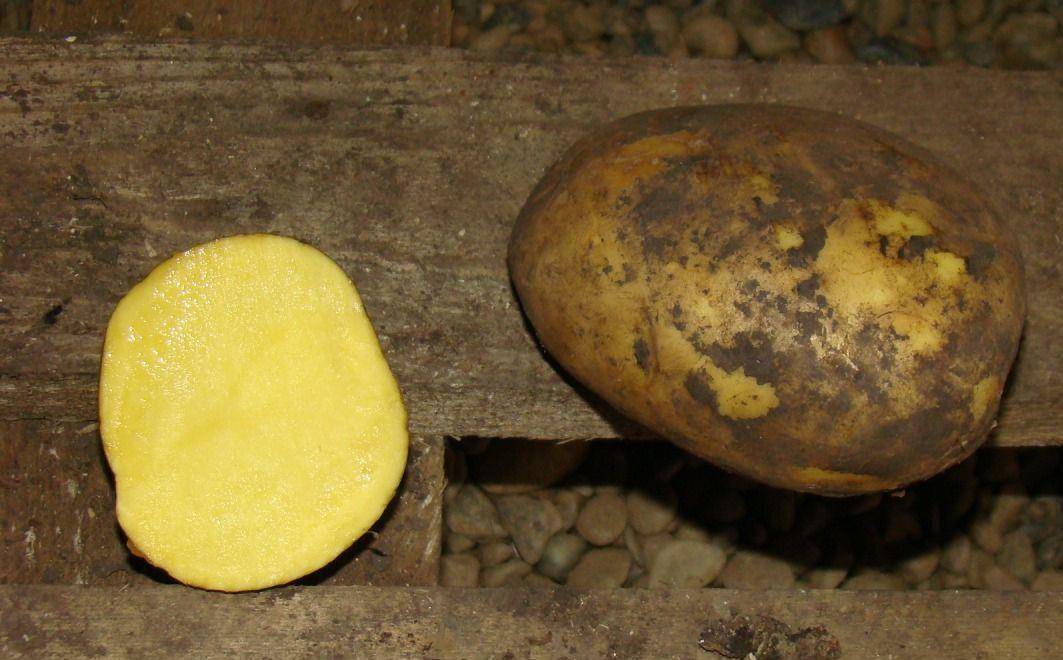
- "Felox" - a variety of table potatoes with elongated tubers weighing up to 110 g. The flesh is colored light yellow, the skin is darker.

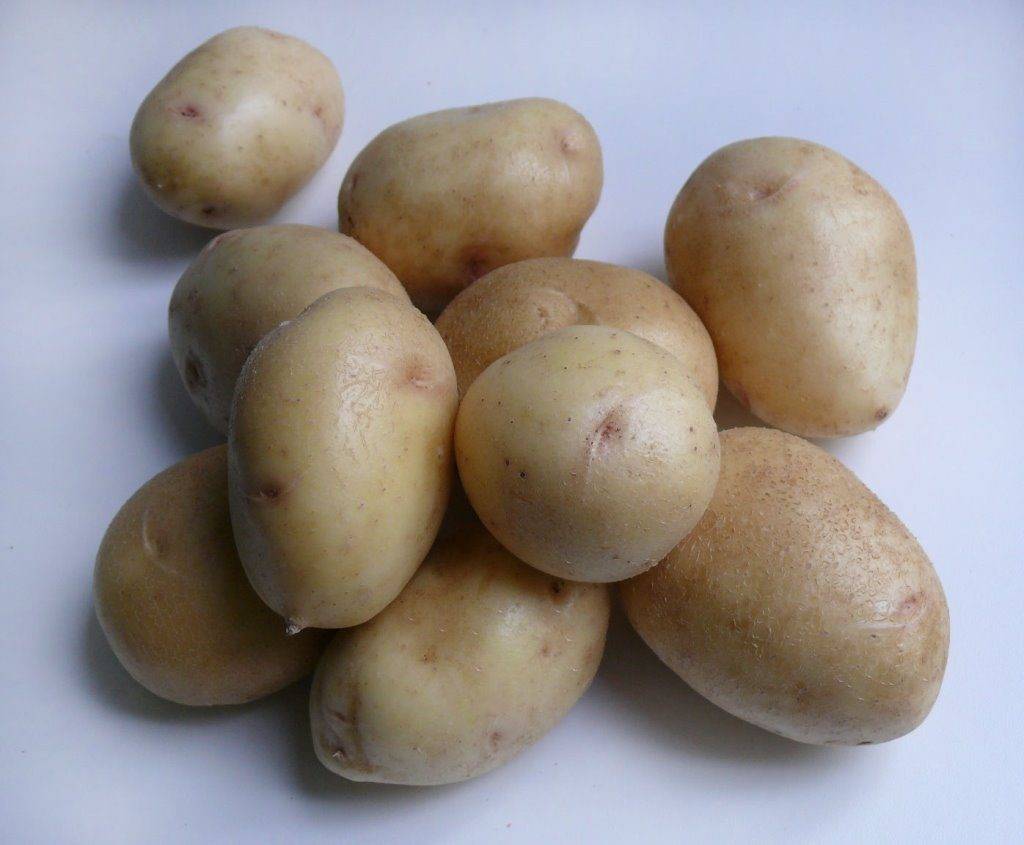
- "Red Scarlett" - a variety of potatoes with oval tubers weighing up to 85 g. One bush contains up to 23 potatoes with smooth red skin and pulp yellow color.

- "Nevsky" - potatoes with oval-shaped tubers with pink eyes and weighing up to 130 g. Upper layer and white flesh.

- "Vitalot" - a variety of purple potatoes, has oblong-shaped tubers up to 10 cm long. It ripens late and has a low yield, so it is not grown commercially.
 Technical varieties of potatoes- are used as raw materials in the industrial production of alcohol and starch. The starch content in tubers exceeds 18%. The most commonly grown varieties are:
Technical varieties of potatoes- are used as raw materials in the industrial production of alcohol and starch. The starch content in tubers exceeds 18%. The most commonly grown varieties are:
- "Accent" - with large potatoes with a smooth yellow surface and light creamy flesh.
- "Alpinist" - medium-sized potatoes. The peel of yellow color is covered with a fine mesh with numerous small eyes. Tuber on the cut cream color.

- "Vytok" - under one bush there can be up to 10 potatoes weighing about 135 g. The surface of the yellow peel is covered with a rare mesh. The flesh is cream colored.

Forage varieties of potatoes are used as feed for livestock. A characteristic feature of fodder potatoes is an increased content of proteins, reaching 3%. Among them are the following varieties:
- "Woltman" is a fodder potato variety that has red tubers with numerous bright eyes and white flesh. They have an irregular shape.

- "Lorch" - oblong tubers covered with a smooth skin beige colour, have white pulp with protein content up to 2.2% and vitamin C up to 18%. Numerous shallow eyes are located over the entire surface of the tuber.

Universal varieties of potatoes occupy an intermediate position between table varieties and potatoes intended for technical use.
- "Berlichingen" - a variety of potatoes with red oval tubers. The peel is strong and thick with superficial eyes. The flesh is white and darkens when cooked.
![]()
- "Arosa" - a variety with oval reddish tubers and yellow flesh. Spreading stems with red-violet corollas.

- "Sante" - has oval-shaped tubers with skin and flesh of light yellow color.

- "Lasunok" - its medium-sized oval-shaped tubers with a mesh peel of light yellow color and creamy flesh.
![]()
Potato maturity.
There is a classification of potatoes according to the timing of its ripening:
- Early varieties of potatoes. The maturity of early potatoes occurs after 50-60 days, so it is practically not intended for long-term storage. The following varieties are popular:
- Minerva;
- Ariel;
- Felox;
- Red Scarlett and others.
- Medium early potato varieties. For a good harvest of medium early potatoes planting material germinated in advance. The duration of the ripening period of this species is up to 80 days. The most popular varieties are:
- Carat;
- Santa;
- Adretta, etc.
- Mid-season potato varieties. The duration of the growing season of mid-ripening potatoes reaches 100 days. The following varieties are in great demand:
- Nevsky;
- Altair;
- Betina;
- Rosinka and others.
- Middle late and late varieties potatoes. The ripening period is from 100 to 120 days. It is designed for long term storage. It is possible to plant such planting material without pre-germination. Good results are obtained by planting such popular varieties as:
- Bernadette;
- Berlinger;
- Folva;
- Accent;
- Slavyanka, etc.



