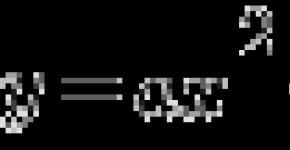Coverage of enterprise funds. Ratary Funds
The formation and use of various cash funds to reimburse capital costs, its accumulation and consumption make up the essence of the financial management mechanism in the enterprise. Aggregate Circuit B. different parts capital capital for the period is its full turn, or reproduction(simple or extended).
Main capital 1 includes: basic production, unfinished long-term investments, intangible assets and new long-term financial investments. The main capital is also included in unfinished capital investments in fixed assets and for the purchase of equipment. This is the part of the cost of acquiring and building fixed assets that has not yet become fixed assets, does not participate in the process of economic activity and is not subject to depreciation. In fixed capital, these costs are also included because they are already withdrawn from working capital.
Long-term financial investments- These are the costs of equity participation in the authorized capital of other enterprises, to acquire shares and bonds on a long-term basis. Financial investments also include long-term loans issued to other enterprises for debt obligations, as well as the value of the property transferred to the long-term lease on the right of financial leasing. Long-term financial investments are reflected in the balance sheet page 160 (Appendix 3).
Fixed assets - These are funds embedded in a set of material and real values \u200b\u200brelating to the means of labor.
The accounting balance sheet accounts are taken into account at the residual value (Appendix 3, p. 120).
The cost of the OS is repaid gradually during their useful exploitation by monthly depreciation deductions, which are included in the cost of production or circulation for the corresponding reporting period (ie, the cost is transferred in parts). When evaluating the effectiveness of investments in fixed assets, when analyzing their economic condition and reproduction, the OS functional use is maintained for a number of years, and their acquisition and operation costs are distributed over time. The moment of their update does not coincide with the moment of their value compensation and unforeseen losses may arise. The effectiveness of their use is estimated depending on their type, belonging, the nature of participation in the production process, as well as their appointment.
Depending on the nature of the participation of the OS in the process of expanded reproduction, they serve the production and non-productive scope of the organization. Therefore, the effectiveness of their use is determined not only by economic, but also social, ecological, etc. factors. Depending on the economic operation of the OS and long-term investments in fixed assets, a multifaceted and versatile impact on the financial condition and the results of the organization's activities are provided.
Each enterprise carrying out economic activity should have working capitalto ensure the continuous production process and product sales process. OS, participating in the circuit of the market economy is a single complex.
Coverages - this is cashAdvanced in revolving industrial funds and circulation funds. The essence of OS is determined by their economic role, the need to ensure the reproduction process, including the production process and the process of circulation.
By participating in the process of production and sales of OS products, they make a continuous circuit, moving from the sphere of appeal to the sphere of production and back.
OS change its natural real form by passing three phases:
OV, having an initial shape of money, turn into production reserves, i.e. transfers from the sphere of appeal to the sphere of production;
OS participate production process and take the form of unfinished production, semi-finished product, finished product;
Communicated again in the field of circulation. As a result of the sale of finished products, OS acquire a new form of funds.
The difference between monetary revenue and originally spent the means determine the amount cash income Organizations. Consequently, the circuit OA is an organic unity of 3 of its phases.
OS function only in one production cycle and fully transferred its value to the newly manufactured product.
Sources of formation OS can be divided into own and borrowed.
Own fundsorganizations received from entrepreneurial activities and incorporation provide financial activities and independent entities.
Borrowed fundsattract in the form of bank loans and cover money needs.
OS, placed in the reproduction process, are divided into:
Processing production facilities operating in the production process;
Foundation for the appeal, functioning in the process of selling products and the acquisition of TMC.
The greatest share is the OPF that participate in the creation of value.
Based on the principles of organization and regulation of production and circulation, OS can be divided into:
normalized - own OS, calculated on economically reasonable standards;
nonormable - means of circulation funds.
It should be constantly monitoring the rational spending of non-normalized OS and not allow them to be unreasonable increase, which will allow to accelerate the turnover of OS in the field of circulation.
Office OS associated with their composition and placement among various business entities. Composition and structure O.Cs are noodynakov. They depend on the form of ownership, the specifics of the organization of the reproduction process, relations with suppliers and buyers, the structure of costs for production, financial condition.
Condition, composition, structure of production reserves, improved production and finished products is an important indicator of the commercial activity of the organization.
The definition of the structure and identification of trends of changes in the elements of O.S. allows you to predict the most effective parameters of the organization's business.
Working capital is reflected in the form No. 1 "Accounting balance" in the FIRADE "Current assets", BIV and V sections - "Long-term obligations" and "short-term obligations" (Appendix 3); In the form number 5 "Annex to the Accounting Balance" (Appendix 4).
Along with the main funds for the work of the enterprise, the presence of an optimal amount is of great importance. current means.
Coverage - Part of the capital of the enterprise invested in its current assets. In other words, these are the investments of financial resources to objects, the use of which is carried out within a single reproduction cycle, or for a relatively short calendar period of time (as a rule, no more than one year). According to material and real sign, labor objects (raw materials, materials, fuels, etc.) are included in the composition of working capital, finished products in the warehouses of the enterprise, the goods for resale, cash (receivables), and funds in the calculations.
A characteristic feature of working capital is the high speed of their turnover. The functional role of working capital in the production process is fundamentally different from fixed capital. Current means ensure the continuity of the production process.
Real elements of working capital are consumed in each production cycle. They completely lose their natural shape, therefore, the whole is included in the cost of manufactured products.
Elements of working capital are continuously moving from the sphere of production in the sphere of circulation and returned to production.
Part of the current funds are constantly in the field of production (circulating funds), and the other in the field of circulation (reference funds). Therefore, the composition and size of the working capital of the enterprise is due not only to the needs of production, but also by the needs of circulation. Under the composition of working capital Understand the combination of elements of forming working capital. The composition of working capital according to the functional role in the production process is shown in Fig. 3.1.
Commodity and material values \u200b\u200bcan be estimated at cost or market value. This is a set of funds advanced to create and use revolving production Funds and conversion funds to ensure the continuous production process and product sales.
Processing production facilities - These are labor objects (raw materials, basic materials and semi-finished products, auxiliary materials, fuel, containers, spare parts, etc.); water, items and tools with a service life of not more than 12 months; Incorrect production and expenses of future periods. Processing production funds enter into production in their natural form and in the process of manufacturing products are consumed and transferred its value to the product being created.
Foundations appeal - These are the funds of the enterprise embedded in the reserves of finished products, goods shipped, but unpaid, as well as funds in the calculations and cash at the box office and on accounts. Reference funds are related to the service of the process of circulation of goods and are not involved in the formation of value, but are its carriers.
The movement of current production funds and the conversion funds is the same character and constitutes a single process, which allows us to combine the revolving production funds and the conversion funds into a single concept - working capital. After the completion of the production cycle, the manufacture of finished products and its implementation, the cost of working capital is reimbursed in revenue from the sale of products (works, services), which creates the possibility of systematic resumption of the production process by continuously circulating the means of the enterprise.
Productive reserves - these are labor items prepared for launching manufacturing process; consist of raw materials, basic and auxiliary materials, fuel, fuel, purchased semi-finished products and components, containers and tare materials, spare stripes for current repairs Funds.
Unfinished production and semi-finished products of their own work out this objects that have entered the production process: materials, details, nodes and products that are in the process of processing and assembly, as well as semi-finished products own manufacture, unfinished by fully manufacturing in some shops of the enterprise and subject to further processing in other workshops of this enterprise.
Future spendingthese are lovely elements of rounding funds, including the costs manufactured in this reporting period, but related or effective in economic content, or at the current practice of accounting and planning - to future periods. For example, these are the costs of preparing and mastering new products that are manufactured in this period, but relate to the cost of products of the future period (costs for designing and developing technology of new types of products, to reinstall equipment, etc.).
Cash I. securities The most liquid part of working capital. Cash funds include money at the checkout, on the calculated, current, currency, etc. Accounts. Securities that make up short-term financial investments include securities of other enterprises, government bonds and securities issued by local authorities.
Receivables- Important component of working capital. Under receivables understand different kinds Debt to this enterprise of individuals and legal entities.
The following types of receivables are distinguished:
Calculations with debtors for goods and services;
Calculations with debtors on promissory benefits obtained;
Calculations S. subsidiaries;
Advances issued by suppliers and contractors and other receivables.
The tasks of the management of receivables are: determining the degree of risk of insolvency of buyers, the calculation of the forecast value of the reserve for doubtful debts, as well as the provision of recommendations for working with actually or potentially insolvent buyers.
The ratio of individual elements of working capital in their total cost is called structure working capital.
The structures of working capital at different enterprises are different.
The largest part of working capital of industrial enterprises is inventive inventory values \u200b\u200b(75-85%), the proportion of expenditures of future periods (9%).
In the overall structure of working capital, funds posted in the field of production (more than 70% of all working capital) predominate.
1. Composition and structure
Coverages - This is a combination of working capital and management funds in monetary terms. These components of working capital maintain the reproduction process in different ways: the first - in the field of production, and the second - in the field of circulation.
The conditions of production and sales require that stocks of material values \u200b\u200bconsumed in the production industry, as well as finished products, are constantly in the warehouses of the manufacturing enterprise. In addition, to ensure uninterrupted work, it is necessary that certain bindings of unfinished products be in the workshops. Finally, the company must have defined cash at the checkout on the bank accounts, in the calculations.
Assets of the enterprise, which, as a result of its economic activities, fully transfer their value to the finished product, take one-time participation in the production process, changing or losing the natural-real form, are called working capital.
Curvas are the most rolling part of assets. In each circuit, working capital takes place three stages: monetary, industrial and commodity.
In the first stage Cash funds are used to acquire raw materials, materials, fuels, containers, purchased semi-finished products, components, etc. necessary for the implementation of industrial activities. In the second stage Production reserves turn into unfinished production and finished products. In the third stage There is a process for selling products and receiving funds. Curvas for the composition and nature of the site in the production process are divided into two components: revolving industrial funds and conversion funds.
Processing production funds serve the sphere of production. They constitute the material basis of production and are necessary to ensure the production process of production, the formation of value. In the second part of working capital, consisting funds consisting of finished products and cash in the enterprise. Funds of appeal are not involved in the formation of value, but are carriers of the already created value. Their main purpose is to provide money to the rhythm of the process of circulation.
The combination of current funds and consumption funds into a unified system of working capital follows from the continuity of the advanced cost in three above-mentioned stages of their circuit.
Consider individual elements of current production facilities. The overwhelming part of the revolving industrial funds make up production reserves. Productive reserves- These are reserves of raw materials and materials, semi-finished products and components, fuel, containers, economic equipment, repair parts, tools.
Raw materials and basic materials - These are objects of labor that make up the material (real) basis of the manufactured product. Raw materials are called products agriculture (grain, wool, cotton, fruits, vegetables) and mining industries (oil, ore, gas, etc.). The main materials consider the products of the manufacturing industry (flour, sugar, fabric, metal, leather, etc.).
Semi-finished products - These are labor objects, the manufacture of which is completely finished in one workshop, but which are subject to further processing in other workshops of the same enterprise or can be implemented.
Auxiliary materials, in contrast to raw materials and purchased semi-finished products, do not form the main content of the manufactured product, but only contribute to the implementation of the technological process and the formation of the product.
Along with production reserves, proceedings include funds in production, including unfinished products and expenditures of future periods. Incomplete production (NWP)- These are labor objects that have entered the production process, but who have not passed all the processing operations provided for by the technological process.
The only one-minded element of current production funds is the expenses of future periods necessary to create the nearests, the installation of new equipment, etc. Expenditures of future periods include the cost of training and mastering new types of products, new technologyproduced in this period, but to be repurchased in the future.
The ratio of individual components of working capital in the total cost characterizes the structure of working capital. This is a ratio between the individual elements of working capital (raw materials, basic materials, fuel, containers, spare parts, finished products, etc.), expressed as a percentage of the result.
According to sources of formation and replenishment, working capital is divided into their own and equivalent means and borrowed.
Own called working capital, which are allocated by participants (founders) for the uninterrupted functioning of their enterprise. The main sources of formation of their own working capital are profits, internal financial resources and their redistribution.
Means that are not belonging to their own working hours are considered to be equivalent, but under the conditions of settlements constantly located in its turnover. These are the so-called sustainable liabilities. These include minimal wage arrears, accruals on wages, Reserve to cover upcoming payments, payables and other sustainable liabilities.
Sustainable wage liabilities The UPSP is calculated by the formula:
UPP \u003d ZPKV × PD / 90,
where ZPKV is the wage fund of the IV quarter of the planned year, taken as a basis when calculating the standard of own working capital, RUB;
PD is a gap between accrual and payroll, days.
The amount of minimum wage debt SZP is determined by the following formula:
ZZP \u003d ZPL × PD / 90,
where ZLPL is a planned market for salary for the corresponding quarter, rubles;
PD - the number of days from the beginning of the month to the day of issuing wages.
Borrowed are called working capital obtained from financial organizations in installed manner in the form of loans and loans.
2. Ramination of working capital
Ramination of working capital - the basis rational use economic means of the enterprise. It is to develop informed standards and standards for their spending necessary to create permanent minimum reserves for the uninterrupted work of the enterprise.
According to the degree of planning, working capital is divided into normalized and non-normalized.
TO normed Requires working capital in production reserves.
TO nonormable Current funds include: cash, shipped goods and jobs, all types of receivables, etc.
In practice, three basic methods of normalization of working capital are used: analytical, coefficient and direct account method.
Analytical method uses actual data on the magnitude of working capital for a period. At the same time, unnecessary and unnecessary reserves are specified, amendments to change the conditions of production and supply are made. The refined result of these calculations is considered a norm of working capital for the planned period. This method is used in cases where significant changes are expected in the conditions of the enterprise and the funds invested in material values \u200b\u200band stocks, have a large specific gravity.
The coefficient method is that the standards for the planned period are calculated by making amendments (using coefficients) in the standards of the preceding period. The coefficients take into account the change in production volumes, turnover turnover, assortment shifts and other factors.
The direct account method is that the amounts of working capital are calculated for each specific type of input and material values, then they are developing, and as a result, a standard for each element of normalized working capital is determined. The overall standard represents the amount of standards for all elements. This method is the most accurate, reasonable, but at the same time quite time consuming.
When ruling working capital, it is necessary to establish the reserve standards for separate species normalized materials, determine the standards for each element of working capital and calculate the aggregate standard on the normalized working capital.
Norms of working capital characterize the minimum stocks of commodity and material values \u200b\u200bcalculated in the days of reserve or as a percentage of a certain base (marketable products, the volume of fixed assets). As a rule, they are installed for a certain period of time (quarter, year), but can act and for a longer period. Norms are established by industrial reserves, incomplete production, stocks of finished products in the warehouse of the enterprise.
Consider the calculation of the norms of production reserves, incomplete production and finished products.
Norm in days of production reserves (raw materials, materials, purchased semi-finished products) consists of time:
unloading, acceptance, warehouse processing and laboratory analysis (preparatory stock);
finding materials in a warehouse for the current manufacturing process (current stock) and insurance, or warranty, stock (insurance);
preparation of materials for production (technological reserve);
staying materials on the way (transport reserve).
The highest share in the general norm of working capital in the material group is occupied by the norm of the current stock.
Current reserve - Permanent stock of materials fully prepared for launch in production and intended for the uninterrupted work of the enterprise. Its value depends on the average daily consumption of materials, the interval between the next supplies, the size of the batches of supply and running batches to production. For many materials, the interval between the next deliveries is taken half of the size or is calculated by the medium-graded method.
Maximum value of the current stock Zmax is determined by the formula:
Zmax \u003d AP × T,
T is the time between two next deliveries, days.
At the same time, the average daily consumption is established by dividing the overall need for this material in the planning period (year, quarter, month) by the number of calendar days for the same period, if the company works continuously, or by the number of working days, if not working on holidays and weekends.
The average value of the current stock (It is often referred to as a transition reserve) ZSR is determined by the formula:
ZSR \u003d Zmax / 2.
The next majority is the insured margin, which is created in case of possible breaks in time, delays in the way, arrival low-quality materials etc. The size of the insurance reserve is usually established as a percentage of working capital standards for the current reserve (from 30 to 50%).
Insurance, or warranty, stock ZS can also be defined by the formula:
Zs \u003d adn × pm,
where ADN is the norm of the insurance stock of materials, days;
PM is the average daily need for this form of materials, rub.
On average, the same duration is the transport reserve, formed in case of discrepancy in the deadlines of the document management and payment on them and the time of finding materials on the way.
The enterprises are also formed by the so-called technological reserve (zeh), which is necessary for preparation for production. The value of such a stock is determined by the formula:
ZTEK \u003d AP × TC,
where ap is the average daily need for this material, natural units of measurement;
TC - the duration of the technological cycle, days.
Total reserves The cobshch in raw materials, basic materials, purchased semi-finished products is determined by the formula:
Zobishch \u003d Ztech + ZS + VR + Zh.
The regulatory need for working capital in spare parts for the current maintenance and repair of equipment is calculated as a product of the value of the reserve in rubles established in relation to a certain indicator, on the total scheduled value of the latter.
For example, the reserve rate of spare parts for maintenance and repair of equipment is established in rubles. per 1 thousand rubles. Balance cost of equipment.
Typical rate of working capital on spare parts The ATIP is determined by the formula:
ATIP \u003d AUBSCH / SO
where Aobshch is a common need for replacement parts, rub.;
Sob - the cost of equipment and vehicles at the end of the planned year.
Improvement rate of incomplete production The NNPP is established on the basis of the duration of the production cycle and the degree of availability of products, which is expressed through the cost increase ratio. The norm is determined like this:
NNZ \u003d TC × KNZ,
where the shopping center is the duration of the production cycle, days;
KNPP - cost increase ratio.
The cost of increasing costs in unfinished production characterizes the level of product availability and is due to the fact that the costs in incomplete production are carried out at different times and increase gradually throughout the entire cycle. The cost increase ratio is always greater than 0 and less than 1.
The rate of stock on finished products depends on the time of registration of payment documents, packaging and labeling, storage in stock before shipment, cleaning products to the transit rate, the duration of transportation of products from the warehouse of the enterprise to the station of departure and loading in vehicles.
After establishing the norms of stocks, the standard of working capital is determined in monetary terms for individual elements of working capital and in general on the enterprise.
Regulatory of working capital - The minimum amount of funds necessary to the enterprise for the organization of production activities.
Mostly regulator by separate elements Current means SNI is by the formula:
SNI \u003d H3I × AI,
where H3i is the value of the reserve of the i-th element, days;
AI is an indicator in relation to which the norm is established.
Consider the calculation of working capital standards on the examples.
Provision of production reserves (raw materials, materials, purchased semi-finished products, etc.) is determined by multiplication of the norm in days for one-day consumption.
Sni \u003d h3i × m / tk,
where M is the consumption of raw materials and materials for the calendar period of time, rub.;
TC - calendar period, days (year - 360 days; quarter - 90 days, month - 30 days).
Regulation of unfinished production AnSP is calculated by multiplying the reserve rate in unfinished production on the average daily release of the product estimated at production cost.
Anzp \u003d psouth × NNPP,
where psout is the average daily production of production costs, rubles;
NNPP - the rate of stock in unfinished production, days.
Regulatory of working capital on finished productsUGP in the warehouse of the enterprise is determined by the formula:
Zgp \u003d psale × nzg,
where the psout is a one-day production of finished production in production cost;
NZG - the rate of the stock of finished products, days.
Calculation of the cost of working capital in expenditures of future periods Ab.P is determined by the formula:
Ab.p. \u003d Zn + zpl - svg,
where is the expenses of future periods at the beginning of the planned period;
ZLV - the costs of the planned period for these purposes;
PSG - costs in the planned period to be debited on the cost of production.
The process of rationing is completed by the establishment of a cumulative standard of working capital by adding private regulations for industrial reserves, incomplete production, expenditures of future periods and finished products.
The average rate of working capital on the enterprise as a whole is calculated by dividing the aggregate standards for a one-day production of commercial production in production costs.
Thus, the rationing of working capital - prerequisite definitions of minimally sufficient funds providing effective work Enterprises in general.
A.S. Palamarchuk, Dr. Econ. Sciences, prof. Raah them. G.V. Plekhanov
An indispensable condition for the exercise of economic activities is the availability of working capital. Curvas - these are cash flowing into current production facilities and conversion funds to ensure the continuous production process and product sales process.
The essence of working capital is determined by their economic role, the need to ensure a reproduction process, including both the process of production and the process of circulation. Unlike the main funds that have been repeatedly involved in the production process, working capital are functioning only in one production cycle and regardless of the method of production consumption completely transfer its cost to the finished product.
William Collins determines the essence of working capital as "... Short-term current assets of the firms that quickly turn around during the production period."
A similar definition of working capital gives the doctor of economic sciences, Professor Blank I.A.: These are assets characterizing "... a set of property values \u200b\u200bof the enterprise serving the current production and commercial (operating) activities and fully consumed within one production and commercial cycle."
G. Schmalen more accurately describes the process that provides working capital, in his opinion, "... Working capital is used to create funds, which are not calculated for a certain period, and they directly provide the process of processing and processing, product sales, as well as the formation of money resources And their spending. "
The composition and classification of working capital are given respectively in Table 1 and Table 2.
Table 1. The composition of working capital industrial enterprise
Production reserves are objects of labor that have not yet entered the production process and are in the enterprise in the form of warehouse stocks. These include: raw materials, basic and auxiliary materials, purchased semi-finished products, spare parts for the repair of fixed assets, fuel, low-value and listening objects, inventory, tools, and also special tools and devices regardless of their value, intended for the release of a limited batch of products or a separate order. The need for production reserves is due to the fact that the production process is performed continuously, and the flow of raw materials, materials, components periodically.
Incorrect production (NZP) (unfinished products) are objects of labor that have already entered the production process, but their processing is not completed. In practice, semi-finished products of their own manufacture, designed for further processing in other workshops of the same enterprise, is considered. Improved production items are on different stages Processing, jobs, but not yet ready to implement.
The expenses of future periods (RBP) are the costs associated with the development of new types of products (payment of designers for the design of a new product, tools and devices, technologists - for the development of technological processes of manufacturing a new product, tools, devices). They are produced in the planned period, accumulate, and are repayable in the future, when new products will be implemented, except for the costs that are funded from the profits, budget funds, or special funds.
Finished products (GP) in the warehouses of the enterprise are products manufactured at the enterprise and to ship by consumers.
Products shipped (software), on the way, but not paid by the buyer, that is, the bank's current account has not yet received money from the buyer.
Free cash at the current account of the enterprise, in the checkout required for the purchase of materials, components, travelers and so on.
Cash invested in stocks, securities are a promotion, securities of other enterprises acquired by the enterprise, short-term banks (up to 1 year).
Table 2. Classification of working capital on enterprise balance
| Group of working capital | Articles Asset Balance | Score accounting |
| 1. Stocks | Productive reserves | 10,15 |
| Animals for growing and fattening | ||
| Unfinished production | 20,221,23,29,44 | |
| Future spending | ||
| Finished products | ||
| Products | ||
| Continuation of table 2. | ||
| Goods shipped | ||
| 2. Value Added Tax on Acquired Values | ||
| 3. Accounts receivable | ||
| Calculations with debtors for goods and services | 62,76 | |
| Calculations with debtors for promissory received | ||
| Debt of founders on deposits in authorized capital | ||
| Advances issued to suppliers and contractors | ||
| Calculations with subsidiaries | ||
| 4. Short-term financial investments | ||
| 5. Cash | ||
| At the register | ||
| At the current account | ||
| On currency account | ||
| Other cash | 55,57 |
It is necessary to distinguish between the concept of working capital and the structure of working capital. The composition of working capital is the elements of current production funds and conversion funds. The structure is the ratio between individual groups, elements of working capital and common volumes, expressed in fractions or percentages.
The volume and structure of working capital of enterprises, a significant influence in modern conditions has many factors, for example:
· Features of manufacturing products - time consuming, material consumption;
· Production type;
· Duration of the production cycle;
· Period of development of new products;
· The location of providers of material resources and consumers of products, conditions of supply and sales;
· Product quality;
· The solvency of the enterprise and buyers.
In enterprises due to a decrease in the share of production reserves and free funds, there is a change in the structure of circulating funds. In the structure of working capital - in stocks of inventory-material values, the largest proportion is accounted for by production reserves and work in progress, and in them for raw materials, basic materials and purchased semi-finished products.
The structure of working capital of enterprises of various industries will be different. The analysis shows that the greatest share, for example, receivables is characteristic of electric power industry enterprises, mechanical engineering, and the smallest - light and food Industrythat is, enterprises operating directly to the consumer.
Curvas are always in motion and have several steps of the circuit, changing their shape.
For funds (D) available on the current account (or accounts), as well as at the checkout, the company acquires the material resources they need. After the acquisition, the materials are not spent immediately, some of them first settles in the form of production reserves (PZ) in stock, and the part that is launched into production - in the form of incomplete production, ready, but not yet realized products (GP). The company returned to sell the finished products, the company returns money (D "), some of which was previously spent on the acquisition of material resources (D) necessary for production, while obtaining a certain amount of profit (ΔD). At the expense of part of the revenue received from The sale of finished products is reimbursed when purchasing new batches of material resources, consumed means of production and objects of labor in the form of raw materials, materials, fuels, energy, depreciation, as well as wages and other costs. This is completed by a circuit circuit in the enterprise.
D "\u003d d + Δd
Movement at the enterprise of current funds and funds of treatment:
PZ - NP - GP - T,
where the PZ is the production reserves of material resources;
NP - incomplete production (materials in the workshops in the processing state (blanks, semi-finished parts, subjected to turning, milling and other technological operations on the appropriate machines and lying in containers near these machines waiting for the next technological operation with them);
GP - sales reserves of finished products;
T - Goods - Products issued by the enterprise (it is the property of an enterprise until their sale).
In order for the production process was not interrupted, the enterprise needs to plan working capital in groups and control over maintaining their required level at each stage of the circuit. The planning of working capital should include indicators of the original and end levels of needs, as well as the indicators of each significant change (growth, reduction) of this need within the planned period. For example, to spend working capital to the enterprise will not have to pay for the average, the same supplies, but to pay for various supplies - small and large, frequent and rare delivered air transport, automotive, etc. Knowing with a certain probability of the dynamics of future deliveries, the company can more reasonably manage production and finance.
The basis of the planning of working capital enterprises is rationing.
1.2 Basic Methods for Ramination Raming
Ramination of working capital solves two main tasks. The first is to constantly maintain the correspondence between the size of working capital of the enterprise and the need for means to ensure the minimum necessary reserves of material values. This task links the dependence of the volume of working capital on the level of stocks. It is understood that for each enterprise it is necessary to establish such a standard so that in normal economic activity it has not experienced financial difficulties to ensure the process of production and implementation. Another task is more complex: using rationing it is necessary to control the size of stocks. Rationing is intended to stimulate improvement of economic activities, finding additional reserves, form a reasonable combination of supply forms, etc.
According to the principles of the organization, working capital is divided into ignorable and non-normalized.
Non-normalized working capital includes products shipped, on the way, but not paid; Cash at the current account, at the checkout. The level of these groups of working capital is more affected external factorsthan the production and economic activity of the enterprise. The legislative framework, as the basis of the contractual supply system, should help reduce the size of unpaid supplies.
The normalized working capital includes all groups of working capital products - these are industrial reserves, improved production, expenditures of future periods; From the sphere of circulation - finished products in stock.
The magnitude of the normalized working capital should always meet the real need for production. The company defines the minimum, but sufficient need for each of these groups of working capital and controls their level at each stage of movement, since large reserves of material values \u200b\u200brequire rates of funds from other purposes, warehouses, security, accounting are needed. Upon underestimation, the company will not be able to ensure the production of necessary reserves, to pay a timely with suppliers, workers, employees, etc. Under the overestimation of the standard, significant excess reserves arise, freezing of funds, which leads to losses. The overestimated standard contributes to the reduction in the level of profitability, an increase in the amount of payment for an increase in the value of the property of the enterprise.
Ramination of working capital is the process of establishing norms and standards on the normalized group of working capital.
In the process of rationing of working capital, the norm and norms of working capital are determined.
The rate of working capital is the relative value corresponding to the minimum, economically reasonable stock of inventive material values \u200b\u200bestablished in days.
Regulatory of working capital is the minimum required amount of funds providing economic activities of the enterprise.
In the practice of rationing of working capital, several methods are used:
· Direct account;
· Analytical;
· Experimental laboratory;
· Reporting and statistical;
· Coefficient.
Analytical method for estimating a norm of working capital is established at the actual amount of working capital for a certain period, taking into account the amendments to surplus and unnecessary reserves, as well as a change in production and supply conditions. This method provides for dividing working capital into two groups:
· Depending on the change in production;
· Independent production.
The experimental laboratory method is based on measurements of their consumption and production volumes (works) in laboratory and experimental production conditions. Consumption standards are set by selecting the most reliable results and calculating the average value using methods mathematical statistics. The most appropriate scope of application of these rules: auxiliary production, chemical, technological processes producing industries and construction.
Reporting and statistical - based on the analysis of data from statistical (accounting or operational) reporting on the actual consumption of materials per unit of production (works) for the last (basic) period. It is recommended for the development of both individual and group norms of consumerial and fuel and energy resources.
In the coefficient method, the standard of working capital for the planned period is established using the preceding period standards and taking into account the adjustment to the change in the volume of production and to accelerate the turnover of working capital. The use of differentiated coefficients for individual elements of working capital is permissible if the standard is periodically specified by direct account.
The main method of rationing of working capital is the direct account method. When using a direct calculation method, the standard is calculated on the basis of a production program, cost estimates for the production of the production process, the material and technical support plan, a portfolio of contracts and orders, an increase in production efficiency plan.
The direct calculation method allows you to most accurately calculate the needs for working capital and applies in the current financial planning when determining the standard for the main elements of working capital.
Other rationing methods are used in industry as auxiliary. The general standards of their own working capital are determined in the amount of their minimal need for the formation of the production and sales of stocks necessary for the implementation of plans, as well as for the implementation of all types of calculations on time.
1.3 Process for the rationing of working capital
The ruling process of working capital includes:
1) establishing an economical order size for each type of material resource consumed;
2) the calculation of one-day consumption (daily need) of each type of material resource;
3) the calculation of the reserve rate;
4) Calculation of the norm of working capital in elements and working capital as a whole.
The economical order size provides a minimum of annual expenses for placement and execution of the order, as well as stock storage. The cost of placement and execution of the order includes the cost of searching for a supplier, conclusion of the contract, control over the order, the cost of its processing and delivery (if paid over the purchase price). Stock storage costs include all costs for warehouse operations (labor, warehouse equipment, warehouse repair, electricity, etc.) and a warehouse rental fee (if it is rented).
In the theory of stock management, the mathematical calculation of the economic size of the order (maximum stock) of the material resource is given. The corresponding formula has the following form:

where G is an economical order size; C - average cost placement of one batch of delivery; S - annual volume of production requirement in this raw material or material; I - the cost of storing a unit of goods in the analyzed period.
The rate of stock (NZ) is the minimum required value of the stock of the material resource in a warehouse that ensures the becigability of production. For the material values \u200b\u200bthat are in the composition of production reserves, work in progress, the expenditures of future periods it is established in days. If the reserve rate at the enterprise is determined in seven days, this means that the enterprise should have a 7-day supply of materials.
The algorithm for calculating the rate of materials is presented by the formula:
The rate of stock is consumed from the current (, insurance (, transport (and preparatory reserves (.
The current stock provides uninterrupted operation of the enterprise between the next resource supplies, it changes from the maximum on the day of the delivery to the minimum before the next delivery. Current stock is set based on the calculation:
![]()
where is the average supply cycle (interval between supplies).
With uniform supplies of materials on graphics and uniform consumption during the year, the average supply cycle is:
where 360 \u200b\u200bis the number of days a year; N - the number of deliveries per year;
where q is the annual need of an enterprise in the material resource; G - economical order size.
Calculated average intervals between supplies are accepted to calculate the norms of working capital on the formation of the current stock. The norm of the current stock varies from the maximum level to zero. Schematically, stock movement is represented in Fig. 1.2.

Fig. 1.2 Stock Motion Scheme
The maximum level of the current stock corresponds to the maximum size of the delivery batch, and the minimum can be taken conditionally equal to zero. At the moment when the reserve reaches zero, the next batch of materials should be done into production.
Insurance stock is created in cases of violation of planned delivery time. It is calculated on average deviations of the actual delivery time from planned or accepted at 50% of the norm of the current stock at small intervals. Insurance stock is created in case of unforeseen abnormalities in the supply:
![]()
The transport reserve is created at the time of finding material values \u200b\u200bon the way from paying bills before their arrival. Its value is determined by the difference between the number of days of the mileage of goods from the supplier to the consumer and the number of days of document management, taking into account the bill payment.
The preparatory reserve is determined on the basis of the timing associated with the definition of time for unloading, storage and preparation for production. It provides time for acceptance, unloading, sorting, warehousing of material values, design of warehouse documents and preparation for production.
Current standards are minimal for normal work Enterprises need for working capital, which ensures the creation of the necessary reserves of material resources in monetary terms. The amount of working capital standards for all types of material resources gives the overall standard of working capital. It consists of the amount of private standards:
where is the standard of working capital in production reserves; - standard of working capital in unfinished production; - standard of working capital in expenditures of future periods; - Regulatory of working capital in finished products.
1) rationing of working capital in production reserves begins with the determination of the average dairy consumption of raw materials, basic materials and purchased semi-finished products in the planned year. The average daily consumption is calculated by groups, and in each group, their most important types are allocated, which make up about 80% of the total value of the material values \u200b\u200bof this group. Unaccounted types of raw materials, basic materials and purchased products and semi-finished products relate to expenses on other needs.
The norm of working capital in production reserves is calculated by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where is the average daily flow rate for each type of material.
The average daily consumption of material resources is private from dividing the sum of all planned annual expenses of raw materials, by the number of working days a year:
where p is the amount of material consumed in the reporting period; T is the duration of the reporting time period.
2) There are products at various stages of processing - from the launch of raw materials, materials and components in production to the adoption of the technical control department of finished products. Incorrect production is determined by the magnitude of the advanced funds embedded in the costs of raw materials, basic and auxiliary materials, fuel, electricity, depreciation and other expenses. All of these costs for each product are growing as they move along the chain of the technological process.
The standard of working capital in unfinished production is calculated by the formula:
where is the average daily volume of manufactured production costs; - the duration of the production cycle for the manufacture of products; - cost increase ratio reflecting product readiness stupus.
The average daily volume of manufactured production costs is calculated by the formula:
![]()
where q is the production of products for the reporting period; - cost of products; T - the reporting period of time.
The duration of the production cycle of the production unit is calculated by the formula:
The cost increase ratio is assumed to be:
![]() ,
,
where A are the costs produced by the same time at the beginning of the production process; B - subsequent costs before the end of the production of finished products (costs not taken into account).
3) The costs of future periods include the costs carried out in this year, and redeemed, that is, the products included in the cost price in subsequent years. They are uneven.
The standard of working capital in expenditures of future periods is calculated by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where P is the overgoing amount of expenses of future periods at the beginning of the planned year; P - spending of future periods in the planned year; C - expenditures of future periods to be debited on the cost of production of the planned year.
4) The following element The working capital standards is the standard of working capital on the finished products to which products include the production cycle ended, they are adopted by the technical control department and are commissioned to the warehouse of finished products. The rate of working capital on finished products is determined by time from the time of acceptance of products to the warehouse before its payment by the customer and depends on a number of factors:
· The order of shipment and time required for acceptance finished products from shops;
· The time required for the recruitment and selection of products to the magnitude of the shipped party and in the assortment, respectively, orders, outfits, contracts;
· The time required for packaging, product marking;
· The time required to deliver packaged products from the warehouse of the enterprise to the train station, pier, etc.;
· Loading time products in vehicles;
· Storage time products in stock.
The standard of working capital on financing the finished products in the warehouse is determined by the formula:
![]() ,
,
where the NZ is the norm of the reserve of working capital in the finished product; Q is the daily volume of shipped finished products in physical terms; - Cost of unit shipped products.
Calculations of working capital standards - labor-intensive work. With the unchanged nomenclature of products and price stability of raw materials, materials, component enterprises adjust the standard of the previous year to change the volume of production.
The economically reasonable standard of working capital allows you to organize working capital in such a way that in the process of their use each ruble embedded in the turn, ensured the maximum return. This standard makes it possible to analyze the condition and level of use of working capital, ensure the system of control over them and the normal economic activity of the industrial enterprise provided permanent sources Coatings of working capital.
2. Analysis of the rationing of working capital of OJSC "Reinforced concrete products"
2.1 a brief description of Enterprises
Limited Liability Company "Plant of Reinforced Concrete Products" was created on January 11, 1993.
Legal address: RF, Udmurt Republic. Izhevsk, ul. Novosmirnovskaya, 22.
Today is a multidisciplinary enterprise, with its established infrastructure that has its own fleet, loading equipment, driveway railway tracks and carrying out the whole complex of manufacturing and delivery of products to their customers.
LLC ZHBI LLC produces products with a nomenclature of products over 200 items. Directions:
· Products for civil and industrial construction;
· Products for the arrangement of petroleum and gas fields.
Production of concrete weights for oil and gas pipes is one of the main activities of the plant.
The plant produces up to 50 items of concrete weights for trunk pipelines - this is: Weightlithors of the rings of the RCK brands, covering the type, TSBM brands, as well as weightlifiers of UBKM brands, UBB and UBB, used in balancing pipes when transitioning through rivers and water barriers, as well as on swamp plots. All weightlifiers comply with quality standards.
This is the only reinforced concrete manufacturer in Russia for the construction of main oil and gas pipelines with a diameter of 325 to 1420 mm.
Thanks to this, the plant participated in deliveries to all major construction of oil and gas pipelines in Russia from St. Petersburg to Sakhalin, including the areas of the Far North and the South of the country.
The main customers of this plant's products are the largest oil and gas producing companies in Russia, such as Gazprom, LUKOIL, TATNEFT, Transneft, Surgutneftegaz and Underbudstroy.
The success of the enterprise achieved over the past 12 years is due to a strict approach to the quality of manufactured products, as well as the competent leadership of the plant, which clearly knows that the quality and knowledge of the market opportuncture is needed. The plant successfully operates its own product quality control laboratory, the range is constantly expanding and the market for manufactured products. The production of reinforced concrete products is growing, like the geography of their deliveries.
The plant continuously increasing production capacity, while introducing new technologies, mastering new products for civil, industrial construction, as well as an energy complex, which indicates the stability of the plant on construction market housing.
LLC ZHBI LLC consists of two autonomous industries, each of which has its own solid-concrete assembly, a warehouse of finished products, a workshop for the production of precast concrete, wall panels and so on for the manufacture reinforcement carcasov, masonry grid, Metalloform repair sites. The plant has its own railway access roads, which make it possible to ship up to 650 tons of products and take cement up to 350 tons per day.
The company has its own vehicle to ensure the production of inert materials and transporting products. Shipment of products can be done at the same time from five points.
The experimental group acting at the factory is engaged in the introduction of new machines and equipment, allowing to increase the amount and improve the quality of products.
The factory acts:
· Production and technical department, which is engaged in planning the production of products, ensuring the production of working drawings for the manufacture and shipment of products, controlling the regulatory consumption of materials during production;
· Department of the main technologist, introducing new technologies in the process of manufacturing products.
Analysis of the financial results of the economic activity of the Reinforcement Plant LLC for 2007-2009. Presented in Table 2.1.
Table 2.1. Analysis of the financial results of ZHBI Factory LLC
| Indicator | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | Deviation in absolute values \u200b\u200bof 2007. by 2006 | Deviation in absolute values \u200b\u200bof 2008. by 2007 |
| Revenues and expenses on ordinary activities revenue (net) from the sale of goods, products, works, services (minus VAT, excise taxes and similar obligatory payments) | +5797 | +17591 | |||
| Product costs | +4309 | +16246 | |||
| Gross profit | +1480 | +1284 | |||
| Commercial expenses | +8 | +60 | |||
| Management expenses | - | - | - | - | - |
| Profit (loss) from sales | +1472 | +1234 | |||
| Other income and expenses interest | - | - | - | - | - |
| Percentage to be paid | - | - | - | - | - |
| Other income | +645 | -120 | |||
| other expenses | +1111 | +595 | |||
| Profit (loss) before taxation | +1014 | +569 | |||
| Deferred tax assets | - | - | - | - | - |
| Deferred tax liabilities | - | - | - | - | - |
| Current income tax | +243 | +138 | |||
| Net profit (loss) of the reporting period | +771 | +431 | |||
| Permanent tax liabilities | - | - | - | - | - |
Profit from sales increased in 2009 compared with 2007 by 2764 thousand rubles, the increase was due to an increase in production cost of 4309 thousand rubles. and an increase of 5797 thousand rubles. Revenue from sales.
In the same period, commercial expenses increased by 8 thousand rubles.
Compared with 2008 Sales profit increased by 1284 thousand rubles. In 2008 in relation to 2007 There was an increase in profit in the amount of 1480 thousand rubles.
2.2 Analysis of working capital of LLC "Reinforced concrete products"
Structure of working capital of LLC ZHBI ZHBI LLC for 2007-2009 Presented in Appendix 1.
From the presented structure, we can conclude that there is a tendency to increase the volume of working capital. In 2008 Curvas for reinforced concrete products OJSC compared with 2007. increased by 2774 thousand rubles. And in 2009 Radiation volume increased by 4391 thousand rubles. compared with 2008
In the overall structure of working capital, stocks take the greatest share. In the period from 2007-2009g. There is a decrease in the proportion of stocks in the structure of working capital.
Rising receivables negatively affects the financial condition of the enterprise. Increases the risk of percent growth of non-return, LLC "Reinforced concrete products" LLC it is necessary to take measures to reduce receivables.
One of the main conditions for the financial well-being of the enterprise is the influx of funds, providing coverage of its obligations. The absence of its minimum required funds of funds indicates its serious financial difficulties. The excessive amount of funds suggests that the enterprise actually suffers losses associated, firstly, with inflation and ensuring money and, secondly, with the impression of the possibility of placing and receiving additional income.
Also, working capital differ in the degree of liquidity.
The liquidity of assets is the value of the reverse time required to turn them into money, that is, the less time it is necessary to transform assets into money, the more liquid. Allocate:
· The most liquid assets (cash, short-term financial investments);
· Quickly realized assets (receivables, goods shipped, other current assets);
· Slowly implemented assets (stocks).
In tab. 3.3. An analysis of the composition and structure of working rounds LLC "Plant of reinforced concrete products" in the degree of liquidity for 2007-2009 isg.
| Group of working capital | Composition of the Included Balance Asset Articles | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | Absolute deviation | |
| 2008 by 2007 | 2009 By 2008 | |||||
| 1. Liquid assets (thousand rubles) | 1.1. Easy tools 1.2 Short-term financial investments | - | - | - | +625 - | +2418 - |
| 2.Fast implemented assets (thousand rubles) | 2.1. Dabitor debt 2.2.Things shipped 2.3.Proch the current assets | - | - | - | +276 - -19 | -57 - +289 |
| 3. Mentally implemented assets (thousand rubles) | 3.1. Packs | +808 | +899 | |||
| TOTAL: |
Page 5 of 7
Topic 4 Coverage Funds
- Current capital and working capital enterprises
- Determining the need for working capital
- Evaluation of the efficiency of working capital
1. Structure of working capital enterprises
Coverages
-
This is a set of funds advanced to create and use revolving industrial funds and conversion funds to ensure the continuous process of production and product sales.
Processing production facilities
-
These are labor objects (raw materials, basic materials and semi-finished products, auxiliary materials, fuel, containers, spare parts dr.); water, items and tools with a service life of not more than 12 months; Incorrect production and expenses of future periods. Processing industrial funds enter into production in their natural form and in the process of manufacturing products are fully consumed, i.e. Move all its cost per product produced.
Foundations appeal
-
These are funds from the enterprise embedded in the reserves of finished products, goods shipped, but unpaid, as well as funds in the calculations and cash at the box office and in accounts. Funds of handling are related to the service of the process of circulation of goods. They do not participate in the formation of value, but are its carriers.
The movement of current production assets and treatment funds is the same in nature and amounts to unified process
. After the completion of the production cycle, the manufacture of finished products and its implementation, the cost of working capital is reimbursed in revenue from sales of products (works, services).
Current production facilities and conversion funds, while in constant motion, ensure uninterrupted cur circuit funds.
At the same time, there is a constant and regular change of forms of advanced cost: from monetary
It turns into commodity
, then B. manufacturing
, again B. commodity
and monetary
:
D-T-P-T-D
Monetary stage of circuit
is an Preparatory: It proceeds in the field of circulation and is to transform funds into the form of production reserves.
Production Stage
represents a direct production process. At this stage, the cost of used industrial reserves continues to be advanced, namely, the costs of wages and its associated costs are additionally advanced, and the cost of fixed assets on manufactured products has been transferred. The production stage of the circuit ends with the release of finished products, after which the stage of its implementation occurs.
On the commodity stage of the circuit
Labor product (finished products) is continued in the same amount as at the production stage. Only after the transformation of the commodity form of the product produced in monetary
Advanced funds are restored due to the part of the proceeds from the sale of products. The remaining amount is monetary accumulations that are used in accordance with the plan of their distribution. Part of savings (arrived)
intended for expansion of working capital
, joins them and makes the subsequent circulation cycles along with them.
Function of working capital
It consists in the payment and settlement service of the circuit of material values \u200b\u200bat the stages of acquisition, production and implementation. In this case, the movement of current production funds at each moment of time reflects the circulation of material factors of reproduction, and the movement of working capital is the turnover of money, payments.
Thus, working capital are in constant motion. For one production cycle, they commit circuit of three stages
.
In the first stage
The company spends money to pay for accounts for the supplied labor objects. At this stage, working capital from money form is transferred to commodity, and cash from the sphere of treatment - in the sphere of production.
In the second stage
The acquired circulating funds go directly into the production process and turn first into production reserves and semi-finished products, and after the completion of the manufacturing process - in finished products.
In the third stage
Finished products are implemented, as a result of which circulating funds from the production sphere come to the sphere of circulation and again take a monetary form.
At each stage, the time of finding working capital is not the same. It depends on the consumer and technological properties of products, the features of its production and implementation. Total duration of circulatory circuit
It is the function of the time of finding these funds at each stage of the circuit. Therefore, an increase in the duration of the circulation of working capital leads to the abolition of own funds and the need to attract additional resources To preserve the continuity of production.
In a market economy, an irrational increase in the duration of turnover of working capital leads to a decrease in the competitiveness of the enterprise as a whole, the deterioration of its economic situation. Therefore, for the market management system, the rational provision of the enterprise with working capital is extremely important and necessitates the need for the corresponding organization of management of these means.
2. Determining the need for working capital
Effective use of working capital
It largely depends on the correct definition of the need for working capital, which will allow the enterprise with minimal costs to make a profit planned under this volume of production. Understood
The values \u200b\u200bof working capital entails the instability of the financial situation, interruptions in the production process and the decline in production and profits. Owliness
The size of working capital reduces the capacity of the enterprise to produce capital expenditures to expand production.
When planning the optimal need for working capital, funds are determined, which will be advanced to create production reserves, incomplete production and accumulation of finished products in stock.
For this, three methods are used: analytical, coefficient and direct account method.
The company can apply any of them, focusing on his work experience and existing activities, the nature of economic relations, registration, the qualifications of economists.
Analytical and coefficient methods
Applicable in those enterprises that operate for more than a year have formed a production program and organized a production process, have statistics over previous periods of changing the magnitude of the planned part of working capital and do not have enough qualified economists for more detailed work in the field of working capital planning.
Analytical method
It assumes the determination of the need for working capital in the amount of their average actual residues, taking into account the growth in production. To eliminate the shortcomings of past periods in the organization of the movement of working capital, it is necessary to hold detailed analysis In two directions:
analyze the actual remnants of production reserves (in order to identify unnecessary, unnecessary, illiquid reserves);
Explore all stages of unfinished production (to identify reserves for reducing the duration of the production cycle, study the reasons for the accumulation of finished products in stock).
When planning the need for working capital, it is also necessary to take into account the specific working conditions of the enterprise in the coming year. This method is applied in enterprises where funds embedded in material values \u200b\u200band costs occupy a large proportion in the total amount of working capital.
For ratio of stock method
and costs are divided into depending on changes in production
(raw materials, materials, work in progress, finished products in stock) and do not depend
(Spare parts, low-value spending items, expenses of future periods). In the first case, the need for working capital is determined on the basis of their size in the base year and the growth rates of production in the coming year. If the enterprise analyzes the turnover of working capital and the possibilities of its acceleration are sought, then the actual acceleration of turnover in the planned year must be taken into account when determining the need for working capital.
According to the second group of working capital not having proportional dependence From the growth of production volume, the need is planned at the level of their average actual residues over a series of years.
If necessary, you can use analytical and coefficient methods. in combination
. First, the analytical method is determined by the need for revolving agents depending on the production volume, and then with the help of the coefficient method, changes in production volume are taken into account.
Direct account method
It provides for the reasonable calculation of reserves for each element of working capital, taking into account all changes in the level of organizational and technical development of the enterprise, transportation of commodity values, the practice of settlement between enterprises. This method is very laborious and requires high qualifications of economists, bringing to the standardization of employees of many enterprise services. At the same time use this method Allows you to most accurately calculate the needs of the enterprise in working capital.
The direct account method is used in creating a new enterprise and a periodic refinement of the need for working capital of existing enterprises. The main condition for the use of the direct account method is to carefully study the supply issues and the enterprise production plan. The stability of economic relations is also of great importance, since the frequency and supply warranty underlie the calculation of the reserve standards. The direct account method involves the rationing of working capital invested in stocks and costs, ready-made products in stock. IN general Its content includes:
Development of stock norms the most important types commodity values \u200b\u200bof all elements of normalized working capital;
Determination of standards in monetary terms for each element of working capital and the cumulative needs of the enterprise in working capital.
3. Evaluation of the efficiency of working capital
To assess the efficiency of working capital uses, two groups of indicators are used:
- indicators of the overall assessment of the efficiency of working capital;
- indicators of the efficiency of working capital in groups of working capital.
The first group includes indicators:
the degree of security of the enterprise with its own working capital;
the duration of one revolution of working capital;
working capital turnover coefficient;
the coefficient of loading means in circulation.
The degree of security of the enterprise with its own working capital (SAP) is determined by the formula:
Coa \u003d OS-nose,
(Preferably a positive value of about 0:\u003e 0)
where: OS is the average annual value of the normalized working capital (the average residue of working capital);
Nose is a norm of working capital.
The duration of one turnover of working capital (software) for a period of duration of N-days is determined by the formula:
PO \u003d OS / N,
(preferably minimum\u003e min)
The turnover coefficient of working capital (KO) is determined by the formula:
Ko \u003d RP / OS * 100,
(preferably maximum value\u003e Mach)
Where: RP is the volume of product sales (realized products).
The caffefficient of loading means in circulation (KZ) is determined by the formula:
KZ \u003d OS / RP * 100
(preferably minimum\u003e min)
The second group includes indicators:
share of debt on remuneration to employees in the accounts payable;
debt share to suppliers of unpaid supply to the accounts of the Company's accounts;
the ratio of receivables and payables of the enterprise;
the ratio of receivables and the volume of production of commercial products;
the ratio of payables and the volume of production of commercial products.
The share of debt on remuneration to workers in the accounts of the enterprise (DOT / KZ) is determined by the formula:
DOT / KZ \u003d KZOT / KZ * 100, (\u003e min)
Where: Labor Labor Debt to employees;
KZ is the creditor of the enterprise's debt.
The share of debt to suppliers to unpaid supply in the accounts of the company's accounts (additional / kz) \u200b\u200bis determined by the formula:
Additional / kz \u003d kzp / kz * 100 (\u003e min)
Where: KZP - debt suppliers for unpaid supply.
The ratio of receivables and short-term accounts of the enterprise (SDZ / KZ) is determined by the formula:
SDZ / KZ \u003d DZ / KZK * 100, (\u003e min)
Where: DZ - receivables of the enterprise;
KZK - Short-term accounts payable company.
The ratio of receivables and the volume of production of commercial products (SDZ / TP) is determined by the formula:
SDZ / TP \u003d DZ / TP * 100 (\u003e min)
The ratio of short-term payables and the volume of production of commercial products (SCS / TP) is determined by the formula:
SCZ / TP \u003d KZ / TP * 100 (\u003e min)
The second group of indicators is more characterized by the rationality of the structure of working capital of the enterprise and in general its financial condition.