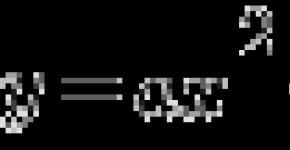Dangerous air transport situations. Terms of Conduct for Transport Accidents
Aviation accidents and disasters are possible for many reasons. Heavier consequences are destroyed by the destruction of individual designs of the aircraft, the refusal of the engines, a violation of the operation of control systems, power supply, communication, piloting, lack of fuel, interruptions in the livelihood of crew and passengers.
How to act when decompression
Decompression is the discharge of air in the cabin of the aircraft in the violation of its tightness. The decompression is usually beginning with a deafening area (air leaves). The salon is filled with dust and fog. Sharply decreases visibility. From the lungs of a person quickly comes out 3rch, and it cannot be delayed. At the same time, there may be ringing in the ears and pain in the intestine. In this case, without waiting for the team, immediately put on the oxygen mask. Do not attempt to provide anyone to help before you wear a mask, even if this is your child: If you do not have time to help yourself and lose consciousness, you both will be without oxygen. Immediately after putting on the mask, stamp seat belts and prepare for a sharp decline.
How to act in a fire on the plane
Remember that in the event of a fire on board the aircraft, the greatest danger is smoke, not a fire. Breathe only through cotton or woolen elements of clothing, if possible, moistened with water. Breaking through to the exit, move nourishing or on all fours, as the bottom of the salon is smaller. Protect open areas of body from direct fire exposure using existing clothes, blankets, etc. After landing and stopping the aircraft, immediately head to the nearest exit, as the probability of the explosion is high. If the passage is lit up, sneak through the chairs, lowering their backs. When evacuations, get rid of hand baggage and avoid output through the hatches near which there is an open fire or a strong slightness.
After leaving the plane, remove from it as far as possible and lie on the ground, pressed my head with my hands - an explosion is possible.
In any situation, act without panic and decisively, it contributes to your salvation.
How to act with a "tight" landing and after it
Before each takeoff and landing carefully customize the seat belt. It should be tightly fixed as low as possible from your hips. Check if you have no heavy suitcases over your head.
Accidents on take-off and landing are sudden, so pay attention to the smoke, a sharp decline, stopping engines, etc. Free the pockets from sharp items, bend and touch your hands tightly under your knees (or grab the ankle). Put your head on your knees or tilt it as low as possible. Legs up to the floor, putting forward them as far as possible, but not under the front chair. At the moment of impact, most and prepare for significant overload. Under no circumstances leave your place until the aircraft stops, do not lift panic.
Regardless that according to statistics, the air transport is considered the safest view of the movement, you need to know several rules that will warn you against danger.
Before using the services of any airline, take a flask with water to the cabin with water and the entire "duty set" for survival, which is clearly adjusted for the season and flight conditions.
With an outdrawal flight, you must have something enough floating with you. For example, you can tie a manual lay in the rubber bag and disguise it in the bag.
When an emergency landing is the safest place is the middle of the cabin. If possible, try to sit down there, without waiting for the incident. Do not forget that during the announcement of the emergency situation, the middle will be in short supply.
Before boarding the plane, check with the workers of the airline, where there is an emergency exit on the aircraft, which evacuation methods from the salon you can use how much oxygen masks are on board and how to run oxygen in them, and whether there is no rescue tools on water.
As a rule, containers with masks are fixed on the ceiling or on the back of the front armchair. Rescue floating media can be inflatable vests under armchairs, ladders, dams, as well as bottom chairlocks.
Try to sit closer to emergency or ordinary outlet from the aircraft. Emergency output is usually over the wing. They can be used if there is a fire or a plane in the cabin sits on the water.
Pay attention to the seat belt in the chair. Adjust it in your body and try to fasten and unzip it as quickly as possible. Remember that the belt should clearly fix your body and not give him a free move.
It is not recommended to disassemble throughout the flight, since the sudden maneuver or the air pit hit can move you to the ceiling. For the same reason, it is forbidden to walk through the cabin. Make sure your neighbor is reliably fastened, otherwise it will fall on you.
Accident when take-off and landing
When the plane begins to take off and sit down, it is best to wear a coat from a hard-coherent material (leather or wool). So you will provide some protection in case of fire. It is not recommended to wear thin-heel shoes, as they pierce an emergency inflatable ladder.
If the risk of emergency landing increases, remove all hard and heavy from the shelves. Your luggage should be keen or under the chair. If an emergency landing is inevitable, clog your head with something out of your clothes, close your face with your hands and make you sweep as much as possible. So you protect yourself from fragments. If there is too close space in the cabin between the seats, you should lie down with your hands in the front chair and put your head on your hands.
In the event of an emergency landing, your main task is to leave the plane as soon as possible, otherwise the fuel can explode and the chances of salvation will decrease sharply. If suddenly you have witnessed the development of panic, then help the crew keep calm.
For example, take all responsibility for yourself and firmly declare: "I know a short way to exit! All over me". Your loud and confident voice will help many passengers to come to themselves and rapidly go to the exit instead of randomly rolling through the cabin. Your self-preservation means are calm, order, and in some cases a fist.
Here are the basic security rules on the plane and recommendations on how it follows themselves in a critical situation. Knowing them, you can always save the life of yourself, your comrade, and maybe even the entire crew.
Emergency situations on aviation transport are cases of partial or complete destruction of the aircraft.
Over the past 10 years, aircraft in Russia began to fall twice as often. The urgent problem of the present is an emergency with helicopters and light aircraft.
They began to fall more often than 3-4 times (excluding the catastrophe of military helicopters).
The safest wide-body aircraft in the world is the domestic IL-86. For 20 years of service with these aircraft in the sky, not a single catastrophe occurred.
More than 80% of the aircraft crash occur due to the "human factor", 15% - the result of the vehicle breakdown. Sometimes it is difficult to prove that the cause of the catastrophe is - piloting errors or a technical fault of the aircraft, since the crew is usually driving along with passengers. The remaining passengers get injuries of various characters and severity. Among them will be persons who will require emergency assistance in connection with them developing acute somatic states (fainting, psychogenic shock, myocardial infarction, angina, or bronchial asthma attack, stroke, etc.).
Any airfather is accompanied by the application of large material damage, which is determined in monetary terms and in the number of damaged, destroyed or disappeared aircraft.
Emergencies at aviation transport are divided into disasters, accidents and breakdowns.
The aviation catastrophe is called an aircraft, which caused the death of one or more person, complete or partial destruction of the aircraft or its without a trace disappearance.
Aviation accident is called airfire without human victims, but caused significant damage to the aircraft.
Aviation breakdown is a situation that reduces the safety of the flight.
Currently, the most dangerous and common tragedy on board the aircraft is the fire and explosion.
Safety of flights is provided:
Strict regulation of design, construction, testing and certification of aircraft, aircraft engines and equipment;
A complete list of technical requirements and standards to the characteristics of aircraft, their elements, systems, aggregates and equipment;
System of technical operation of aircraft with a list of mandatory rules for their preparation and maintenance;
Technical requirements and regulations to airports, airfields, airways;
The rules of the organization of air traffic management;
The procedure for the work of the meteorological service providing aircraft;
The system of investigation of airfire.
The rules for the behavior of passengers in the airfather. It is necessary to accurately follow the crew guidelines and respect sober calm. It is very important to overcome in my own and other participants in the flight panic and stupor.
The behavior of the air passenger during decompression. Decompression is the range of air in the cabin of the aircraft in the violation of its tightness. There is a deafening roar - from the salon, air is very quickly leaving, and then the interior begins to fill with dust and fog, which reduces visibility; The airplane sharply drops the air temperature. A person from the lungs rapidly pulls the air, no matter how straining the chest, it is impossible to hold it. At the same time, drumpipens are overloaded, pain and noise in the ears are occurring, headache. In the intestines are expanding gases and sharp pain appear. After a few seconds, the loss of consciousness comes from suffocation.
With the sound of the air from the interior, you need to immediately put on an oxygen mask, which is located in the back of the chair located in front. First of all, it is necessary to protect yourself: the symptoms of decompression man cannot control, quickly loses consciousness and does not have time to assist others, including his own child. Then fasten your seat belts, since the plane starts to quickly decline and you can be thrown out of the chair. Prepare for a sharp decrease: remove solid, sharp, cutting items, lighter, remove the tie, glasses.
The behavior of the air passenger in the fire on board the aircraft. When smoking the cabin, protect the respiratory organs with a damp cloth, the subject of clothing; Upper clothes do not remove, as it protects the body from the direct action of high temperature. Synthetic clothes adjacent to the body, tights, linen better remove: melting, synthetics will cause heavy skin burns.
If the plane is on Earth, make your way to the nearest exit, nourishing or on all fours, and if the passage is littered - through the chairs, lowering their backs. Manual sting do not take - it can cost life. In the crowd, the exit will not stand - there are other outputs.
Do not open hatches near which there is a fire or a strong smalleriness.
Send from the plane, drop away from it as far as possible, it will save from a possible explosion.
The passenger behavior with the "tight" landing and after it. Get free from sharp, cutting and heavy items, from glasses and a tie and take one of the fixed pos.
Pose I (optimal): Buck up and tightly pin your hands under your knees or take the ankle. Put your head on your knees, and if it does not work, tilt it as low as possible. Legs up to the floor, putting forward them away, but not under the front chair.
Pose 2: Put soft things under the chest and stomach. Crossed hands Place on the back of the front armchair and press it with them. Lay your legs away, but not under the front arm chair, and you will be shed into the floor.
If a child flies with you, put it on your knees and close your body.
At the moment of impact, most accurately, to facilitate the effects of significant aircraft overload when it is moving forward and, possibly down. Under no circumstances leave your place until the aircraft stops.
With a forced landing, enhanced safety measures are used. The evacuation of passengers on inflatable traps is organized. In this case, it is necessary to remove the shoes on the heels in order not to break the tightness of the ladder and do not release air out of it.
Emergency-speaking work in the emergence of emergencies at aviation transport.
Asdran can be divided into 2 types: conducted by members of the crew and organized by ground services. A crew for taking measures, as a rule, not enough time, as everything happens very quickly. Typically, the crew will give a distress signal and lands in the near airport. In some cases, the Guide to Saving an Airplane, tolerant In the Air, Ground Services take over.
The main part of the emergency part of the airport (about 80%) occurs in the airport area (parking, take off, landing, landing). Conducting emergency rescue works here, rescue teams (ASK), which include calculations from each service: dispatch, start-up, fire and rescue, firewall, medical, engineering, special transport, transportation, police. After receiving information about the accident at the ASC aircraft, they are obliged to immediately proceed to work.
The priority events are related to evacuation. The evacuation capabilities of aircraft of various classes differ from each other. They depend on the layout of the salons, the number of passengers, the presence of spare and emergency exits, their time to prepare them to work. According to the requirements of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), all passengers should leave the aircraft in the event of an emergency on board through the outlets located on one side, in 90 seconds. In an emergency, all major, official, spare doors should be used to evacuate people. It can be carried out through faults in the fuselage, special hatches made by rescuers, cargo hatches, windows in the cockpit. The design of emergency output locks ensure the possibility of opening them both from the inside of the salon and outside. From the inside the outputs open crew members or passengers. Outside this ra - the bot is performed by rescuers. They caught up to emergency output mobile ladders, special vehicle, hanging rope systems. Handles of locks on emergency exits are simply arranged, they are noticeable and do not require great effort when opening.
Sometimes the deformation of the fuselage and the high temperature resulting from the fire leads to the encoding of doors and hatches. In these cases, rescuers are starting to open the fuselage. The opening sites cannot be arbitrary, since the entire length of the fuselage is laid electrical pipes and high-pressure hydraulic pipelines. Their damage can lead to additional difficulties. Optimal opening sites are marked on the fuselage. Yellow corners on a white background. An autopsy should be made using disk saws, electrical power machines, special bodies and axes. These works must be made quickly and in compliance with all precautions.
The evacuation of passengers and crew members from the board of the aircraft at emergencies can be carried out using mobile gears, attachments and fire stairs, large-scale buildings, rope systems.
In the aircraft itself, there are also special means for evacuation: inflatable ladders, plated gutters, rescue ropes. Inflatable TN-2 laces are placed under the floor of the floor in front of the entrance door (IL-62) or on the folding platform (Tu-154), the TN-3 ladder on the folding platform at the front inlet door. To bring the inflatable ladder TN-2 (TN-3) to the working position it is necessary to open an emergency door, a hatch in the floor (IL-62), remove the ladder and secure the hatch. At the same time, stiletto stiletts from the cover of the cover should be pulled out. At the same time, the case will open and the ladder will fall out of it. If, with a strong wind, the ladder, after it was poured, wrapped under the fuselage, then it must be pulled out for the bottom end of the aircraft. After refining the ladder, you need to strongly turn the cylinder valve handle with carbon dioxide. The ladder is filled with gas for 10-12 s and occupies a working position at an angle of 45-50 ° from the aircraft to the ground.
It is allowed simultaneously to descend by TN-2 and TN-3, no more than 2 people. The throughput of one inflatable ladder is 100 people for 2.5-3.0 minutes.
Mantle gutters, as a rule, are near the exits on the right side of the fuselage. The cloth groove tray is designed to descend people to the ground during emergency evacuation through service and spare outputs. It is made of the material "Cloak Tent Case" with a combined impregnation. After opening the door (Luke), you need to remove the chute from the cover and insert the hooks of the gutter into the upper and lower parts of the door. Throwing a chute to the ground, stretched with 4-5 m from the aircraft. Holding down the loop, let down the passengers down. It is allowed simultaneously to lower no more than 1 person through its mandatory injury.
Over each emergency exit, as well as above the window in the crew or hatch, there are rescue ropes attached to the fuselage bracket.
Opening the window or hatch, the rope is thrown out.
On IL-86 and Yak-42 for emergency evacuation of passengers and crew members there are emergency doors with inflatable ladder embedded in them. In the process of emergency door opening, an automatic emission from the inflatable ladder container and filling it with air from a cylinder occurs.
On the IL-86 - a dangle of two tracks, at the same time the aircraft can leave and be on a trapp of 4 people. On the Yak-42 - the pallever lane, at the same time 2 people can be on the database.
When evacuating rescuers together with the crew provide assistance to passengers and their insurance. First of all evacuate children, women, older people and only then - all others. Passengers who are in an unconscious state or having heavy bodily injuries are carefully removed on stretchets, tarpaulin, shields and lowered to earth with rope.
After the end of the evacuation, rescuers check the hidden places in passenger compartments and the crew cabin, as well as kitchens, wardrobes, sanitary and hygienic and luggage rooms to make sure there are no people aboard. If there is information about the number of passengers and the composition of the crew, they are compared with the data on the saved and, with discrepancies, they continue to search until the victims are detected. A special danger is aviation incidents accompanied by fire.
Fires inside passenger salons belong to fires in closed volumes. They are characterized by a large density of smoke, a small size of the combustion zone, a high temperature gradient and a small (compared to outer fires) the temperature of the fire, as well as the presence of significant concentrations of high-thicing substances in combustion products. The fire in passenger salons may occur due to accidents, careless handling of fire, closure of electrical wiring, passenger wires of flammable substances, etc.
One of the main reasons for the defeat of people inside the salons in the fires is poisoning combustion products. 2-3 minutes after the propagation of fire, carbon dioxide in the salons reaches a deadly concentration. The air temperature increases sharply at the height of the cabin: if at the floor level it is 50 ° C, then at an altitude of 1.3-1.5 m from the floor already 250 ° C.
Fire extinguishing inside the salons, the rescue of passengers and the crew begins with the penetration of rescuers inside the emergency ship. When opening the fuselage, the intensity of burning increases, the volume of space covered by flames and the temperature of the fire increases sharply.
Rescuers must be equipped with individual means of thermal and gas protection, a working sleeve, filled with a solution of the foaming agent, and a bumpy trunk.
The presence in the salons of a large amount of dense smoke and toxic substances significantly complicates the position of both the affected and the rescuers themselves.
Since the temperature in the height of passenger salons is sharply increasing during the fire inside the aircraft, then the rescuers must in the initial stage of extinguishing until the mid-payable temperature will be reduced, work, nourishing, cooling the upper high-temperature layer of the passenger compartment.
Upon acts in the smoke atmosphere, one rescuer must be outside the fuselage and have the same means of protection as lifeguards working inside the vessel. Its responsibilities include maintaining a permanent connection with rescuers in the smoked salons, rendering immediate assistance to both victims and, if necessary, other rescuers.
In case of fires inside passenger salons, such a complex and life-threatening situation is created that salvation becomes possible only with immediate evacuation. It should be carried out simultaneously with fire extinguishing, and through all doors, holes and hatches, preferably from the windward side. Opening the fuselage is expedient to start just starting with the doors, since they have bandwidth higher than that of the holes done in the trim. These holes should be used when evacuation through the doors is impossible.
Some aircraft crashes do not occur in the airport zone, which causes the need to organize and prompt search for an aircraft. Search and rescue work are organized in cases:
Receiving a disaster signal from the aircraft;
If within 10 minutes after the current time, the aircraft did not arrive at the destination and there is no radio communication with it;
If the carriage of the aircraft received permission to land and did not produce it at the set time, and the radio communication ceased to it;
If there is no connection with the crew and its location during flight on the track and its location for 20 minutes, as well as in all other cases where the aircraft crew requires help.
Sewing and rescue work is carried out with the involvement of aircraft and helicopters equipped with search engine and rescue equipment kits, as well as ground vehicles of increased passability and rescue boats. If necessary, the funds of the International Space System of the search for the disaster of air and sea courts "Cospassat" can be involved.
When the aircraft is detected, its coordinates are determined, communication is established with it, the state of the health of people and the size of the necessary assistance is specified. The possibility of landing and the routes of extending to the location of the aircraft of land vehicles are determined. If it is impossible to carry out the landing of search aircraft, then the search-selling detachment (PSO) and the equipment necessary for work are packed into the place of the PSR.
After disembarking, the PSO immediately proceeds to evacuation and movement of passengers of the disaster of the aircraft to the safe distance. It takes not only to save people from rescuers, but also to create them the necessary household conditions that protect them from bad weather, to provide them with first aid. It is also necessary to calm people and prevent panic.
In the case of the inaccessibility of the disaster area, rescuers unfold a temporary camp with the necessary system of life support.
If the passengers and the crew are needed immediate and serious medical care, and there is no opportunity to deliver them to the medical institution, then in the distress area, a temporary field hospital unfolds.
A feature of rescue work in the field is the absence of powerful special equipment at the initial stages, then the fuselage opening is made by a hand tool (ax, scrap, sledgehammer, shovel, etc.).
Rescue work is terminated only after the evacuation of all people who were on board the aircraft. Then, if possible, proceed to the salvation of the aircraft itself and the cargo transported by them, the search for "black boxes".
The exceptions are cases where cargoes have a greater material and artistic value, as well as dangerous goods (explosives and radioactive substances, Ahkh et al.). In such cases, the salvation of people and cargo is carried out at the same time.
Forced landing for water. When saving the intake, the aircraft has enough buoyancy so that you can have time to save people. Before planting the water, each passenger needs to get and put on a life jacket, and all passengers must be instructed in advance about the rules for using them.
If there is a risk of water intake through the entrance doors, when they open the evacuation of passengers and crew members, it is carried out through spare outputs (if they are above the water level) or upper hatches (astroinders) and the vehicle in the crew cockpit. When evacuating from the aircraft, group rescue floating agents (rafts) are used, which first of all serve children, wounded, sick and elderly passengers.
After the transition to the Flux is necessary: \u200b\u200bCheck the number of passengers, sail to a safe distance from the aircraft (at least 100 m) until it began to dive into water; Prepare emergency radio accessories, alarm tools and file a disaster signal.
Being on a raft, it is necessary to organize round-the-clock control over the observance of the course of movement, the appearance of the shore, marine and aircraft, and when they are detected, to try to communicate with the help of an emergency radio station.
With great remoteness of the place of emergency landing from the shore to rescue people, aviation equipment is used (helicopters, hydroplanes, screenwall).
The aircraft during emergency landing on the water can sink entirely or, when it collapses, in parts. In the sunken aircraft there remains a stock of air, which passengers and crew members should be enough for a while. Then special diving teams are involved in rescue people who have appropriate preparations for the management of ASR. When holding an ASR on a sunken aircraft, open his fuselage in such a place so that the air, preserved in the salons, does not disappear.
Aviation accident- The event associated with the operation of the aircraft, which occurred during the period of its board of passengers or crew members, resulting in damage or destruction of the aircraft and caused people's injuries or not caused bodily harm.
Aviation incidents are divided into flight and ground.
Under flight incident Understand the event associated with the performance of the flight task and caused the consequences of varying severity for those who were on board the aircraft (injury or death) or the aircraft itself (damage or destruction).
Terrestrial incident The aircraft that took place before or after the flight is considered.
Depending on the consequences for passengers, crew and aircraft The flight and terrestrial accidents are divided into breakdowns, accidents and disasters.
Breaking - Aviation accident, followed by the death of crew members and passengers, which led to damage to the aircraft, the repair of which is possible and economically appropriate.
Accident - aviation accident that did not result in the death of crew members and passengers, but led to complete destruction or severe damage to the aircraft, as a result of which its restoration is technically and economically impossible impossible,
Catastrophe - aviation accident, which entailed the death of crew members or passengers during the destruction or damage to the aircraft, as well as the death of people from the wounds received, which arrived within 30 days from the moment of the incident.
World statistics indicate that almost 50% of the aircraft crash occur on the flight field. For example, at the airport of Havana in 1989, the IL-62m plane crashed, 125 people were killed., In the Sverdlovsky airport in 1990, the Yak-42 aircraft crashed, 122 people died.
In other cases, the catastrophe occurs in the air at various heights, and the aircraft confusing is the cause of the death of not only passengers and the crew, but also people on Earth. So, in 1994, 125 people died in the fall of the aircraft Tu-154, of which 1 local resident accidentally turned out at the scene; In 1988, the residential neighborhoods of the Scottish city of Lockerbi from the height of 10 thousand m fell "Boeing 747" with 258 passengers on board, along with them 15 mesita residents of the city.
Catastrophes in civil aviation, seemingly very frequent and dramatic compared to other traffic incidents, are characterized by more modest average sanitary loss. At the same time, almost 100% of crew and passengers often occur in aviation catastrophes, exceptions are rare here. Usually, sanitary loss sizes in these cases can reach 80-90% of the total number of people in the aircraft.
Every year there is an average of 60 plane crash, of which all passengers and crew are dying. The survivors of 40-90% may be mechanical injuries; Combined and combined lesions are found at 10 and 20%, respectively, in 40-60%, cranopy and brain injuries are possible, 10% of victims develop shock. Damage to severe can have almost half of passengers and members, the crew of the aircraft.
According to the EMERCOM of Russia, in 1996, 40 accidents occurred in air transport, including 14 plane crash, in which 232 killed and 334 people suffered.
Based on the information given, we can assume that the task of providing medical care to the mass number of victims in aviation catastrophes will not be typical. Most often it will occur in cases of terrestrial incidents or after the forced landing of the aircraft.
According to reports, the maximum number of victims depending on the type of aircraft can be: An-2 aircraft - 12 people, An-24 - 47, Yak-42 - 113, Tu-154 - 168, IL-86 - 324 people.
Statistics for 1981-1989. It indicates that 100 thousand hours of flight during passenger traffic accidents in the USSR was 0.11 cases in 1981 and, gradually decreasing, 0.03 - in 1989, these figures in the United States were 0.06 and 0.04, respectively ; According to the International Organization of Civil Aviation ICAO (without USSR), during these years the accident was 0.14. The number of victims (crew + passengers) by 1 million transported over the same years, respectively, was: USSR - 2.34 and 0.30; US - 0.01 and 0.60; ICAO data (without USSR) - 0.56 and 1.00 people.
Aviation accidents and disasters are possible for many reasons and lead to severe consequences. Accidents at take-off and landing belong to the way where there is hope for salvation, as they usually occur when the plane is still on Earth or low above it, and its speed is relatively small. Moreover, they, as a rule, happen in the area of \u200b\u200bthe airport, where there are rescue teams and the necessary equipment.
The actions of passengers in the event of an accident at take-off and landing:
The back of the chair is put into vertical position;
Remove the glasses, high-heeled shoes, loosen the tie, unbutton the collar, remove sharp items out of pockets;
Put soft things on your knees, pon the seat belt and button;
Left to lean forward, lower my head down, rub the back in front of the standing chair (with his absence, clap his knees and put his head on them).
Leaving the plane through the exit with the ladder released and inflated, you need, without stopping, jumping on it, and not sit on the edge and then move down. Only a jump is achieved an increase in evacuation rate. Before jumping, shoot glasses, high-heeled shoes.
For decompression. Air discharge in the cabin of the aircraft as a result of depressurization, the latter is filled with dust and fog. The visibility is sharply reduced, air quickly leaves the air, and it cannot be delayed. At the same time, ringing in the ears and pain in the intestines may arise.
Fast decompression usually begins with a deafening roar (air leaves). In this case, without waiting for the team, immediately put on the oxygen mask. Do not try to assist anyone before you wear a mask, even if this is your child: if you do not have time to help yourself and lose consciousness, both will find yourself without oxygen. Immediately after putting on the mask, fasten the seat belts and prepare for a sharp decline.
Actions by fire air passengers:
Listen and follow the crew members;
Protect open body parts from direct fire exposure using existing clothes, plaida.;
Make and enjoy to get out on all fours;
If the passage is blocked, move on top of the lowered aircraft spots;
Once out the plane, go away from it as far as possible.
When evacuations, get rid of hand baggage and avoid output through the hatches near which there is an open fire or a strong slightness.
For emergency leaving the aircraft, passengers and crew use all the main and spare doors, as well as emergency exits, located, as a rule, on the left and right sides of the fuselage. Outputs for passengers, approaches to them and the opening tools have a noticeable labeling that facilitates their detection. All inscriptions are highlighted from the inside regardless of the main lighting system. The device of emergency hatches and their locks with handles is made simple, noticeable and not requiring great effort to open. The instructions for opening them are applied on the doors (hatches).
Forced landing of the aircraft on the waterit happens rarely. Before sinking, the plane can be afloat from 10 to 40 minutes. However, if the fuselage is damaged, this time is significantly less. Airplanes, whose engines are located on the wings will be afloat in a horizontal position, and those whose two or more engines are on the tail, will float the tail part down.
In one case, the plane can touch the water surface very smoothly, in the other to fall apart on the pieces and quickly sink. Therefore, when driven, it is necessary to act clearly on the commander of the crew or flight attendant.
Activities of air passengers with forced (emergency) landing for water:
Put the life jacket and inflate it slightly;
Take with you or put on warm clothes;
Take the place on the rescue raft.
After a forced landing on the water, rescue rafts are descended. The time to bring the dam in the working condition is approximately 1 min. in summer and 3 minutes. in winter.
Using oars and rented items, you need to move away from the place of immersion of the aircraft. After that, straighten and quit the floating anchor overboard, which will reduce the drift drift speed in the wind and will hold back in the accident area.
The most dangerous month for flights is September. This conclusion was made by Internet edition of PlaneCrashInfo.com after analyzing data on aircraft crashes that occurred from 1950 to 2013. More than 15% of annual brushes falls on September. May accounts for the smallest share of the annual aircraft crash - about 6%. The most risky days for air travel are 12th and 29 August, July 3 and 11, October 2, November 23, 7, 8, 21 and 22 December. On December 22, there were more disasters in different years than on other days - 17.
Most experts converge in the fact that there is no safe place in the plane. However, a study conducted by one of the American magazines showed that this is not. As part of the study, the statistics of accidents of American passenger liners were analyzed for the period from 2001 to 2013. In total, during this time there were 25 aircraft crashes. As it turned out, the most safe to sit in the tail part of the aircraft - for passengers that are closer to the tail, chances of survival when crashes are 40% higher than for those who sits in the forefront of the front of the cabin.
Counting security levels of various places in the aircraft showed that for passengers in the rear of the chance to survive is 69%. For those whose chairs are on the lines of the wings - 56%. Most of all risk business-class passengers, which is traditionally located in the front of the cabin, immediately behind the cabin of pilots - their chance is estimated at 49%.
According to the international association of air transport, in most cases the main cause of the disaster is the mistakes of pilots (including forced - for example, due to the influence of adverse weather conditions) - pilots are guilty of 53% of accidents. In 20% of cases of disasters, due to mechanical problems, in 11% - due to weather influence (including hurricanes, fogs, lightning strikes, etc.), 8% - due to sabotage acts (terrorism, attack on pilot, etc.).
According to Boeing, the most dangerous phase of the flight is landing. 45% of accidents occur at the time of landing, another 13% - during the landing. 12% of accidents fall at the time of takeoff, 13% of the height set, 6% - for the main flight, 5% - for the period of preparation for the rise, load baggage and cargo, landing of passengers, etc.
According to the International Association of Air Transport, Russia and other former Soviet republics have the worst air transport safety indicators.
In the emergency ranking of the International Air Transport Association (IATA), which takes into account the aircraft irretrievably lost in the catastrophes, the CIS, including Russia, is in the wrong first place, overtaking asia, Africa and Latin America.
So, in the CIS, 5 aircraft per million flights die, in Africa - only 3.5. In North Asia, Europe and North America - less than 0.5 aircraft for the same million flights. So, according to IATA in 2010, one serious accident accounted for 1.6 million flights. In total in 2010, 786 people died in them.
At the same time, airlines in North America were recognized as safe, where the accident coefficient was only 0.1. In Europe, this indicator is 0.45, in Japan - 0.34.
The European Union leads a list of airlines having dangerous aircraft in its park. It has 17 Russian airlines.
This is associated with the fact that the quality of maintenance has fallen in the market years. Experts indicate that fault detection before the flight has become commonplace. Until now, the repair of domestic aircraft is often conducted due to the decompliament of the part of the airfield standing on joke. Until recently, scandals with fake spare parts trade did not stop.
The pilots began to fly more often, but the level of preparation is still insufficient. To prepare the pilot, it is necessary to burn tons of fuel, and not any airline will go to it. Air carriers prefer to lear the pilots from competitors, and not to invest in their upbringing. As a result, the average salary is growing, and the quality of flight composition above does not become.
Today in Russian aviation there is a process of gradual degradation. Officials are striving to reduce the number of airlines, hoping that it will increase the safety of flights. As a result, the entire sphere of air transport began to shrink. Closed airports in remote territories.
The list of most secure airlines of the world is published annually. At the end of 2013, the top ten included:
10. British Airways.
9. Virgin Australia.
8. Hainan Airlines (China)
6. Eva Air (China)
5. ETIHAD AIRWAYS (UAE)
4. Emirates (UAE)
3. CATHAY PACIFIC AIRWAYS (Hong Kong)
2. Air New Zealand. The only incident with the carrier aircraft occurred in 1979.
1. Finnair. On aircraft, the world's safest airline did not occur in the past 49 years.
According to the estimates of the US Department of Transport, the risk to die during the airliner flight is estimated as 1 to 52.6 million. The risk of death for passengers of smaller aircraft performing short flights is noticeably higher - 1 to 581.4 thousand for passengers of small aircraft (sports, aerotexix, etc. p.) - Even above - approximately 1 to 164 thousand.
According to a study conducted by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, the risk of passenger to die in a plane crash on domestic airlines of industrialized countries is 1K 8 million. In developing countries on domestic flights, this probability increases to 1 chance to 500 thousand percentage of passenger death during international flights between industrial Developed countries are 1 to 5 million. International flights between developing and developed countries of the world are more dangerous - 1 to 600 thousand on flights committed between developing countries, the risk is the highest - 1K 400 thousand.
According to the Emergencies Ministry of the Russian Federation, in Russia every year about 60 air transport disasters occurs. Aviation catastrophes occur more often when landing than when taken. Their cause is subjective (human) factor, as well as the proper function. The human factor includes a crew fatigue, loss of orientation, miscalculations when landing and a number of other reasons. Unlike motor vehicles drivers, pilots pass psycho-physiological selection, and this factor is less important than during catastrophes on the vehicle.
Technical malfunctions of aircraft and helicopters in the early years of accidents, due to their worn, began to play a large role than the human factor. Technical malfunctions include a significant reduction in reliability characteristics, deterioration of the quality of maintenance and repair.
The priority measures to save people with such an accident, as a rule, are associated with the evacuation of passengers from the aircraft. According to the requirements of the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), all passengers should leave the aircraft in the event of an accident on board through the outlets located on one side, in 90 seconds.
To reduce losses at aircraft crashes necessary minimum passenger preparation for flight.
First, you need to use seat belts, in the period of lifting and landing. Secondly, know the location of emergency exits from the salon. Thirdly, during the accident period, it is necessary to take a safe pose, bend and tightly pin your hands under the knees, put on your knees, and if it does not work out as low as possible. The legs should be left to the floor, push them as far as possible, but not under the front chair, which you need to put crossed hands, but to press your head, stretch your legs and move away. Both postures are accepted with an endless belt. In the destruction of the cabin at the height and outlet of air from the salon, decompression is developing, which is accompanied by a deafening roar (air leaves). The salon is filled with dust and moisture (fog), the visibility is sharply reduced, air from the lungs to exit, pain in the intestine due to gas intake. In these cases, it is necessary to wear an oxygen mask. The crew of the aircraft during decompression reduces the height of the flight to 3000 m, where the oxygen content in the atmosphere is close to normal.
In case of decompression, without waiting for the team, immediately:
· Put the oxygen mask.
· Do not attempt to assist anyone before you put the mask yourself, even if this is your child. If you do not have time to help yourself and lose consciousness, you both turn out without oxygen.
· Immediately after putting on the mask, fasten the seat belts and prepare for a sharp decline.
With emergency leaving of the aircraft through the doors on one passenger, one second is spent. In addition, from the aircraft, it is necessary to make food, water, medicines and an emergency radio station. The captain of the aircraft must check, there is no il in an aircraft of someone's passengers or crew members, and leave it the last.
When organizing emergency and rescue work in case of fire on board the aircraft It must be remembered that: after 2-3 minutes. After the emergence of fiery burning, carbon dioxide in the cabin reaches a deadly concentration; The temperature inside the passenger salons increases sharply by their height (at the floor level - 50 0 C, and at a height of 1.5 m from the floor - 250 0 C.
When accidental accidents, up to 80% of passengers die. At the same time, 60-80% of the affected, survivors are obtained, 60% - shock, 70% - the gap of the internal organs, 60% - limb injuries.
Similar information.
Accident on transport - This is damage to the vehicle. For example, a car, railway composition, aircraft, ship can suffer an accident. At the same time, the accident with the tragic consequences associated with the death of people is called catastrophe.
Protection with car accidents (catastrophes)
The car accident is one of the main causes of the death of people in peace times.
In most cases, car accidents arise due to non-compliance with elementary safety measures and road rules, as well as insufficient awareness of the consequences of one or another violation of road safety rules. For example, few people know that a collision with a fixed obstacle at a speed of 50 km / h without a seat belt is equivalent to a leap down from the 4th floor.
About 75% of all accidents on road transport occurs due to violation by drivers of traffic rules. The most dangerous types of violations still remain speeding, ignoring road signs, departure to the head of the counter movement and controlling the car in a drunken state.
Often lead to accidents bad roads (mostly slippery), malfunction of machines (in the first place - brakes, on the second - steering, on the third - wheels and tires).
The feature of automotive accidents is that 80% of the wounded dies in the first three hours due to the abundant blood loss.
There are several recommendations how to protect yourself during an accident. So, when an accident occurs in the vehicle in case you see that it is impossible to prevent it, try to take the safest position, grouped and closing your head with your hands. During the accident, all muscles must be up to the limit. The most important thing is to hinder your move forward. To do this, in case you are sitting on a driver's seat, you need to twist in the back seat and, straining all the muscles, lean your hands into the steering wheel; If you are sitting on the front seat as a passenger, then you should move to the "Facial Panel"; And if you are back in front of the front seat. In case you, being driving, did not fasten your seat belt, you should be clouded to the steering column, and on the site of the passenger - you must close your head with your hands and falling the side. Do not leave the car until it stops, since the chances to survive in the car is 10 times more than when emphasizing it.
If the accident is associated with tipping or fireing the vehicle, try to leave it as soon as possible, using for this if it is necessary not only the doors, but also windows.
If the machine fell into the water, you should not open the doors, as the water immediately rushes inside, and the car will begin to dive sharply. It is necessary to get out in this case through an open window.
If a fire occurs in public transport, firstly, immediately inform the driver. Secondly, try to open the doors to the emergency opening button. If it fails, break the side windows or open them according to the instructions as emergency outputs. Thirdly, try to put out the fire yourself, and if you do not succeed, then leave the salon immediately.
Electrical food of trams and trolleybuses creates an additional threat to human lesion with electricity. Therefore, choosing out from the tram salon or trolleybus, do not touch its metal parts.
In any case, the main thing is to keep calm and in no way panic, as a panic can lead to greater damage. Decide in which location of the car and in what position you are, whether the car is not lit and there is no gasoline (especially when tipping). Selecting from the car, go away from it - an explosion is possible.
If nothing serious happened to you, help the victims, organize the first help and take measures to eliminate the consequences of the accident. If necessary, call "ambulance" and inform about what happened to the police.
Accidental protection (catastrophes) on railway transport
As statistics show, the death of people on railway transport is mainly related to the crash of trains. Therefore, it is necessary to know and apply the rules and security measures in this emergency.
When brushing or emergency braking, the most important thing is to gain and prevent your move forward or throwing on the sides. To do this, during the strike, the point that has arisen as a result of the accident, try to grasp for fixed parts of the car or grouped, cover your head, to avoid injuries. When turning the wagon tightly hold on with your hands and rest on the legs into the wall, the upper shelf, etc. After the car acquires stability, take the way out of it. At the same time, if the wagon is overturned or damaged, selected through the windows, pulling the children and affected by the hands. In the event of a cliff of the wires of the contact network, depart from the wagons by 30-50 m, so as not to fall under step voltage.
Of course, ensuring the safe movement of trains depends mainly from machinists and dispatchers, but you can reduce the risk with a possible crash of the train if you know some rules:
- when trains collide, head and tailings are the most dangerous;
- unfilted doors in the extreme position in the coupe lead to injuries from their sharp movement when stopping;
- bulky malls, glassware, located on the upper shelves, also lead to passenger injuries with a sharp stop;
- on electrified railways of the railway, broken supports and lying on the Earth of the electric conduction are of particular danger in the crash of trains.
A large risk for passengers of railway transport is also a fire in the car. This is due to the focusing in the passenger cars of a large number of people and the difficulty of their evacuation, speed of increasing the temperature and the propagation of toxic gases in closed spaces, the distance of the train located on the way, from fire units.
When a fire occurs on the way, first of all, inform the conductor or the driver. Try to take all measures to stop the train, using a stop-crane or emergency braking system for this, and fire eliminate. (Remember that during the fire it is impossible to stop the train on the bridge, in the tunnel and other places where the evacuation will complicate.) If it is impossible to extinguish the fire on your own forces immediately leave the car, using all the outputs, including the windows, without forgetting to render Assistance in evacuation to children and elderly ages. Remember that in case of fire, the material that the walls of the wagons are lined with a little car, highlights toxic gas, life-threatening. Therefore, during a fire on the train, try to secure the protection of the respiratory authorities.
When evacuating, be careful not to get under the counter train. Leaving the train, do not stay near him, but try to move away for a safe distance.
Safety for accidents (catastrophes) in air transport
The safety of flights depends primarily from the reliability of aircraft and professionalism of crews and dispatchers. However, and you can comply with certain security rules when using aviation transport.
If you have the opportunity to choose, then sit down in the chair, which is located near the way out and, if possible, closer to the middle or tail of the aircraft. Ask, where the outputs are located (main and emergency) on your plane and how they open. When takeoff and landing, make sure that your seat belt is tightly tightened. Be careful to commands and signals that are transmitted over the microphone, on the light scoreboard or flight attendants.
One of the emergency situations that can occur in flight is decompression - reduced oxygen content due to the "departure" of air. Decompression usually begins with a deafening roar, the aircraft salon is filled with dust and fog, visibility is sharply reduced. At the same time, people appear ringing in the ears and pain in the intestine (gases are expanding), air quickly goes out of the lungs, and people lose consciousness. Therefore, at the first signs of decompression, you need to immediately wear an oxygen mask (about where it is stored and how to use it, informs the stewardess at the beginning of the flight) and prepare for a sharp decrease or emergency landing, the gap as an emergency related to decompression is corrected by a decrease in flight height .
When an emergency landing should take the safest position. To do this, lower the chair and grouped by pressing your head to the hands and left legs along the movement. At the moment of impact, the most strain. When the plane make a forced landing, strictly follow all the crew instructions.
If the fire occurs in flight is not a panic, but try to assist in eliminating a fire or protect against fire and smoke, using clothing and water for this. Get ready for an emergency landing and be sure to mentally imagine your way to the nearest exit. After an emergency landing, try to leave the plane faster, using emergency hatches and ladders for this (you have one or two minutes). At the same time try to protect your skin and do not breathe smoke. The main thing is to keep calm and do not panic, as not only your salvation depends on this, but also the salvation of other passengers (according to the National Military Office of the US Transportation Safety, over 70% of people who have fallen into air crashes with fires remain alive). Once behind the aircraft, help affected and try as soon as possible to move away with them to a safe distance.
If the aircraft suffered an accident in a deserted area, then try to capture the most necessary things with an emergency evacuation from the aircraft (medical aid kits, warm things in winter time) and think about how to give signals from the ground visible from the air.
Protection with accidents (catastrophes) on water transport
For timely and organized work on saving passengers and the vessel itself, each of them developed Alarm timetables. They feature all the actions of the team and passengers on the appropriate alarms when an emergency occurrence. In addition, each passenger seat establishes a cabin card of the passenger in Russian and English, in which the alarm value is indicated; the place of collection of passengers on anxiety; the room and location of the rescue boat; Illustrated brief instructions for managing individual rescue means indicating their place storage.
Therefore, before settling in the cabin, carefully read this card.
There are three signals of ship alarms:
- "Occupational alarm" is one long signal with a loud battle ring for 25-30 s, after which the announcement of "Oblast Alarm" on the overall live broadcast in the forced mode of operation. Anxiety is declared when an emergency occurrence or in a pre-emergency period, when it becomes clear that the accident cannot be avoided. However, this does not mean "leave the ship".
- Anxiety "Man overboard" - three long-lasting signals with a loud combat call 3-4 times. Following this, the public broadcast is given by the voice announcement with the indication of the boat number to the descent. Anxiety applies only to the members of the crew of the vessel. The output of passengers on this alarm on open decks is prohibited.
- "Boat alarm" - seven short and one long signal with a loud battle ring, repeated 3-4 times, and after this announcement by voice on the public broadcast. Served only when the state of the emergency vessel does not leave hope for the success of the struggle for the vitality and the ship must immediately die; Announced only by order of the captain. On the boat alarm, the crew members responsible for the safety of passengers will lead you to the landing site in collective rescue.
As statistics show, the main danger during shipwreck comes from a sinking vessel, which can be carried away with him under the water of people. In addition, with shipwreck, people are dangerous during evacuation from a sinking ship, as well as when they are in water, on the rafts or on boats.
Among the preliminary protection measures, you can advise you to remember the road from your cabins to the rescue funds to the upper deck, since during the disaster to navigate it is very difficult, especially when the ship is smoking and the shy. Preventive measures also include learning instructions on actions in emergency situations, rules for use of rescue means and practical development on the use of rescue.
With the evacuation of people with the disaster of the ship, the danger occurs when refusal of triggers, tipping and blows of rescue tools, improper use, and if necessary, jump into the water from a dying vessel from a high height. During evacuation, you should take with you only the necessary things. Places on rescue means are primarily provided to women, children, elderly people and wounded.
When evacuating from the vessel, it is necessary to wear warm clothes, and from above - a protective suit from waterproof fabric and a life jacket. Go down to the rescue vessel follows trapam or ropes. If circumstances allow, then in rescue means it is necessary to immerse additionally blankets, clothes, emergency radio, drinking water and food reserves. If necessary, jump into the water should be shrinking the nose and mouth with one hand, and the other is tightly kept for the rescue vest.
Once in water, a person is hazardous to drowning, supercooling the body and exhaustion. To slow down the offensive of the hypothermia, while in the water, it is necessary to keep the head as high as possible above the water, while trying to spend the minimum of physical effort to hold itself on the surface of the water. Slow should only be saved to the rescue.
In the open sea, two basic principles should be observed on rescue means: all rescue means hold on together and to be at the place of the death of the vessel, if there is no firm confidence in the possibility of reaching the shore or enter the ship paths.
When on damage or boats, the main danger comes from the supercooling of the body, and with a long stay on them - and from lack of water and food. Therefore, being on a rescue agent, you should first keep the legs with dry and cover the body, strictly riding the water (500-600 ml per day per person, divided into numerous low doses) and there is only an emergency stock. However, in any case, it is necessary to maintain composure and not give in to a panic, otherwise it will only reduce the chances of salvation and speed up death.