Buttercup creeping: description, cultivation rules and application. What does buttercup look like? From leg cramps.
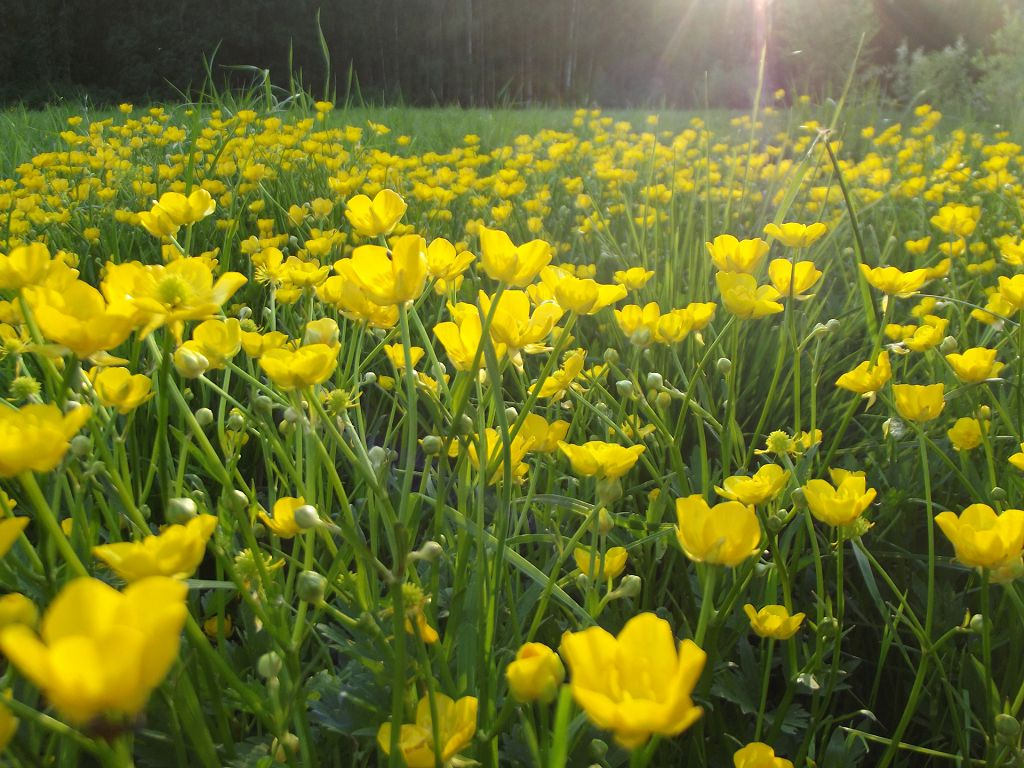
Buttercup - gentle herbaceous plant with amazingly beautiful flowers. Particularly interesting garden molds with large spherical heads. The plant belongs to the Ranunculaceae family. The genus is represented not only decorative species, but also weeds with caustic and poisonous juice. Buttercups are common in temperate and cold climates throughout the Northern Hemisphere. They live in open meadows and fresh water. The scientific name for buttercup, ranunculus, comes from the word for frog. It is given for the ability to grow where amphibians live.
Larger bulbs contain more stored food energy to support a stronger plant with big amount colors. In warm climates, ranunculus can be planted in beds and borders, cut into gardens and containers. They make good companions for other spring flowers such as primroses, pansies and a lark. In cooler climates, ranunculus grows best in pots and planters. This makes it easy to give away your center of flowers and admire them up close. Plant them in pots in the fall for flowers in late winter and early spring.
What does buttercup look like
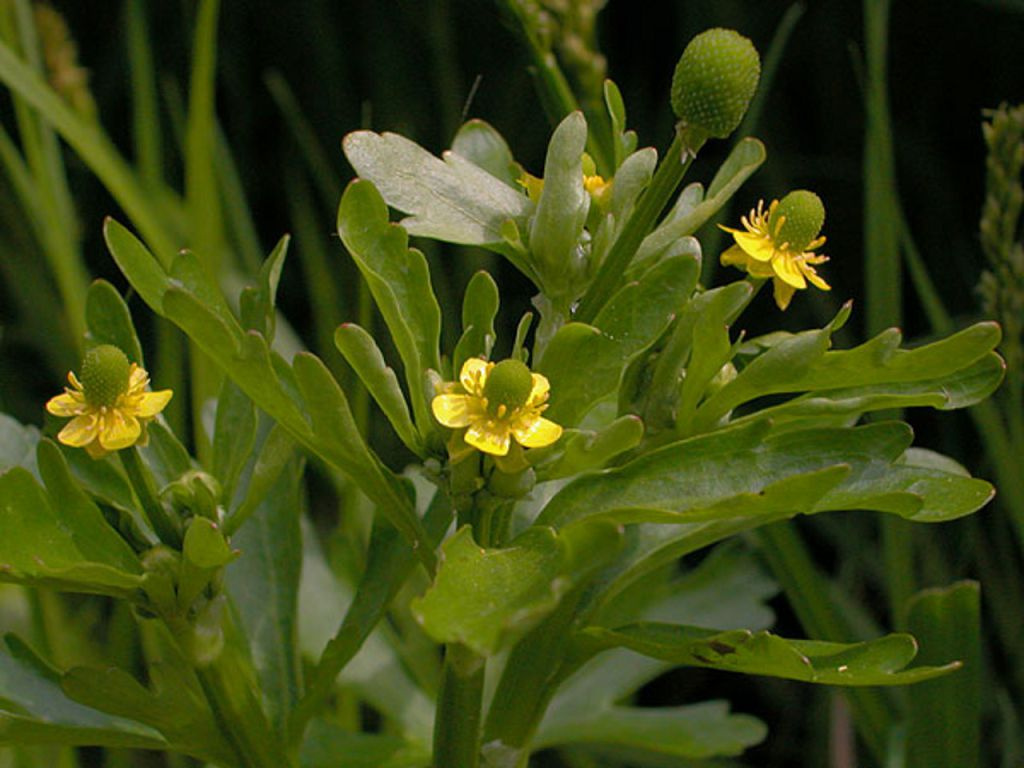
Buttercup is a perennial or annual with straight branched shoots up to 20-100 cm high. It has a fibrous root system, on the processes of which palmate, spider-like tubers are formed. On a thickened ribbed stem is another foliage with whole serrated or dissected plates. It has a bluish-green or dark green color. The leaves do not differ in large sizes, usually the length does not exceed 6 cm.
Loosen the soil in the garden or fill the pot with a coarse, well-drained plant mixture. Set the bulbs 4 apart and 2 deep with the side down. Cover the bulbs with soil and water as needed. Ranunculus are cold weather plants. They do not like warm temperatures and hot sun. For best results, plant your bulbs in light, well-drained soil. Avoid soil that remains damp as this can cause the bulbs to rot.
In warm climates, ranunculus plants form a rather large root ball. When planting bulbs in the garden or in a pot, remember to fill the plants. For long lasting bouquets, ranunculus flowers should be cut open when they begin to show color. Widely grown for cut flowers, lungunus bulbs reliably produce many individual flowers from a single tuber flask. Also called Persian buttercups, they bloom for several weeks. late spring and make lovely cut flowers.
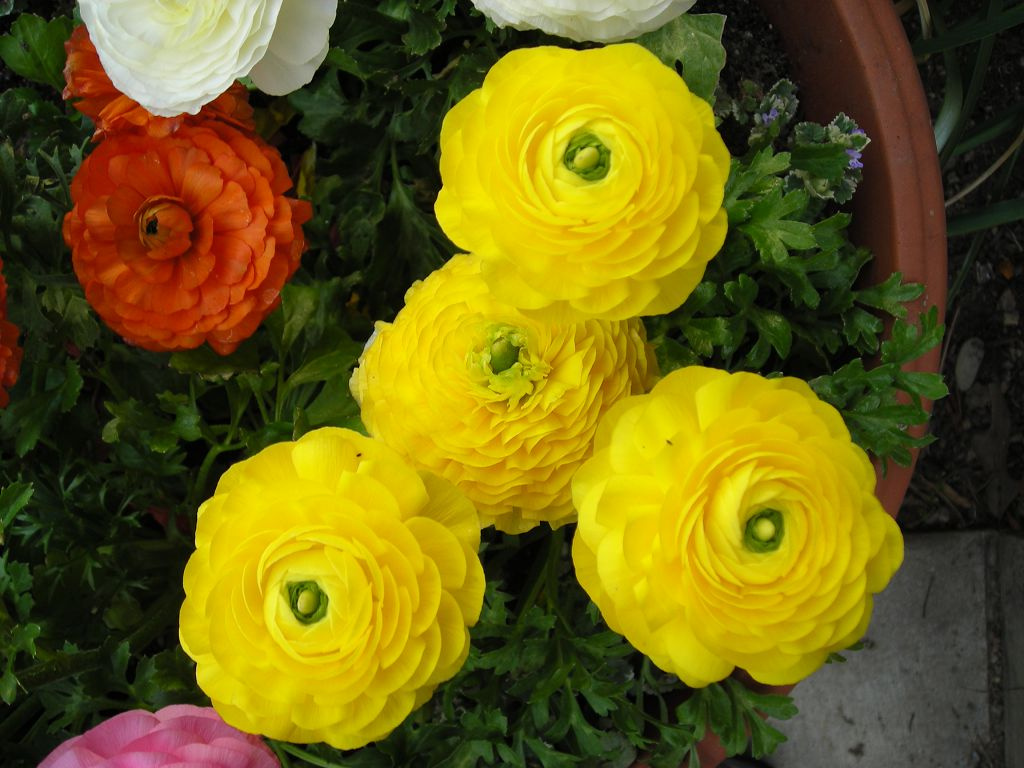
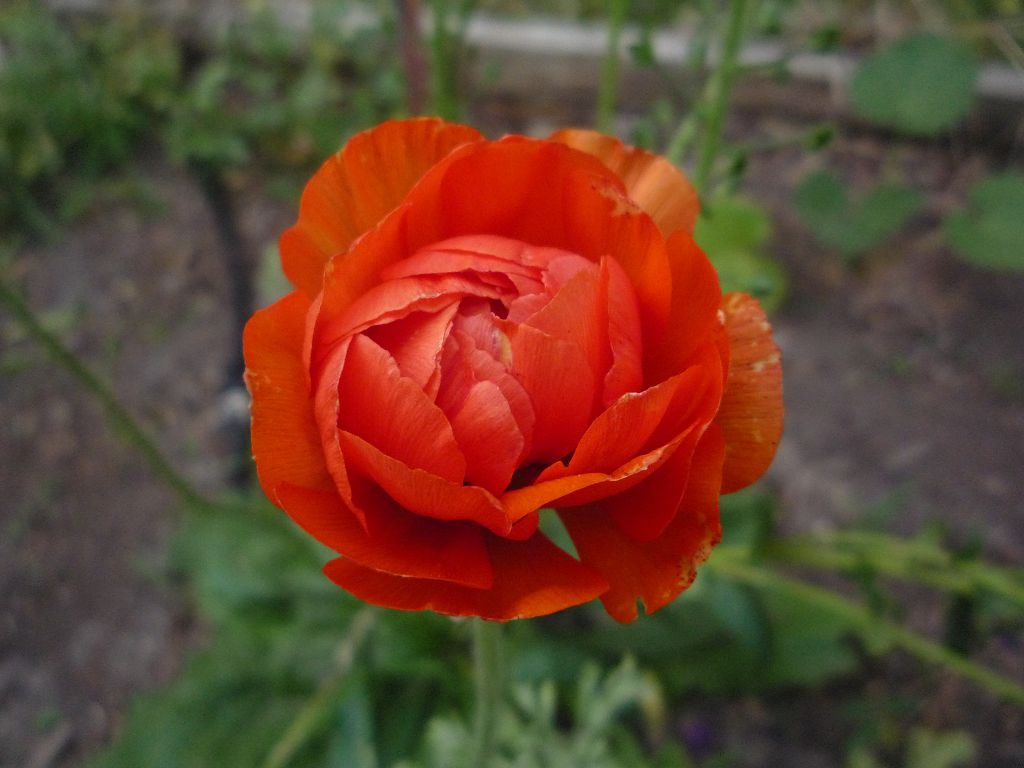
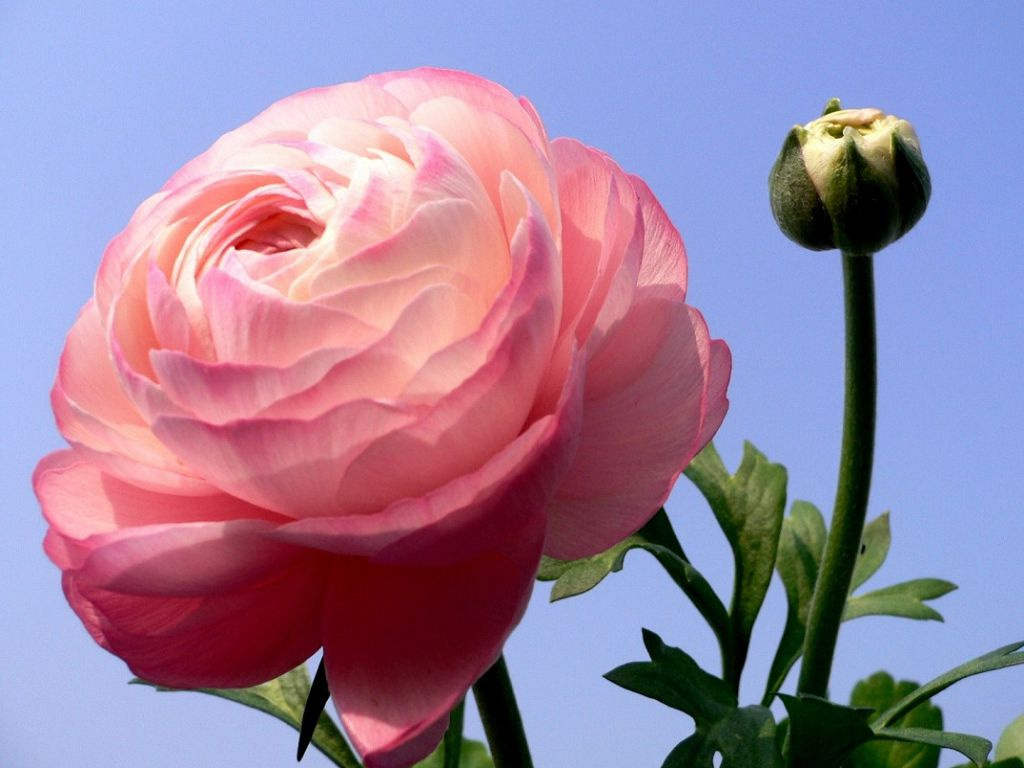
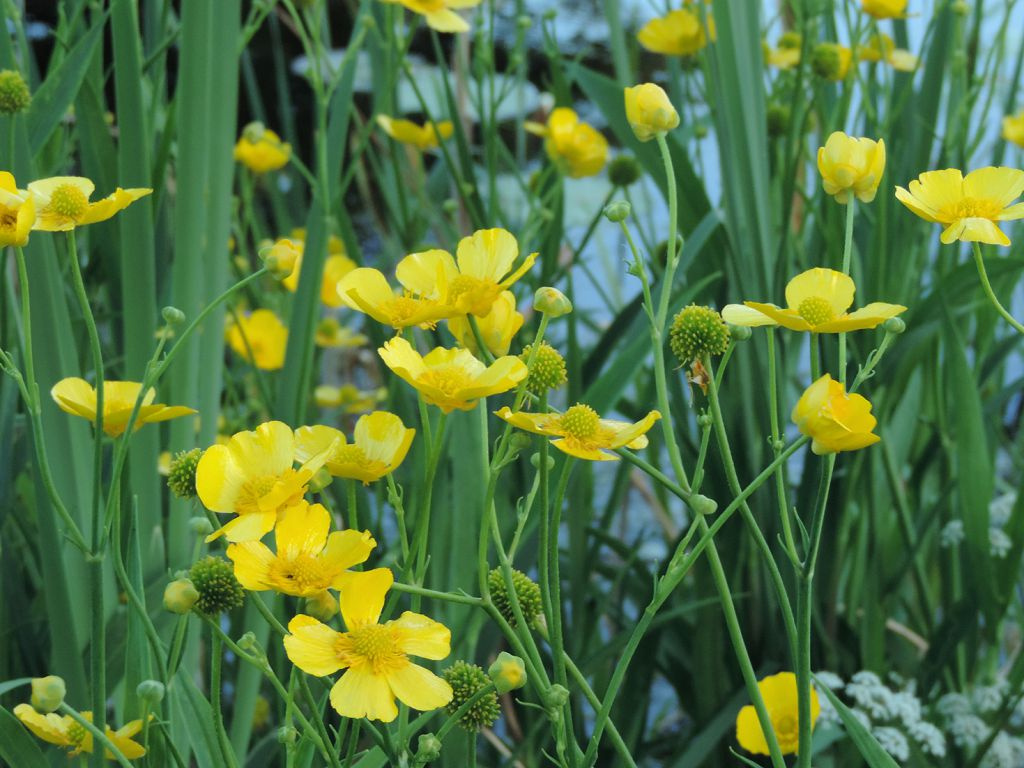
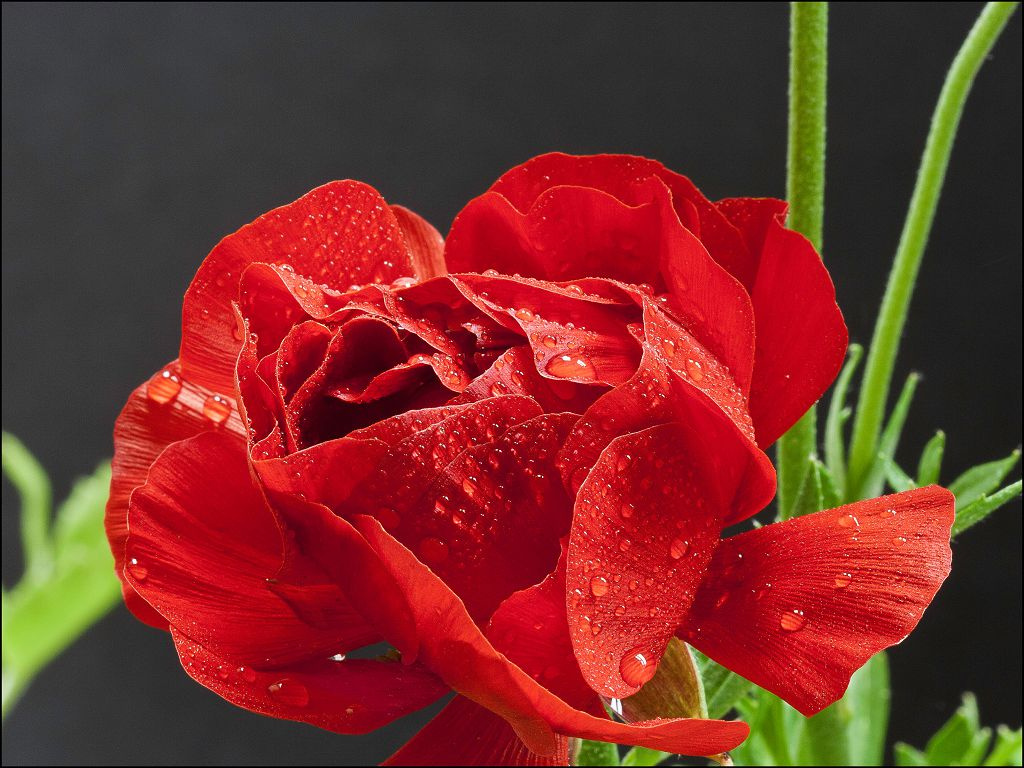
In June-July, on the tops of the stems bloom beautiful flowers. They can be simple or double, similar to flowers of roses and peonies. The number of flower elements is a multiple of 5 (rarely 3). The diameter of the corolla depends on the variety and can be 2-10 cm. The color of the flowers is very diverse (solid or variegated): bright salmon, purple, yellow, orange, cream, white. In the center are many short stamens and pistils. The flowering period lasts about a month. Cut flowers will last at least a week in a vase.
Replace them in early spring as soon as the soil thaw. The double or semicircular flowers look like old-fashioned pink cabbages and last for weeks like a cut flower. Crepe paper flower petals can be red, orange, pink, yellow, white, cream or variegated.
The dark green basal leaves of ranunculus are lobed and hairy. Grow ranunculus in full sun to partial shade. They prefer light soil but will grow in loamy soil. clay soil if she is well emaciated. Department Agriculture.





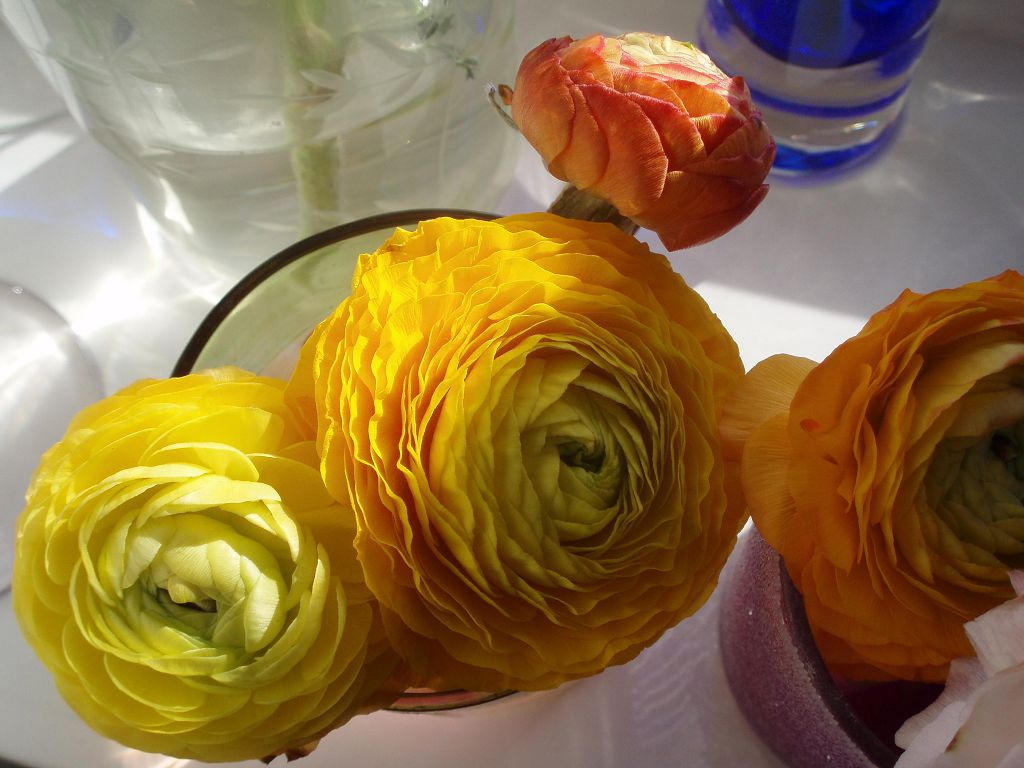









Collection and preparation
Resistance zones 7 up to. Ranunculus grows from prickly bulbs or tubers. Increase your stock by dividing the tubers as they grow and have multiple "eyes" or growing buds. Cut them into smaller sections, ensuring that each section has at least one eye from which new growth can emerge.
Application in traditional medicine
Soak them in water at room temperature for 24 hours before planting. Tubers space about 6 inches apart in groups of three to five bordered with flowers or rows spaced 12 to 18 inches apart in a blooming garden. Do not water until stems appear. Cut off dried flower heads to increase flower production. When foliage dries out after midsummer, hold back water or dig them up and store in a dry area until planting time.
After pollination by insects, complex fruits are formed - multi-nuts. When ripe, they burst on their own, releasing fleecy convex seeds. There are several dozen of them in each fruit.
Attention! Buttercup juice is poisonous. Its name comes from the word "fierce", capable of destroying an animal and a person. It can cause skin irritation and poisoning, so all work is carried out with gloves, and animals and children are not allowed near the flowers.
classic views
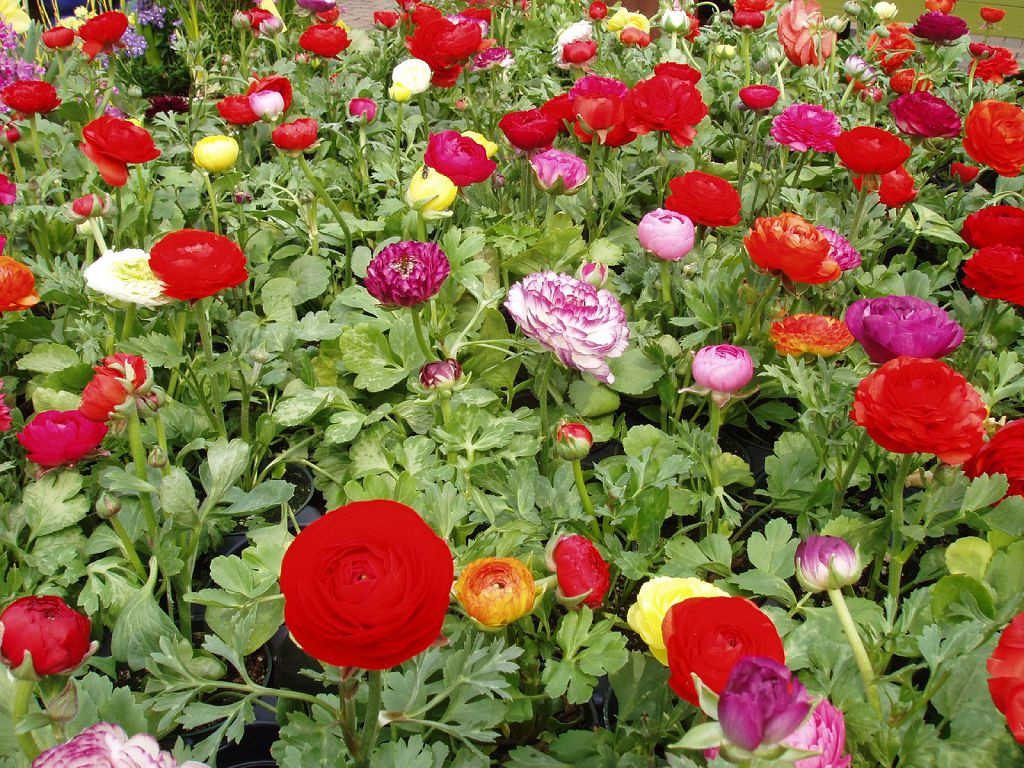
Already today, more than 400 plant species are included in the genus of buttercup, and the list continues to grow.
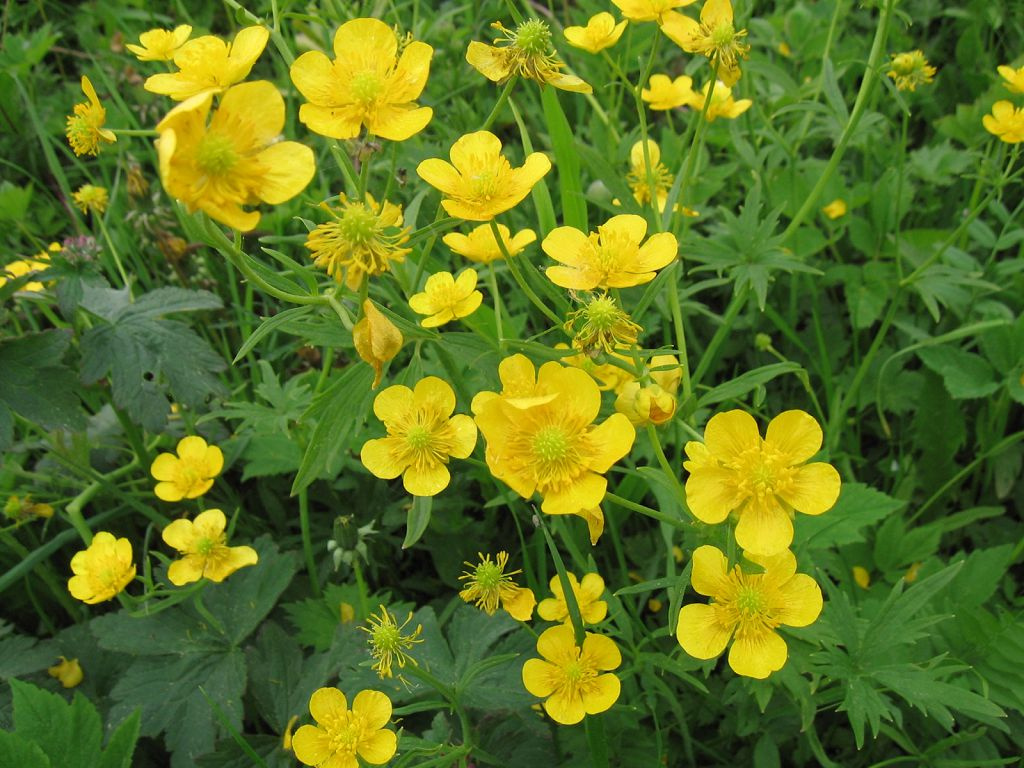
Buttercup caustic (night blindness). Herbaceous perennial with a height of 20-50 cm consists of erect, branched stems. Foliage is located along the entire height of the shoots, but quite rarely. Below it is larger, almost whole. The upper leaflets are strongly dissected, with linear lobes. Simple appear in June yellow flowers with 5 wide petals. In diameter, they do not exceed 2 cm.
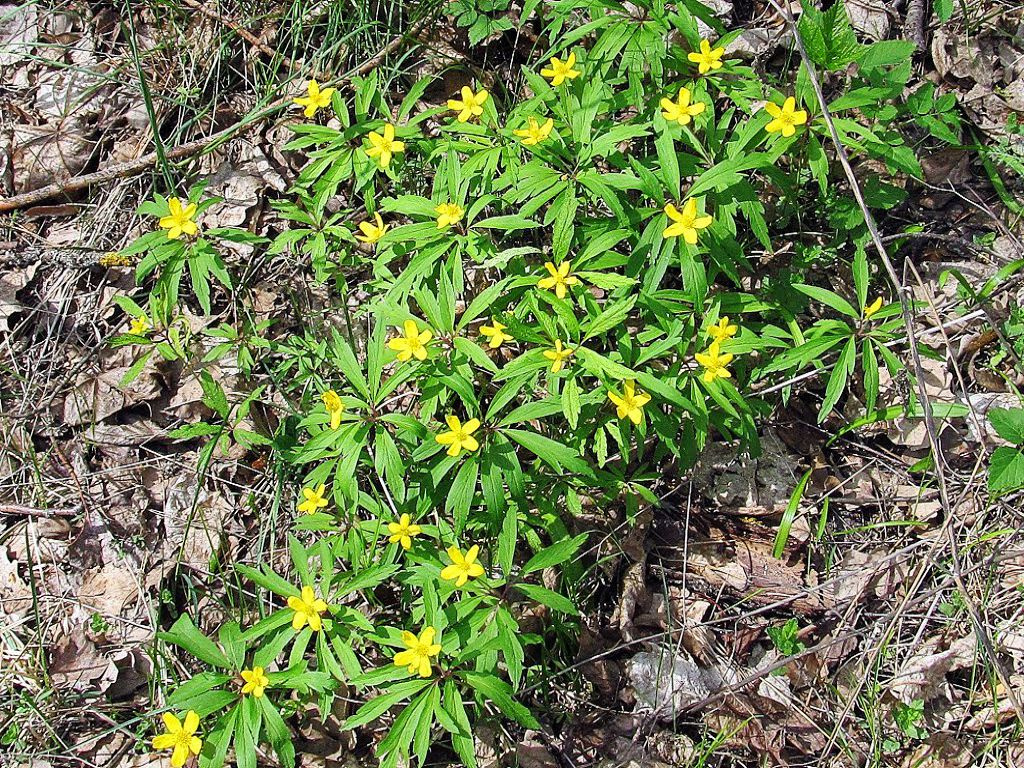

Buttercup golden (yellow). An inhabitant of damp shady meadows grows 40 cm in height. There are almost no leaves on a straight stem. The basal rosette consists of rounded toothed leaves on long petioles. At the top is a linear sessile foliage. Small yellow flowers have a pubescent calyx and a simple bell-shaped corolla. They bloom in April-June.
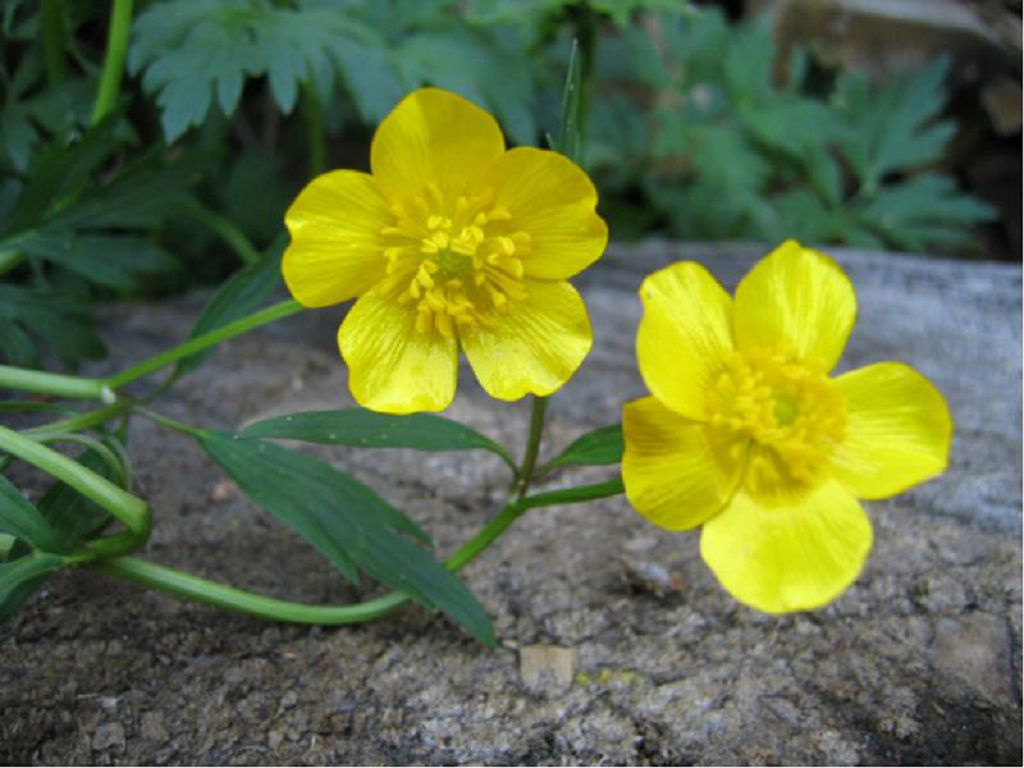

A perennial plant with decumbent shoots 15-40 cm tall, it easily takes root at the nodes upon contact with the soil. The stem is covered with a short pile. Petiolate bright green foliage grows along the entire length. Regular simple yellow flowers consist of 5 petals. They open at the beginning of summer.
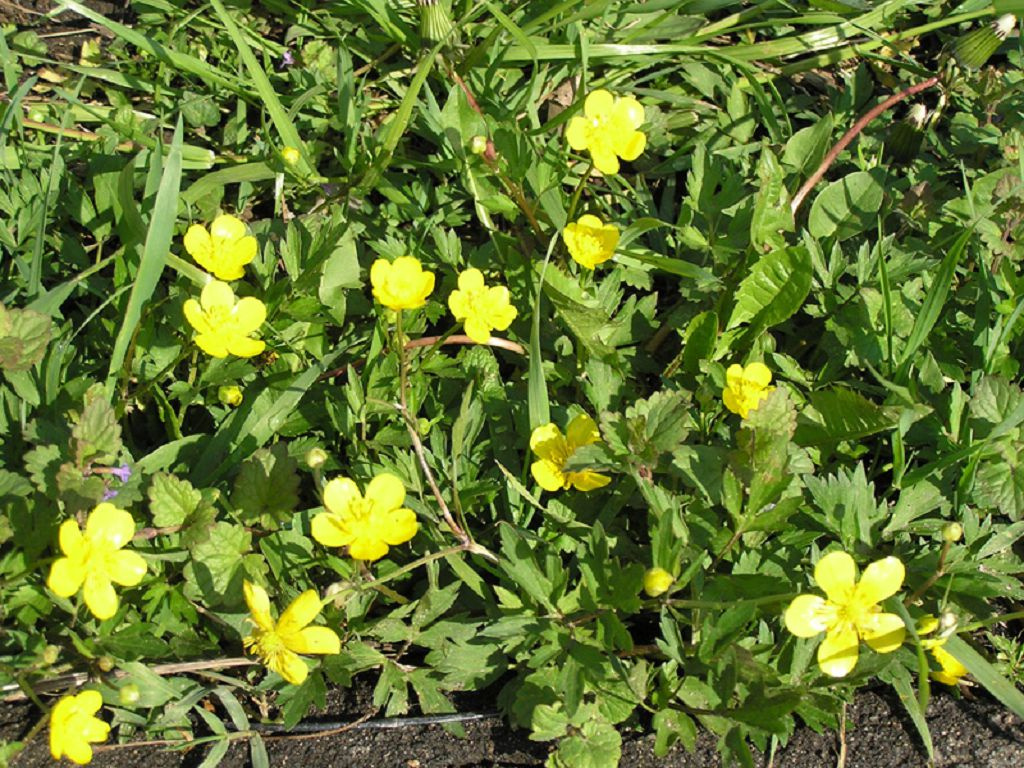

Underage or annual plant with an upright branched stem grows 10-70 cm in height. On the shoots are openwork trifoliate leaves with serrated sides. The ovoid broad lobes are dark green. In May-June, small umbellate inflorescences with small (7-10 mm wide) light yellow flowers appear on the tops of the shoots.
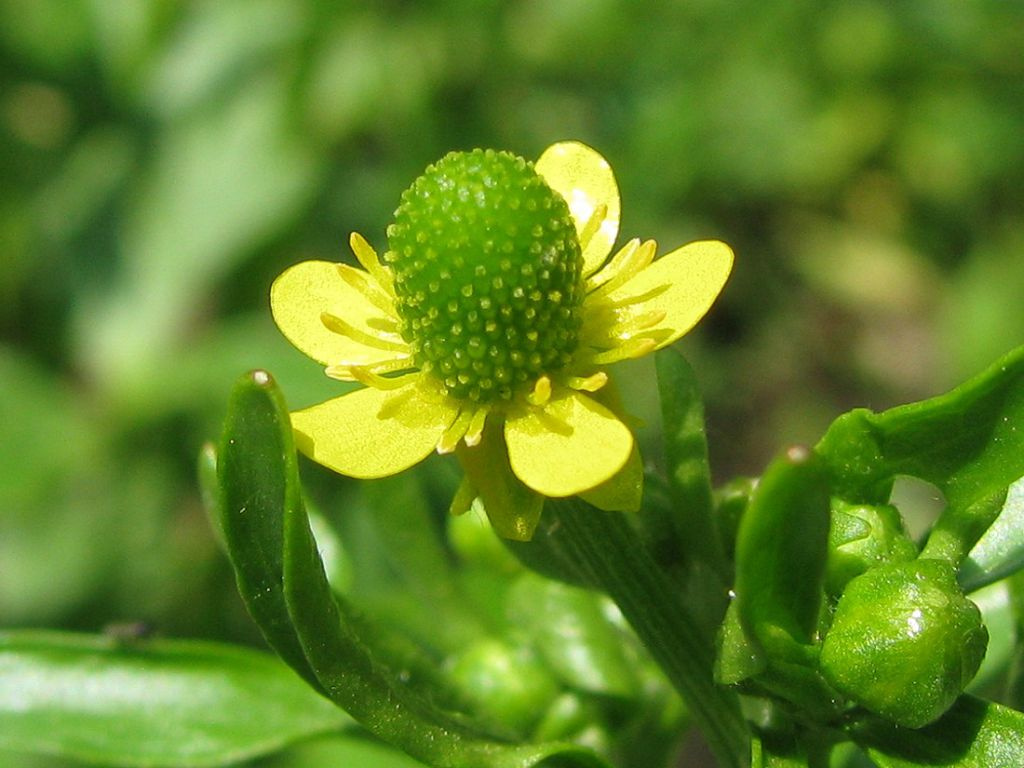

Buttercup Asian (asiaticus). Perennial with a branched erect stem up to 45 cm in height grows bright green pubescent leaves. In July, flowers bloom, located singly or 2-4 pieces in an inflorescence. They have a variety of colors and grow 4-6 cm in diameter.
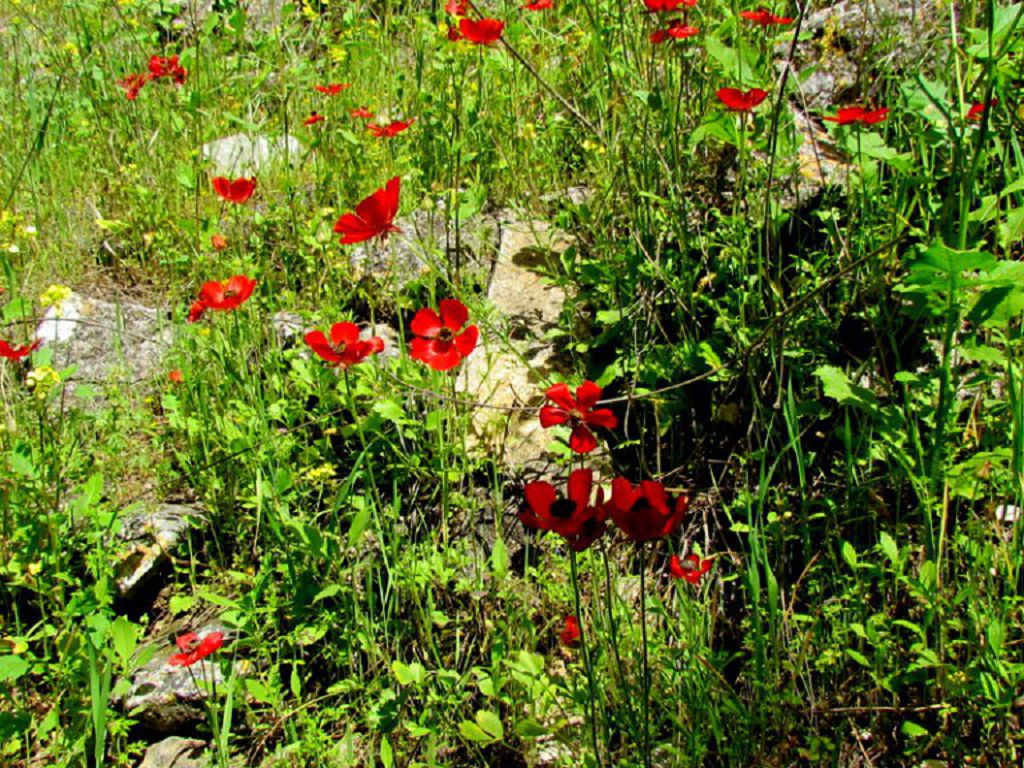

A perennial plant with a bare ascending or erect stem grows 20-50 cm in height. The foliage has a diamond-shaped or oval shape. The lower leaves are attached with long petioles, and the upper ones sit on the stem. Small flowers (0.8-1.2 cm) grow singly and are yellow. The sap of the plant is poisonous and irritates the skin.
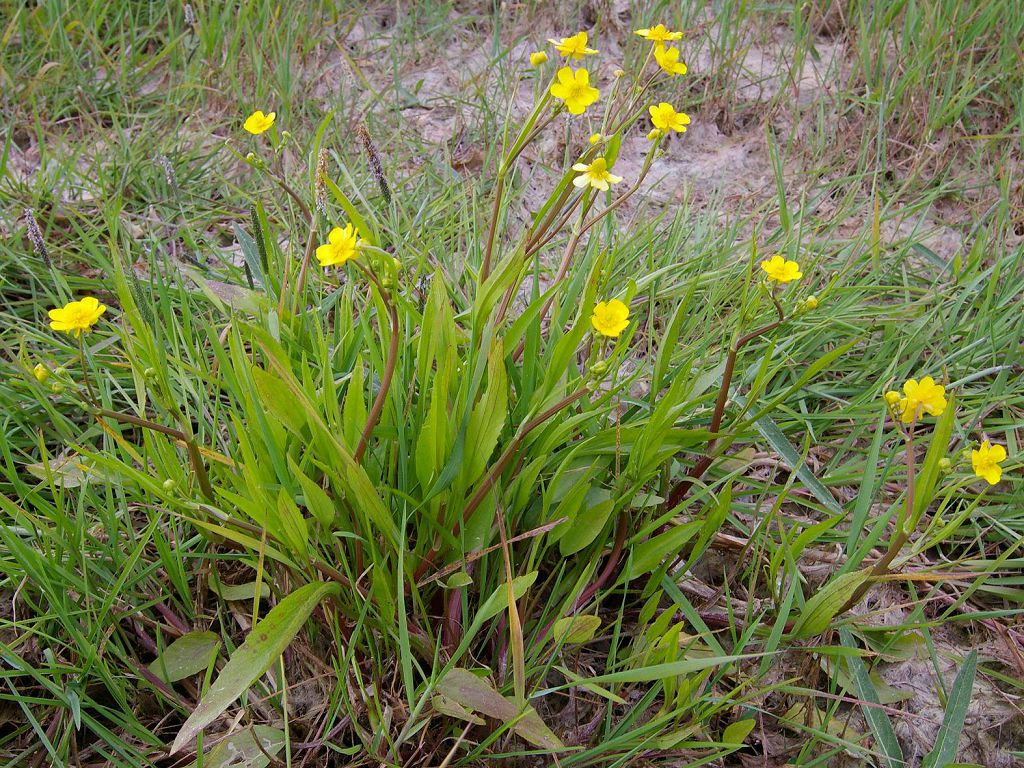

The inhabitant of swampy reservoirs of Australia due to creeping shoots is very modest in size. Its height is about 5-20 cm. On straight petioles, carved leaves look like green snowflakes. The plant looks quite decorative and is often used in the aquarium hobby.
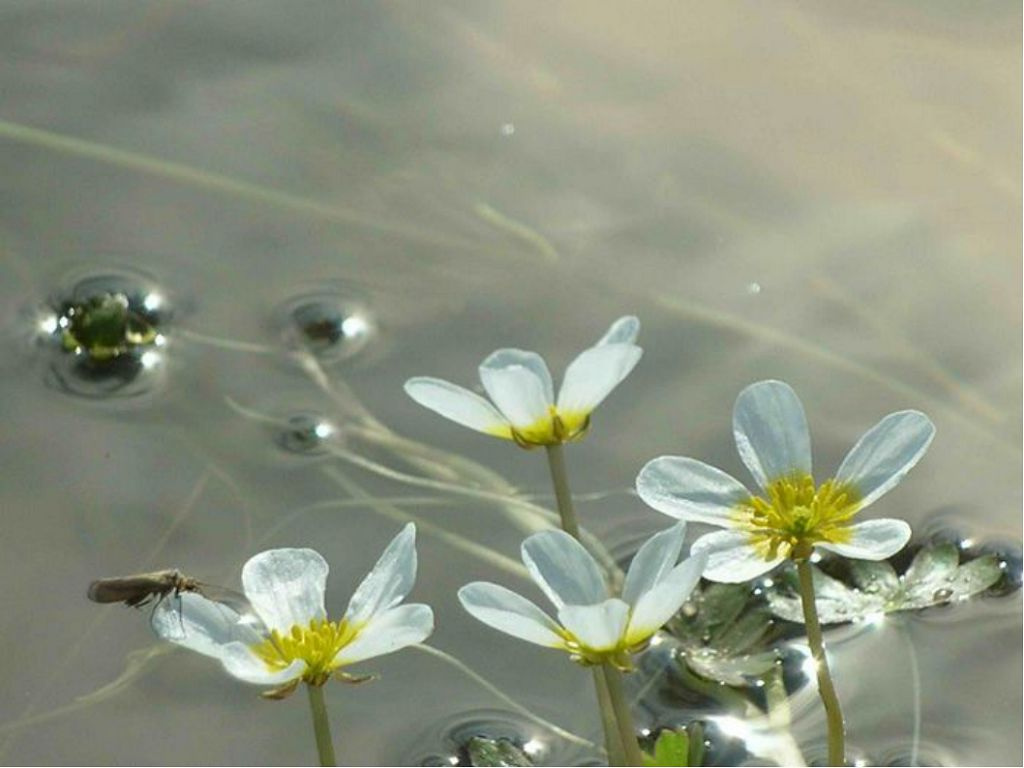

Herbaceous perennial 40-80 cm in height consists of erect, branched stems with a short pile. The palmately dissected foliage is also pubescent. It has elongated lanceolate lobes with incised edges. Simple bright yellow flowers adorn the plant from June to August.
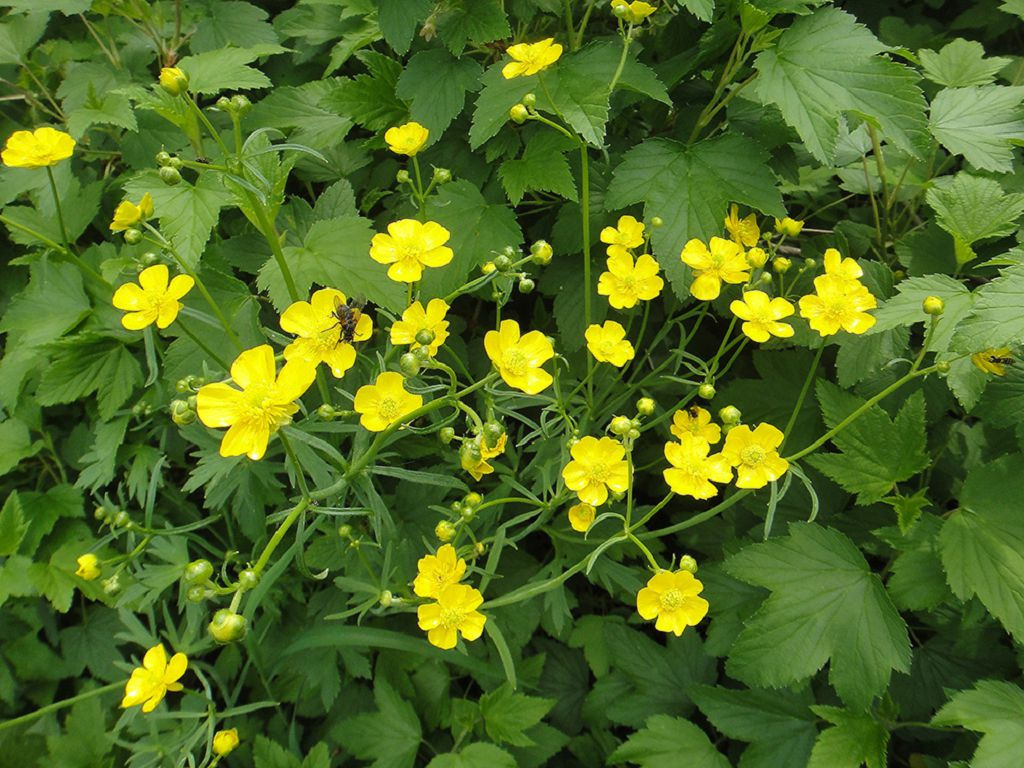

A flowering plant with curved stems 20-30 cm high grows round or heart-shaped leaves 2-3 cm in diameter. The lower ones are located on long petioles, the upper ones are sessile. In early summer, solitary yellow flowers with a hairy receptacle appear.
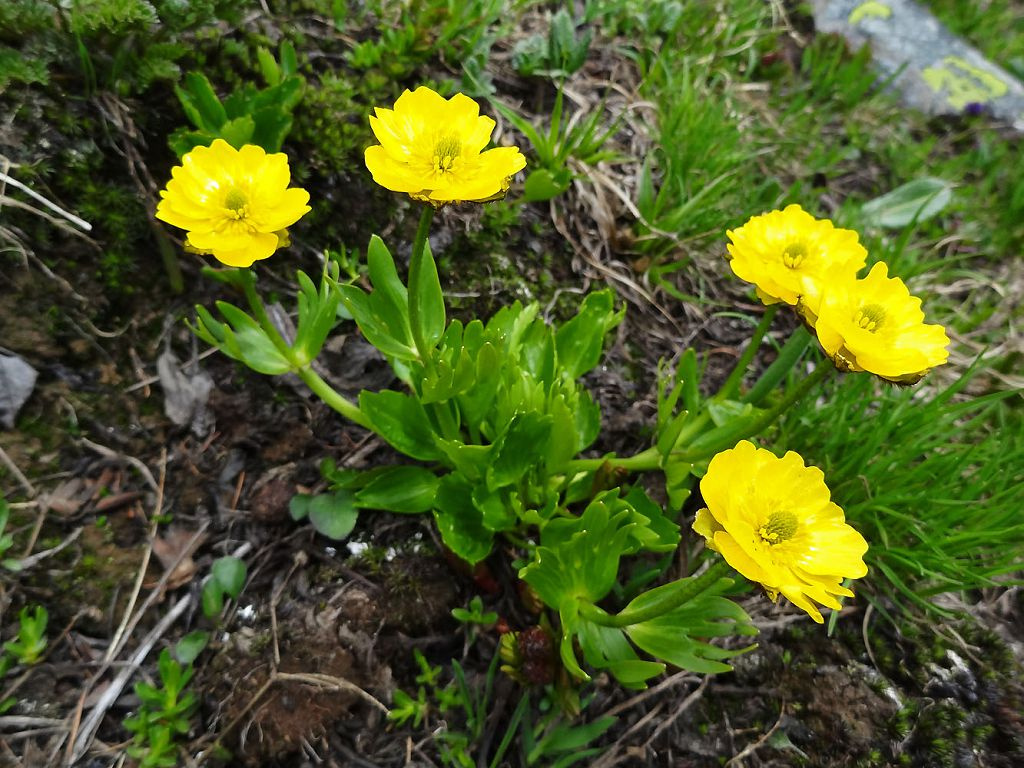

A perennial plant with a straight stem, branched only in the upper part, 30-60 cm high. whole leaves rounded or heart-shaped, located on petioles at the base of the shoot. The upper leaves are palmately dissected, small. Single flowers of a light yellow shade in diameter are 2-3 cm. They bloom in April.
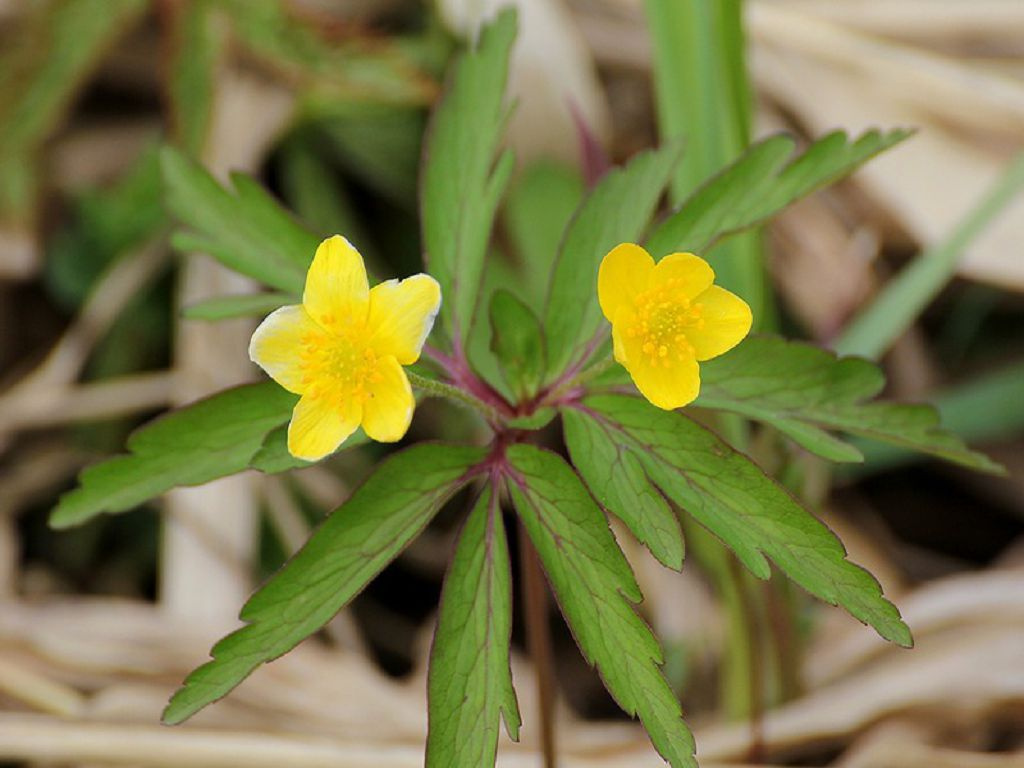

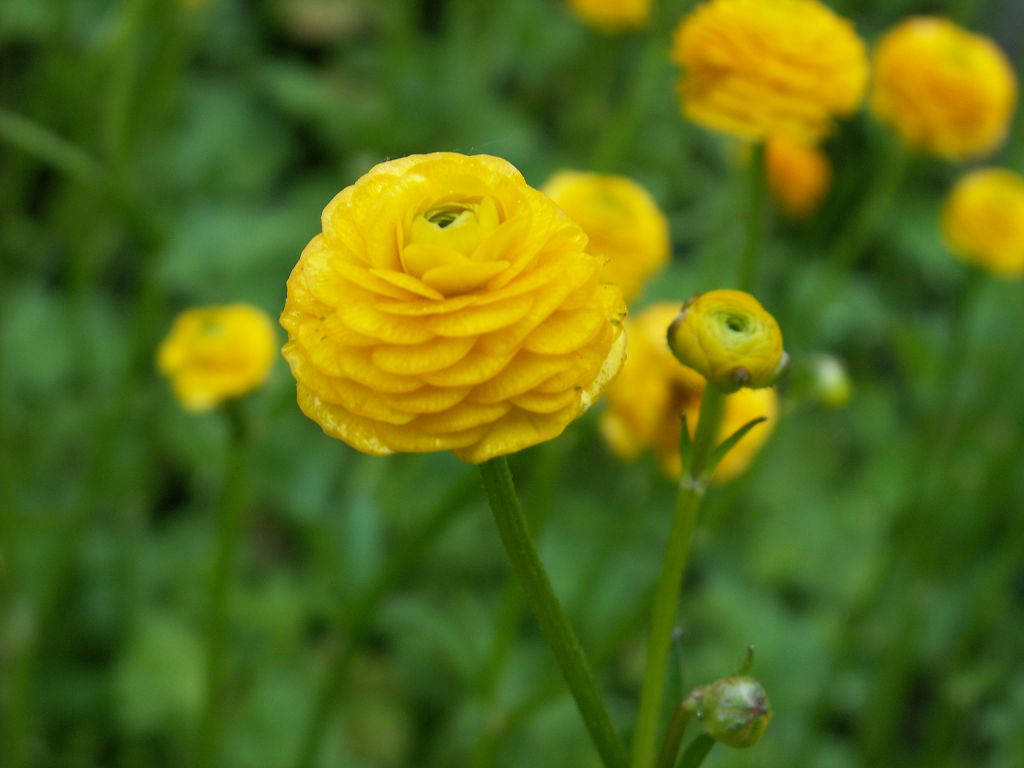
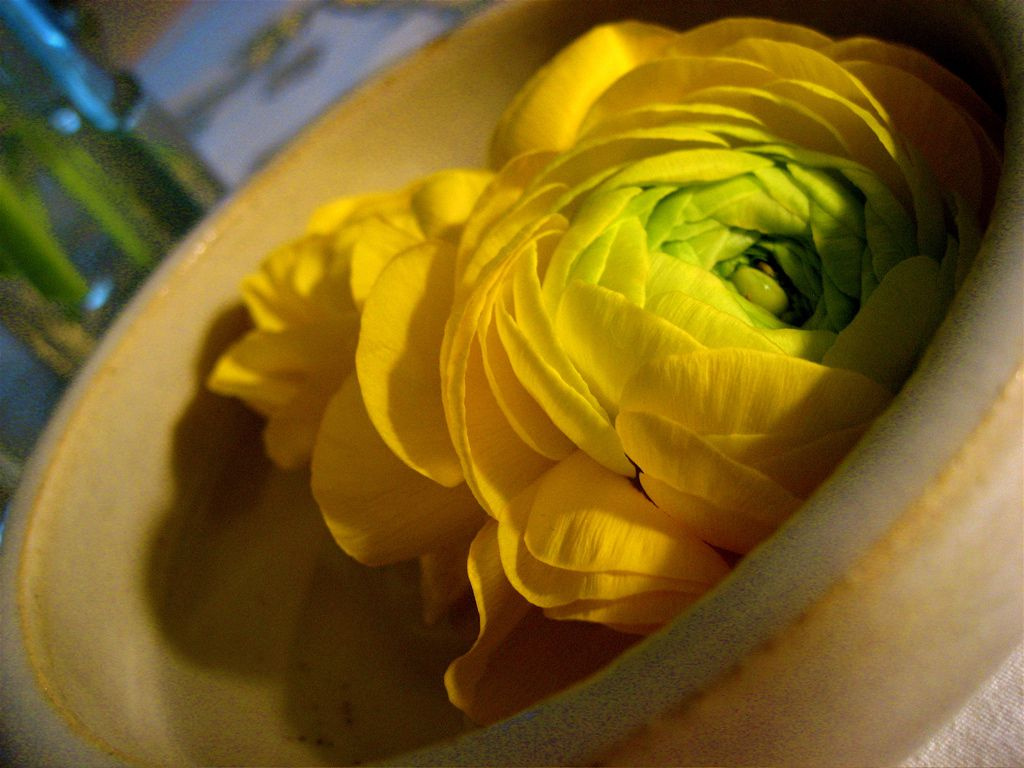
Decorative garden ranunculus
This group of plants is highly decorative and is most common among gardeners. The most interesting varieties:
- Buttercup Masha. A compact plant with a branched stem up to 30-40 cm in height blooms double flowers with white petals and a bright border.
- Buttercup terry (peony). Large plain flowers with closely spaced petals.
- French. Semi-double flowers consist of 2-3 rows of wide petals.
- Persian. Small single or semi-double flowers.
- Chalmoid. It blooms with dense, spherical flowers.
Reproduction methods
Buttercup is propagated by seeds and division of the rhizome. Since most ornamental buttercups do not pass on varietal properties to offspring, purchased seeds are needed for sowing.
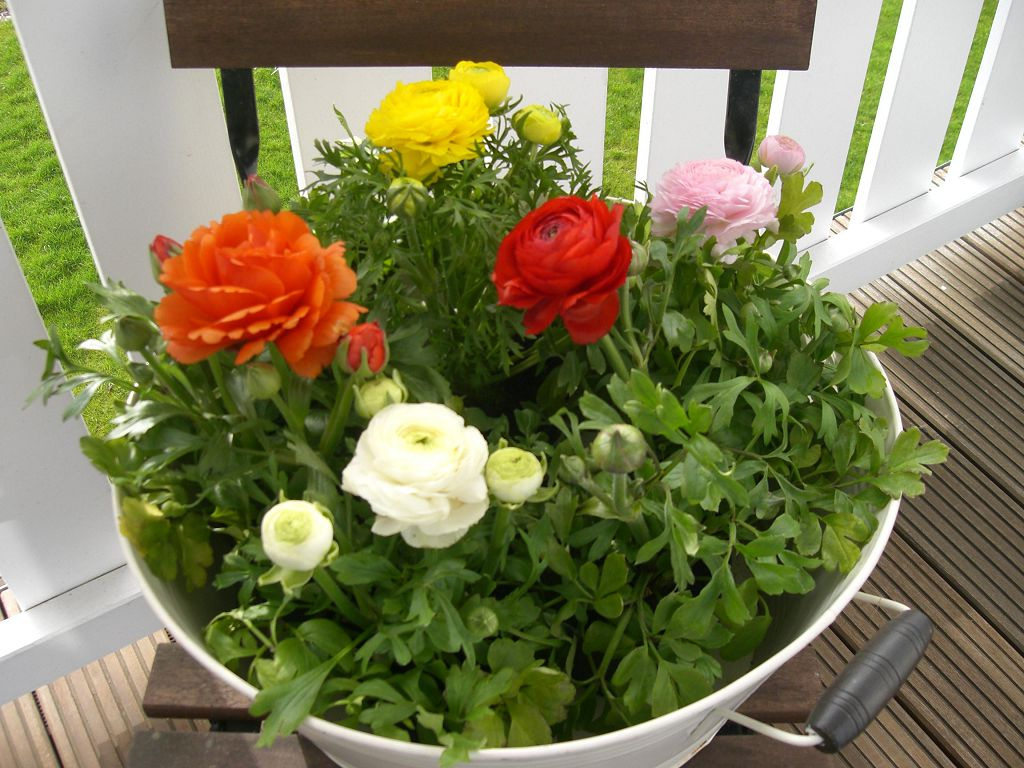

Seedlings are pre-grown. To do this, already in the second half of February, seeds are sown in boxes with sandy-peat or loose garden soil and sprinkled with a thin layer of earth. They are carefully watered and covered with a transparent material. The greenhouse is kept in a bright place with a temperature of + 10 ... + 12 ° C. Shoots appear quite amicably in 15-20 days. From this moment, the shelter is removed and the pot is transferred to a warmer (+ 20 ° C) room. Lighting should be diffused, but quite intense. Phytolamps are used if necessary. When 4-5 leaves appear on the seedlings, it is dived into separate peat pots.
Every year, new tuber growths form on the roots. When dug up in September, they are separated. In a frosty winter, the roots do not survive on the street. A cool room is more suitable for them (+ 19 ... + 21 ° C). In the spring, cones are planted in a flower bed.
Planting and care in the open field
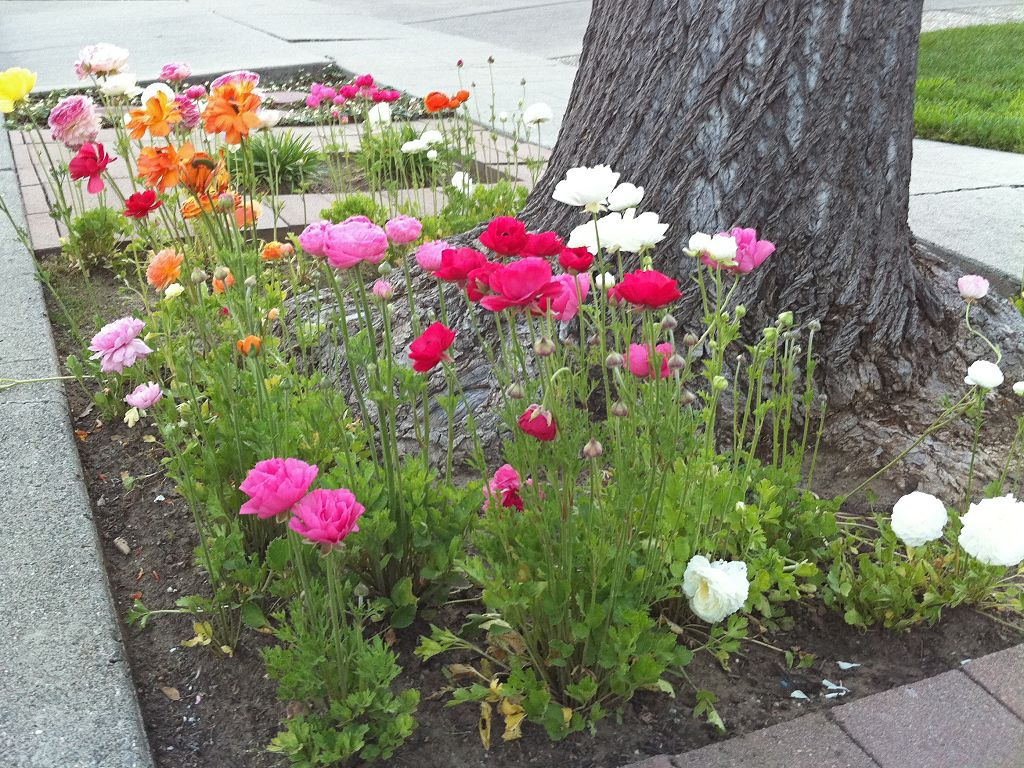
Buttercups are planted in the garden at the end of May, when the likelihood of frost will finally disappear. Pick up sunny or slightly darkened areas with good draft protection. Constant exposure to direct sunlight is undesirable, as flowering will be short-lived and less abundant.
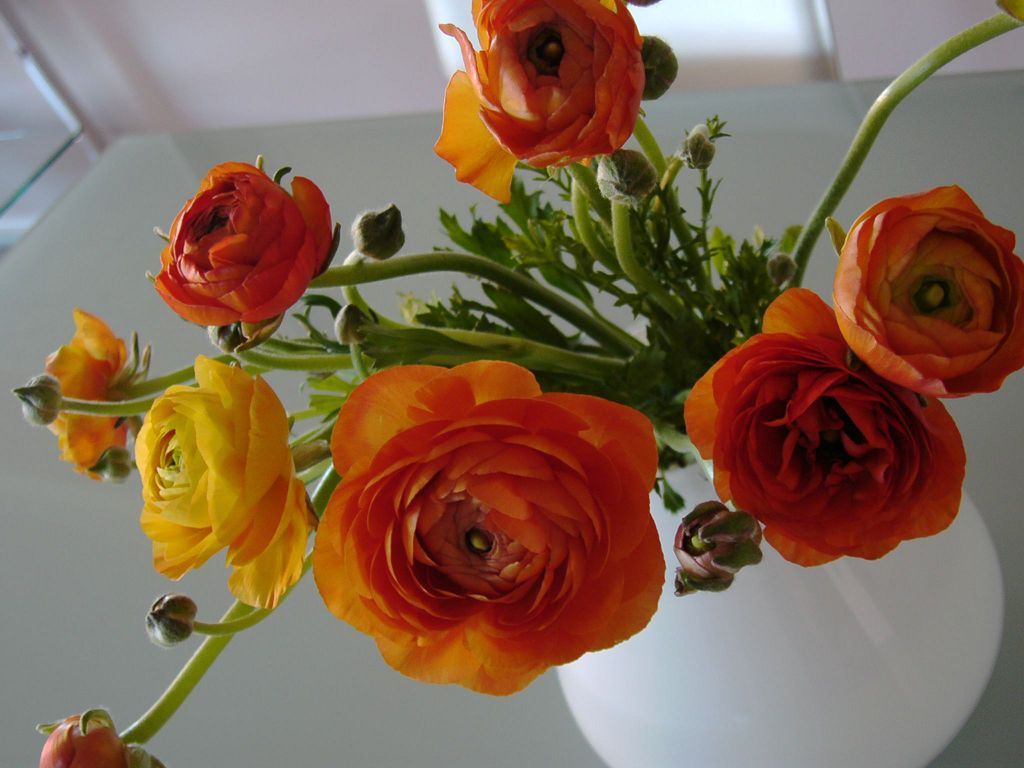

The soil should be neutral or slightly acidic. close occurrence ground water contraindicated. It is best to choose fairly loose, nutritious soils with moderate moisture. The site is dug up in advance and pits are prepared to the depth of the root system. The distance between plants is 15-20 cm. A little sand or vermiculite is poured into the bottom of each hole. Planting is best done with a pot or a large clod of earth flush with the root collar.
Nodules are pre-soaked for 12 hours in warm water with potassium permanganate and growth stimulator. They are planted to a depth of 8-10 cm. The soil is compacted and watered abundantly.
Further care of the plant is not very burdensome. Periodically, weed the beds, remove weeds and break the crust on the surface of the earth.
Watering should be moderate. Only in the absence of precipitation, the flower bed is watered twice a week. From August, plants need to be watered much less frequently so that the tubers ripen and do not rot. In case of prolonged rainy weather, the plantings are covered with a film.

Every 15-20 days the buttercup is fed with mineral complexes. At the beginning of growth, nitrogenous compounds are used, and with the advent of buds, they switch to potassium-phosphorus.
To make the flower bed look neat, wilted flowers should be cut immediately.
Buttercups are quite heat-loving plants, so winter in open ground they can not. In autumn, when the entire ground part begins to dry out, the tubers are dug up. They are dried in a ventilated place and stored in cloth or cake pots.
Buttercup is sick infrequently, mainly with fungal infections that develop with regular flooding of the soil. The first signal is the dropping of even unblown buds and flowers. Also, brown or whitish plaques may appear on the leaves and stems. If a disease is detected, it is necessary to temporarily stop watering and treat with a fungicide.

Beneficial features
Although buttercup is considered poisonous plant, in small quantities it can have a positive effect on the body. It is used in folk and official medicine. The juice contains saponins, fatty oils, tannins, glycosides, ascorbic acid. Taking drugs inside stimulates the production of hemoglobin and stabilizes the work nervous system. Outwardly, fresh leaves and lotions with decoctions and water infusions are used. They help fight joint diseases, gout, lupus, scabies, calluses.
It is very important not to exceed the dosage, so it is better to use pharmaceutical products rather than self-prepared ones. Also, buttercup treatment is contraindicated in pregnant and lactating women, as well as people prone to allergies.
Use in the garden
Garden terry or simple buttercups with large, bright flowers will become wonderful decoration mixed flower bed. Depending on the height, they are used in the foreground or central plan of the flower garden, as well as in rockeries, alpine slide or mixborder. Some species are successfully cultivated in pots, such as houseplants. In the flower garden, buttercup is usually combined with bluebells, cornflowers, hostas, evergreen shrubs.
With scrofula, rheumatism and scabies, buttercup creeping is applied to diseased areas of the skin - tumors and abscesses. The stem is applied to dissolve abscesses or accelerate their maturation. For drinking, 1 teaspoon of dried leaves and flowers is brewed with a glass of boiling water, after the infusion is wrapped and infused for 30 minutes, then filtered and drunk 1 tbsp. spoon three times a day for headaches, epilepsy.
Important! When using buttercup creeping when applying it to the skin, it cannot be used for a long time, since the plant irritates the skin, sometimes leading to tissue necrosis and ulceration.

Buttercup likes shady areas best, but plants can also grow in the sun. But it should be remembered that buttercups bloom in very bright light for a short time. Still plants do not tolerate drafts.
It is best to plant them under a tree that has a wide, but not too dense crown.
Buttercups require loose and soft soil. They do not like sandy or loamy soil. In heavy soils, it is required to pour sand and peat land. It is necessary that the soil absorb moisture during irrigation, but it does not linger in the ground.

Buttercup seeds are sown in containers at home in February and April or by root cuttings in August and September. Mature plants are propagated by division. Propagation by seeds is used quite rarely, as the seeds germinate very poorly.
Proper reproduction of buttercup creeping seeds:
- Sow seeds in containers in late winter and early March.
- Seeds are poured with grooves, and then sprinkled with earth with a layer of 2 cm.
- At this time, they need a low room temperature of + 10-15 ° C.
- Seedling containers are covered with foil.
- After 2-3 weeks, the containers are placed in a warmer room with a temperature of +20 ° C.
Seedlings grown in the house are placed in the ground in the spring, when the soil warms up by 6-8 cm, since buttercups prefer to grow in warmth. This can be done in late April or early May. If there is a risk of frost, then plantings are covered with straw from above. For planting, pits are dug 5 cm deep. The indentation between the pits is 10 cm. Drainage from gravel is placed in them. After planting sprouts grown from seeds.
Tuber planting:
- Before planting, the tubers are placed in water. room temperature at 10 o'clock.
- Swollen tubers are planted in a hole 5 cm deep.
- Tubers need to be placed with their legs down, otherwise they will not germinate.
- After planting, it is advised to water the soil with a small amount of water.
When planting tubers, seedlings will appear in 1.5-2 weeks. The larger the tuber you plant, the more flowers will bloom on this plant. Flowers will bloom in 2.5 months. And by the end of August, fruits ripen - multi-nuts, one multi-nut contains 500 small seeds.

Buttercup is easy to care for, even beginners can grow it:
- Watering. It is necessary to water intensively and regularly, but not overflowing the plants, as their roots may rot. If you still poured too much water, then immediately dig up the buttercups, rinse the roots, treat with a solution of potassium permanganate and leave for 2-3 hours to dry the roots. Then plant it back in the ground. Still plants do not tolerate drought, their rhizomes dry and die. fungicide. Put the tubers in plastic bags, cover with sand or peat soil and place until spring in a cool room with an air temperature of + 5-10 ° C. Or just put it in a box and sprinkle with peat. You can put the boxes in the basement or cellar. Inspect the tubers from time to time to detect any diseases. If diseases are detected, treat diseased areas with brilliant green or colloidal sulfur. If almost the entire root is sick, then destroy it, and pour new peat or sand into the boxes.

Buttercups can be damaged various diseases and pests:
- Blackleg. With it, white spots are visible in young seedlings at the bottom of the stem, which then turn brown and the plants die.
- Root rot. With this disease, plants grow slowly, then turn yellow, and then die. Buttercups should not be planted in soil with fresh manure, so that they do not get sick with root rot.
- Fusarium wilt. When the disease occurs, brown spots are visible on the leaves and stems. The plant develops more slowly, and then dies.
- Powdery mildew. In case of disease, a powdery coating is visible on the leaves and petioles, and then black dots appear.
- Peronosporosis. When diseased, plants lag behind in growth, spots appear on the leaves.
- Rust. With it, fistulas form on the leaves, when they crack, then rust-colored powder begins to pour out of them.
These are tiny worms that grow and develop with an excess of moisture. A plant affected by nematodes may die.
Nematofagin BT is well suited for the destruction of nematodes. It is introduced into the soil to a depth of 15-20 cm before planting seedlings, and if the plant is already planted, then holes are made and the substance is introduced into them. The drug is safe for animals, humans and beneficial insects.
For all these diseases, biological fungicides are used: Baktofit, Fitop, Barrier, Fitosporin, Planzir, Zaslon, Integral, Agat, Trichodermin. They have a good effect on fungal diseases and have low toxicity.
Even a beginner can grow it. The most important thing is to plant it in the right place and water it properly, as it does not like drought and overflow.
More information can be found in the video:


