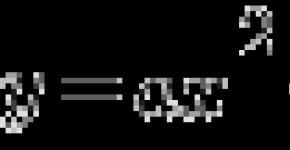How to incline nouns by cases. Declination of nouns in Russian
National names are very widely represented in Russian. They can act as the main and secondary sentences. Using the case of nouns names, speaking and writing can bind these parts of speech with others in the context of the sentence. With case, another category of noun is directly related - his declination. From the correct definition of which, by the way, the spelling correctness written is dependent.
Category of case
Padege names of nouns - such a grammatical category, which indicates the ratio of this part of speech to other words in the proposal. These links may be implemented not only with the help of case forms - help in this prepositions, as well as intonation painting and even the order of words.
In modern Russian, there are only 6 pelvic forms.
Name of case | Issues of the case of nouns names | |
Nominative | ||
Genitive | Who? What? | |
Dative | Who? What? | |
Accusative | Who? What? | |
Instrumental | ||
Prepositional | O Com? About what? |
Once in ancient Russian language there was another, seventh, charting case. But he lost his importance in the development of language culture. Echoes of the charting case remained in the surroundings. Previously, he was comparable to the very famous and indicated the appeal: Father, human. On the modern stage The development of the Russian language is implemented in such colloquial appeals: sing, vash, tan, etc.
The value and shape of the expression of cases. Nominative
In addition to grammatical significance, the case of nouns have a lexical. We will analyze them.
Nominative. This is the main form of the noun. Used in academic literature (vocabulary). In this case, it is always subject to, also the word in it. p. maybe part of faithful.
Example: Roses dismissed on time. Subject roses stands in the nominative case.
Another example: This tree is birch. Subject wood (Named, leaving birch - Named part of the composite name of the fag, stands in it. P.).
Values \u200b\u200bof the genitive case
Genitive. Can bind nouns with various parts speech. So, if the genitive case binds two nouns, then it will mark:
- the substance that means measure: liter kvass;
- affiliation: mine shoesb;
- object any action: boiling water;
- definition relationships: beauty fields.
Parental case applies with a comparative degree of adjectives: stronger (whom?) Bull. With quantitative: thousand (what?) rubles.

As for the verb and verb forms, this case is applied in the following cases:
- indicates a specific object when the transition verb is associated: disposition;
- used after such verbs like be afraid to achievei and DR: to achieve (what?) Permissions.
A genitive case is used when an accurate date is reported. For example: She was born sixth (what?) March thousand nine hundred eighty second.
Values \u200b\u200bof dative and vinitive cases
Other cases of nouns names are not so rich in lexical values \u200b\u200band grammatical connections. Thus, the dating case binds to the verbs and some noun (ungalled). It has a side facility: to help parents (Compare: help around the house - direct object).
The accusative case indicates that we have a direct addition to us: i am writing a poem.

Current and proposed case
The noun in the arterial case will be the following values:
- weapon or method of action: beat (than?) fist (method), beat (than?) hammer (instrument);
- subject acting: wrong (who?) Mom; washed off (than?) rag;
- it is part of the name of the said: she was (by whom?) by a doctor.
The proposed case is special, it is applied from his name. He always requires a pretext. May mean:
- the topic of conversation, thoughts, and so on.: let's talk (about what?) About the work of Goethe; i think about whom?) About an excellent stranger;
- temporary and geographic indicators: meet (when?) last weekend; work (where?) in the cafe.
- used to designate the date, but not complete, but indicating the year: i was born (when?) Thousands of nine hundred and ninety year.

Declination of nouns
To write spelling spectacularly, you need to know not only the case. The declination of nouns has a primary role. In Russian, three types of declination, each of them requires certain expirations. To determine the belonging to one of them, the names of the nouns, the case, the genus you need to know first.
Such nouns as homeland, land, frame, refer to the first decline. They are united by belonging to the female genus and ending -A / -E. Also in these declines got small nouns for men: Vitya, Grandfather, Dad. In addition, they are united by endings -A / -E.
A much extensive group of nouns of male genus type: son-in-law, wolf, sofa. They have a zero ending. These words are given to the second decline. The same group includes nouns medium-sized flexions - well: sea, building, crime.
If you have a noun female genus ending on soft sign (zero ending), it will refer to the third decline: rye, young people, daughter, brooch.
There may be nouns to have an adjective decline, that is, they change on cases of cases like adjective and communion. These include those who have made the transition from these parts of speech into the noun: living room meeting.
To determine which cases of nouns' names are used in the sentence, it is necessary to find the word to which the noun and ask a question.
For example, we define cases and decline in nouns in the sentence: Motorcyclist drove at a flat terrain.
Subject motorcyclist does not apply to any other word because it is major Member Offers, therefore, stands in the nominative case. Determine the declination: the zero ending and male genus indicate that the word is 2 declines. Noun with pretext by terrain Depends on the word ekal. We ask the question: rode (where?) By terrain. This is a question of the proposed case. Locality - female genus, ends on b, Therefore, the third decline.

The declination of the nouns
To determine how ending it is required to write a name noun, genus, the number, the case and the decline to know necessarily. The declination is solid and soft: the word can end on a soft or solid consonant. For example: lamp - solid type; pan - Soft.
We give examples of the decline in the names of the nouns single and pay attention to the end in some forms.
First declination
Solid type | Soft type | ||
Nominative | Provocation |
||
Genitive | Provocations |
||
Dative | Provocations |
||
Accusative | Provoci-Yu |
||
Instrumental | Provochai |
||
Prepositional | About prvokation and |
Attention should be paid to the duty and proposed case. They require graduation. In noun to-formation, on the contrary, in these cases, it should be written ending.
Second declination
Male Rod | Neuter gender |
||||
Solid type | Solid type | Soft type | |||
Nominative | |||||
Genitive | |||||
Dative | |||||
Accusative | |||||
Instrumental | |||||
Prepositional | |||||
Here we pay attention to the proposed case: it requires ending-. If the noun ends on -y / -th, then in this case you need to write-and.
Third declination
We pay attention to the case of the PAID, the duty and the proposed: they require the end-. It should also be remembered that after those hissing in the singular in this decline it is required to write a soft sign. In multiple number He's not needed.
The declination of nouns
We will analyze the case of nouns of the multiple number.
1 declination | 2 declination | 3 declination |
|||
Solid type | Soft type | Male Rod | Neuter gender | ||
Nominative | Pans | ||||
Genitive | Castre | ||||
Dative | Pictures | Pans | |||
Accusative | Pans | ||||
Instrumental | Pictures | Pans | Barracks | ||
Prepositional | About pictures | About saucepan | About barracks | ||
Nouns in the dutiful, cleaner and complained Pades Have identical endings.
End expirations are nouns in a plural. The first can be in all three decons, the second - in some nouns of the second decline: director, Storam, Professor.
To distinguish lexical meanings Nouns, set in the form of a plural, use different endings: sheet,but Leaves (at the tree)and Sheets (at the book).

Such nouns like contracts, elections, engineers, officers, designers It is required to write only with the end. Other flexia is a violation of the norm.
Different noun
In Russian, there is a unique group of nouns. When changing the cases, they have the end of various decline. The group includes those words that end on -th (for example, time, elder), as well as the word way.
Singular | Plural |
|||
Nominative | strive | |||
Genitive | stupid | |||
Dative | stupid | stone | ||
Accusative | strive | |||
Instrumental | strive | strive | ||
Prepositional | oh painting | ohrone | ||
Like noun 3 declosion, these words in the singular, the patent, the duties and the proposed costs require the end.
Unchanging noun
Another special group of nouns - unchangeable. They are not put in the form of a number and case. They always have one form: without kimono (R. p.) - about Kimono. (P. p.); new Kimono. (un.) - bought Kimono. (mn. h.).

How to determine in this case how is the name of the noun grammatically expressed? The number, the case, look according to the word to which it applies. Premes:
1. Pedestrians hurried over the new highway.
2. The new highway is laid.
In the first sentence, we determine the number and case of adjective new (un. h., D. p.). In the second - also by adjective new (MN., NAM.P.).
Unchanging nouns are, as a rule, foreign language words like nominal ( tyro, cafe) and your own ( Baku, Hugo). Also unchangeable comprehensive words (abbreviations). For example: EUM, NPP.
Many of us still have a school bench remember that is referred to. But reproduce all aspects associated with it will be delarious not to everyone. But the knowledge of the rules associated with the declination of names nounswill help not make us spelling errors in the upcoming.
Actually Any independent part of speech (except for adventure and verprices) may vary in their rules. Verbs changing on persons and numbers hideAnd the names of the speech are inclined. What still means that? The declination of words is the ability of nouns, adjective, numerical and communities to change by:
- Childbirth (male, medium, ladies, not counting them. SUN.).
- Numbers (only multiple).
- Pades.
The recognizable Code of Russian Rules Grammar-80 in a different way explains what is called declining. He proposes to define it as a change in the class of peredsems. Which of the definitions closer and what is referred to, everyone is free to choose himself.
Based on the definition of declining in Russian, we need to remember what the case is. They are called grammar formthat binds at least what name noun with the words other parts of speech. The case indicates how specifically consistent with the part of speech.

For a long time, the pelvic system was subject to change. IN old Russian The language has not 6, as in our time, and seven cases. Others called the charitable. Today he is already abolished, and now they are left 6.
- Nominative. Special case, since only it is called directly (who? What?), Other indirect. In the form of them. Pad. Speakers subject to proposals. Another one of his feature: it is the source form for the names of speech.
- Genitive. This form answers any questions? What? So as not to confuse it with other cases, you can apply the auxiliary word No: the cat them. n, (no) cat rod. P.
- Dative. This case is named this way, as it answers the questions to anyone? What? The declination of words will be easier if you substitute the word to give: the cat's cat. P.
- Accusative. A rather controversial form. It has a similar taste for inanimate objects - what? True, in relation to live creatures ask the question of whom? The word blame substituted to the verifier. SUD It will help for you to understand the rules of declination: (blame) Cat wines. P.
- Instrumental. Special case. Answers questions by whom? Than? Certification word for him to create: Cat TV. Pad.
- Prepositional. The form responsible for questions about whom? About what? For easy memorization, we substitute the word to think: about the cat. P.
We remembered the case system, which is studied by Russian. The declination depends on the same from the category of numbers. There are only two of them in our language - the only and multiple. Almost all names nouns have both forms. But, as in any rule, there are exceptions. Some words are used exclusively in a single form. An example of those from which only the only number: the sun (well, it is reasonable, it exists in one instance), milk, foliage, highway (it is an input).
But russian The language is so diverse that it has in his own arsenal words used only in a plural. Example: scissors, pants, glasses, hours, people.

The decline system in the Russian language, as clear, consists of 3 groups. Any of them has its own characteristics. 1st declination has subsequent special features:
- Words calling some kind of male people who have endings or either. Uncle, man, dad, Vanya.
- Nouns names that also have ending and either me. Denotic people and objects of the ladies: Spring, hand, aunt, Anna.
- The same endings (-A / -I) with nouns In general, in other words, they denote the people of both male and ladies at once): Plaks, grinding, sonia, sludge.

- Nouns names that have in the original form zero endings and belonging to the male family: table, stump, ceiling, spouse.
- Words spouse. kind, but ending on or e. Domishko.
- Them. SUD With the endings about either the middle kind: the sky, a stain, the sea, a gun.
This group of nouns is the most special. It includes only the words of the ladies and only with zero ending: mouse, oven, life, yawn.

Need to keep in my head principal ruleRegarding the third decline: when the word ends on one of the hissing sounds, it will certainly be written in a soft symbol (daughter, night, stove). Do not confuse them with noun second declining on a hissing (beam, cloak, tick). They relate to the male race, and therefore do not require writing a soft sign at the end.
Summing up the above, we were able to gather together the declination of nouns. The table shows more and more clearly. Examine it intently.

Now we know that they are referred to as declining and what words belong to each of them. But not the whole lexical composition of our tongue obeys these rules. There are such nouns that have absorbed the end of both the first and second decline. They are called variables.
What are the features of such nouns? The 1st, almost they all end on My: time, name, burden, stirring and others. And the word path also belong to this group.
The 2rs, the rules for the decline in the detachable nouns such that, when changing these words, in all forms, there will be suffix (except I.P. and VP): time, aspiring, seed.
Thirdly, inclining these words, we can see that in parental, the last and proposed cases they took the end and in 3 SKL. And in the hardware appeared ending, as in 2 declination.

Our speech is swift replenished new words of foreign language origin. They do not have forms of decline in Russian and therefore are called the unlock.
- Foreign words that came to us from other languages \u200b\u200bon oh, -e, and - at. Coat, fillet, Sochi, Kangaroo. In all cases, they will have the same shape, therefore it makes sense to decline simply. (Go to the coat, go to the kangaroo, go to Sochi.)
- Surnames ending on Ko, agree. Yurchenko, Zhivago, White. (To be visiting Kozarenko, come to the red.)
- Words formed by abbreviation: USSR, PBX.
With this topic, the correct writing of letters and e at the end of the nouns names is connected. Observing the rules of declination, we were able to identify that the end of E is written in words:
- The first decline (is the exception of the genus. P.): To the river (dat.p.), about mom (PR), on the topic (dat.p.).
- Second decline: about the beam (PP.), about the sea (PP.)
- Third decline: in the steppe (PP), by night (dat.p.)
- First SKL. Used in domestic. Pade: At the river.
- In the words ending on the ie, ya. in planetarium, in stock, about the event.
- Almost closed nouns also write and. On the way, about time.

After reading these simple rules, you will know what is called a declination. It is not necessary to confuse it with the word-byment of other parts of speech, such as, for example, leasing in the verbs.
It must be studied, since our practical literacy depends on theoretical knowledge. From our article we can draw the following conclusions:
- Nouns names change not only by cases, but also by numbers.
- But it is worth remembering that not all words of this part of speech have these categories. Some of them at all can not be inclined (unclear) and do not have one of the numerical forms (only multiple or only).
- Each of the decline has its own characteristics, so it is worth carefully studying them. We led to an example of the declination of nouns (table).
- Personal endings that do not have accents are subject to the sum of certain rules. Depending on the declination and case, the letter will be written either e. Either. This topic is one of the most difficult to study the names of nouns.

Bluboo D1: New video demonstrates capabilities Double Camera We have already told enough about the model D1, but it is time to get acquainted with her double chamber. Today we have video demonstrating possible.

Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few people wondered why he can be needed. Interestingly, he was originally a place for XP.

15 Cancer Symptoms, which women in most cases ignore many signs of cancer similar to the symptoms of other diseases or states, so they are often ignored. Pay attention to your body. If you are noticeable.

15 of the most beautiful wives of millionaires Meet the list of wives of the most successful people World. They are stunning beauties and are often successful in business.

10 early signs dementia dementia is more than a simple memory loss. Explore the following 10 warning Symptoms to recognize the disease on time.

What looks younger: the best haircuts for those for those for 30, 40, 50, 60 girls at 20 years old do not worry about the form and the length of the hairstyle. It seems that youth is designed for experiments on appearance and bold curls. However, there is already a post
Declination of nouns in Russian
The declination is a change in the existence of cases. Depending on the combination of endings that are inherent in one or another nouns, there are three main types of declining them. The noun M.R. belongs to the 1st decline. with zero ending in the initial form, i.e. in I.P. units ( chemist, analysis researcher) and nouns cf. With endings on -about, -E. (substance, field). To the 2nd decline belongs to the words Zh.R., M.R. and the general kind with the endings -but, -I (hypothesis, a drop, operation, junior, starost.).
The nouns of the 1st and 2nd declination have two varieties of the foundation - solid, to which nouns include the final consonant solid (factory, plant., factory; the game, games, game), and soft with finite consonant soft ( writer, writer, writer; song, songs, song, song).
To the 3rd decline of the noun belong to the words Z.R. with zero ending in the initial form, therefore having only soft variety (thaw, night). (In school practice, another numbering of declining types: to the 1st decline in nouns include the fact that in scientific grammar is recognized for the 2nd, and vice versa.)
In addition to these three main types of declining, there is a separate declination of nouns formed from adjectives ( sick, working and etc.). In tab. 14 shows the samples of the main types of nouns and comments on them.
Comment. 1. U. inanimate nouns M.R. The endings and I.P. and V.P. units ( a computer, dance). In animated noun M.R. ( contractor, representative, doctor) Coincide endings in the R.P. and V.P. units ( control, representative, doctor).
First declination
|
Noun male and medium kind on solid and soft consonants |
||||||
|
Singular |
||||||
|
Paide |
Male Rod |
Neuter gender |
Male Rod |
Neuter gender |
||
|
on solid consonant |
on soft consonants |
|||||
|
contractor |
device |
representative |
biopol |
|||
|
a computer |
anniversary |
|||||
|
control |
devices |
representative |
bioplasol |
|||
|
computer |
jubilee. |
|||||
|
contractor |
device |
representative |
biofolu |
|||
|
computer |
jubilee. |
|||||
|
control |
device |
representative |
biopol |
|||
|
a computer |
anniversary |
|||||
|
contricier |
device |
representative |
biopolem. |
|||
|
computer |
jubileem. |
|||||
|
(about) control officer |
(about) device |
(about) representative |
(about) biopol |
|||
|
(about) computer |
(about) jubilee |
|||||
|
Paide |
Plural |
|||||
|
controuting |
devices |
representatives |
bioplasol |
|||
|
computers |
jubilee |
|||||
|
contract soldiers |
devices |
representatives |
biopoles |
|||
|
computers |
jubileev |
|||||
|
contract soldiers |
devices |
representatives |
bioplasia |
|||
|
computers |
jubileeam |
|||||
|
contract soldiers |
devices |
representatives |
bioplasol |
|||
|
computers |
jubilee |
|||||
|
contract soldiers |
devices |
representatives |
bioplasia |
|||
|
computers |
anniversaries |
|||||
|
(about) contract soldiers |
(about) devices |
(about) representatives |
(about) biopoles |
|||
|
(about) computers |
(about) anniversaries |
|||||
|
Noun male genus based on well, h, sh, sh, c and medium kind on -Ith |
||||||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
||||
|
Male Rod |
Neuter gender |
Male Rod |
Neuter gender |
|||
|
doctor |
company |
doctors |
enterprises |
|||
|
dance |
dancing |
|||||
|
doctor |
enterprises |
doctors |
enterprises |
|||
|
dance |
dance |
|||||
|
doctor |
enterprise |
doctors |
enterprises |
|||
|
dance |
dance |
|||||
|
doctor |
company |
doctors |
enterprises |
|||
|
dance |
dancing |
|||||
|
doctor |
enterprise |
doctors |
enterprises |
|||
|
dance |
dancing |
|||||
|
(about) doctor |
(about) enterprise |
(about) doctors |
(about) enterprises |
|||
|
(about) dance |
(about) dance |
|||||
|
Noun male genus type domishko, domysche |
||||||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
||||
|
domishko |
domashi |
|||||
|
domysche |
domysi |
|||||
|
domashka |
domiers |
|||||
|
domysi |
domysch |
|||||
|
domier |
domashka |
|||||
|
doming |
domyshme |
|||||
|
domishko |
domashi |
|||||
|
domysche |
domysi |
|||||
|
domasho |
domashki |
|||||
|
domashchi |
domyshmi |
|||||
|
(about) domishke |
about Domashki |
|||||
|
(about) domysche |
(about) domyshi |
|||||
2. Some inanimate nouns M.R. may have in R.P. units Not only ending -but (-I), but also -U. (yu). For example, variant endings can receive:
- a) real nouns when the amount of something is indicated ( ton sugar — sahara, a lot of snow — snow) or the absence of some amount (nor gram Sahara — sahara, not a drop of soup - soup); This especially applies to material nouns with diminitious suffixes ( take the Medsk to the sugar);
- b) abstract nouns in the same cases ( how many noise — shumma; neither scream — scream, neither noise — shumma);
- c) words included in sustainable combinations (without year week, not to laugh). End -U., -Yu In general, characteristic of conversational speech: And this marina root — highly is ... It has a bouquet color ... Holie's crimson. Her OT cancer drink ... (E. Evtushenko); Knocked you S. sust This teaching — here and wind the white light (V. Shukshin).
3. Noun M.R. Basis on j., c., sh, sh In the T.P. units may have a shock end - (doctor) And unstable -eat (comradist).
4. Noun M.R. With the basis of c. In the T.P. have percussion end - (end) And unstable -eat (. Plain), in R.P. MN.ch. have percussion end -One (ends) And unstable -Ev (dance).
5. Noun SR.R. With the basis of c. in I.P. etc. units have when stroking at the end, respectively -about (ring) I. - (ring), not at the end -E. (the sun) I. -eat (sun.).
6. Some inanimate nouns M.R. In p.p. units With a pretext in when specifying on finding inside something and with the pretext on the When specifying to find on the surface of something may end -U. (-yu) (in the forest, in the rank, on the shore). End -U. (-yu) Always drums.
Note. To the most common noun M.R., having in pp units End -U. (-yu) (They are only about 200), belong: shore, board (ship), forest, bridge, port, row, garden,angle (in the corner of the room, on the corner of the street), cupboard (in the closet, on the wardrobe). In the presence of endings options, -U. In some words (" vacation — on vacation, in the workshop - in tseshu., in the cold — on cold) The first is neutral, the second is spoken.
7. Noun M.R. With the basis of -y. (sanatorium) in p.p. units have ending -and (in a sanatorium, about Genius).
8. Noun M.R. on the g., to, h. in I.P. MN.ch. ends on -and (mechanic, mechanics).
A number of noun M.R. in I.P. MN.ch. has shock endings but (-I): Side — boca, address — addresses, director — director. To the most common nouns that are consistently obtained in I.P. MN.ch. ending -but (-I) relate: address, shore, side, camp, master, number, order, island, passport, a train, professor, tom, color. There are cases of oscillations in the choice of variant endings: years — of the year, inspectors — inspector, spotlights — chapel, sectors — sectors, fiction — locksmith, tokari. — tokary, popoli — poplar., tractors — tractor, yakori. — anchor. In the presence of oscillations in use - (-and) — but (-I) The latter are more peculiar to household or professional speech. At the same time, do not mix the variables that differ in values: images (artistic and literary) and image (icons), teachers (ideological leaders) and teachers (teachers), flowers (plants) and colors (color), etc.
9. Separate nouns have non-standard forms I.P. MN.: brother — brothers, englishman — british, kitty — kittens, human — people, child — children.
10. Some groups of nouns M.R. in R.P. MN.ch. have the form I.P. units (without end). Such groups are: 1) individual names of persons by national affiliation buryat, georgian,lezgin, turk, gypsy; but arabs,mongols.); 2) Separate names of people related to military service ( hussar, partisan, soldier; but captains, majorov); 3) the individual names of the units of measurement when specifying their number ( ampere, watt, volt, hertz, oh., x-ray).
In the case of oscillations of forms with zero graduation and s --s, the first characteristic of the conversational speech, and the last - strictly literary language (hectare, -s; apricot, -One).
Second declination
|
Nouns for women, male and common sort of end -but (-I) |
|||||
|
Paide |
Basic samples |
Nouns on -and I and with the foundation on the g, k, x, c, w, h, their, u |
|||
|
Singular |
|||||
|
star man starost. |
fable |
company disco |
bird junior |
||
|
stars men starosts |
basni. |
companies disco |
birds yunoi |
||
|
star men staroste |
basne |
companies disco |
bird junior |
||
|
star. men starosta |
bassanya |
company disco |
bird youth |
||
|
star man starostora |
basney |
company disco |
bird junior |
||
|
(about) star (about) men (about) staroste |
(about) basne |
(about) companies (about) disco |
(about) bird (about) junior |
||
|
Plural |
|||||
|
stars men starosts |
basni. |
companies disco |
birds yunoi |
||
|
star men. starost. |
bassen |
companies discos |
birds junior |
||
|
stars men. old builders |
basnyam |
companies disco |
birds junior |
||
|
stars men. starost. |
basni. |
companies disco |
birds junior |
||
|
stars men old builders |
basnia |
companies disco |
birds junior |
||
|
(about) stars (about) men (about) old buildings |
(about) basnya |
(about) companies (about) disco |
(about) birds (about) junior |
||
Comment. Nouns in the " units Various endings -Oh (-to her) I. -Oy (-hy.) (hand, bird —hero., poultry). Recent forms are usually in verse.
Third declination
|
Declination of the nouns of the female - |
||||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
||
|
model |
night |
models |
night |
|
|
models |
night |
models |
night |
|
|
models |
night |
models |
night |
|
|
model |
night |
models |
night |
|
|
model |
at night |
models |
nights |
|
|
(about) models |
(about) night |
(about) models |
(about) night |
|
Comment (all types of declination).
1. In invisible nouns of all kinds coincide endings in I.P. and V.P. MN.ch. ( computers, stars, disco, devices, bioplasol, night). In inanimate noun M.R. and J.R. Coincide endings in R.P. and V.P. MN.ch. ( contract soldiers, representatives, doctors; boys; birds).
2. When used after the transition verbs of the perfect species of nouns in the form not V.P., A R.P. It is indicated for the use of not the whole subject (product), but only its parts: buy sugar (all) - sahara (some part); take candies (everything) - candies (Some of them).
3. When declining the nouns, there are alternations of sounds. The most common one includes: a) alternation of vowel with zero sound: about (e.) — zero ( forehead - forehead, lBU, forehead; Lode - Ice., ice, ice); e - zero ( pepper - Pepper, pERSU, pepper; Guy - Guy, guy, man); Zero - O. (e.) (window - windows, glass - Stalkov); zero - E. (ring - Rings, heart - Hearts, friends of friends, earth - Land, village - villages); b) alternation of consonant with consonants ( sUK - SUCHYA, friends - friends).
Nouns having pelvic endings characteristic of different types Declination is called variables. These include 10 noun CP.R. on the -My (burden, time, udder, banner, name, flame, tribe, seed, stirrup and top) and noun M.R. wayhaving in R.P., DP. and pp units End of nouns of the 3rd declination -and (no time, to the banner, in flame; on my way), and in the like. - Nouns M.R. Type ship, sable (time, banner; way). Nouns on -My in R.P., DP, etc. and pp in units additionally get suffix - (-) (banner — on the banner, on signs), nouns seed, stirrup in R.P. MN.ch. - Suffix. - man (seeds). Samples of declining such nouns are shown in Table. 17.
Nezernaya Types of Declination of Nouns
|
Nouns medium typebanner |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
banner |
banner |
|
|
banners |
banners |
|
|
banners |
banners |
|
|
banner |
banner |
|
|
banner |
banners |
|
|
(about) banners |
(about) banners |
|
|
Nouns male rhodationway |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
way |
path |
|
|
path |
path |
|
|
path |
paths |
|
|
way |
path |
|
|
way |
paths |
|
|
(about) path |
(about) ways |
|
|
russian , alien |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
russian, alien |
russians, aliens |
|
|
russian, alienna |
russians, aliens |
|
|
russian, alien |
russian, alien |
|
|
russian, alienna |
russians, aliens |
|
|
russian, alien |
russians, aliens |
|
|
(about) russian(OB) alien |
(about) russians(OB) inoplans. |
|
|
Nouns female typemother anddaughter |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
mother, daughter |
mother, daughter |
|
|
mother, daughter |
mother, daughters |
|
|
mother, daughter |
mothers, daughters |
|
|
mother, daughter |
mother, daughters |
|
|
mother, daughter |
mother, daughters (-) |
|
|
(about) mother, daughter |
(about) mothers, daughters |
|
|
Noun male genus typewolf, fox |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
volconok, fox. |
volchata, lisyata |
|
|
volconka, lessinka |
volchat, lisyat |
|
|
wolf., fox |
volchatam, lisatam |
|
|
volconka, lessinka |
volchat, lisyat |
|
|
volconkom, fisy |
volchatami, lishta |
|
|
(about) volcchonka, fisy |
(about) volchatas, lisata |
|
|
Nouns typehalf an hour |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
|
|
half an hour |
||
|
half an hour |
||
|
picky |
||
|
half an hour |
||
|
half-one |
||
|
(about) half |
||
|
Nouns, having the endings of adjectives and communities |
||
|
Male Rod |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
new Russian, russian-speaking |
new Russians, russian speakers |
|
|
new Russian, russian-speaking |
new Russians, russian-speaking |
|
|
new Russian, russian-speaking |
new Russian, russian-speaking |
|
|
As I.P. or R.P. |
||
|
new Russian, russian-speaking |
new Russians, russian-speaking |
|
|
(about) new Russian, (about) russian-speaking |
(about) new Russians, (about) russian-speaking |
|
|
Neuter gender |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
predicate, subject |
taken, subject |
|
|
taken, subject |
taken, subject |
|
|
taken, subject to |
takem, subject to |
|
|
predicate, subject |
taken, subject |
|
|
takem, subject to |
taken, subject |
|
|
(about) baudeem, (about) subject |
(about) taken, (about) subject |
|
|
Feminine gender |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
comma, servant |
commas, servants |
|
|
comma, servant |
commas, servants |
|
|
comma, servant |
comma, servant |
|
|
comma, servant |
commas, servants |
|
|
comma, servant |
commas, serving |
|
|
(about) comma, (about) servant |
(about) commas, (about) servants |
|
|
Declination of the names-in. and-Ev |
||
|
Paide |
Singular |
Plural |
|
Yudin., Andreev |
Yudina, Andreevy. |
|
|
Yudina, Andreeva |
Judines, Andreev |
|
|
Yudeu, Andreev |
Yudina, Andreyev |
|
|
Yudina, Andreeva |
Judines, Andreev |
|
|
Yudina, Andreyev |
Yudy, Andreevy |
|
|
(about) Yudine(OB) Andreev |
(about) Judines(OB) Andreev |
|
Oh, this is a decline ... When studying the name of the noun, it is this topic that makes it necessary to break the head to remember all the unstressed endings in all sorts of cases and numbers. How to determine the declination of nouns names? Table and examples will facilitate the task! Let's try to figure out and become more literate!
What is declining?
The declination of the noun (table of examples is given in the text) is a change in the word case and its number. Consider examples in the table.
The table of decline in the names of nouns by cases shows that all names of the nouns are distributed to groups depending on which endings they acquire in the form of a case. Accordingly, all words related to one elephant will have the same set of expirations. Able to determine decline, you can avoid mistakes in writing the endings of nouns in weak position, in other words - not under the emphasis.
How many decons can be a noun?
The table of decline in the names of the existence of cases, shown in the previous section, showed that any words of the same declination in the form of the same case will be the same endings. It presents the three most common types of leaning our language. But he is known, very rich, and simple rules It does not exist. In addition to the three presented, there are other types of decosals.

So, what types of decosals exist? The most common is the first, second and third decline.
A separate group make up words that end on -Ith: Intention, crime, coordination, etc.
Next group - words ending on -and I: Mania, Natalia, Waist, Session, Commission, etc.
There is a small group of words ending on -My, which are also inclined in a certain way: time, tribe, etc. Such words are called differential nouns (they will be devoted to a separate item). Diagrable are also considered to be such words as the path and child.
And finally, there are also such words that cannot be changed in neither cases, nor in numbers, and in all forms they look "the same. These are the unlock, or immutable, nouns names: Kangaroo, Kiwi and others.
Why do you need to be able to determine the declination?
How to determine the decline in the noun, the table will tell us a little later. But it often sounds the question of what to do for? Why remember all these cases, endings, many "special" words you need to remember? But for what. Take for example the word "path": I go on the path, or i'm walking along the path? How to be? What letter to choose? But another word: "Winter". It is also a female kind with the end-and-. We put in the same case: (who? What?) - winter. And we already know that all the words of one declination acquire the same ending when changing. So you need to write like this: i am going by (to whom; to what) tropinka. The question is resolved!
How to determine the declination of the noun? The table and examples in the following items will help not be mistaken in this fairly simple question!

Nouns 1 decline
These are words of female and male genus, in which there are endings in the initial form -but or -I (Recall that the initial form for the name of the noun is a nominative case and the only number).
Words of the female kind with such endings in Russian is a lot of: Mom, Masha, Pajamas, Apartment, work, daughter and many, many others. The words of the male race are smaller, but they are and are very common: Dad, grandfather, Vasya, Peter and other male names.
The nouns table of 1 decline compares the words with a shock and unstressed ending to show that all the words of this decline in the case will be similar.
Nouns 2 declines
These are words of male genus having (it is not expressed in the letter in the nominative case, but "appears" in other forms) and the middle kind with the end -o, -e:the raft, horse, lake, sea, field, etc. The table names for nouns 2 declines will show which endings are acquired by words when changing the case.
As you can see, there are different endings in the divergent. And difficulties can cause only the forms of the proposed case with an unstressed ending, so it should be remembered that in this form you need to write - e..

Nouns 3 declinations
These are words of female genus having a zero ending. All of them ends on a soft sign: mouse, brooch, area, passion, and so on. Let's see which endings acquire these words in different forms.
Very easy to remember: in the forms of the parent, dative and proposed case, these words acquire the end - and.
Nouns on -y, -i
The word "desire" is the middle kind, but it is impossible to attribute it to 2 declusions; The word "mantle" is a female kind, but does not change as words 1 decline. The nouns of the nouns of the nouns on the case will show the difference in the end.
As can be seen from the table, the words on -Ith differ from the words of 2 decline only in the proposed case, and the words on -and I From words of 1 decline - in the duty and proposed.
To remember the words ending on YeahIn all forms behave like words 1 decline. Therefore, for example, the forms of one name Natalia and Natalia will be inclined in different ways: (give) Natalia, Natalia, (speak) about Natalia, about Natalia.
Table of exposure of nouns names
Summarizing said table paddy endings Words related to different decisions.
| Paide | -1 Skl- | -2 Skl- | -3 Skl- | -Ith | -and I |
| I.P. | paw, bullet | __ -o, -e. house, dish | |||
| R.P. | paws, bullets | houses, dishes | |||
| D.P. | lap, bullet | house, dish | |||
| V.P. | paw, Pullet | __ - / -E. house, dish | |||
| T.P. | -You / --y peta, bullets | - / -M. house, dish | majesty | ||
| P.P. | about the paw, about the pool | about the house, about dish | about greatness |
Let's hope that no one will make it difficult to choose the desired ending and determination of the nucleation names in Russian. The table explained everything in detail.
It should be noted that -Ith and -and I You can not allocate as a separate morphum, the end. In this case, it is just the letters to which the word ends. Such words are the topic of another article.

The declination of nouns in the plural (table here, in general, without need) very rarely cause difficulties, since letters are mostly clearly audible. In the dutiful, cleaner and proposed case, in the plural, all three declines of the end will be the same. We offer independently drawn away any words in a plural and make sure that.
Different noun
Different words among the nouns of the Russian language are a bit. Why are they spreadless? Because they cannot be attributed to some one decline, in different cases they "behave" in different ways. These are words ending on -My (There are only about ten), the words "path" and "child". Let's look at the features of the declination of the names of the rustic in Russian (table) - those words that are considered variables.
| I.P. | stirrup | way | child |
| R.P. | storm | put-I. | dit-yat-and |
| D.P. | storm | put-I. | dit-yat-and |
| V.P. | stirrup | way | child |
| T.P. | storm | pUT-EM | dit-yat |
| P.P. | about storm and | about Poot and | oh diet-yat-and |
As you can see, the word "child" is inclined in a completely special way. The word "path" in the parent, dating and proposed case "behaves", as the word 3 of declination, and in the hardware - as a word of 2 decline. Well, the words ending on -MyIn indirect cases, suffix acquire -En-.
These words need to remember not to make a mistake in choosing the desired ending.
Unclear words
Basically, these are borrowed words - come from other languages. They may designate the names of animals, plants, dishes, as well as the names or surnames of people, names of items. Having come to our language, such words retained the feature not to change their shape, falling into a sentence. In whatever case or the number should have to put such a word, it will sound equally.
- I pour me coffee - I admire the morning coffee - we are talking about coffee.
- This is my kakada - I do not have a cockatoo - let me feed the cockatoo - remember Cockada.
- Roman Dumas - dedicated to Dumas - writes about Duma.
Including such words in the proposal is incorrect and illiterate. Everyone knows the phrase-joke "I sit in Kine on a first row with a trap in the tooth." We will not be like a hero of this joke! The inclined words need to be used correctly, and the unlocks are not needed at all.

Let's summarize
Determining the decay of nouns names (table above) is not a completely complex process that will help avoid errors when writing. Let's try to summarize all of the above.
Major decline in Russian three, but there are still special words ending on -and I and - ie, And somewhat differential words. Words are distributed in three main groups depending on the genus and ending in the nominative case.
All words of one declination in have similar endings. They can be learned so as not wrong. And it is possible to do differently: instead of words with an unstressed ending, to substitute any word of the same decline, but the emphasis falls to the end. The letter in the end of these words will be the same!
Words on -and Iand -Ith Not included in three main groups, because they change according to cases and numbers in a special way, and they need to be remembered.
Also remember the small group of differential words. Their end set does not coincide with any of the above declosion, so they require special attention.
Well, finally, the unclear words: they do not change, in any context they are neither. Inclined in the proposal such words as cinema, coat, coffee, purse, kangaroo, - Sign of low literacy and common culture.

We hope that the article turned out to be useful and helped to figure out such a difficult topic as the declination of the noun. The table and examples were understandable, and therefore the choice of the right ending is no longer difficult.
Be competent!
Good afternoon, dear student! Today we will talk about typical mistakes that are committing foreigners who study Russian. One of these errors is confusion in the end when the nouns are declining. But before we proceed to the analysis of errors, I want to remind you that in Russian all nouns are divided into 3 types of decline. Declination is a change in nouns by numbers and cases. In Russian, the genus is divided into 3 types: female, male and medium genus. In previous articles, I also spoke about common genderwhich also causes doubts from foreigners. In order to correctly draw the name noun by cases, it is necessary to determine the genus and the type of declination. In Russian, only 3 types of declination and they include nouns of the following kind:
1 Declusion End Example
Female Rod -a, - I Akula / Earth - A Shark / A Ground
Male Rod -a, - I uncle / Grandfather - An Uncle / A Grandpa
2 ending ending example
Middle Rod -o, -e Saddle / Sea - A Saddle / The Sea
Male genus Zero Bull / Angle - A Bull / A Corner
3 ending ending example
Female genus Zero branch / smooth - A Branch / A Smooth Surface
To correctly draw a noun, you must first define the genus, look at the end in the nominative case (this is the form that is given in the dictionary), the only number and thus determine the declination, for example, from our plate you can see that the word "land" of the female First, in this word, the ending is, and we know that the endings are usually in Russian relate to the female genus. In the nominative case, the singular this word It remains in the form of "earth". Accordingly, the ending -A / is a female genus and refers to 1 decline.
And now let's see how nouns 1 decline in cases change and what graduations acquires the word in a particular case. We have only 6 cases to remember them it was easier, imagine such an offer:
ANDvan Rkilled D.rova, INarvara T.opit Ptank - Ivan Is Chopping Wood, Varvara Is Heating An Oven.
Please pay attention to the first letters of each word in this sentence, they begin with the same letters that there are cases in Russian and to be easier for you to remember, invented such fun russian sentence, and below our cases:
ANDmeaning
Reasy
D.astana
INrelative
T.vorious
Predemeted
In Russian, each case has its own question in order to make it easier to be blocked by words, but I believe that a foreigner needs to know them, especially if the level is not bad, it will become a good support. I also recommend using assistant words, for example:
Let's draw for example the word "dawn" of the 1st decline, the female kind (since the ending is)
Thus, we see from the example that the noun "dawn" changes its ending depending on the case. Consider which endings are the words of the 1st decline of the female kind:
Now consider which endings have nouns 1st decline of male genus finishing on-/ -u:
So, as can be seen from the plate, the nouns of the 1st decline in the male genus the same end, as well as the nouns of the 1st decline of the female kind, which facilitates the task of the Russian.