Decorative appliqué in dhow
Galina Kaptsova
Goals: fix the names of geometric shapes in children, introduce wintering birds (crow, dove, bullfinch, woodpecker, sparrow); to teach children to recognize birds by the description of external signs in the pictures; to develop in children general and fine motor skills of hands, orientation in space, fantasy; learn to cut a square into two triangles; learn to stick bird figures on a landscape sheet in a certain place.
Equipment: white landscape sheet, glue with a brush, napkins, rags, details applications,bird pictures, bird pattern (bird market) .
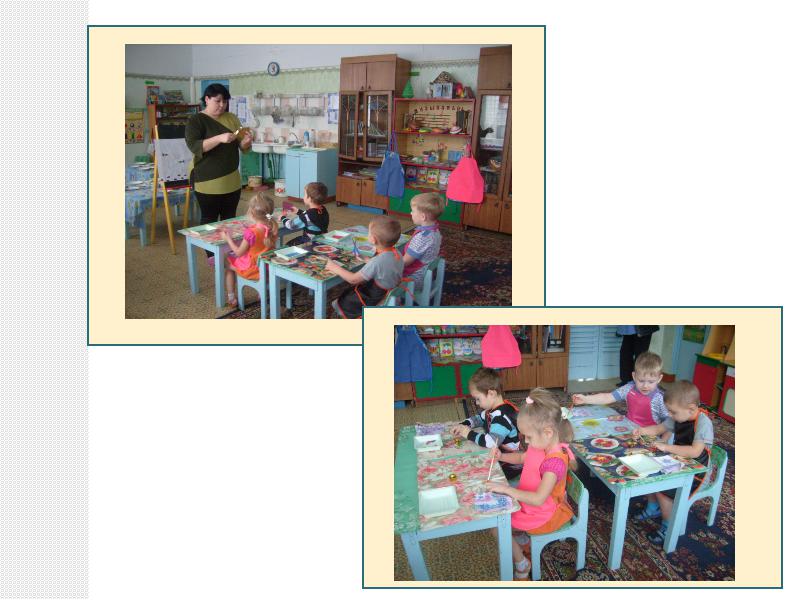
Before you start doing application, with the kids, preliminary work was carried out. We talked about the life of birds in autumn and winter. Learned how to write a descriptive story about a toy bird (similar to teacher). Read poems about birds.
All details for applications the teacher cuts out in advance.
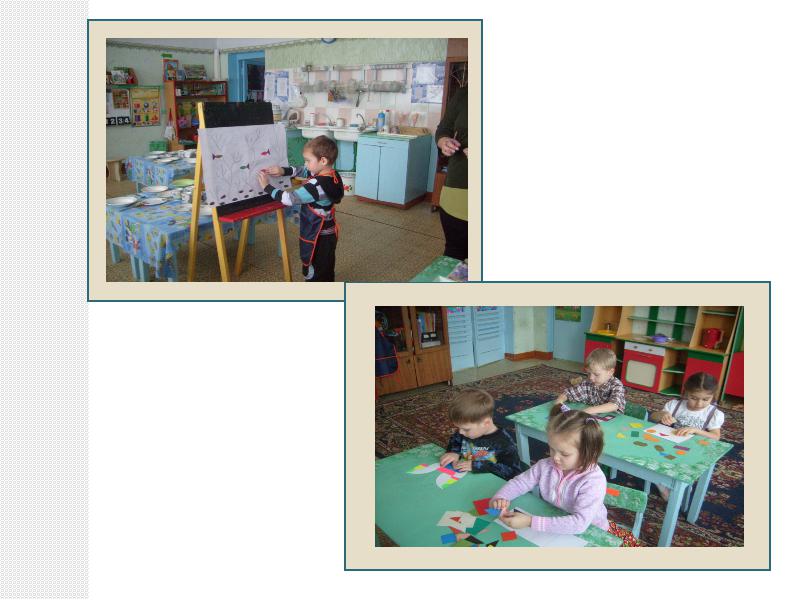
1. First, the children lay out the details applications on a white landscape sheet without glue according to the sample.

2. Then we glue the parts in a certain order, starting with the largest ones.
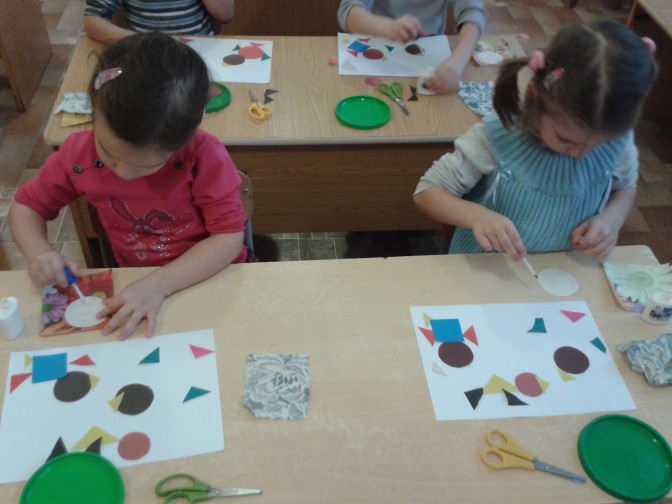

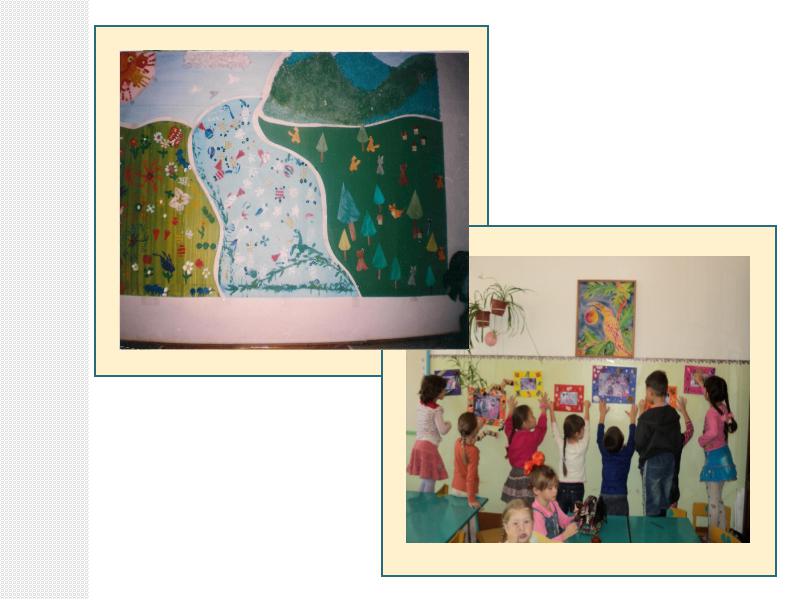
3. Smoothing out application with a napkin from the middle of the parts to the edges. And here's what we got.
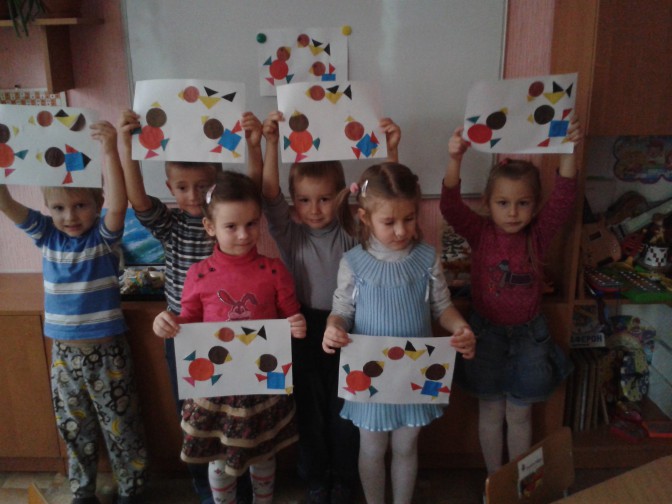

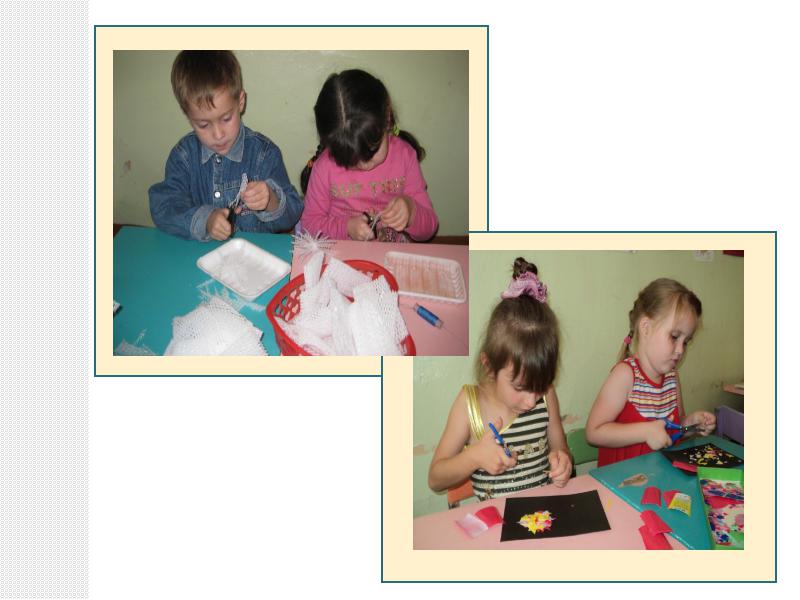
The kids really enjoyed cutting, pasting and fantasizing.
Related publications:
Application "Bus for animals" middle group Objectives: to consolidate the ability to depict objects from ready-made forms, convey their structure, hold scissors correctly and cut a narrow strip evenly.
On April 12, the whole world celebrates Aviation and Cosmonautics Day. This is a special day - on this day in 1961, a citizen of the USSR, Major Yu. A. Gagarin.
Application. middle group from 4-5 years old. Theme: Magic garden. Purpose: To teach how to create a collective composition, independently determining the content.
From black paper and using a hole punch, we make blanks of black dots for ladybug. Cut out an oval from black paper.
Subject: Decorate a cup. Objectives: Educational: learn to arrange and stick objects in a certain sequence. Developing: fix.
Target. Develop Creative skills children, the desire to engage in application. Tasks. To consolidate children's knowledge of round and oval shapes.
We look out the window - it's raining. We remember the nursery rhyme: Rain, rain, drip and drip, Wet paths. We can't go for a walk - We'll get wet.
Topic: The concept and content of the application in the preschool educational institution.
Application - from the Latin word "application" - overlay.
Originated in the 17th century.
A method of creating artistic images from various figures, cut from some material and pasted or sewn onto an appropriate background.
Are used different materials: leather, felt, cloth, birch bark, fur, cloth, straw, paper. Available for preschoolers various equipment: creasing, rolling, different kind cutting (cutting in a straight line to obtain geometric shapes- squares, rectangles; cutting corners in a straight line to obtain a trapezoid; cutting corners along a rounded line to obtain circles, ovals; office cutting, silhouette cutting; multilayer cutting); cutting, weaving.
The application is the most simple and affordable way the creation by children of artwork that preserves the realistic basis of the image itself;
This didactic tool for the development of spatial thinking, fine motor skills of the hand, therefore, the development of speech and intelligence.
An activity that develops the ability to listen, understand and follow instructions, perform sequential actions, and coordinate the work of hands and eyes.
The application uses different techniques for attaching parts to the base (cardboard, fabric): gluing (the entire plane of the part or part of it) and sewing. Both are available to children.
The child needs to master not only special, but general labor skills: set a task, select necessary materials and means for its implementation, plan the progress of work, monitor and evaluate the results.
Throughout early childhood this species labor becomes more complex and enriched, its content becomes fuller and deeper:
a) decorative patterns become more diverse and complex; objects and plots depicted in an applicative way;
b) the material used becomes more diverse;
c) the technique of performance becomes more diverse and complex, children can transfer the technique of work learned on one material to another, taking into account the characteristics of the new material;
d) works become more and more expressive due to the combination of material and variety of performance techniques, enrichment colors and compositional solutions.
The application contributes to:
The formation of certain knowledge in children, the development of skills, the development of skills and the education of the individual;
Assimilation of knowledge about color, structure of objects, their size, planar shape and composition;
Learning about symmetry and asymmetry;
Development of orientation in space and on a limited surface, small muscles of the hand.
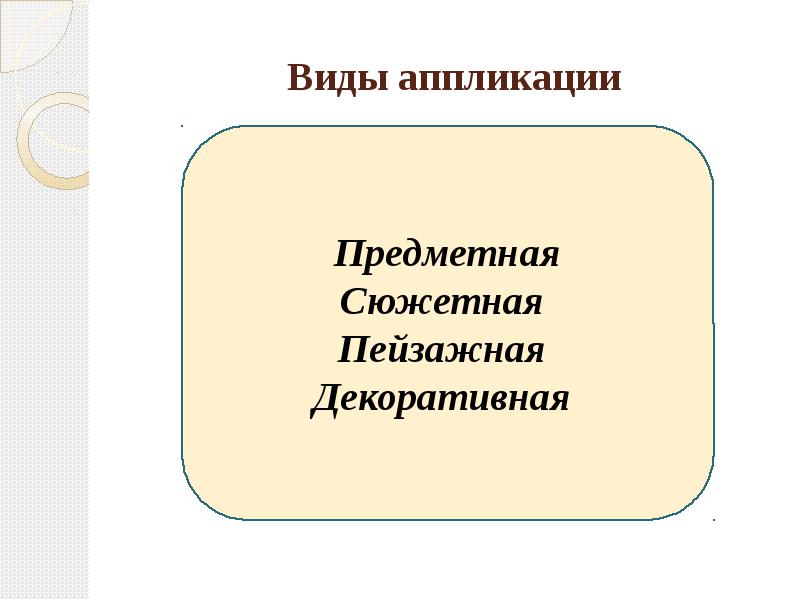
Application types
Subject, Story, Landscape, Decorative
Teaching children applications, the teacher decides the following general tasks :
1. Forms the ability to make a decorative pattern from various geometric shapes and plant (leaf, flower) details, placing them in a certain rhythm on a cardboard or fabric base various shapes.
2. Forms the ability to compose an image of an object from separate parts; portray the story.
3. Teaches to master various equipment obtaining parts for application from different materials.
4. Forms a sense of color, teaches to recognize primary colors and their shades, master the ability to compose harmonious color combinations.
5. Forms a sense of form, proportion, composition.
Cutting methods
Cutting regular geometric shapes.
Cut out paper folded in half. It is used for cutting objects of symmetrical shapes (leaves, flowers).
Cutting out paper folded several times. For cutting objects more complex symmetrical shape.
Cutting out of paper folded with an accordion. For cutting several identical shapes and for garlands.
Partial cutting.
Office cutting.
Paper torn.
Second junior group
Introduce children to the different properties of paper as a material;
To acquaint with the methods of laying out and sticking finished forms on a sheet of paper;
Learn to navigate on a sheet of paper;
Familiarize yourself with the techniques of working with glue and a brush;
To teach how to compose a plot composition from geometric shapes;
Develop arm mobility.
At this age, the content of the work is peculiar: semi-volumetric (from paper lumps, balls) and mosaic (from pieces) subject application, which depicts the simplest objects (colored balls, a branch with rowan berries, cherries, a branch of mimosa, lilac, various vegetables, fruits , animal figurines, etc.).
These works, made on a colored background and framed, delight children with their brightness and can find practical use for decorating the interior of a doll corner, group, preschool, a children's room in the family, etc. Performing individual actions together with the teacher who makes the application, children get the first ideas about it as a way of depicting using paper transformed by hand or using a scissors tool.
Mastering specific actions with material, tools, objects in early age occurs through communication with an adult. Only he can convey to the child information about the functions of objects, tools, show the methods of using materials, etc. in joint activities with him.
The teacher includes a separate action of children to transform the material into a holistic process of creating crafts. This action (crumpling paper into a ball, rolling into a ball, etc.), which gives an intermediate result, acquires practical meaning for the child.
Paperwork is getting more and more difficult. The simplest action is tearing off, then creasing - first large lumps (up to 1 cm in diameter), then small ones, and then rolling the balls, the most difficult thing is cutting the paper with scissors. Why is it necessary to have a variety of actions with paper and their gradual complication? Firstly, depending on what is used to create the application (piece, lump or ball), children learn to convey the specifics of the depicted object. For example, with the help of pieces it is better to make a tree, a festive fireworks, from lumps - a sprig of mimosa, lilac, an elegant Christmas tree . Secondly, the child's hand acts differently: now the whole hand, then the palm, then the fingers, then the fingertips. This is a kind of gymnastics for the hand, preparing it for more complex, requiring fine coordination of actions with paper and other materials, tools.
The first manual productive actions jointly with an adult, included in the context of creating a certain “product”, emotionally prepares the child for systematic and more meaningful participation in the application.
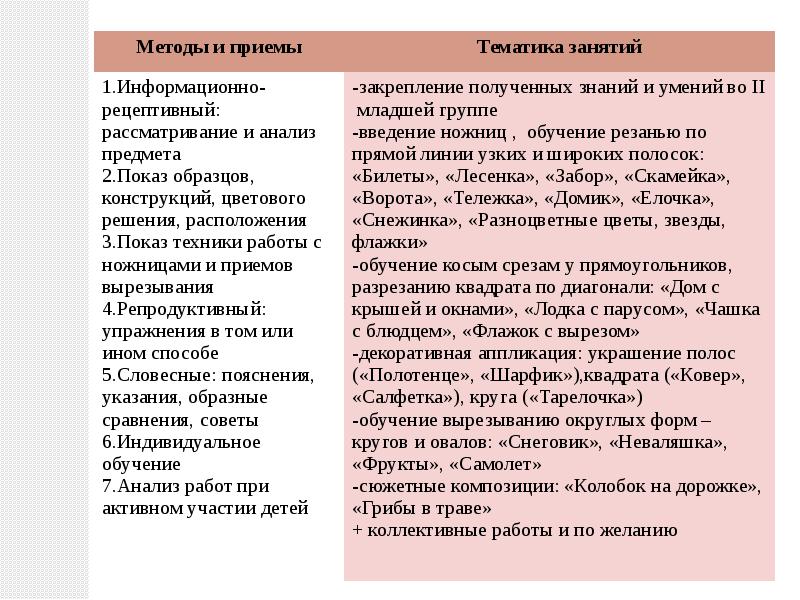
middle group
Learn to hold scissors correctly and act with them;
To teach techniques for cutting out shapes by cutting corners, cutting circle and oval shapes from a square and a rectangle
Learn to stick a pattern on the base irregular shape;
Familiarize yourself with paper cutting techniques;
Continue to teach children to stick ready-made forms according to the model, compose a composition;
Continue to develop fine motor skills of the hand;
To introduce children to the creation of applications from dry leaves, to correct the methods of gluing leaves to the base.
Average preschool age the child's hand acts more firmly and more confidently, therefore more difficult ways cutting: children themselves can make such details as an oval, a circle, rounding the corners of rectangles; cutting corners in a straight line, make a trapezoid, cut the squares diagonally to get triangles. Children of this age can be given stencils to cut out the details of the subject content (fungus, flower). They do not yet know more complex (symmetrical and silhouette) cutting, and in the application they want to use the details of the subject content. With the help of a stencil, children realize their desire without resorting to the help of an adult. If children master scissors early, then by the end of middle age they can cut out details. different ways from the fabric, as a result, applique on the fabric is possible. For the base, burlap, drape, cotton dyed are used. Patterns can be placed on the fabric both by alternating details different color and form, and by creating compositions from elements of national ornaments different peoples.
Children 4-4.5 years old can learn applications from dry plant leaves: make a pattern, alternating leaves in shape, size, color and placing them symmetrically on a cardboard base of different geometric shapes: stripe, square, etc.
When working with this type of material, it is important to encourage children to convey an associative image that arises on the basis of the ability to see the shapes of leaves and correlate them with the shape of certain objects of living objects: insects, animals, fruits, vegetables, humans.
Methods and techniques:
1. Information-receptive: consideration and analysis of the subject.
2. Showing sample designs, color solution, location.
3. Showing the technique of working with scissors and cutting techniques.
4. Reproductive: control in one way or another.
5. Verbal explanations, instructions, figurative comparisons, advice.
6. Individual training.
7. Analysis of work with the active participation of children.
Senior group
To learn to find and highlight familiar shapes in objects, to distinguish and name a square, a rectangle; circle, oval, triangle according to the main features.
Refine knowledge about different colors and differentiate them into bright, light, dark tones.
Learn to compare figures in size: high, low, narrow, wide, thick, below, above, below, one after another, next to, to the left, to the right.
Continue to teach cutting + accordion cutting and symmetrical cutting.
At older preschool age, children master a more complex cutting technique - symmetrical, silhouette, multilayer, as well as the technique of cutting, weaving. They can combine techniques.
Preschoolers master new way attaching parts - sewing them to the fabric. In this case, children receive two versions of the image; flat and semi-volumetric (when cotton wool is placed between the base and the part). In the second case, the image is more expressive. A semi-volumetric appliqué is also obtained with partial gluing of details, for example, only the middle of a snowflake, flower, butterfly, etc.
Expanding the content of the application. Children create more complex decorative patterns from both geometric and plant shapes. Subject applications become more complex with large quantity parts, with a wide variety of materials used.
Preschoolers can perform multi-layer plot applications from paper, fabric, dry leaves. This type of application is the most difficult. Teaching preschoolers how to create a plot, a landscape from dry leaves, grass, flowers, twigs, the teacher continues to develop their associative thinking: what the detail looks like and how it looks in combination with one or another object. For example, in a landscape, a birch or poplar leaf in the background will play the role of a whole birch or poplar tree; a yarrow flower in the foreground looks like a cherry blossom or an apple tree, a part of a ruby leaf is the body of a butterfly, etc. The child needs to be helped to see this. Examination of pictures, photographs, observation in nature contribute to the solution of this problem.
Systematic training of children in various ways of application from various materials creates the basis for the creative expression of a preschooler in independent activity: he can choose content applications (decorative pattern, object, plot), material(one or more in combination) and use different technique, suitable for a more expressive execution of the plan; use applique as decoration voluminous crafts.
Methods and techniques:
Consideration and independent analysis of the subject without leading questions.
Sample display.
Verbal: advice, indication, indirect questions, reminder.
Analysis of work with the active participation of children, independent summing up of the lesson.
Tasks:
continue to refine children's knowledge of acquaintances geometric shapes+ polygons with different amount corners.
learn to differentiate the shades of the main spectral tones, to distinguish between cold and warm colors, light and dark shades.
continue to teach orientation on the plane of a sheet of paper + opposite in pairs, at the same level.
learn to “draw” with scissors - cutting without first drawing the contour line with the transfer of the characteristic features of various silhouettes.
to form the ability to independently plan work.
Methods and techniques:
In everyday work - examination of objects, toys, works of arts and crafts, handicrafts.
Consideration and independent analysis of the subject without leading questions + figurative verbal explanation.
Partial demonstration of cutting techniques.
Verbal: indirect questions, reminder, instructions, advice.
Analysis of works - independent with finding errors and their causes + exhibition of works.

Application in preschool
3rd year student 3 courses "DPP" Kashkareva I.A. APPLICATION
From the Latin word "applicatio" - overlay.
It originated in the sixteenth century.
A method of creating artistic images from various figures, cut from some material and pasted or sewn onto an appropriate background.
Various materials are used: leather, felt, cloth, birch bark, fur, fabric, straw, paper.

APPLICATION
this is the easiest and most affordable way for children to create artwork that preserves the realistic basis of the image itself;
this is a didactic tool for the development of spatial thinking, fine motor skills of the hand, therefore, the development of speech and intelligence;
an activity that develops the ability to listen, understand and follow instructions, perform sequential actions, coordinate the work of hands and eyes

APPLICATION promotes
the formation of certain knowledge in children, the development of skills, the development of skills and the education of personality
mastering knowledge about the color, structure of objects, their size, planar shape and composition
learning about symmetry and asymmetry
development of orientation in space and on a limited surface, small muscles of the hand

Application types
Creation of a developing environment (a corner of aesthetic activity)
Kashkareva I.A. APPLICATION
From the Latin word "applicatio" - overlay.
It originated in the sixteenth century.
A method of creating artistic images from various figures, cut from some material and pasted or sewn onto an appropriate background.
Various materials are used: leather, felt, cloth, birch bark, fur, fabric, straw, paper.

APPLICATION
this is the easiest and most affordable way for children to create artwork that preserves the realistic basis of the image itself;
this is a didactic tool for the development of spatial thinking, fine motor skills of the hand, therefore, the development of speech and intelligence;
an activity that develops the ability to listen, understand and follow instructions, perform sequential actions, coordinate the work of hands and eyes

APPLICATION promotes
the formation of certain knowledge in children, the development of skills, the development of skills and the education of personality
mastering knowledge about the color, structure of objects, their size, planar shape and composition
learning about symmetry and asymmetry
development of orientation in space and on a limited surface, small muscles of the hand

Application types

Creation of a developing environment (a corner of aesthetic activity)
From the Latin word "applicatio" - overlay.
It originated in the sixteenth century.
A method of creating artistic images from various figures, cut from some material and pasted or sewn onto an appropriate background.
Various materials are used: leather, felt, cloth, birch bark, fur, fabric, straw, paper.
this is the easiest and most affordable way for children to create artwork that preserves the realistic basis of the image itself;
this is a didactic tool for the development of spatial thinking, fine motor skills of the hand, therefore, the development of speech and intelligence;
an activity that develops the ability to listen, understand and follow instructions, perform sequential actions, coordinate the work of hands and eyes
the formation of certain knowledge in children, the development of skills, the development of skills and the education of personality
mastering knowledge about the color, structure of objects, their size, planar shape and composition
learning about symmetry and asymmetry
development of orientation in space and on a limited surface, small muscles of the hand
White, colored and diversified paper, cardboard
Sets of scissors, glue, brushes, napkins
Colored pencils, felt-tip pens and markers, accessories,
waste material
Compilation didactic games
Albums and books to review
blanks
stencils
Albums with samples, algorithms, models and schemes
Games with counting sticks
Card file finger games
Plane Geometric Mosaic
A set of exercise games and materials for finger
massage 
Artwork corner in preschool educational institution

Cutting methods
1. Cutting regular geometric shapes must match 2
cut diagonally
side matches side
diameter corresponds to the side

Cutting methods
cut diagonally
side matches side
diameter corresponds to the side

Cutting methods
cut diagonally
side matches side
diameter corresponds to the side

Cutting methods
side matches side
diameter corresponds to the side

Cutting methods
side matches side
diameter corresponds to the side

Cutting methods
diameter corresponds to the side

Cutting methods
2. Cutting from paper folded in half
Used for cutting objects of symmetrical shapes (leaves, flowers)
3. Cutting from paper folded several times
For cutting objects of a more complex symmetrical shape
4.Cutting out of paper folded like an accordion
For cutting several identical shapes and for garlands
5.Part cutting
6.Cutting along the contour
7. Paper tearing 
I junior group (2-3 years old)

In the I junior group not provided program, but the work of the educator is aimed at preparing the child to master a new type of visual activity Children learn: - lay out figures in a given order - make objects from 2-3 parts - correlate them in shape, color, size, spatial arrangement Topics of classes: "Track for a bunny", "House for Masha", "Balls", "Pattern", "Flags", plot mosaic: "Sun and Rain", "Ryaba Hen"

2 junior group (3-4 years old)

Tasks
Introduce children to the different properties of paper as a material.
To acquaint with the techniques of laying out and sticking finished forms on a sheet of paper.
Learn to navigate on a sheet of paper.
Familiarize yourself with the techniques of working with glue and a brush.
Learn to compose a plot composition from geometric shapes.
Develop arm mobility.


Middle group (4-5 years old)

Tasks
Learn to stick a pattern on an irregularly shaped base
Learn how to hold scissors and act with them
To teach techniques for cutting out shapes by cutting corners, cutting circle and oval shapes from a square and a rectangle
Familiarize yourself with paper cutting techniques
Continue to teach children to stick ready-made forms according to the model, compose a composition
Continue to develop fine motor skills of the hand.

Senior group (5-6 years old)

Tasks
Learn to find and highlight familiar shapes in objects, distinguish and name a square, rectangle, circle, oval, triangle according to the main features
Clarify knowledge about different colors and differentiate them into bright, light, dark tones
Learn to compare figures by size: high, low, narrow, wide, thick, thin, long, short, above, below, in the middle, one behind the other, side by side, left, right
Continue to teach cutting techniques + accordion cutting and symmetrical


Preparatory group (6-7 years old)

Tasks
Continue to refine children's knowledge of familiar geometric shapes + polygons with a different number of angles
To learn to differentiate the shades of the main spectral tones, to distinguish between cold and warm colors, light and dark shades
Continue to teach orientation on the plane of a sheet of paper + on the contrary, in pairs, on the same level
Learn to “draw” with scissors - cutting without first drawing a contour line with the transfer of characteristic features of various silhouettes
To form the ability to independently plan work


Organization of classes







