A beautiful leaf of a tree. Leaves of trees. Tree structure
BIRCH- one of the most beautiful and poetic plants in the Russian forest. This is a fast-growing light-loving tree with dense carved leaves on thin drooping branches by the age of 40-50 it reaches 25-30 meters in height.
OAK - On the globe there are up to 600 species of oak, in our country - up to 20 species. One of them is pereshy, or summer (beech family) occupies the main area of oak forests.
ASPEN- one of the types of poplars. Aspen is a fast-growing dioecious tree 20-30 meters in height, lives up to 80-100, and sometimes even more years. The trunk is straight, semi-timber.
ROWAN- a small tree of the Rosaceae family with a round, compact crown, with white flowers in the spring and red-orange clusters of hanging fruit in the fall.
POPLAR- genus of deciduous trees, willow family. Differs in unusual rapidity of growth, large trees (25-30 m), relatively slender trunk, with light gray bark, spreading crown, leaves are often ovoid; poplar is unpretentious, easily propagated by seeds and cuttings.
ELM. Of the elm family, the most common is smooth elm. In the first years it grows very quickly, by the age of 40 it reaches a maximum of 20-30 meters in height and over one meter.
LINDEN . The genus of lindens has several hundred species. In Russia, the most common small-leaved linden is a tree up to 30 meters in height, up to one meter in diameter. She lives 300-400 years, and sometimes more.
ALDER(black or sticky) named for dark color the bark of old trees and for the fact that young buds, shoots and leaves are sticky. It is a fast growing tree of the birch family. By the age of 10 it reaches 10-12 meters, by 50 it has a height of 30 meters, a diameter of 40-60 centimeters, lives up to 100-300 years, blooms in early spring brown-brown earrings.
The tree leaf is one of the most versatile and interesting organs ever created by nature. Classic form leaf - a flat plate, narrow or wide. The leaf is connected to the stem at a point called the nodule with a petiole of varying length. The latter may, however, be absent (then the sheet is called sedentary). The leaf blade can be solid in shape with smooth edges (like a magnolia), or it can have jagged edges like a chestnut or cherry. If there is only one leaf blade on the petiole, then such a leaf is called simple. Sometimes on one petiole there are several leaves, connected to a common (rod) petiole with the help of petioles. Such leaves are called complex leaves. Complex leaves, for example, are typical for robinia (one of the varieties of white acacia).
Many plant species can be easily identified by the shape of the leaf.
This section contains drawings of leaves, flowers, crowns of trees common on the territory of Russia. Larch, spruce, pine, juniper, elm, oak, alder, birch, hazel, linden, aspen, willow, bird cherry, mountain ash, acacia, chestnut, maple, ash, elder, plum.
|
Birch drooping |
Hazel common |
||
|
|
How does a tree grow from seed to fruit? We teach with the child the branches of rowan, birch, poplar, maple, oak. Acquaintance with a tree begins for a child in his earliest childhood. Each courtyard has its own good-natured giant who will gladly shelter from the scorching sun, rain, share fallen leaves and dry twigs for all kinds of games.
However, many children perceive trees as unnamed satellites, not thinking that each of them bears its own name, has a complex structure and performs important tasks. Therefore, with a deeper study of trees, babies make many discoveries for themselves.
For example, children will be interested to know what parts a tree consists of. To do this, we use a schematic image of a tree and talk about each part of it:
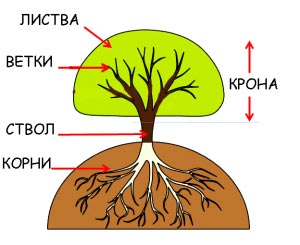
- The roots of a tree are its foundation. They feed the tree by sucking in nutrients dissolved in water, and also keep it upright. The larger the tree, the richer its root system.
- The trunk of a tree is like its body. All substances obtained by the roots pass up the trunk, and branches begin to depart from the trunk. It is important to note that a real tree has one trunk, but shrubs have several, even large, trunks.
- Tree branches - support for leaves; it is on the branches that buds are formed, from which leaves and flowers then appear. Nutrients also pass inside them. Over time, the branches become wider and harder (lignify), and new branches appear from them.
- The foliage of the tree is the organ that allows the tree to exchange substances with environment... Thanks to the leaves, the tree absorbs carbon dioxide, harmful to humans, from the air; here, under the influence of sunlight, organic matter, and through the leaves the tree releases oxygen to the outside, which we breathe.
- All the leaves and branches of the tree form its crown - a lush cap that gives shade and shelters us from the rain.
Having studied the structure of a tree, you can move on to the next stage - find out how it is born. Where and how do trees grow? The answer to this question can be drawn in a circular pattern.

So, we disassemble the whole life cycle fruit tree:
The seed is the source of life for every plant, including the tree. It contains a small embryo and an initial supply nutrients, which the embryo needs in order to germinate through the seed coat. Getting into the soil, the embryo begins to actively develop, hatch through the shell, grows and lets out roots, with which it sucks up the substances necessary for its growth from the ground.
After many years, the embryo turns into a tree, which, having reached a certain age, acquires the ability to reproduce its own kind.
In spring, buds are formed on the branches of a tree, in which an organ of amazing beauty and smell - a flower - develops.
The flower of a fruit tree is designed in such a way that when pollinated (by wind or insects), a small fruit bud is formed in it.
The fruit of a tree is the result of its vital activity. The inside of the fruit contains seeds. In order for the seeds to spread as far as possible, nature has made most of the fruits tasty and attractive to animals and people who, by collecting the fruits, contribute to the spread of seeds over long distances. Not harvested fruits fall from the tree, rot, and after that the seeds fall into the soil.
The development of a tree can be seen from any moment: starting with the fruit, bud, seeds. Each stage can be considered the beginning of a life cycle.
The life cycle of a tree depends greatly on the season.

The beginning of its development and rapid growth occurs in the spring, when buds are actively formed on the branches, from which leaves and flowers subsequently appear. It is not without reason that it is said that in spring trees come to life after winter sleep.
In the summer, trees appear before us in all their glory. They constantly interact with the world around them, feed, replenish the reserves of substances necessary for their life. The leaves of the trees are constantly working in summer, turning into a real processing factory carbon dioxide, and the production of oxygen and nutrients from it.
In autumn, all life processes in the tree decline: the daylight becomes shorter, and the amount of sunlight is insufficient for the formation of new chlorophyll molecules in the leaves, so the foliage gradually changes its color and falls off. Falling leaves not only saves the strength of the tree, which it will need to survive the harsh winter, but also saves tree branches from breaking off, which can occur under the weight of the falling snow.
In winter, the tree seems to freeze. It sparingly spends the stocks accumulated over the summer and looks forward to the arrival of the first spring heat.
But not all trees go through such a cycle of transformations, but only those that have leaves, that is, deciduous ones. But the trees, whose branches are covered with needles - needles (conifers) all winter look the same as in summer.
The most famous conifer tree Is a spruce. Of course, it became famous thanks to the Russian tradition of decorating spruce branches on New Year's Eve. Spruce reproduces by means of cones that form during the summer.

But among the deciduous, the most common trees are:
- Rowan is a tree with bright berries and beautiful jagged foliage that looks especially impressive in autumn. There is a version that it was called mountain ash because its leaves are small enough and when the wind blows, they tremble, causing ripples in the eyes of the one who looks at him.

- Birch is a symbol of Russia, unique tree with white bark color. Its very name comes from Slavic word, meaning "to glow, to turn white." The birch is also interesting for its flowers, which look like earrings, and the fact that its branches are very long and thin, they seem to hang down.

- Poplar is a frequent companion of human habitation. Poplars are planted near houses because they grow quickly, which means that they begin to purify the air early and absorb excess moisture well. In the wild, poplar is often found in wetlands, for which it got its name, which translated from Slavic means "swampy place, swamp". Poplar fruits are capsules from which seeds spill out, covered with many silky hairs - poplar fluff. This fluff gives people a lot of inconvenience, so poplars are often cut off, leaving only non-fruiting branches at the top.

- Oak - a tree - a giant, especially revered by our ancestors. Its fruits - acorns - were used to prepare a drink that replaced coffee, but the bark and wood of oak, which is distinguished by its strength and beautiful color, found even greater use in humans.

- Maple - owner beautiful leaves with sharp edges. A sweet, aromatic maple syrup is obtained from its juice.

- Elm is a tree, wood, branches and bark of which people have used for the manufacture of furniture, tools and even weapons for a long time. The bark of the elm tree (bast) is strong and flexible; various objects were tied to it, for which the tree got its name. Shoes were woven from bast.

- Chestnut is a tree with unusual fruits, the core of which resembles a nut. It is believed that the word "chestnut" has the same root with the word "porridge", since the fruit of the chestnut was often eaten.

- Willow is a tree with unusual long branches and narrow leaves. Its name comes from the word "vit", which is explained by the main use of willow branches - baskets were woven from them, furniture was woven.
In order to better remember the names of the trees, you can play simple game: Shuffle the cards with the leaves and the trees themselves, then match and name them.
Images of leaves are more vivid in coloring pages, where you can see their outline and give color depending on the expected season and shades characteristic of a particular tree.





![]()
While the child is working with the coloring, you can ask him thematic questions, read rhymes or make riddles to consolidate what he has learned. For example, such:
Both graceful and beautiful, it grew by the river ... (willow).
They protect both houses and fields from wind and moisture ... (poplars).
The Russian land does not even need roses, its relatives paint it ... (birches).
And handsome, and strong, and useful, he generously shares own juice... ... (maple).
And in the heat, and in a blizzard, it is equally beautiful ... (spruce).
If there are several children, you can arrange a mini-quiz based on the material covered, and use bouquets of live or bright cardboard leaves or fruits of trees (for example, apples) as prizes.
In this article we have collected material on the topic of "tree leaves" and "tree structure". Acquaintance with a tree begins for a child in his earliest childhood.
Each courtyard has its own good-natured giant who will gladly shelter from the scorching sun, rain, share fallen leaves and dry twigs for all kinds. However, many children perceive trees as unnamed satellites, not thinking that each of them bears its own name, has a complex structure and performs important tasks. Therefore, with a deeper study of trees, babies make many discoveries for themselves.
For example, children will be interested to know what parts a tree consists of. To do this, we use a schematic image of a tree and talk about each part of it:

- The roots of a tree are its foundation. They feed the tree by sucking in nutrients dissolved in water, and also keep it upright. The larger the tree, the richer its root system.
- The trunk of a tree is like its body. All substances obtained by the roots pass up the trunk, and branches begin to depart from the trunk. It is important to note that a real tree has one trunk, but shrubs have several, even large, trunks.
- Tree branches - support for leaves; it is on the branches that buds are formed, from which leaves and flowers then appear. Nutrients also pass inside them. Over time, the branches become wider and harder (lignify), and new branches appear from them.
- The foliage of a tree is the organ that allows the tree to exchange substances with its environment. Thanks to the leaves, the tree absorbs carbon dioxide, harmful to humans, from the air, here organic substances are formed from it under the influence of sunlight, and through the leaves the tree releases oxygen to the outside, which we breathe.
- All the leaves and branches of the tree form its crown - a lush cap that gives shade and shelters us from the rain.
Having studied the structure of a tree, you can move on to the next stage - find out how it is born. Where and how do trees grow? The answer to this question can be drawn in a circular pattern.

So, we analyze the entire life cycle of a fruit tree:
The seed is the source of life for every plant, including the tree. It contains a small embryo and the initial supply of nutrients that the embryo needs in order to germinate through the seed coat. Getting into the soil, the embryo begins to actively develop, hatch through the shell, grows and lets out roots, with which it sucks up the substances necessary for its growth from the ground.
After many years, the embryo turns into a tree, which, having reached a certain age, acquires the ability to reproduce its own kind.
In spring, buds are formed on the branches of a tree, in which an organ of amazing beauty and smell - a flower - develops.
The flower of a fruit tree is designed in such a way that when pollinated (by wind or insects), a small fruit bud is formed in it.
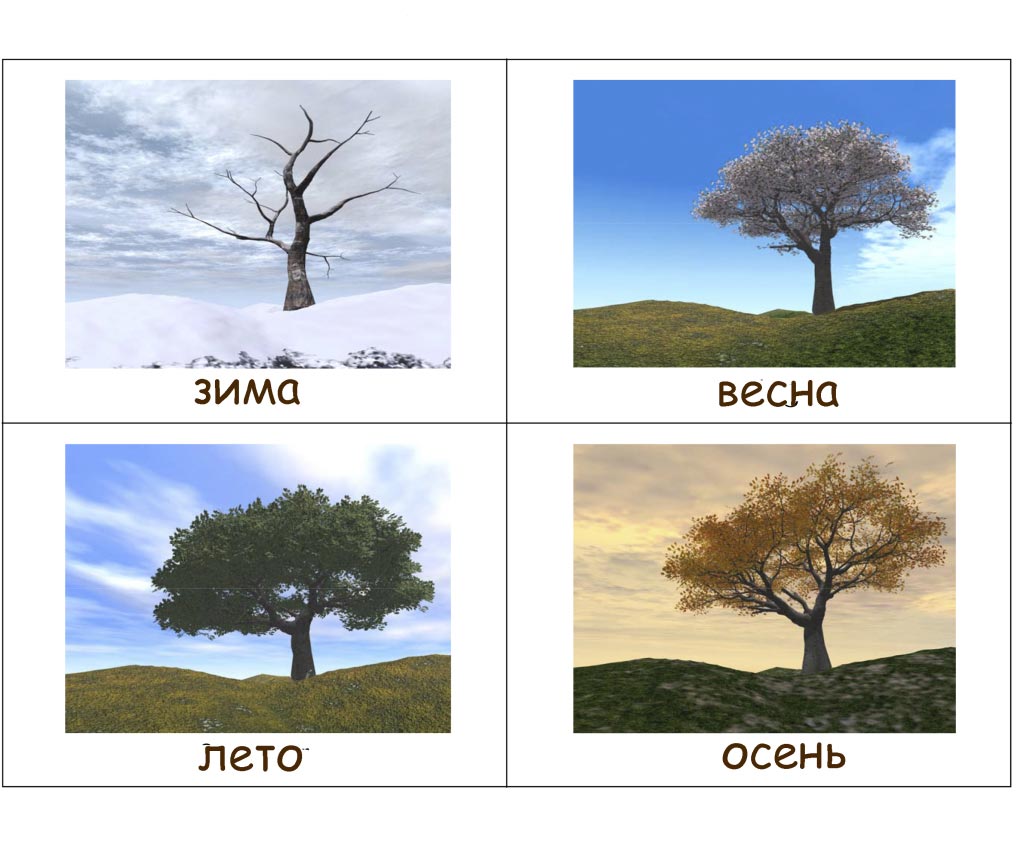
The beginning of its development and rapid growth occurs in the spring, when buds are actively formed on the branches, from which leaves and flowers subsequently appear. It is not without reason that it is said that in spring trees come to life after winter sleep.
In the summer, trees appear before us in all their glory. They constantly interact with the world around them, feed, replenish the reserves of substances necessary for their life. In summer, the leaves of the trees are constantly working, turning into a real factory for the processing of carbon dioxide, and the production of oxygen and nutrients from it.
All vital processes in the tree are declining: daylight becomes shorter, and the amount of sunlight is insufficient for the formation of new chlorophyll molecules in the leaves, so the foliage gradually changes its color and falls off. Falling leaves not only saves the strength of the tree, which it will need to survive the harsh winter, but also saves tree branches from breaking off, which can occur under the weight of the falling snow.
The tree seems to freeze. It sparingly spends the stocks accumulated over the summer and looks forward to the arrival of the first spring heat.
But not all trees go through such a cycle of transformations, but only those that have leaves, that is, deciduous ones. But the trees, whose branches are covered with needles - needles (conifers) all winter look the same as in summer.
The most famous coniferous tree is this. Of course, it became famous thanks to the Russian tradition of decorating spruce branches on New Year's Eve. Spruce reproduces by means of cones that form during the summer.
But among the deciduous, the most common trees are:
- - a tree with bright berries and beautiful jagged foliage, which looks especially impressive in autumn. There is a version that it was called mountain ash because its leaves are small enough and when the wind blows, they tremble, causing ripples in the eyes of the one who looks at him.

- Birch is a symbol of Russia, a unique tree with white bark. Its very name comes from the Slavic word meaning "to shine, to turn white." The birch is also interesting for its flowers, which look like earrings, and the fact that its branches are very long and thin, they seem to hang down.

- Poplar is a frequent companion of human habitation. Poplars are planted near houses because they grow quickly, which means that they begin to purify the air early and absorb excess moisture well. In the wild, poplar is often found in wetlands, for which it got its name, which translated from Slavic means "swampy place, swamp". Poplar fruits are capsules from which seeds spill out, covered with many silky hairs - poplar fluff. This fluff gives people a lot of inconvenience, so poplars are often cut off, leaving only non-fruiting branches at the top.
- Oak - a tree - a giant, especially revered by our ancestors. Its fruits - acorns - were used to prepare a drink that replaced coffee, but the bark and wood of oak, which is distinguished by its strength and beautiful color, found even greater use in humans.

- Maple has beautiful sharp-edged leaves. A sweet, aromatic maple syrup is obtained from its juice.

- Elm is a tree, wood, branches and bark of which people have used for the manufacture of furniture, tools and even weapons for a long time. The bark of the elm tree (bast) is strong and flexible; various objects were tied to it, for which the tree got its name. Shoes were woven from bast.
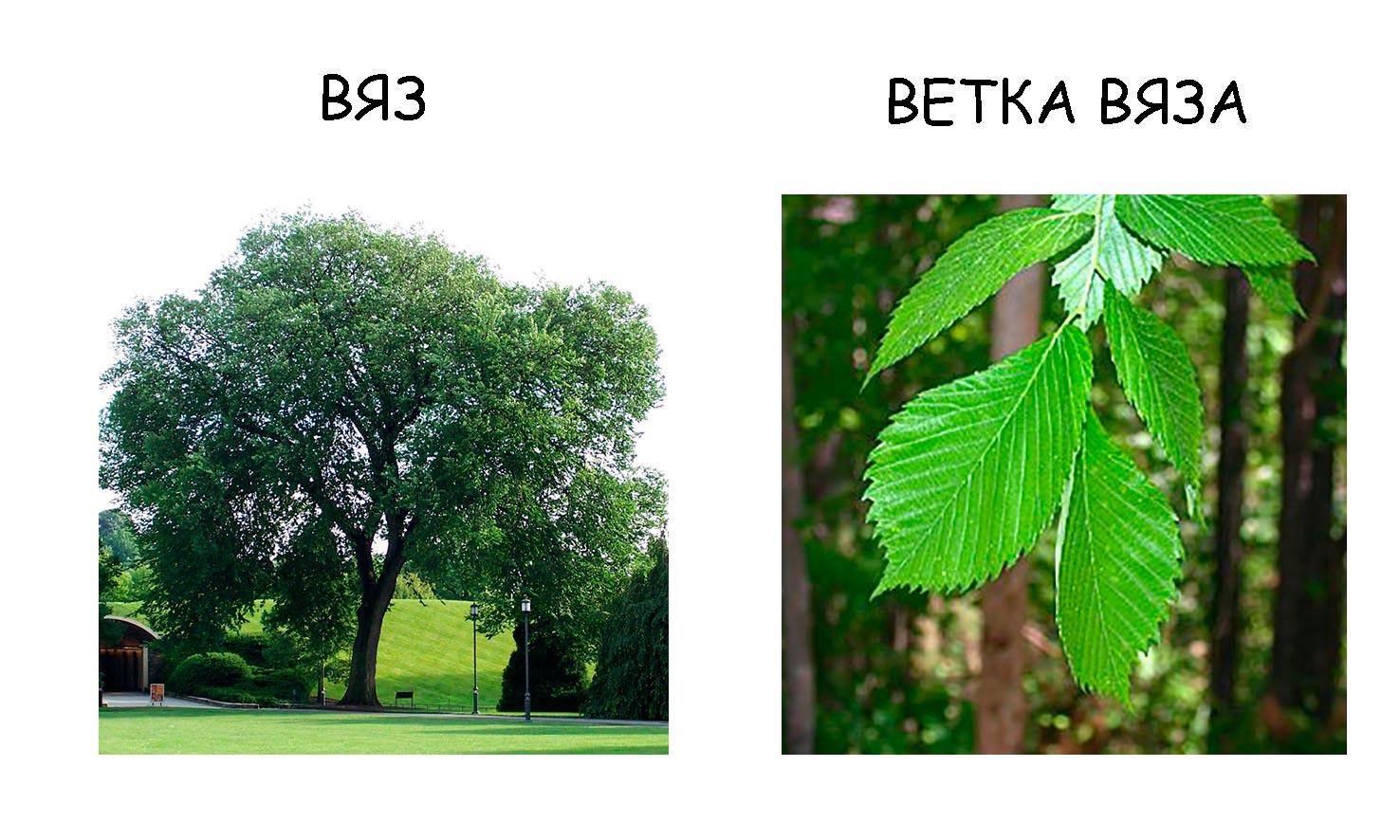

- Chestnut is a tree with unusual fruits, the core of which resembles a nut. It is believed that the word "chestnut" has the same root with the word "porridge", since the fruit of the chestnut was often eaten.

- Willow is a tree with unusual long branches and narrow leaves. Its name comes from the word "vit", which is explained by the main use of willow branches - baskets were woven from them, furniture was woven.

In order to better remember the names of the trees, you can play a simple game: mix cards with the image of leaves and the trees themselves, and then compare and name them.
Leaves can be used to make a very interesting visual aid for children. To do this, you need to collect leaves. different types and laminate them.

Cut out the leaves slightly stepping back from the edge.

We get a living guide to the study of leaf species.

Print out the names of the trees from where you collected the leaves on a separate piece of paper. We compare the name of the tree with the leaf itself, studying and memorizing its shape and structural features.

Images of leaves are more vivid in coloring pages, where you can see their outline and give color depending on the expected season and shades characteristic of a particular tree.






While the child is working with the coloring, you can ask him thematic questions, read rhymes or make riddles to consolidate what he has learned. For example, such:
Both graceful and beautiful, it grew by the river ... (willow).
They protect both houses and fields from wind and moisture ... (poplars).
The Russian land does not even need roses, its relatives paint it ... (birches).
And handsome, and strong, and useful, he generously shares his own juice. ... (maple).
And in the heat, and in a blizzard, it is equally beautiful ... (spruce).
If there are several children, you can arrange a mini-quiz based on the material covered, and use bouquets of live or bright cardboard leaves or fruits of trees (for example, apples) as prizes.
Video: "What is a tree?"


