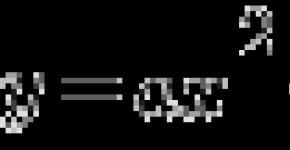Some lines and points of the heavenly sphere. Celestial sphere
2.1 Heatline and Concepts associated with it
2.2 Daily rotation of heaven and related concepts
2.3 Terms, born in the intersections of the concepts "sheer line" and "the rotation of the heavenly sphere"
2.4 The annual movement of the sun on the celestial field and the concepts associated with it
Introduction
1. History
2 elements of the heavenly sphere
Three curious facts
Introduction

The celestial sphere is divided by heavenly equator.
Celestial sphere- Imaginary sphere of an arbitrary radius on which celestial bodies are projected: it serves to solve various astrometric problems. The center of the heavenly sphere takes the eyes of the observer; In this case, the observer may be on the surface of the Earth and in other points of space (for example, it can be attributed to the center of the Earth). For a terrestrial observer, the rotation of the heavenly sphere reproduces the daily movement of the shone in the sky.
Each celestial luminaire corresponds to the point of the heavenly sphere, in which it intersects the straight line connecting the center of the sphere with the center of the shine. When studying the provisions and visible movements, the luminaries on the celestial sphere choose the other system of spherical coordinates. Calculations of the provisions of the luminaries on the celestial sphere are carried out with the help of heavenly mechanics and spherical trigonometry.
1. History
The idea of \u200b\u200bthe celestial sphere arose in ancient times; It was based on a visual impression on the existence of a dome-shaped celestial arch. This impression is due to the fact that as a result of the huge remoteness of the heavenly, the human eye is not able to estimate the differences in distances to them, and they seem equally remote. In the ancient peoples, this was associated with the presence of a real sphere that limits the whole world and carrying numerous stars on its surface. Thus, in their presentation, the celestial sphere was the most important element of the Universe. With the development of scientific knowledge, such a look at the heavenly sphere. However, the geometry of the celestial sphere laid in ancient times as a result of development and improvement received modern viewin which it is used in astrometry.
2. Elements of the heavenly sphere

Precession of the equinoxies of the planet Earth, thanks to which the time of year is possible
2.1. Heba Line and Concepts related to it
Sheer line- Direct, passing through the center of the celestial sphere and the observation point on the ground surface. The sheer line intersects with the surface of the celestial sphere in two points - zenitabove the head of the observer and nadirdunder the legs of the observer.
Mathematical horizon- Large circle of heaven sphere, the plane of which is perpendicular to the sheer line. The mathematical horizon divides the surface of the heavenly sphere on two hemispheres: visible hemispherwith a vertex in Zenith and invisible hemispherwith a top in Nadir. The mathematical horizon does not coincide with the visible horizon due to the elevation of the observation point above the earth's surface, as well as due to the curvature of the rays of light in the atmosphere.
Circle of heightor verticalluminous - a large semicircle of the heavenly sphere, passing through the shining, Zenit and Nadir. Almuqantarat(Arab. "Circle of equal heights") - a small circle of heaven, whose plane is parallel to the plane of the mathematical horizon. Circles of height and almuqantarata form a coordinate grid, specifying horizontal coordinates of the shining.
2.2. The daily rotation of the heavenly sphere and the associated concepts
Ax of the world- Imaginary line passing through the center of the world around which the sky is rotated. The axis of the world intersects with the surface of the heavenly sphere in two points - north Pole of the worldand southern Pole of the World. The rotation of the heavenly sphere occurs counterclockwise around the North Pole, if you look at the celestial sphere from the inside.
Celestial equator- A large circle of heaven sphere, the plane of which is perpendicular to the axis of the world. Heavenly Equator divides the heavenly sphere for two hemispheres: northand south.
Circle of declination- A large range of heavenly sphere passing through the poles of the world.
Daily parallel- Small circle of heaven sphere, the plane of which is parallel to the plane of the celestial equator. Visible daily movements of the luminaire are made through daily parallel. Circles of declination and daily parallels form a coordinate grid on the celestial sphere that specifies the equatorial coordinates of the shining.
2.3. Terms born in the intersections of the concepts of "sheer line" and "the rotation of the heavenly sphere"
Heavenly Equator intersects with a mathematical horizon in point of Eastand west point. The point of the East is called that in which the points of the rotating celestial sphere are upgraded due to the horizon. Height semicircle passing through the point of the East, is called first vertical.
Heavenly Meridian- A large circle of heaven, whose plane passes through a sheer line and the axis of the world. Heavenly Meridian divides the surface of the heavenly sphere for two hemispheres: eastern hemisphereand western hemisphere.
Midday line- Line of the intersection of the plane of the celestial meridian and the plane of the mathematical horizon. The midday line and heavenly meridian crosses the mathematical horizon at two points: point of northand point of South. The point of the North is called the one that is closer to the North Pole of the world.
2.4. The annual movement of the sun on the heavenly sphere and the associated concepts

P, P "- Poles of the World, T, T" - Equinox Points, E, C - Soltesta Points, P, P "- Ecliptic Poles, PP" - Axis of World, PP "- Ecliptic Axis, ATQT" - Heavenly Equator, Etct "- Ecliptica
Ecliptic- A large range of heavenly sphere, according to which the visible annual movement of the sun occurs. The plane of the ecliptic intersects with the plane of the celestial equator at an angle ε \u003d 23 ° 26.
Two points in which the ecliptic intersects with the celestial equator are called the equinox points. IN point of spring equinoxThe sun in its annual movement passes from the southern hemisphere of the heavenly sphere to the North; in point of autumn equinox- from the northern hemisphere to the southern one. Two points of ecliptic, separated from 90 ° equinox points and thereby the most remote from the heavenly equator, are called solstice points. Point of summer solsticelocated in the northern hemisphere, point of winter solstice- In the southern hemisphere.
The axis of ecliptic- diameter of the celestial sphere, perpendicular plane of ecliptic. The axis of the ecliptic intersects with the surface of the celestial sphere in two points - north Pole Eclipticalying in the northern hemisphere and south Pole Eclipticalying in the southern hemisphere. The North Pole of Ecliptic has the equatorial coordinates of R.A. \u003d 18h00m, Dec \u003d + 66 ° 33, and is located in the constellation of the dragon.
Circle of ecliptic latitude, or simply circle latitude- a large semicircle of the heavenly sphere passing through the poles of ecliptic.
3. Curious facts
Word zenithcame to us from Arabic, where it is pronounced as round. As zamt rewritten by Latin letters, it was subsequently distorted by the correspondence, turning into Zanit, and then to Zenit.
Our site is designed to help you solve your sleep. Only our dream book online will help you make it easy and quickly. To find out the meaning of dreams, you need to decompose it to the components, allocate the brightest episodes. After that, it is necessary to designate them in one word, for example, the "heart" or "wedding" and find it on the pages: Dream Interpretation Interpretation will be determined by his meaning. Dream intercoms include dreams of dreams from 4 famous interpreters. Information is free.
Intense dreams together:
|
You dream that you are at the height. This dream to change. But for the better or worse? |
Appearing in nightly Gresses, animals personify the very dream ... |
||
|
Native, friends, random acquaintances and strangers. What does their appearance in dreams mean? |
Can the dreams predict the future? It seems that it is impossible ... |
||
|
Did you ever happen to you that in a dream you understand what you sleep? |
Prophetic dreams come to us extremely rarely and foreshadow very important events. |
Dreams are the activities of our subconscious and psyche, which even continues to work in a dream. The psyche is designed to resolve our daily problems using the method of predicting the most likely event outcome. Thus, something that can be in an unconscious state, but to be determined is impressed, expressed through dreams. We only need to learn the interpretation of dreams, which will become the key to knowing yourself. For example, quite often dreams help on early diagnosis of diseases, help us pay attention to the state of health. Also, dreams often reveal our desires through the implementation of the fact that it really causes difficulties. In this case, the mechanism of displacement of unpleasant information is triggered with the subsequent replacement to a more enjoyable one. Dreams can even become an assistant in search of answers to the questions exciting in reality.
Celestial sphere - Abstract concept, imaginary sphere of infinitely large radius, the center of which is observer. At the same time, the center of the heavenly sphere is as it were at the level of the eye of the observer (in other words, all that you see above your head from the horizon to the horizon - and there is this very sphere). However, for the simplicity of perception, it can be considered the center of the heavenly sphere and the center of the Earth, there is no mistake in this. The provisions of the stars, planets, the sun and the moon are applied to the sphere in this position, in which they are visible in the sky at a certain point in time from this point of finding the observer.
In other words, although watching the position of the shone on the heavenly sphere, we are in different places Planets, we will constantly see a few different pictures, knowing the principles of "work" of the heavenly sphere, looking at the night sky. We can easily navigate on the ground using a simple technique. Knowing the view above the head at a point A, we compare it in with the view of the sky at the point B, and on deviations of familiar landmarks, we can understand where we are now.
People have long come up with whole line Tools facilitating our task. If you focus on the "earthly" globe simply with the help of latitude and longitude, then a number of similar elements - points and lines are also provided for the "heavenly" globe - the heavenly sphere.
Heavenly sphere and position of the observer. If the observer is shifted, then the whole sphere visible will be shifted
Elements of heavenly sphere
The celestial sphere has a number of characteristic points, lines and circles, consider the basic elements of the heavenly sphere.

Vertical observer
Vertical observer - Direct, passing through the center of the heavenly sphere and coinciding with the direction of the remove thread at the observer point. Zenith - Point of intersection of the vertical observer with the celestial sphere, located above the observer head. Nadir - Point of intersection of the vertical observer with the heavenly sphere opposite to Zenit.

True horizon - a large circle on the celestial sphere, the plane of which is perpendicular to the vertical of the observer. The true horizon divides the celestial sphere into two parts: the commercial hemispherin which Zenit is located and podgorizonal hemispherin which Nadir is located.

The axis of the world (earth axis) - Direct, around which is visible daily rotation of the heavenly sphere. The axis of the world is parallel to the axis of rotation of the Earth, and for an observer located on one of the Earth's poles, it coincides with the axis of the earth's rotation. The visible daily rotation of the celestial sphere is a reflection of the actual daily rotation of the Earth around its axis. Poles of the world - the intersection of the axis of the world with the heavenly sphere. Polyus of the world, located in the field of the constellation of the Small Malar, is called North Pole in the world, and the opposite pole is called South Pole.

A large circle on the celestial sphere whose plane is perpendicular to the axis of the world. The plane of the heavenly equator divides the heavenly sphere on northern semifierin which the North Pole of the World is located, and Southern half faultin which the South Pole of the World is located.

Or the supervisor meridian is a large circle on the heavenly sphere passing through the poles of the world, Zenit and Nadir. It coincides with the plane of the terrestrial observer and divides the heavenly sphere on eastern and western hemispheres.

Points of the north and south - Points of intersection of heavenly meridian with a true horizon. The point closest to the North Pole of the world is called the point of the North of the True Horizon C, and the point closest to the southern pole of the world is the point of the south of Yu. Points of the East and West - the intersection points of the heavenly equator with a true horizon.
Midday line - Straight line in the plane of the true horizon connecting the points of the North and the South. Halfood is called this line because at noon on local true sunny time the shadow from the vertical pederate coincides with this line, i.e. with the true meridian of this point.

Points of intersection of heavenly Meridian with heavenly equator. The point closest to the southern point of the horizon is called point of South of Heavenly Equator, and the point closest to the northern point of the horizon is - the point of the North of the Heavenly Equator.

Vertical Svetila
Vertical Svetila, or circle of height- A large circle on the celestial sphere passing through Zenith, Nadir and shining. The first vertical is a vertical passing through the points of the East and the West.

Circle of declination, Or, is a big circle on the celestial sphere passing through the poles of the world and shone.

Small circle on the celestial sphere spent through the luminous parallel plane of the celestial equator. The visible daily movement of the luminaire occurs in daily parallels.

Almuqantarat Svetila
Almuqantarat Svetila - Small circle on the celestial sphere, spent through the shining parallel to the plane of the true horizon.
All the elements of the heavenly sphere are actively used to solve the practical orientation tasks in space and determining the position of the luminaire. Depending on the purpose and conditions of measurement, two different systems are used. Spherical celestial coordinates.
In one system, the luminaire oriented relative to the true horizon and call this system, and in the other - relative to the heavenly equator and is called.
In each of these systems, the position of the luminaries on the celestial sphere is determined by two angular values, just as the position of the points on the surface of the earth is determined using latitude and longitude.
CELESTIAL SPHERE
When we observe the sky, all astronomical objects seem to be located on the dome-shaped surface, in the center of which is the observer. This imaginary dome forms the upper half of the imaginary sphere, which is called "heavenly sphere." It plays a fundamental role when specifying the situation of astronomical objects.
Although the moon, the planets, the sun and stars are located at different distances from us, even the closest of them are so far away that we are not able to appreciate their remoteness. The direction on the star does not change when we move along the ground surface. (True, it changes slightly when the Earth moves in orbit, but it is possible to notice this parallact displacement with the help of the extreme devices.) It seems to us that the celestial sphere rotates, because the luminaries are torn in the east and enter the West. The reason for this is the rotation of the Earth from the West to the East. The apparent rotation of the celestial sphere occurs around the imaginary axis, which continues the earth's axis of rotation. This axis crosses the celestial sphere at two points, called the North and South Poles of the World. The North Pole of the world lies in about a degree from the polar star, and near the southern pole there are no bright stars.

The axis of rotation of the Earth is inclined by about 23.5 ° relative to the perpendicular, carried out to the plane of the earth orbit (to the plane of the ecliptic). The intersection of this plane with the heavenly sphere gives a circle - the ecliptic, the visible path of the Sun for the year. The orientation of the earth's axis in space is almost unchanged. Therefore, every year in June, when the northern end of the axis is tilted towards the Sun, it rises high in the sky in the northern hemisphere, where the days become long, and the nights are short. Moving to the opposite side of the orbit in December, the land turns out to be deployed to the Sun southern hemisphere, and in the north days become short, and the night are long.
see also SEASONS . However, under the influence of solar and lunar attraction, the orientation of the earth's axis is still gradually changing. The main movement of the axis caused by the influence of the Sun and the Moon on the Equatorial Swimming of the Earth is called precession. As a result of the precession, the earth's axis slowly turns around the perpendicular to the orbital plane, describing the cone by a radius of 23.5 ° for 26 thousand years. For this reason, in a few centuries, the pole will no longer be near the polar star. In addition, the axis of the Earth makes small oscillations, called the nutation and associated with the ellipticity of the Earth and the Moon orbits, and also so that the plane of the lunar orbit is slightly tilted to the plane of the earth orbit. As we already know, the kind of heavenly sphere changes due to the rotation of the Earth around the axis. But even if you observe the sky at the same time during the year, his appearance will change due to the appeal of the Earth around the Sun. For a total turnover of orbit at 360 ° Earth requires approx. 3651/4 days - about degree per day. By the way, a day, or rather, the sunny day is the time for which the Earth turns once around the axis towards the Sun. It consists of time for which the land makes turnover towards the stars ("Star days"), plus a short time - about four minutes, which is necessary for turn compensating for the orbital movement of the earth per day for one degree. Thus, the year is approx. 3651/4 sunny day and approx. 3661/4 star.
When observed from a certain point
Earth stars located near the poles, or are always over the horizon, or never rise above it. All other stars rise and come, and every day the sunrise and entering each star happens 4 minutes earlier than in the previous day. Some stars and constellations rise in the sky at night in winter time - We call them "winter", and others - "summer". Thus, the kind of heavenly sphere is determined by three times: the time of day associated with the rotation of the Earth; time of the year associated with the appeal around the Sun; The era associated with the precession (although the last effect is hardly noticed "to the eye" even for 100 years).
Coordinate systems. Exist various methods To indicate the position of objects in the celestial sphere. Each of them approaches the tasks of a particular type.
Alt-azimuthal system. To indicate the position of the object in the sky in relation to the surrounding observer, the Earth objects use "alt-azimuth", or "horizontal", coordinate system. It indicates the angular distance of the object above the horizon, called the "height", as well as its "azimuth" - the angular distance along the horizon from the conditional point to the point lying right below the object. In astronomy, azimuth is counted from the south point to the west, and in geodesy and navigation - from the point of the North to the East. Therefore, before using azimuth, you need to find out what system it is specified. The dot of the sky, which is right above the head, has a height of 90 ° and is called "Zenit", and the dot diametrically opposite to it (under the legs) - "Nadir". For many tasks, a large circle of heavenly sphere is important, called "Heavenly Meridian"; He passes through Zenith, Nadir and the Poles of the World, and the horizon crosses at the points of the North and the South.
Equatorial system. Because of the rotation of the Earth, the stars are constantly moving relative to the horizon and the parties of the light, and their coordinates are changed in the horizontal system. But for some problems of astronomy, the coordinate system should be independent of the position of the observer and the time of day. Such a system is called "Equatorial"; Its coordinates resemble geographical latitudes and longitude. In it, the plane of the earth's equator, continued before the intersection with the heavenly sphere, sets the main circle - "Heavenly Equator". The "declination" of the star resembles breadth and is measured by its angular distance to the north or south of the heavenly equator. If the star is visible exactly in Zenith, then the latitude of observation places is equal to the decline of the star. Geographic longitude corresponds to the "direct climbing" stars. It is measured east of the intersection point of ecliptic with the heavenly equator, which the sun passes in March, on the day of the beginning of the spring in the northern hemisphere and autumn - in South. This important point for astronomy is called the "first point of the Aries", or the "Point of Spring Equinox", and denote the sign
Other systems. For some purposes, other coordinate systems are used in the heavenly sphere. For example, when the movement of the body in Solar systemThe coordinate system is used, the main plane of which is the plane of the earth orbit. The structure of the galaxies is studied in the coordinate system, the main plane of which is the equatorial plane of the galaxy, presented in the sky around the world passing along the Milky Way.
Comparison of coordinate systems. The most important details Horizontal and equatorial systems are shown in the drawings. In the table, these systems are compared with the geographic coordinate system.
Transition from one system to another. Often there is a need for the Alt-azimutic coordinates of the star to calculate its equatorial coordinates, and vice versa. To do this, you need to know the point of observation and position of the observer on Earth. Mathematically, the problem is solved using a spherical triangle with vertices in Zenith, the North Pole of the world and the star x; It is called the "astronomical triangle". Angle with a vertex in the northern pole of the world between the monidian of the observer and the direction at any point of the heavenly sphere is called the "hour angle" of this point; It is measured to the west of Meridian. The hour angle of the point of spring equinox, expressed in hours, minutes and seconds, is called "Star Time" (Si. T. - Sidereal Time) at the observation point. And since the direct climbing of the star is also a polar angle between the direction on it and the point of spring equinox, then the starry time is equal to the direct ascent of all points lying on the observer meridian. Thus, the hour angle of any point in the celestial sphere is equal to the difference in the star time and its direct climb:
![]()
Let the width of the observer be equal to j. If the equatorial coordinates of the star A and D are given, its horizontal coordinates A and can be calculated according to the following formulas: you can solve the inverse task: according to the measured values \u200b\u200bof A and H, knowing time, calculate a and d. The declination of D is calculated directly from the last formula, then N, and from the first, if the stellar time is known, is calculated a.
Representation of the heavenly sphere. Many century scientists were looking for best ways Presentations of the heavenly sphere for studying or demonstration. There were two types of models: two-dimensional and three-dimensional. The celestial sphere can be depicted on the plane in the same way as spherical land is depicted on the maps. In both cases, you need to choose a system of geometric projection. The first attempt to present the sections of the heavenly sphere on the plane were rocky drawings of star configurations in the caves of ancient people. Nowadays, there are various star maps, published in the form of drawn or photographic star atlases covering all the sky. Ancient Chinese and Greek astronomers represented the heavenly sphere in the form of a model known as the "reinforcement sphere". It consists of metal circles or rings connected together to show the most important circles of the heavenly sphere. Now they often use star globes, which marked the positions of stars and the main circles of heavenly sphere. Arillar spheres and globes have a common drawback: the position of the stars and markup of the circles is applied on their external, convex side, which we are considering outside, whereas on the sky we look at the inside, and the stars seem to us placed on the concave side of the heavenly sphere. This sometimes leads to confusion directions of the movement of stars and figures of constellations. The most realistic representation of the celestial sphere gives a planetarium. The optical projection of stars on the hemispherical screen from the inside allows you to very accurately reproduce the view of the sky and all sorts of movements shone on it.
see also
Astronomy and astrophysics;
Planetarium;
STARS .
The encyclopedia of the colley. - Open Society. 2000 .
Large encyclopedic Dictionary - Imaginary auxiliary sphere of an arbitrary radius, on which heavenly lights are projected. It is used in astronomy to study the mutual location and movement of space objects based on the determination of their coordinates in the heavenly sphere. ... ... encyclopedic DictionaryImaginary an auxiliary sphere of an arbitrary radius on which heavenly shine is designed; It serves to solve various astrometric tasks. The idea of \u200b\u200bN. s. It appeared in deep antiquity; It was based on a visual ... ... Great Soviet Encyclopedia
The imaginary sphere of an arbitrary radius, on the swarm of heavenly lights are depicted as they are visible from the observation point on the earth's surface (topotrich. N. p.) Or how they would be visible from the center of the Earth (Geocentrich. N. s.) Or the center of the Sun ... ... Big Encyclopedic Polytechnic Dictionary
celestial sphere - Dangaus Sfera Statusas T Sritis Fizika Atitikmenys: ANGL. Celestial Sphere Vok. Himmelskugel, F; Himmelssphäre, F Rus. Heavenly sphere, f; Neck notge, m pranc. Sphère Céleste, F Fizikos Terminų žodynas
§ 48. Heavenly sphere. Main points, lines and circles on the celestial sphere
The celestial sphere is called the sphere of any radius with the center in an arbitrary point of space. For its center, depending on the task setting, the observer eye, the center of the instrument, the center of the Earth, etc.Consider the main points and circles of the heavenly sphere, the center of which is taken by the eye of the observer (Fig. 72). Through the center of the heavenly sphere, we will conduct a sheer line. The points of intersection of the sheer line with the sphere are called zenith z and nadir n.
Fig. 72.
The plane passing through the center of the heavenly sphere perpendicular to the sheer line is called plane of the True Horizon. This plane, intersecting with the heavenly sphere, forms a circumference of a large circle called the true horizon. The latter divides the celestial sphere into two parts: commercial and subgribore.
Direct, passing through the center of the heavenly sphere parallel to the earth's axis, is called the axis of the world. Points of intersection of the axis of the world with heavenly sphere are called poles of the world. One of the poles, respectively, the Poles of the Earth is called the North Pole of the world and denote PN, the other - the southern pole of the world PS.
The QQ plane ", passing through the center of the heavenly sphere perpendicular to the axis of the world, is called plane of heavenly equator. This plane, crossing the celestial sphere, forms a circumference of a large circle - celestial equator, Which divides the celestial sphere on the northern and southern parts.
A large range of heavenly sphere, passing through the poles of the world, Zenit and Nadir, are called meridian observer PN NPSZ. The axis of the world divides the supervisor meridian on the midday PN ZPS and the midnight PN NPS part.
The supervisor meridian intersects with a true horizon at two points: point of the North N and the south point S. Direct, connecting the points of the North and the South, called midday line.
If you look at the center of the sphere from the center of the sphere, then the point of the East O ST, and the left is the point of the west W. Small circles of the heavenly sphere of AA, "parallel planes of the true horizon are called almuCantarata; Small BB "Parallel Planes of Heavenly Equator, - heavenly parallels.
Circles of the Heavenly Zon sphere, passing through the points of Zenith and Nadir, are called verticals. The vertical passing through the points of the East and the West is called the first vertical.
Circles of the Heavenly Pnops sphere, passing through the poles of the world, are called circles of decline.
The supervisor meridian is simultaneously vertically and the circle of declination. He divides the celestial sphere into two parts - oriental and western.
The pole of the world, located above the horizon (under the horizon), is called an increased (reduced) pole of the world. The name of the high pole of the world is always the same name with the name of the latitude of the place.
The axis of the world with the plane of the True Horizon makes an angle equal geographic latitude Places.
The position of the luminaries on the celestial sphere is determined by the help of spherical coordinate systems. In nautical astronomy, the horizontal and equatorial coordinate system are used.