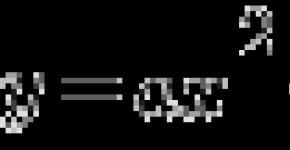How to transfer a division into a fraction. Translation of decimal numbers in an ordinary fraction
Touching to decide math problems With fractions, the schoolboy understands that he is not enough for him only the desire to solve these tasks. Knowledge of calculations with fractional numbers are also needed. In some tasks, all initial data is submitted to the condition in a fractional form. In the others, they can be fractions, and some are integer numbers. To produce some calculations with these specified values, you must first lead them to a single form, that is, the integers are transferred to fractions, and then engage in calculations. In general, a way, as an integer to translate into fraction, is very simple. To do this, it is necessary in the numerator of the final fraction to write a given number, and in its denominator - one. That is, if you need to translate into the fraction number 12, then the resulting fraction will be 12/1.
Such modifications help bring the fraction to a common denominator. It is necessary in order to be able to conduct subtraction or addition of fractional numbers. With their multiplication and division, the overall denominator is not required. You can consider on the example how to translate the number in the fraction and then make the addition of two fractional numbers. Suppose it is necessary to fold the number 12 and fractional number 3/4. The first term (number 12) is given to the form 12/1. However, its denominator is 1 at a time, as the second term, it is equal to 4. For the subsequent addition of these two fractions, it is necessary to bring them to a common denominator. Due to the fact that one of the numbers denominator is equal to 1, it is simple to do it at all. It is necessary to take a valve of the second number and multiply on it and the numerator, and the denominator of the first.
As a result of multiplication, it turns out: 12/1 \u003d 48/4. If 48 is divided into 4, then it turns out 12, then the fraction is shown to the correct denominator. Thus, you can at the same time and understand how the fraction is translated into an integer. This concerns only the wrong fractions, because they have a numerator more than the denominator. In this case, the numerator shares the denominator and, if the residue does not work, there will be an integer. With the rest, the fraction remains the fraction, but with the dedicated whole part. Now about bringing to the general denominator on the example considered. If the first term, the denominator would be equal to some other number, except for 1, the numerator and the denominator of the first number would have been multiplied by the denominator of the second, and the number and denominator of the second one - the denominator of the first.
Both components are given to their common denominator and are ready for addition. It turns out that in this task you need to fold two numbers: 48/4 and 3/4. When adding two fractions with the same denominator, only their upper parts are needed, that is, numerals. The value denominator will remain unchanged. In this example, 48/4 + 3/4 \u003d (48 + 3) / 4 \u003d 51/4 should be obtained. This will be the result of addition. But in mathematics, incorrect fraction is taken to bring to the right one. The above was considered how to turn the fraction into a number, but in this example there would not be an integer from the fraction 51/4, since the number 51 is not divided without a residue to the number 4. Therefore, it is necessary to highlight the whole part of this fraction and its fractional part. The whole part will be the number that is obtained by fission the first smaller than 51, numbers.
That is, that which can be divided into 4 without a residue. The first number in the number 51, which is divided into 4, will be the number 48. Separating 48 to 4, the number 12 is obtained. It means a whole part of the desired fraction will be 12. It remains only to find a fractional part of the number. The valve of the fractional part remains the same, that is, 4 in this case. To find the numerator of the fractional part, it is necessary to subtract from the initial numerator to the number that was divided into the denominator without the residue. In the example, the example requires for this to subtract from among the number 51 number 48. That is, the fractional part number is equal to 3. The result of the addition will be 12% and 3/4. The same is done when subtracting fractions. Suppose it is necessary from an integer number 12 subtracting fractional number 3/4. For this, an integer 12 is translated into fractional 12/1, and then driven to a common denominator with the second number - 48/4.
When subtracting, the denominator of both fractions remains unchanged, and with their numerals and conduct subtraction. That is, the numerator of the first fraction is subtracted from the numerator of the first fraction. IN this example It will be 48 / 4-3 / 4 \u003d (48-3) / 4 \u003d 45/4. And again it turned out the wrong fraction, which should be brought to the right one. To highlight the whole part, determine the first to 45 number, which is divided by 4 without a residue. This will be 44. If the number 44 is divided into 4, it turns out 11. So the whole part of the final fraction is equal to 11. In the fractional part, the denominator is also eliminated and from the numerator of the original incorrect fraction, the number that was divided into the denominator without the residue. That is, it is necessary out of 45 subtracts 44. So the numerator in the fractional part is 1 and 12-3 / 4 \u003d 11 and 1/4.
If one number is given an integer and one fractional, but its denominator is 10, then the second number is easier to translate into a decimal fraction, and then perform calculations. For example, it is necessary to fold an integer 12 and fractional number 3/10. If the number 3/10 is written in the form of a decimal fraction, it turns out 0.3. It is now much easier to add 0.3 to 12 and obtain 2.3 than to give a fraction to a common denominator, to produce calculations, and then select the whole and fractional parts from incorrect fraction. Even the simplest tasks with fractional numbers suggest that the schoolboy (or student) knows how to translate an integer in the fraction. These rules are too simple and easily remembered. But with the help of them, it is very easy to calculate fractional numbers.
Drobi.
Attention!
This topic has additional
Materials in a special section 555.
For those who are strongly "not very ..."
And for those who are "very ...")
The fractions in high schools are not very annoyed. For the time being. So far, do not come up with degrees with rational indicators and logarithms. And here .... You give, you give a calculator, and he all the complete scoreboard does not seem to. I have to think about thinking as in the third grade.
Let's figure out with the fractions finally! Well, how much can you get confused!? Moreover, it's simple and logical. So, what are the fractions?
Types of fractions. Conversion.
The fraraty is three species.
1. Ordinary fractions , eg:
Sometimes instead of horizontal screenshots, they put an inclined line: 1/2, 3/4, 19/5, well, and so on. Here we will often be this writing to use. The upper number is called numerator, Lower - denominator. If you constantly confuse these names (happens ...), tell me with the phrase expression: " ZZZZapumnney! ZZZZnamer - Vni zZZZy! "You look, everything and zzzzozomnikh.)
Chertochka that is horizontal that inclined means division top number (numerator) to the bottom (denominator). And that's all! Instead of a screw, it is quite possible to put a fission sign - two points.
When the division is possible, it must be done. So, instead of fractions "32/8", it is much more pleasant to write the number "4". Those. 32 Just divide by 8.
32/8 = 32: 8 = 4
I'm not talking about the fraction "4/1". Which is also just "4". And if it is not divided by a lot, we leave, in the form of a fraction. Sometimes there is a reverse operation to do. Make an integer fraction. But about this below.
2. Decimal fractions , eg:
It is in this form that will need to record the answers to the tasks "B".
3. Mixed numbers , eg:
Mixed numbers are practically not used in high school. In order to work with them, they must be translated into ordinary fractions. But it's necessary to be able to do! And then there will be such a number in a task and hang ... in an empty place. But we will remember this procedure! Slightly lower.
The most universal Ordinary fractions. With them and start. By the way, if there are all sorts of logarithms, sinuses and other beaks, it does not change anything. In the sense that all actions with fractional expressions are no different from action with ordinary fractions!
The main property of the fraction.
So let's go! To begin with, I will surprise you. All fraction transformation varieties is provided by one-sole property! It is called the main property of the fraci. Remember: if the numerator and denominator of the fraci multiply (divided) per and the same number, the fraction will not change. Those:
It is clear that you can write further before the formation. Sinuses and logarithms let you do not embarrass, we'll figure it out with them. The main thing is to understand that all these diverse expressions are one and the same fraction . 2/3.
And we need it, all these transformations? And how! Now you will see. To begin with, we will use the main property of the fraction for reducing fractions. It would seem that the thing is elementary. We divide the numerator and denominator for the same number and all things! It is impossible to make a mistake! But ... a person is creative creature. Make a mistake everywhere! Especially if you have to reduce the fraction of type 5/10, but a fractional expression with all sorts of beaks.
As properly and quickly cut the fraction, without making any extra work, you can read in a special section 555.
The normal student is not bothering the division of the numerator and the denominator on the same number (or expression)! He simply jumps all the same on top and bottom! Here and lighten typical error, LAP, if you want.
For example, you need to simplify the expression:
There is nothing to think here, you jump up the letter "A" from above and a twice from below! We get:
That's right. But really you divided all Numerator I. all danger on "A". If you are used to simply cross, then, you need, you can cross "A" in expression
and get again
What will be categorically incorrect. Because here all Numerator on "A" already not divide! It is impossible to cut this fraction. By the way, such a reduction is, GM ... a serious challenge to the teacher. This is not forgiven! Remember? When cutting, we need to share all Numerator I. all denominator!
Reducing fractions greatly facilitates life. It turns out somewhere you have fraction, for example 375/1000. And how now to work with her? Without a calculator? Multiply, say, fold, in a square to erect!? And if you don't be lazy, yes, it is accurate enough to cut five, and even five, and even ... while it is reduced, in short. We get 3/8! Much more pleasant, right?
The main property of the fraction allows us to translate ordinary fractions to decimal and vice versa without calculator! This is important to the exam, right?
How to translate fractions from one species to another.
With decimal fractions, everything is simple. As heard, it is written! Let's say 0.25. This is a zero whole, twenty-five hundredths. Yes, we write: 25/100. We reduce (divide the numerator and denominator on 25), we get the usual fraction: 1/4. Everything. It happens, and nothing is reduced. Type 0.3. These are three tenths, i.e. 3/10.
And if integers are not zero? Nothing wrong. We write down the entire fraction without any commas In the numerator, and in the denominator is what hearse. For example: 3.17. These are three integers, seventeen hundredths. We write in the numerator 317, and in the denominator 100. We get 317/100. Nothing is reduced, it means everything. This is the answer. Elementary Watson! Of all the told useful conclusion: any decimal fraction can be turned into an ordinary .
But the inverse transformation, ordinary to decimal, some without a calculator cannot do. But you must! How do you write to write on the exam!? Carefully read and master this process.
Decimal fraction than characteristic? She has in the denominator always It costs 10, or 100, or 1000, or 10,000 and so on. If your usual fraction has such a denominator, there are no problems. For example, 4/10 \u003d 0.4. Or 7/100 \u003d 0.07. Or 12/10 \u003d 1.2. And if in response to the task section "in" turned out 1/2? What will we write in response? There are decimal required ...
Remember the main property of the fraci ! Mathematics favorably allows you to multiply the numerator and denominator for the same number. For any, by the way! In addition to zero, of course. So applies this property to yourself! What can be multiplied by the denominator, i.e. 2 So that it become 10, or 100, or 1000 (smaller better, of course ...)? 5, obviously. Boldly multiply the denominator (this us it is necessary) by 5. But, then the numerator must be multiplied, too, for 5. This is already mathematics Requires! We obtain 1/2 \u003d 1x5 / 2x5 \u003d 5/10 \u003d 0.5. That's all.
However, the denominators are all sorts. Will come, for example, the fraction 3/16. Try, figure out here, on which 16 multiply, so that 100 it happens, or 1000 ... does not work? Then you can simply separate 3 to 16. Behind the lack of a calculator, you will have to divide the corner, on a piece of paper, as in junior grades. We get 0.1875.
And there are completely bad denominants. For example, a fraction of 1/3, well, do not turn into a good decimal. And on the calculator, and on a piece of paper, we will get 0,3333333 ... This means that 1/3 in an exact decimal fraction does not translate. Just as 1/7, 5/6 and so on. Many of them undeveloped. From here another useful conclusion. Not every ordinary fraction is translated into decimal !
By the way, that's helpful information For self-test. In the section "B" in response, you need a decimal fraction to record. And you have it, for example, 4/3. This fraction is not translated into decimal. This means that somewhere you made a mistake on the road! Return, check the solution.
So, with ordinary and decimal fractions figured out. It remains to deal with mixed numbers. To work with them, they must be translated into ordinary fractions. How to do it? You can catch a sixth grader and ask him. But not always the sixth grader will be at hand ... you have to. It's not hard. It is necessary a denominator of a fractional part to multiply by a whole part and add a fractional part numerator. It will be a numerator of the usual fraction. And the denominator? The denominator will remain the same. It sounds difficult, but in fact everything is elementary. We look an example.
Let in a challenge you with horror saw a number:
Calmly, without panic, we think. The whole part is 1. one. Fractional part - 3/7. Therefore, the denominator of the fractional part is 7. This denominator will be a denominator of an ordinary fraction. We consider the numerator. 7 Multiply with 1 (whole part) and add 3 (numerator of the fractional part). We get 10. It will be a numerator of an ordinary fraction. That's all. Even easier, it looks in a mathematical record:

Clear? Then secure success! Translate into ordinary fractions. You should work 10/7, 7/2, 23/10 and 21/4.
Reverse operation - Translation of incorrect fraction in a mixed number - in high schools is rarely required. Well, if so ... and if you are not in high schools - you can look into a special section 555. There, by the way, and about the wrong fraraty will learn.
Well, almost everything. You remembered the types of fractions and understood as Translate them from one species to another. The question remains: what for do it? Where and when to apply these deep knowledge?
I answer. Any example suggests necessary actions. If an example was mixed into a bunch of ordinary fractions, decimal, and even mixed numbers, we translate everything into ordinary fractions. It can always be done. Well, if it is written, something like 0.8 + 0.3, then I believe without any translation. Why do we need extra work? We choose that path the solution that is convenient us !
If in the task all decimal fractionsbut um ... angry some, go to ordinary, try it! You look, everything will work. For example, it will be in a square to erect a number 0.125. Not so easy if you did not pay off from the calculator! Not only you need to multiply the column, so think, where to insert comma! In mind it will not be exactly! And if you go to an ordinary fraction?
0.125 \u003d 125/1000. Reducing on 5 (this is for starters). We get 25/200. Once again by 5. We get 5/40. Oh, still cuts! Again on 5! We get 1/8. Easily erected into a square (in the mind!) And we get 1/64. Everything!
Let's summarize this lesson.
1. Fruit is three species. Ordinary, decimal and mixed numbers.
2. Decimal fractions and mixed numbers always You can translate into ordinary fractions. Reverse translation not always available.
3. Selecting the type of fractions to work with the task depends on this very task. In the presence of different species We fractions in one task, the most reliable - go to ordinary fractions.
Now you can take care. To begin with, translate these decimal fractions to ordinary:
3,8; 0,75; 0,15; 1,4; 0,725; 0,012
There must be such answers (in disorder!):
On this and end. In this lesson, we refreed in memory key moments for fractions. It happens, however, it is especially nothing to refreshing ...) If someone who has completely forgotten, or has not mastered ... the one can go into a special section 555. There all the foundations are detailed. Many suddenly understand everything Start. And decide the fraraty with the lea).
If you like this site ...
By the way, I have another couple of interesting sites for you.)
It can be accessed in solving examples and find out your level. Testing with instant check. Learn - with interest!)
You can get acquainted with features and derivatives.
That click on the buttons, and the task is made. As a result, you will have either an integer or a decimal fraction. The decimal fraction can work out with a long residue after. In this case, the fraction needs to round up to a certain, discharge you need, using rounding (numbers up to 5 are rounded down to the smaller side, from 5 inclusive and more - in the most side).
If the calculator is at hand not, but will have. Write a piece of fractions with a denominator, between them a corner, meaning. For example, translate the fraction 10/6. To begin 10, divide by 6. It turns out 1. Record the result in the corner. Multiply 1 to 6, it turns out 6. Delete 6 out of 10. It turns out the residue 4. The residue must be divided again by 6. Extract to 4 digit 0, and divide 40 to 6. It turns out 6. Record 6 to the result, after the comma. Multiply 6 to 6. It turns out 36. Delete 36 out of 40. It will turn out again the residue 4. Next, you can not continue, since it becomes obvious that the result will be the number 1.66 (6). Round this fraction to the discharge that you need. For example, 1.67. This is the final result.
Related article
Sources:
- translation of fractions with an integer
The fractions are needed to designate numbers that consist of one or more parts of the unit. The term "fraction" occurred from the Latin Fractura, which matters "crushing, breaking out." Ordinary and decimal fractions differ. At the same time, in ordinary fractions, the unit can be divided into any number of parts, and in decimal - this amount must be more than 10. Any fraction may have both ordinary and decimal.

You will need
- To count the result you will need a calculator or sheet and handle.
Instruction
So, to start take ordinary fraction And divide it into parts. For example, 2 1 \\ 8, in which 2 is a whole part, and 1 \\ 8 fraction. It can be seen from it that the number was divided into 8, but they took only one. The part that was taken, the numerator, and the number of parts on which they divide is the denominator.
note
Often there are fractions that cannot be completely translated into decimal. In this case, rounding comes to the rescue. If you want to round up to thousands, then look at the fourth after the comma. If it is less than 5, write in response, the first three digits after the comma unchanged, otherwise it is necessary to add a unit to the last digit of the three. For example, 0, 89643123 can be written as 0,896, but 0, 89663123 - 0.897.
If you calculate the result manually, before dividing the fraction is better to reduce as much as possible, as well as allocate entire parts from it.
Sources:
- how to translate fraci
Fraction It is one of the elements of the formula, to enter which in the Word text processor there is a Microsoft Equation tool. With it, it is possible to introduce any complex mathematical or physical formulas, equations and other elements that include special characters.

Instruction
To start the Microsoft Equation tool, you must go to the address: "Insert" -\u003e "Object", in the dialog box that opens, on the first tab from the list you need to select Microsoft Equation and click "OK" or click on the selected paragraph. After starting the editor, you will open the toolbar and the input box will appear: a rectangle in dotted. The toolbar is divided into sections, in each of them there is a set of signs of actions or expressions. When you click on one of the sections, the list of tools in it will unfold. From the opening list, you must select the desired symbol and click on it. After selecting, the specified symbol will appear in the selected rectangle in the document.
The section in which elements are located for writing fractions are in the second line of the toolbar. When you hover the mouse cursor, you will see a prompt "patterns of fractions and radicals". Click the section once and expand the list. In the dropping menu there are patterns for fractions with horizontal and oblique. Among the options that appeared, you can choose the one that is suitable for your task. Click on the desired version. After pressing, in the input field, which opened in the document, a symbol of the fraction and space for entering the numerator and the denominator framed by the dotted line will appear. The default cursor is automatically installed in the field for entering the numerator. Enter a numerator. In addition to figures, you can also enter characters, letters or signs of action. They can be entered both from the keyboard and from the corresponding sections of the Microsoft Equation toolbar. After the water of the numerator, pressing the Tab key, go to the denominator. You can go and clicking the mouse in the field for entering the denominator. As soon as written, click the mouse pointer anywhere in the document, the toolbar closes, entering the fraction will be completed. To edit, double click on it with the left mouse button.
If when you open the "Insert" menu -\u003e Object, you did not find the Microsoft Equation tool in the list, it must be installed. Run the installation disk, disk image or Word distribution file. In the installer window that appears, select "Add or remove components. Adding or deleting individual components "and click" Next ". In the next window, mark the "Extended Application Setup" item. Click "Next". In the next window, find the list of Office Tools and click on the plus side on the left. In the unfolded list, we are interested in the item "Editor formula". Click on the icon next to the inscription "Formula Editor" and, in the menu that opens, click "Run from Computer". After that, click "Update" and wait until the installation of the required component passes.
The decimal fraction consists of two parts, which are separated by commas. The first part is a whole unit, the second part is dozens (if the number after the semicolon is one), hundreds (two numbers after a comma, as two zero in a hundred), thousands of itd. Let's look at the examples of decimal fractions: 0, 2; 7, 54; 235,448; 5.1; 6.32; 0.5. All this is decimal fractions. How to translate a decimal fraction in ordinary?
Example of the first
We have a fraction, for example, 0.5. As already mentioned above, it consists of two parts. The first number 0 shows how many units of the fraction. In our case, they are not. The second number shows dozens. The fraction is even read by zero as many as five tenths. Decimal number translate into fraction Now it's not work, we write 5/10. If you see that the numbers have a common divider, you can reduce the fraction. We have this number 5, sharing both parts of the fraction on 5, we get 1/2.
An example of the second
Take a more complex fraction - 2.25. It is read like that - two whole and twenty-five hundredths. Pay attention - hundredths, since the numbers after the semicolons are two. Now you can translate into an ordinary fraction. Record - 2 25/100. Whole part - 2, fractional 25/100. As in the first example, this part can be reduced. A common divider for numbers 25 and 100 is the number 25. Note that we always select the largest common divisor. Dividing both parts of the fracted on the nodes, received 1/4. So, 2, 25 is 2 1/4.
Example Third
And to secure the material, we take the decimal fraction of 4,112 - four whole and a hundred twelve thousandths. Why thousands, I think clearly. We write now 4 112/1000. According to the algorithm, we find nodes of numbers 112 and 1000. In our case, this is the number 6. We get 4 14/125.
Output
- We divide the fraction on the whole and fractional parts.
- We look at how many digits after the comma. If one is dozens of two - hundreds, three-thousandthly yttr.
- Record the fraction in ordinary form.
- Reducing the numerator and denominator of the fraction.
- Record the resulting fraction.
- We carry out the check, we divide the upper part of the fraction on the bottom. If there is a whole part, add to the resulting decimal fraction. It turned out the original option - wonderful, it means you did everything right.
At the examples, I showed how to transfer a decimal fraction to ordinary. As you can see, make it very easy and simple.
Materials for fractions and study sequentially. Below for you detailed information with examples and explanations.
1. Mixed number in an ordinary fraction.We write to general number:
We remember a simple rule - the whole part multiply on the denominator and add a numerator, that is:

Examples:

2. On the contrary, an ordinary fraction in a mixed number. * Of course, it is possible to make it only with the wrong fraction (when the numerator is more denominator).
With the "small" numbers no action, in general, and do not need to be done, the result "can be seen" immediately, for example, fractions:

* Read more:
15:13 \u003d 1 residue 2
4: 3 \u003d 1 residue 1
9: 5 \u003d 1 residue 4
But if the numbers are more, then without computation can not do. Here everything is simple - we divide the corner the numerator to the denominator until the balance does not work out less divisor. Division scheme:

For example:
* Numerator with us is a divisible, the denominator is a divider.

We get a whole part (incomplete private) and the residue. We write - the whole, then fraction (in the numerator of the residue, and the denominator leave the same):
3. Decimal translate into ordinary.
Partially in the first paragraph, where they told about decimal fractions, we already touched it. As hearing and write. For example - 0.3; 0.45; 0.008; 4.38; 10.00015
The first three fractions with us without a whole part. And the fourth and fifth have it, we will transfer them to ordinary, it is already able to do it:

* We see that the fraction can also be reduced, for example 45/100 \u003d 9/20, 38/100 \u003d 19/50 and others, but we will not do this here. By contraction, a separate point is awaiting you below, where everything will be described in detail.
4. Ordinary translate into decimal.
Not everything is so simple. For some fractions are immediately visible and clear what to do with it so that it becomes decimal, for example:
We use our wonderful basic property of the fraction - multiply the numerator and denominator, respectively, 5, 25, 2, 5, 4, 2, we obtain:

If there is a whole part, then nothing is difficult:

We multiply a fractional part according to 2, 25, 2 and 5, we obtain:
And there are those for which without experience and not to determine that they can be translated into decimal, for example:
What numbers multiply the numerator and denominator?
Here again, a proven method comes to the rescue - dividing the corner, the method of universal, they can always be used to transfer ordinary fractions to the decimal:

So you can always determine whether the fraction is translated into decimal. The fact is that not every ordinary fraction can be translated into decimal, for example, such as 1/9, 3/7, 7/26 are not translated. And what then it turns out for the fraction when dividing 1 to 9, 3 to 7, 5 to 11? I answer - an infinite decimal (spoke about them in paragraph 1). We divide:

That's all! Success to you!
Sincerely, Alexander Krutitsky.