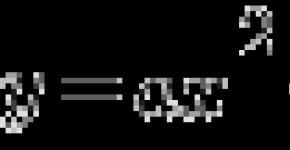Do you need a gap between vapor barrier and insulation on the walls. Woodering of a wooden house: typical errors Wall insulation under siding without a ventzazor
In this article, I will consider the ventilation issues of inter-space and about the connection of this ventilation and insulation. In particular, I would like to understand what a ventilation gap is needed than it differs from the air, what is its functions and whether the clearance in the wall can perform heat-insulating function. This question becomes quite recently recently and causes many misunderstandings and questions. Here I give my private expert opinion, based only on personal experience and anything else.
Denial of responsibility
Already writing an article and rereading it once again I see that the processes occurring during the ventilation of the interconnect space, much more difficult and multifaceted than I described. But I decided to leave like this, in a simplified version. Especially meticulous citizens, please write comments. We will complicate the description in working order.
The essence of the problem (subject part)
Let's deal with the subject matter and agree on the terms, and it may turn out that we are talking about one thing, but we mean absolutely opposite things.
This is our main subject. The wall may be homogeneous, for example, brick, or wooden, or foam concrete, or cast. But the wall may consist of several layers. For example, the wall itself (brickwork), a layer of insulation-thermal insulator, a layer of external finish.
Air gap
This is a layer of wall. Most often it is technological. It turns out by himself, and without it, it is either impossible to build our wall, or it is very difficult to do it. As an example, you can cite such an additional element of the wall as the leveling frame.
Suppose we have a freshly built wooden house. We are hunting to separate him. We first apply the rule and make sure the wall is a curve. Moreover, if you look at the house from released, you see a completely decent house, and how we apply a rule to the wall - it becomes clear that the wall is a horror curve. Well ... nothing can be done! It happens with wooden houses. Wall align the frame. As a result, space filled with air is formed between the wall and the outer finish. Otherwise, without a frame, to make a decent exterior finish of our house will not work - the angles will "erupt". As a result, we get air gap.
We remember this important feature of the term under consideration.
Ventilation clearance
This is also a layer of the wall. It looks like an air gap, but has a destination. Specifically, it is designed for ventilation. In the context of this article, ventilation is a number of measures aimed at the injection of moisture from the wall and maintaining it dry. Can this layer combine the technological properties of the air gap? Yes, maybe about this, in essence, this article is written.
Physics processes inside the wall condensation
And why dry the wall? She is what, wait? Yes swing. And in order for it to get wet, it does not need to be watered from the hose. It is enough to drop the temperature from the day heat to night coolness. The problem of wetting the wall, all of its layers, as a result of the condense of moisture could be irrelevant in the frosty winter, but here the heating of our house is released on the scene. As a result of what we slept our homes, warm air tends to get out of the warm room and the moisture condensation in the thickness of the wall occurs again. Thus, the relevance of drying wall persists at any time of the year.
Convection
Please draw attention to the fact that the site has a good article about condensate theory in the walls
Warm air tends to climb up, and cold drop down. And it is very regrettable, because we, in our apartments and houses, do not live on the ceiling, where warm air is going, and on the floor where it is going to cold. But I seem to be distracted.
It is completely impossible to get rid of convection. And it is also very regrettable.
But let's consider a very useful question. What convection in a wide gap differs from the same convection in a narrow? We already understood that the air in the gap moves in two directions. On the warm surface, it moves up, and on the cold descends down. And here I want to ask a question. What happens in the middle of our gap? And the answer to this question is quite complicated. I believe that the air layer directly at the surface moves as quickly as possible. He pulls the air layers that are nearby. As far as I understand, this happens because of friction. But the friction in the air is rather weak, so the movement of the neighboring layers is much less fast than the "wall" but still there is a place where the air, moving up, comes into contact with air moving down. Apparently in this place where there are multidirectional streams, something like twists occurs. Drugs are the weaker than lower the flow rate. With a sufficiently wide gap, these swirls may generally be absent or completely invisible.
But if the gap is 20 or 30 mm? Then the swirls may be stronger. These twists will not only move streams, but also to brake each other. It seems that if you do an air gap, then you need to strive to make it thinner. Then two multidirectional convection fluxes will interfere with each other. And we need to.
Consider some fun examples. First example
Let us have a wall with an air gap. Clearance deaf. The air in this gap does not have connection with air outside the gap. On the one hand the wall is warm, on the other cold. Ultimately, this means that the internal parties in our gap differ in the same temperature. What happens in the gap? On the warm surface of the air in the gap rises up. On cold goes down. Since this is the same air, then a circulation is formed. In the process of this cycle, heat is actively transferred from one surface to another. And actively. This means that strongly. Question. Useful function performs our air gap? Looks like no. It seems that he is actively cooled by us. Is there anything useful in this our air gap? Not. It seems that nothing useful in it. In principle, and forever.
The second example. 
Suppose we did at the top and at the bottom of the holes so that the air in the gap communicates with the outside world. What have we changed? And the fact that now there is no cycle. Either it is, but there is also a sacrifice and air outlet. Now the air heats up from the warm surface and, possibly partially, flies out (warm), and the street comes from the bottom to its place. Is this good or bad? Is it very different from the first example? At first glance it becomes even worse. Heat goes outside.
I note the following. Yes, now we warm the atmosphere, and in the first example we gotten the trim. How much is the first option worse or better than the second? You know, I think it is about the same options in your harmfulness. This is my intuition to me, so I, just in case, do not insist on my right. But in our second example, we turned out one useful feature. Now our gap has become an air ventilation, that is, we added a function of carrying out wet air, and it means that the drying of the walls.
And in the ventilation gap convection or there the air is moving in one direction?
Of course have! Similarly, warm air moves up, and cold goes down. Just this is not always the same air. And harm from convection is also there. Therefore, the ventilation clearance is exactly the same as the air, do not need to be done wide. The wind in the ventilation gap we do not need!
And what is good in the drying wall?
Above, I called the heat transfer process in the air gap active. By analogy, I will name the process of heat transfer inside the wall passive. Well, maybe such a classification is not too strict, but my article, and in it I have the right to such disgrace. So here. The dry wall has thermal conductivity significantly less than raw. As a result, the heat will be slower to reach the inside of a warm room to a malicious air gap and to endure the outside will also become less. Banally convection will slow down, because the left surface of our gap will not be so warm. The physics of increasing the thermal conductivity of the raw wall is that the pair molecules are transmitted during collisions with each other and with air molecules greater than the energy than simply air molecules when weaning with each other.
How is the Wall ventilation process?
Well, just here. Moist is performed on the wall surface. The air moves along the wall and takes moisture from it. The faster the air moves, the faster the wall slips, if it is wet. It's simple. But more interesting.
What is the speed of the wall ventilation walls? This is one of the key questions of the article. Having answered him, we will understand a lot in the principle of building ventilation gaps. Since we are not dealing with water, but with steam, and the latter most often represents just warm air, we need to get this warmer air from the wall. But reducing warm air, we cool the wall. In order not to cool the wall, we need such ventilation, such a speed of air movement, in which the steam would be assigned, and a lot of heat from the wall would not take away. Unfortunately, I can't say how many cubes per hour should pass through our wall. But I can imagine that there is not much at all. A certain compromise is needed between the benefit from ventilation and harm from heat removal.
Intermediate conclusions
It's time to bring some results, without which I would not like to move on.
There is nothing good in the air gap.
Yes indeed. As shown above, a simple air clearance does not bear any useful functions. This should mean that it should be avoided. But I always mildly treated such a phenomenon as an air gap. Why? As always for a number of reasons. And by the way, I can justify each.
First, the air clearance is a technological phenomenon and without it can simply do not do.
Secondly, if you do not do, then why should I unnecessarily intimidate honest citizens?
And thirdly, harm from the air gap does not occupy the first places in the rating of damage to thermal conductivity and construction flats.
But please remember the following, in order to avoid future misunderstandings. The air clearance never and under any circumstances can carry the function of reducing the thermal conductivity of the wall. That is, the air clearance cannot make the wall warmer.
And if you do a gap, then you need to do it already, not wider. Then convection streams will prevent each other.
At the ventilation gap, the useful function is only one.
It is so sorry. But this single function is extremely just vital. Moreover, it is simply impossible without it. In addition, then we will consider the options for reducing harm from air and ventilation gaps while maintaining positive functions of the latter.
Ventilation gap, in contrast to air, can improve the thermal conductivity of the wall. But not due to the fact that the air in it has low thermal conductivity, and due to the fact that the main wall or layer of the heat insulator becomes land.
How to reduce harm from air convection in the ventilation gap?
Obviously, to reduce convection - means to prevent it. As we have already found out, we can prevent convection, encountered two convection flows. That is, the ventilation clearance is completely narrow. But we can also fill out this clearance with something that would not stop convection, but it would be significantly slowed down. What could it be?
Foam concrete or gas silicate? By the way, the foam concrete and gas silicate are quite porous and I am ready to believe that there is a weak convection in the block from these materials. On the other hand, we have a high wall. It can be 3 and 7 and more tall meters. The greater the distance you have to go through the air, the more porous material should be. Most likely foam concrete and gas silicate are not suitable.
Especially the tree is not suitable, ceramic brick and so on.
Styrofoam? Not! Polyfoam is also not suitable. It is not too easy to penetrate the water vapor, especially if they need to pass more than three meters.
Bulk materials? Type of ceramzit? Here, by the way an interesting offer. Probably can work, but the ceramzite is too uncomfortable in use. Dust, wakes up and all that.
Wool low density? Yes. I think cotton wool is a very low density - the leader for our purposes. But wool is not produced by a very thin layer. You can find the canvas and plates at least 5 cm thick.
As practice shows, all these arguments are good and useful only in theoretical plan. In real life, you can go much easier and prosaus, what I will write about in a pathocence in the next section.
The main result, or what, after all, do in practice?
- During the construction of a personal house, it is not necessary to specifically create air and ventilation gaps. You will not achieve a lot of benefit, but you can apply harm. If on the construction technology you can do without clearance - do not make it.
- If it is impossible to do without the gap, then you need to leave it. But it is not necessary to make it wider than the circumstances and common sense.
- If you got an air gap, should it be adjusted (turning) it to ventilation? My advice: "Do not bother on this and act in circumstances. If it seems that it is better to do, or just want, or this is a fundamental position - then do ventilation, but not - leave the air. "
- Never, under no circumstances, do not use for the stability of the external finishing materials less porous than the materials of the wall itself. This refers to rubberoid, polystrance and in some cases to foam (expanded polystyrene) and still to polyurethane foam. Note, if careful vaporizolation is arranged on the inner surface of the walls, then the failure to comply with this item will not harm other reservoir of funds.
- If you make a wall with external insulation, then use cotton and do not make any ventilation gaps. Everything will be fine through your cotton wrestling. But in this case, it is necessary to previre the access of the air to the ends of the insulation from below and from above. Or just on top. It is necessary in order for convection, though weak, but was.
- And what if the house on technology is finished outside the waterproof material? For example, a framework house with an OSB external layer? In this case, you need to either provide access to the air in the interconnect trap (bottom and above), or provide for vaporizolation indoors. I like the last option much more.
- If vaporizolation was provided when the internal finishing device was provided, is it worth doing ventilation gaps? Not. In this case, the ventilation of the wall is unnecessary, for it does not have access to moisture from the room. No additional thermal insulation ventilation gaps provide. They only dried the wall and that's it.
- Windproof. I believe that windproof is not needed. The role of windproof is remarkably performed by the external finish itself. Lining, siding, tile and so on. Moreover, again, my personal opinion, the cracks in the clap are not so helping the blowing of heat to use the windproof. But opinion is my personally, it is quite controversial and I do not sign on it. Again, the windproof manufacturers also want to eat. The rationale for this opinion I, of course, is and I can lead it for those interested. But in any case, it must be remembered that the wind cool the walls very much, and the wind is a very serious reason for concern to those who want to save on heating.
ATTENTION!!!
To this article
there is a comment
If the clarity did not arise, then read the answer to the question of a person who, too, not everything became clear and he asked me to return to the topic.
I hope that the above article responded to many questions and made clarity
Dmitry Belkin
The article was created on January 11, 2013.
The article was edited on 26.04.2013
Similar materials - select by keywords
| 7 years ago | Tanya (Expert BuilderClub) To begin with, I will describe the principle of work properly made insulated roof, after which it will be easier to understand the reasons for the appearance of condensate on vapor barrier - pos.8. If you look at the drawing above - "Insulated roof with slate", then parosolation Ensumed under the insulation in order to delay the water vapors from the inside of the room, and thereby protect the insulation from wetting. For complete tightness, the joints of vapor barrier are sampled by a vaporizolation ribbon. As a result, the pairs accumulate under vaporizolation. In order for they weathered and not soaked internal cladding (for example, GLC), 4 cm gap is allowed between vaporizolation and inner cladding. The gap is provided by laying the crate. From above the insulation protects against wetting waterproofing material. If steam barrier under the insulation is laid on all the rules and perfectly gumitichna, then vapors in the insulation itself will not be and, accordingly, under waterproofing too. But in case, if the vaporizolation is suddenly damaged when laying or during the operation of the roof, the ventilation gap is made between waterproofing and insulation. Because even the slightest, not a noticeable eye, damage to vapor barrier allows water vapors to penetrate the insulation. Passing through the insulation, the pairs accumulate on the inner surface of the waterproofing film. Therefore, if the insulation will be laid close to the waterproofing film, it will wet from water vapor accumulated under waterproofing. To prevent this wetting of the insulation, as well as so that the pairs are weathered, the ventilation gap 2-4 cm should be weathering between waterproofing and insulation. Now we will analyze the device of your roof. Before you laid the insulation 9, as well as vaporizolation 11 and GLC 12, water vapors accumulated under vaporizolation 8, there was free air access and they were weathered, so you did not notice them. Up to this point, you have essentially the correct design of the roof. As soon as you laid an additional insulation of 9 closely to the existing steam barrier 8, water vapors have nowhere to go more, except to be absorbed into the insulation. Therefore, these pairs (condensate) have become noticeable to you. A few days later, you laid steam barriating 11 and sewed GLK 12. If you laid down the lower vapor insulation 11, you laid down all the rules, namely, there are at least 10 cm with a minimum of 10 cm and glued all the joints with a steamproof ribbon, then water vapors will not penetrate the roofing and not Will soak insulation. But until the laying of this lower vaporizolation 11, the insulation 9 was supposed to dry. If he did not have time to dry, then the likelihood of formation is high in the mold insulation. The same threatens to insulation 9 in the case of the slightest damage to the lower vaporizolation 11. Because a pair of nowhere will go beyond how to accumulate under vaporiozolation 8, to soak at thermal player and contribute to the formation of fungus in it. Therefore, in a good way, you need to remove vaporizolation 8, and there are 4 cm ventilation gap between vapor insulation 11 and GLK 12, otherwise GLC will wet and with time to bloom. Now a few words about waterproofing. The first, the runneroid is not intended for waterproofing the pitched roofs, it is a bitumenting material and in a strong heat, bitumen simply stalks to the sink of the roof. Simple words - the ruberoid will not last long in the pitched roof, it is difficult to even say how much, but I do not think that more than 2-5 years. The second, waterproofing (runner) is not stored correctly. Between it and insulation should be a ventilation gap, as described above. Considering that the air in the underfloor space moves from the sink to the skit, the ventilation gap is provided by either due to the fact that the sling is higher than the layer of the insulation laid between them (you in the figure rafter as the same time), or by laying along the rafter controls. You have a waterproofing laid on the crate (which, unlike the counterclaim, lies across the rafted), so the whole moisture that will accumulate under waterproofing will pump the crate and it will not last for a long time. Therefore, in a good way, on top of the roof, too, it is necessary to redo it: replace the rubberoid on the waterproofing film, and to put it on the rafter (if they protrude above the insulation at least 2 cm) or to a counterclaim laid along the rafted. Specify clarifying questions. reply |
When insulation of the walls of a wooden house, many make at least one of the four most insidious errors that lead to the rapid rotting of the walls.

It is important to understand that the inner warm space of the house is always rich in pairs. Couples are found in the exhaled air of the air, it is formed in large quantities in the bathrooms, kitchens. At the same time, the higher the air temperature, the greater the amount of steam it can hold. When the temperature decreases, the ability to hold moisture in the air is reduced, and the excess falls in the form of condensate on colder surfaces. What will lead to the moisture of wooden structures - it is not difficult to guess. Therefore, I want to designate four major errors that can lead to a sad result.
Wall insulation from the inside is extremely undesirableSince the dew point will move inside the room, which will lead to moisture condensation on a cold wooden wall surface.
But if it is the only available version of insulation, then it is necessary to take care of the presence of vaporizolation and two ventilation gaps.

In the ideal case, "pie" walls should look like this:
- interior decoration;
- Ventilation gap ~ 30 mm;
- high-quality vaporizolation;
- insulation;
- membrane (waterproofing);
- the second ventilation gap;
- Wooden wall.
It should be remembered that the thicker layer of the insulation, the smaller the outer and internal temperature drops will be required to form condensate on a wooden wall. And in order to provide the necessary microclimate between the insulation and the wall, several ventilation holes (trunks) with a diameter of 10 mm are drilled into the bottom of the wall at a distance of about one meter from each other.
If the house is located in the warm regions, and the temperature drops inside and outside the room does not exceed 30-35 ° C, then the second ventilation clearance and the membrane theoretically can be removed, putting the insulation directly on the wall. But to say for sure, it is necessary to calculate the position of the dew point at different temperatures.
Using vapor insulation when insulation outside
Placing vapor barrier on the outer part of the wall is a more serious error, especially if the walls indoors are not protected in this very vapor barrier.
The bar absorbs moisture out of air well, and if it is waterproofing from one side - wait for troubles.
The correct option of "cake" with the outer insulation looks like this:
Interior decoration (9);
- vapor insulation (8);
- Wooden wall (6);
- insulation (4);
- waterproofing (3);
- ventilation gap (2);
- Exterior finish (1).
Use of low vapor permeability insulation
The use of a low vapor permeability insulation when the walls are insulated outside, for example, plates made of extruded polystyrene foam, will be equivalent to accommodation on the wall of vapor polypoles. Such material is a ban of moisture on a wooden wall and will contribute to rotting.
On wooden walls placed insulation equivalent or greater vapor permeability than the tree. It is perfectly suitable for various mineral wool insulation and eco-art.
Lack of ventilation gap between insulation and outer decoration
The pairs that penetrate the insulation will be able to effectively remove from it only under the condition of the pre-permeable ventilated surface, which is the moisture protection membrane (waterproofing) with a ventilation gap. If it is close to it, the same siding, the yield of vapors will be very difficult, and the moisture will be condensed either inside the insulation, or, even worse, on a wooden wall with all the ensuing consequences.
You may also be interested:
- 8 errors in the construction of frame houses (photo)
- The cheaper to get the house (gas, firewood, electricity, coal, diesel)
Article assessment:
Warming a stone cotton house from a bar from the inside with only vaporizolation to make vapor barrier with the outside where sofa on the attic floor
Put the hand on the heart, the house of solid wood is better not to warm at all. High-quality massive logs and timber, being preserved in natural form, provide an optimal microclimate in the house. The tree, unlike most other wall materials, "breathes", in this one of his main advantages. However, in the case of insufficient thickness of wooden walls, or if the house has already stood a lot of years and the login needs to be protected from external influences, outdoor insulation and trim are justified measures, help reduce heating costs and extend the life of a destroying tree. The most practical material for outdoor clamping a wooden house is vinyl siding. It is inexpensive, the service life is half a century and more, easily mounted, is repaired without problems. House, covered with siding, looks neat. We will tell you how to make the right warming of a wooden house under siding.
To improve thermal insulation, without worsening the microclimate and not harm the structure, you need to understand the specifics of the construction and operation of a wooden house. Let's start with theory: a little about woodworking and a bit of building physics.
Wood moisture and harmful mushrooms
We all know how quickly amazed by mold mushrooms wood, constantly in a wet state. The loss of material strength comes in a matter of months, and for the year or two logs, in the thickness of which favorable conditions for the life of mushrooms are created, can turn into a duch. The basic condition for growing mold is a sufficient amount of moisture. Accordingly, to keep the wooden house for many years, its walls and other structures need to protect against the convergence. The absolute humidity (the ratio of the mass of water for the weight of absolutely dry wood) of the freshly dredged forest of coniferous rocks reaches 90%, the cut before installation is 25-35%, a wooden house, in normal conditions that have defined during the year - 10-20% depending on the season. At the same time, the fungal lesion of the wood begins to develop from a moisture level of 22%, which is only a little higher than the natural state of the cut. By the way, the same conditions are suitable in order for the brices to settle the beetle-tree.
It is important to know: in no case cannot be allowed to moisten the wood - the main reason for its destruction.
The mooring of the tree leads to its rotting
Where in the tree penetrates moisture
It is believed that moisture in the walls of a wooden house falls outside with oblique rain, fogs and snow. The precipitate really moisturize the walls. But raw weather lasts not so long, the sun and especially the wind contribute to the rapid removal of excess moisture. The attentive reader will say: the average annual air humidity on the street is 78% (data for the Moscow region), and in the house hesitates within 40-70% - it means that moisture on the street is greater and it should penetrate outside inside.
But actually it is not. The fact is that climatologists operate with relative humidity, this is the ratio of the lobe of water vapor to the maximum possible taking into account the temperature. And the colder the air, the less moisture it can contain. To understand the actual moisture content in the air, the values \u200b\u200bof absolute humidity use in construction physics. In the summer, when the street is about the same on the street and in the house, the humidity is similar. But in winter and in the off-season painting is completely different. For example, at a temperature outside -20 ºС and the relative humidity of the outer air in 80%, an absolute value is 0.6 g / m3, and within a house at 20 ºС and a relative humidity of 60% absolute will be 10.4 g / m3. Accordingly, the actual moisture content in the air inside the house above is 17 times. It is not surprising that wood, like a pump, absorbs moisture from the inside and gives it out through the micropores and joints between the logs, filled with flax, moss, jute, either by a different "breathable" interventional insulation.
It is important to know: most of the year, with the exception of a warm period, the water vapor penetrates the wood from the inside of the house and seeks to go outside, the amount of it is the greater, the colder on the street and warmer in the house.
Ventilation - vaporizolation - windscreen
We found out that the prerequisite for preserving a log and a healthy microclimate in it is that the insulation of the walls of a wooden house under siding should not prevent the free output of the water vapor outward.
Modern designs in wooden (and not only) house-building implies the widespread use of vapor insulation and windproof films. The first is absolutely sealed, do not miss the air or steam. The second repel water drops, but do not prevent the penetration of water vapor. In frame houses, the wall from the inside is closed with vapor barrier, thereby excluding the penetration of moisture from the premises in the insulation and wooden structures. Outside the "burst" windproof walls: it counteracts the blowing of the insulation, does not give water drops outside to fall inside (condensate can fall on the inner surface of the siding), while the water steam freely comes out. Since the insulation is closed with a finishing material (in our case, it is siding), there must be a ventilation gap between the insulation and trim, so that excessive moisture can leave the wall design.
It is important to know: ventilation gap - a mandatory element of the design of insulation for siding and other shearing materials.
Many shabashniki, Internet sources, construction companies managers and even professional builders argue that it is necessary to act in the same way when the house is insulated from solid wood. That is, the first layer, on brothers, steamproofing is stretched, then the insulation, on top of the windproof, completes the design of the ventilation and finishing material, siding in our case. At the same time, it is not taken into account that the moisture, seeking the outside, will surpass the vapor barrier, the moisture in the area adjacent to vapor barrier will increase, when the dew point occurs, condensate will fall. Conditions for germination of fungal dispute will be created, and from the inside we will not note the resulting destruction of wood for a long time.

The windproof film (diffusion membrane) has many micro-rectacles, at the expense of what pairs passes, at the same time, water drops are rolled from the material.
Eternal question: What to do?
We support the point of view of those specialists in building physics and technologists working in the field of wooden house-building, which vaporizoation with the insulation of a wooden house is not needed. The only case when the placement of vapor barrier between the carrier wall and the insulation can be justified - the house (cottage) is used seasonally, in winter it is rarely either in the premises the minimum temperature is maintained and they are well ventilated. With this mode, the temperature difference and, accordingly, absolute humidity outside and inside is low. For the house where people live constantly, there are internal sources of moisture (people's breath, couples from kitchen scenes and a soul, moisture from raising home plants), vaporizolation, rather, will harm than the benefit. You can not always do without a film, especially if the brica is uneven, and the insulation is too soft or in general flowing. In this case, you can pave windproofing as a limiting material between the wall and design of insulation under siding (with the greatest value of steaming), construction cardboard, kraft paper and even served your spunbond bed.
As a counterproof, the lack of vaporizolation supporters of its placement say that the insulation unprotected from the penetration will moisturize and its heat engineering characteristics will deteriorate. Alas, they are right. But the ventilation gap contributes to the withdrawal of moisture, and a relatively small (5-15%) drop in thermal protection properties is a forced victim in the struggle for the durability of the building.
It is important to know: vaporizoation with the insulation of a wooden house in which they live year-round, not needed.

So you can not do if the house is having year-round! Walls, "woven" in Pergamine, replete and become defenseless before the defeat of mold mushrooms
Material for frame and "Right" insulation
For a frame, only smooth wooden bars should be used, preferably antiseptic. Steel profiles that recommend applying "sofa" wizards are freezing, besides, they are condensate, which does not benefit to the insulation, nor the walls.
The cross section of the bars must correspond to the thickness of the insulation, for mineral wool, it is usually 5 cm. Accordingly, the bars - 5x5 or 4x5 cm. The recommended value of the ventilation is 4-5 cm, therefore, for the counterbasion that ensures the required distance between insulation and siding, you can use The same material.
The insulation must be vapor permanent and light. The most affordable one-west mineral wool mats, you should not use soft rolls, they will eventually give shrinkage in the wall. Ideal for a wooden house, an eco-friendly, very durable, but alas, the sceneled material - flax and hemp mats. Between the wall and windshield, you can float cellulose wool, wool waste. Repeat, the main thing for the insulation is vapor permeability. Minvata can be located in two layers (10 cm) or one (5 cm). What should be the overall layer of insulation, decide on the basis of the climatic conditions and the thickness of the existing walls.

Linen mats have much longer fibers than mineral wool, so better and longer hold the form
Technology of work production
The technology of insulation of a wooden house for siding is pretty simple, perform such work under the power of any "hand" man.
- The distance between the bars should not exceed 60 cm, better so that it is equal to the width of the insulation, for mineral wool it is 50 cm.
- The first level of bars is recommended to fix vertically. The second, if the insulation is placed in two layers - horizontally. The counterfear, to which siding will be directly attached - vertically.

Frame for warming of a minister of Minvata in two layers.
- On the uneven walls of the bars it is convenient to mount with perforated heavy-mounted heavy-mounted suspension. Thoughtful, but preferable from the point of view of heat engineering will be the traditional method: adjust the distance from the wall with the lining of wooden bosses. Screws will fix the frame better than nails.

Options for the framework of the frame and insulation under siding.
- If the mats of mineral wool are too soft, we recommend to mount one or two horizontal jumpers in each vertical section, it will reduce the drawdown of the material.
- Nashiva frame and filling the gaps between its elements insulation, fasten the windproof, on top of it - counterbuch.

Frame filled with insulation, the next stage - windscreen
- Finishing work - the cover of a wooden house siding.

"Right" design of the Wall insulation for siding with a double layer of Minvati.
A free air current must be provided in the ventilated gap. To do this, in the outer trim below and at the top of the wall leave slots (closed with mesh from mice and insects) or insert the lattice siding panel.
It is important to know: ventilation holes should be located in the lower and upper part of the walls of the walls.
Not everyone has the opportunities and the necessary skills to perform similar works. If there is no confidence in your abilities, it is better to entrust the insulation of your own home and the trimming of his siding to experienced masters.
Video: Wooden house - than to seize and how to insulate
Bridges of the cold They call the sections of the enclosing structures of the building through which the greatest occur, leading to a variety of negative consequences. Today we will tell about how to prevent the appearance of cold bridges in the structures of the insulated (indulgent).
Cold bridges in the structures of the insulated pitched roof are caused by many problems:
- First, they reduce the effectiveness of the heat-preserves of the building, which increases the consumption of energy to increase, which, in turn, turns around to increase the cost of exploitation of the house.
- Secondly, in the cold season, condensate accumulates in the freezing zone, which leads to wetting and gradual damage used for the roof insulation (which also deteriorates the thermal protection of the building).
- Thirdly, due to condensate they can be covered with mold, rot and over time the wooden structures of the roof can collapse. Often condensate causes deformation of the finish.
- Finally, in fourth, condensate in winter can climb and break the gaps and gaps that he filled.
Errors when insulation
Why do cold bridges appear? According to experts, in most cases this is due to errors in the device of the thermal insulating layer of the roofing "cake". Recall that the most common construction of the attic roof It assumes the insulation of the skates (at the same time, the plants of the attic) with fibrous materials: plates and - less often - mats based on or.
Another dangerous in terms of freezing knot - roof Connection Place With Fronton Building.
Valery Nesterov, General Director of the company "Durken":
"In place of the roof connection with the fronton building, the likelihood of freezing is very high. To prevent it in the West there are special P-shaped elements from extruded expanded polystyrene foam, which "wear" on the frontal wall. In our market there are special diffusion hydraulic displacement membranes with an integrated layer of insulation with a thickness of 30 mm from nonwoven material: they can also protect this section from the freezing. However, the traditional solution is to fill in mineral insulation space between the extreme rafter beam and the frontal wall (usually about 50 mm), the gap between the upper surface of the wall and the hydraulic protection film, and also lay the insulation along the top edge of the wall. As a result, a continuous thermal insulation circuit is created, closing the fronton and carrying the dew point inside the wall, thereby eliminating the possibility of condensate in the thickness of the roofing insulation. "

- The first difficulty lies in the fact that it is often over the entire top of the inclined front-wall walls there are ledges formed by masonry (from bricks, blocks). To align the wall, the "cold" cement-sandy solution is often used, which becomes the cold bridge. It is better to use a "warm" solution instead with the addition. Or fill out irregularity with thermal insulation.
- The second difficulty is to warm up this place. It is necessary to leave the distance of at least 50 mm between the nearest to the frontton with the rafter foot and the frontal wall, filling this space with thermal insulation. In addition, it is desirable that the upper wall plane is 50 mm below the top plane of the rafter legs, and then the insulation is laid and over the wall to the height of the leg, providing its dense fit to isolation going along the rafter. If possible, the insulation is also mounted along its edge from the street - a layer of thickness equal to the thickness of the insulation on the roof scap.
Fixing through rafyla
There are other places of joints of the roofs of wooden elements of the roof (located between its warm and cold zones), as well as composite rafting legs, made by combining two beams into one. Cold bridges may appear here for several reasons: due to a loose fit of the elements to each other (caused including their curvature), due to the precipitation of the rafter system, etc. To avoid this, the joints of the joints should be laid by sealing materials, for example, syntheps or foamed polyethylene. However, a number of roofers believe that the latter reduces the reliability of the joint elements. If you have to seal the joints after installing the rafter, you can use specialized sealants, psuli (pre-compressed self-seated sealing tapes) or mounting foam, but it is not no one and quite laborious. This solution has another substantial minus: foam, being inelastic, can collapse when the wooden design is sediment.Effective way to prevent heat loss - Create an additional layer of roof insulation, overlapping possible cold bridges.

On the picture:
1. On the roofs of a complex configuration, it is inevitably shortening the plates of the insulation to put them in the space between the rafted.
2. Fastening a vapor barrier film to a rafter foot.
3. Installation of a trimmed plate in the range of the ridge.
4. The slots in the layer of insulation are constituted by fragments from the same heat-insulating material.
The freezing is possible in places of exit through the wall on the street Mauerlat, skate or intermediate runs, which are based on the distilled rafters. To prevent cold air movement here, first of all qualitatively compact the gaps between the beam and the wallAlso not to forget to seal (glue or special tape), where the beam is bypassing vapor insulation and hydraulic film.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe attic window is another area of \u200b\u200bthe roof, where cold bridges can occur.

Often, this is due to the lack of or insufficient thickness of the layer of insulation along the perimeter of the window frame and in the docks. In order to prevent freezing, it is necessary to leave a gap of 20-30 mm around the frame, filling it with thermal insulation, which should be brought to the roof insulation circuit.

To simplify installation, manufacturers of windows offer ready kits for thermal insulation around the frame perimeter (for example, from foamed polyethylene). Some firms produce windows with the heat-insulating frame already provided on the frame. Note that it is categorically forbidden to warm the frame using the frame with the assembly foam.
Marina Prosarovskaya, Chief Engineer Velux:
"Among the reasons for the freezing in the area of \u200b\u200bthe attic window - the absence of thermal insulation around the perimeter of the window box. Often this is caused by too small mounting gaps between the box and the rafters. It should be left around the perimeter of the frame of the gap of at least 30 mm, setting around it or a finished heat-insulating contour from foamed polyethylene, or a fibrous insulation. It is impossible to apply the installation foam for these purposes: it is inelastic and under the influence of periodic loads (roof sediment, snow, wind load) crumbs, as a result of which the slots appear in thermal insulation. If the width of the window is equal to the width of the intercremile loop or exceed it, then to ensure the necessary installation gaps around the frame, it will have to customize rafters, while maintaining their carrying ability. It is sometimes possible to be made without a special calculation according to the schemes specified in the installation instructions. Usually it assumes the installation of an additional beam, the cross section of which coincides with the cross section of the rafting leg. "
In most cases, cold bridges are the result of condensate lossleading to the wetting of the insulation in the window zone. The reasons for his education can be a lot. In particular, non-cross joints of a vapor barrier film with a window frame: water vapor has a high penetrating ability, and falling into the cold zone, condensed. Often condensate - this is a consequence of certain errors with roof design ventilation system.

For example, there are no conditions for the influx of air or its drawing, there is no control process that generates a ventilation, or its height is insufficient to ensure the necessary movement of air under. However, the leaky joints and places of the adjoins of both underpants films, as well as insufficient ventilation of the underpants space - errors that lead to the appearance of condensate and freezing not only in the window zone, but also all the roof. Just in the window zone, it becomes noticeable in the first place. Moreover, many errors cannot be corrected during the operation of the building without a complete dismantling of the roof.
According to experts, in the conditions of the Moscow region every 5 cm heat insulation give savings on the heating on average 18 rubles. per quarter. m square roof per year.
A few more words about the squirrel window. Problems arise I. with improper installation of drainage horod Over the window opening. This horror takes water from the window (leakage, condensate), which flows along the hydraulic protection membrane to the window. Before its styling, the membrane is cut, and then it is put on its edge into it, fastening with a special klemmer, after which the top edge of the window waterproofing apron is started under it. If the engine mounting technology is not observed, leaks are possible in the insulation with all the ensuing consequences.
Those or other passing elements - pipes, antennas, flagpoles, etc. Therefore, they should be warm and tightly allowed to play vapor insulation and hydraulic films with them.

To minimize the freezing through the walls, the specialists advise to create an additional heat insulating belt with a height of about 250 mm over the standard circuit of insulation (that is, above the roof). To protect against precipitation, the belt should be closed with one or another apron.
Ekaterina Kolotushkina, Saint-Goben CIS product manager:
"Make a attic to the most comfortable for living and ensure the durability of the roof design allows the creation of an additional insulation circuit. The fact is that the wooden bearing roof elements are to some degrees of cold bridges. In addition, according to calculations, a layer of heat insulation in the central part of Russia should be 200 mm, but the thickness of the most popular on the market of beams used for the device rafters is 150 mm (and the insulation is placed in the interconnection space). Thus, it makes sense to create an additional thermal insulation layer, which will provide the required thickness of insulation and block the bridge of the cold, going through rafters. This layer can be placed above and under the rafters, laying the insulation between the bars born across the rafter. The thermal insulation above the rafters is preferable, since in this case they are not freezing. "
Additional layer of insulation
Despite all the efforts of roofers, heat loss are inevitable in those places of the roof, where the area of \u200b\u200bthe inner "warm" surface is less than the area of \u200b\u200bthe outer "cold". It is basically the corners of the hip or tent roofs (in the zone of convergence of the ridge and the cornese swell), the location of the ridge to the frontoth and others. In addition, wooden rafting legs are also in a certain extent the cold bridges. Yes, and qualitatively insulate complex areas of the roof, where filigined trimming is required (endandes, ridges, adjoining) is difficult. Finally, the thickness of the heat-insulating layer in the middle band of Russia should be, according to SNiP 23-02-2003 "Thermal Protection of Buildings", not less than 200 mm. While the most popular material for the construction of the rafter is still a cross section of 150 × 50 mm, which implies the thickness of the interconnection layer of insulation - 150 mm. All these factors explain the need to create additional contour of the heat insulation of the roof.It can be mounted over timer and under them. In the first case:
- Stripped the wooden bars of the desired section, between which the insulation plates are installed.
- A hydraulic protection membrane is laid on top of the bars.
- It is fixed on it, a doomer or solid flooring, and on them - roofing material.
- Fixation of the roof to the base is less reliable due to the additional wooden substructure.
- In addition, when the device, the hydraulic coils of the joints can be on the insulation (and not on a wooden base), and the film will be pushed by installers, moving on the roof.
There is another effective, but so far almost not used method of insulation - installation over rafted solid flooringon which plates made of stone fiber high density, wood fiber, polyurethane foam. The roof is mounted directly on the plates. 
1. Stropile foot.
2. Additional insulation contour.
3. Transverse bar.
4. Finishing attic.
We note another moment. In the fight against the frozen roof will help modern methods of detection of cold bridges - Examination with the help of a thermal imager or thermoanemometer. The cost of purchasing or renting these devices is less than the cost of repairing the frozen roof. 
In most cases, the private developer is more profitable not to buy a thermal imaging camera, but to contact a specialized company that is engaged in thermographic examination of buildings.
Types of insulation for a scope roof
For the insulation of the pitched roof, the plates (or mats) are most often used from stone or glass fiber.- In our market, stone fiber materials are represented by Rockwool (Denmark), Paroc (Finland), Nobasil (Slovakia), Tekhnonikol, Isoroc, Knauf (all - Russia), etc.
- Glass fiber insulation offers Isover (France), URSA (Spain), etc.
Materials from extruded polystyrene foam or polyurethane foam, although they have very good thermal insulation properties, are not fireproof: Polystyrene foam refers to the group of hydroforal materials (M4), and polyurethane foam to a group of moderately or weakly manual (G2-G3). At the same time, fibrous insulation are non-combustible (NG).
Material prepared Alexander Levenko.
If you live in the Leningrad region, you know that our climate is not the most affectionate. Sunny days is small, the average annual temperature is from 2 to 4.5 degrees Celsius.
Therefore, it is comfortable to spend time at the cottage only in three year old months (even looking at what summer).
But this period can be lengthened if you warm the house when wearing siding.
And in this article we will share together, what errors are possible when insulation under siding if non-professionals are performed.
The most frequent mistakes when insulating at home under siding
Immediately bring clarity: the professionals do not allow these errors. Each patient installation professional has its own individual handwriting, but there are general rules that we all adhere to.
If you notice that people who insulate your home make these mistakes - chase them in the neck.
It is better to turn to professionals and pay a little more, but get the result that you do not have to redo.
Let's find out which mistakes can be allowed when insulating the house under siding.
Rolled insulation instead of slab
This error is caused by the desire to save on materials when insulation at home.
Rolled insulation is cheaper than slaughterhouse, and those who do not understand the insulation technology, the temptation arises to save.
It is impossible to warm the vertical surfaces with a rolled insulation. It is designed for horizontal surfaces and flat roofs (with an angle of inclination 6: 1 and more flat).
If you warm the walls with a roll insulation, it will very quickly fall to the bottom of the wall, and the top of the wall will give all the warmth of your home to the street.
Therefore, when warming at home, a slab insulation should always be used under siding (we usually use mineral wool).
Lovely joints between insulation stoves
If the plates fit to each other, then, in fact, the gap is formed in the warm wall of your house.
Heat - like water, breaks there, is much easier to flow. And the cracks between the plates of the insulation will be just at that places.
That is why there are such cold houses from the bar. By the way, we have excellent.
Your home will become warmer than before insulation, but part of the heat, it will still go. And you, I think it is not necessary.
Therefore, watch people who insulate the walls of your home, the insulation plates are tightly without cracks.
When they close all this with wind hydrogen insulation, you will not see anything already, and your home will be insulated under siding inefficient.
Locked insulation plates
Some homegrown "craftsmen" will confidently tell you that the slab insulation is tight enough, and it can not be attached to the wall.
And if you believe them, it will be a mistake. Because over time, the insulation of the walls of the house under siding will settle under its own weight.
Weighs the insulation a bit, but also his carrying ability is very low. Therefore, the stove on which the mineral wool will press the height of three meters, one way or another, will settle.

Professionals are attached to each insulation plate with special "parachutes". This allows you to unload the bottom plate, because each upper plate hangs on its own fastener.
Wall insulation under Siding without Ventzazor
Side installation technology provides for the creation of a ventilated gap between siding and a wall of the house.
This space serves to output condensate into sofit under the roof.
In the ventzazor, the ascending flow of air blows the condensate, which is located on the wind hydrogen insulating membrane, and the wall remains dry.
If your home is insulated without vaporizolation, then the absence of a ventilation between insulation and siding is the guarantee of the formation of fungus and mold.
In the Leningrad region with our humidity it is a matter of a couple of weeks.

When mounting siding with the insulation of the house, the STC specialists are used by a double ventilated frame, which provides condensate conclusion in the roofing sv, and reliable insulation ventilation under siding.
Cold bridges when insulation of walls under siding
Most Shabashnikov, "Wild Brigades" and even some firms are mounted siding siding on "destruils".
The destroy is a piece of wood between the wall and the frame, to which the siding is then attached. It aligns the frame in the vertical plane, so that the wall after the sheathing siding has become smooth.
The destroyer is screwed to the wall, and the bar is screwed to it 50x50 mm, between which the insulation is laid.
This is the most common way among unprofessional ways of insulation of walls under siding.
But the question arises: and what prevents warmth to leave your home in places where the framework goes?
Nothing interferes.
Heat breaks through these gaps in the insulation. It turns out in the case of the slits between the insulation plates, only much worse.
Because the cracks under the frame is much wider (in the width of the bar).
This problem is solved in a fundamentally different approach To the insulation of the house under siding. We in the STC standard found this solution and insulate the house under siding without cold bridges.
If you contact the STK standard, you can be sure that the loss of heat through the slots on your house will not be.