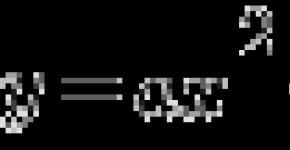How to determine the average speed if the speed is known. How to find mid speed
2 . The first portion of 120 m long skier was held in 2 minutes, and he passed the second length of 27 m in 1.5 minutes. Find middle speed Skier movement all over the way.
3 . Moving along the highway, the cyclist drove 20 km over 40 minutes, then he overcame for 2 min long, and the remaining 39 km 400 m along the highway he drove in 78 minutes. What is the average speed on the whole path?
4 . The boy for 25 minutes was 1.2 km away, then half an hour rested, and then ran another 800 m in 5 minutes. What was his average speed all over the way?
Level B.
1 . What speed is medium or instantaneous - this is speech In the following cases:
a) the bullet flies out of the rifle at a speed of 800 m / s;
b) the speed of the earth around the sun 30 km / s;
c) The maximum speed limiter is installed on the road - 60 km / h;
d) past you drove a car at a speed of 72 km / h;
e) The bus overcame the distance between Mogilev and Minsk at a speed of 50 km / h?
2 . The path of 63 km from one station to another electric train takes place in 1 h 10 min at an average speed of 70 km / h. What time does stop stopping?
3 . Self-propelled mower has a width of the capture of 10 m. Determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe field, bevelled in 10 minutes, if the average mower rate is 0.1 m / s.
4 . On the horizontal section of the path of the car drifted at a speed of 72 km / h for 10 minutes, and then drove a rise at a speed of 36 km / h per 20 min. What is the average speed on the whole path?
5 . Cyclist The first half of time when moving from one point to another was driving at a speed of 12 km / h, and the second half of the time (due to the prolque of the tire) was walking at a speed of 4 km / h. Determine the average cyclist speed.
6 . The schoolboy drove 1/3 of the total time by bus at a speed of 60 km / h, another 1/3 of the total time on a bike at a speed of 20 km / h, the rest of the time passed at a speed of 7 km / h. Determine the average speed of the schoolboy.
7 . The cyclist was driving from one city to another. Half the path he drove at a speed of 12 km / h, and the second half (due to the prolque of the bus) was walking at a speed of 4 km / h. Determine the average speed of its movement.
8 . From one point to another motorcyclist moved at a speed of 60 km / h, the return route was passed at a speed of 10 m / s. Determine the average speed of the motorcyclist for all the time of movement.
9 . The schoolboy drove 1/3 ways by bus at a speed of 40 km / h, another 1/3 ways to bike at a speed of 20 km / h, the last third of the way was held at a speed of 10 km / h. Determine the average speed of the schoolboy.
10 . Pedestrian part of the path was held at a speed of 3 km / h, spending 2/3 of his movement time. The remaining time he passed at a speed of 6 km / h. Determine the average speed.
11 . Train speed on the rise of 30 km / h, and on the descent - 90 km / h. Determine the average speed on the field of the path, if the descent is twice as long as lifting.
12 . Half of time when moving from one point to another car moved at a constant speed of 60 km / h. At what constant speed, it should move the remaining time if the average speed is 65 km / h?
Remember that the rate is given as a numerical value and direction. The speed describes the speed of changing the position of the body, as well as the direction in which this body moves. For example, 100 m / s (south).
Find a common movement, that is, the distance and direction between the initial and endpoint paths. As an example, consider the body moving at a constant speed in one direction.
- For example, the rocket was launched in the northern direction and moved within 5 minutes at a constant speed of 120 meters per minute. To calculate the overall movement, use the S \u003d VT formula: (5 minutes) (120 m / min) \u003d 600 m (north).
- If permanent acceleration is given in the task, use the S \u003d VT + ½AT 2 formula (in the next section describes a simplified method of working with constant acceleration).
Find the total time on the way. In our example, the rocket moves for 5 minutes. The average speed can be expressed in any units of measurement, but in the international system units, the speed is measured in meters per second (m / s). Convert moments per second: (5 minutes) x (60 seconds / minute) \u003d 300 seconds.
- If even in the scientific task, the time is given in hours or other units of measurement, it is better to first calculate the speed, and then convert it to m / s.
Calculate the average speed. If you know the value of moving and the total time on the way, calculate the average velocity can be calculated according to the V CP \u003d ΔS / ΔT formula. In our example, the average rocket speed is 600 m (north) / (300 seconds) \u003d 2 m / s (north).
- Do not forget to specify the direction of movement (for example, "forward" or "north").
- In the formula v cp \u003d ΔS / Δt The "Delta" symbol (Δ) means "change in value", that is, ΔS / ΔT means "change in time change".
- The average speed can be recorded as V Wed or as V with a horizontal feature from above.
Decision more complex tasks, for example, if the body rotates or acceleration is not constant. In these cases, the average speed is still calculated as the ratio of the general movement to the total time. It does not matter what is happening with the body between the initial and endpoint paths. Here are some examples of tasks with the same common movement and general time (and, consequently, the same average speed).
- Anna goes to the West at a speed of 1 m / s for 2 seconds, then instantly accelerated to 3 m / s and continues to go west for 2 seconds. Its general movement is (1 m / s) (2 s) + (3 m / s) (2 s) \u003d 8 m (west). Total travel time: 2 C + 2 C \u003d 4 s. Its average speed: 8 m / 4 C \u003d 2 m / s (west).
- Boris goes to the West at a speed of 5 m / s for 3 seconds, then unfolded and goes east at a speed of 7 m / s for 1 second. We can consider movement east as a "negative movement" to the West, so the general movement is equal to (5 m / s) (3 s) + (-7 m / s) (1 s) \u003d 8 meters. The total time is 4 s. The average speed is 8 m (west) / 4 C \u003d 2 m / s (west).
- Julia passes 1 meter to the north, then takes 8 meters to the west, and then passes 1 meter south. Total time on the way is 4 seconds. Draw the scheme of this movement on paper, and you will see that it ends 8 meters to the west of the starting point, that is, the overall movement is 8 m. The total time in the way was 4 seconds. The average speed is 8 m (west) / 4 C \u003d 2 m / s (west).
This article describes how to find an average speed. It is given to the definition of this concept, and also discussed two important private events of the average speed. Presented detailed analysis Tasks for finding the middle velocity of the body from the tutor in mathematics and physics.
Definition of medium speed
Average speed The movement of the body is called the ratio of the path passed by the body by the time during which the body moved:
We will learn to find it on the example of the following task:
Please note that in this case this value did not coincide with the average arithmetic velocity and, which is equal:
m / s.
Private cases of finding medium speed
1. Two identical portions of the path. Let the first half of the way the body moved at speeds, and the second half of the journey is at speed. It is required to find the average velocity of the body.
2. Two identical movement intervals. Let the body moved at a speed for a certain period of time, and then began to move at a speed during the same period of time. It is required to find the average velocity of the body.
Here we received the only case when the average speed of movement coincided with the average arithmetic velocity and on two parts of the path.
Finally, the task of the All-Russian Schoolchildren Olympiad in physics last year, which is connected with today's lesson today.
| The body was moving with, and the average speed was 4 m / s. It is known that over the past from the movement, the average speed of the same body was 10 m / s. Determine the average body rate for the first from the movement. |
The path traveled by the body is: ![]() m. You can also find the path that the body passed in the last from its movement: m. Then, for the first from his movement, the body overcame the path in m. Consequently, the average speed in this section of the path was:
m. You can also find the path that the body passed in the last from its movement: m. Then, for the first from his movement, the body overcame the path in m. Consequently, the average speed in this section of the path was: ![]() m / s.
m / s.
The tasks of finding the average speed of movement are very like to offer on the exam and OGE in physics, entrance exams, as well as the Olympiads. Learning to solve these tasks should each schoolboy, if he plans to continue his studies at the university. Help to cope with this task can know the comrade, a school teacher or a tutor in mathematics and physics. Good luck to you in learning physics!
Sergey Valerievich
There are mean values, the improper definition of which entered the anecdote or to the parable. Any incorrectly produced calculations are commented by a matter of communication with a consecutive reference to such a sensible absurd result. Each, for example, will cause a smile of sarcastic understanding of the phrase "average temperature in the hospital". However, the same connoisseurs often, without thinking, fold the speeds on separate sections of the path and divide the calculated amount by the number of these sites to get an equally meaningless answer. Recall from the course of high school mechanics, how to find an average speed correct, and not absurd way.
Analogue of "Middle Temperature" in Mechanics
In what cases are the favors of the task, the tasks are pushing us to a hasty rapid response? If it is said about the "parts" of the path, but their length is not indicated, it is alarming even a little sophisticated in solving such examples of a person. But if the task is directly indicated on equal intervals, for example, "the first half of the train followed at a speed ...", or "the first third of the paths of a pedestrian fascinated with soreness ...", and then describes in detail how the volume was moved on the remaining equal plots, that is, the ratio is known S 1 \u003d s 2 \u003d ... \u003d s n and accurate values Speed v 1, V 2, ... v n.Our thinking often gives an unforgivable mischief. It is considered arithmetic velocity, that is, all known values v. add up and divided by n.. As a result, the answer is incorrect.

Simple "Formulas" calculation of values \u200b\u200bin uniform movement
And for the entire path traveled, and for individual sections in the event of averaging the speed of validity, written for uniform movement:
- S \u003d VT.(1), "Formula" path;
- t \u003d S / V(2), "Formula" settlement of traffic time ;
- v \u003d S / T(3), "Formula" definitions of medium speed in the field of the path S.traveled t..
That is, to find the desired value v. Using the ratio (3), we need to know the other two. It is solving the question of how to find an average speed of movement, we must first of all determine what the whole path passed S. And what is all the time t..

Mathematical detection of hidden error
In our example, the path traveled by the body (by train or pedestrians) will be equal to the work nS N.(since we n. Since we add equal sections of the path, in the examples of the examples - halves, n \u003d 2., or a third, n \u003d 3.). It is not known anything about the full time of movement. How to determine the average speed if the denominator of the fraction (3) is clearly not specified? We use the relation (2), for each site we define the path t n \u003d s n: v n. Amount we write the time intervals in this way under the fraction (3). It is clear that in order to get rid of the signs of "+", you need to give everything S n: v nto a common denominator. As a result, it turns out a "two-story fraction". Next, we use the rule: the denominator of the denominator goes to the numerator. As a result, for the task with the train after the reduction on S N. have v cp \u003d nv 1 v 2: v 1 + v 2, n \u003d 2 (4) . For the case with a pedestrian, the question - how to find an average speed, is even more difficult: v cf \u003d NV 1 V 2 V 3: V 1V2 + V 2 V 3 + V 3 V 1, N \u003d 3.(5).

Explicit confirmation of the error "in numbers"
In order to "confirm" on the fingers "that the definition of the average arithmetic is an erroneous path when calculating v. cf., specify the example, replacing abstract letters numbers. For the train will take speed 40 km / h and 60 km / h (erroneous answer - 50 kM / C.). For pedestrian - 5 , 6 and 4 km / h (average - 5 km / h). It is easy to see, substituting the values \u200b\u200bin relation (4) and (5) that the loyal answers will be for locomotive 48 km / h And for a person - 4, (864) km / h (Periodic decimalThe result mathematically not too beautiful).

When the arithmetic average "does not fail"
If the task is formulated as: "During equal intervals, the body moved first at the rate v 1., then v 2., v 3.and so on, "a quick response to the question of how to find an average speed can be found in the wrong way. We will provide the reader to make sure of this, having lifting equal intervals in the denominator and using the numeric v cf.relation (1). This is perhaps the only case when the erroneous method leads to a correct result. But for guaranteed accurate calculations you need to use the only correct algorithm, consistently turning to the fraction v cp \u003d s: t.
Algorithm for all occasions
In order to certainly avoid mistakes, when solving the question, how to find an average speed, just remember and perform a simple sequence of actions:
- determine the whole path by losing its length of its sections;
- establish all the time path;
- to divide the first result on the second, unknown, not specified in the value of the value at the same time (subject to the correct wording of the conditions) reduced.
The article discusses the simplest cases when the initial data is given for equal liabilities or equal sections of the path. In the general case, the ratio of chronological intervals or the distances passed by the body can be the most arbitrary (but at the same time mathematically defined, pronounced integer integer or fraction). Rule turning to the ratio v cp \u003d s: tabsolutely universally and never fails, how difficult at first glance algebraic transformations did not have to perform.
Finally, we note: no unnoticed for observation readers practical significance The use of the right algorithm. Correctly calculated average speed in the above examples turned out to be somewhat lower. " average temperature"On the highway. Therefore, a false algorithm for systems that fix speeds would mean more Errbial focus of traffic police sent in the "letters of happiness" drivers.
Very simple! It is necessary to split all the way for a time that the object of movement was on the way. I am expressed differently, you can determine the average speed as the arithmetic average of all the speeds of the object. But there are some nuances in solving the tasks of this direction.
For example, such a task is given to calculate the average speed: the traveler first walked at a speed of 4 km per hour for an hour. Then the passing car "picked up" him, and he drove the path in 15 minutes. And the car went at a speed of 60 km per hour. How to determine the average movement speed of the traveler?
You should not just fold 4 km and 60 and divide them in half, it will be the wrong decision of the solution! After all, the paths covered on foot and on the car are unknown to us. So, you first need to calculate the whole path.
The first part of the way to find easily: 4 km per hour x 1 hour \u003d 4 km
With the second part of the way, small problems: the speed is expressed in the clock, and the time of movement is in minutes. This nuance often interferes finding the right answer when questions are raised how to find an average speed, path or time.
Express 15 minutes in the clock. For this, 15 min: 60 min \u003d 0.25 hours. Now we calculate what path the traveler did on the traveler?
60 km / h x 0.25h \u003d 15 km
Now finding the whole traveleled path will not be much difficulty: 15 km + 4 km \u003d 19 km.
Movement time is also fairly easy to calculate. This is 1 hour + 0.25 hours \u003d 1.25 hours.
And now it is already clear how to find an average speed: you need to share the whole way for a time that the traveler spent on its overcoming. That is, 19 km: 1.25 hours \u003d 15.2 km / h.
There is such an anecdote in the subject. A man in a hurry on asks the field owner: "Can I go to the station through your plot? I'm a little late and I would like to cut my way by passing directly. Then I definitely have time to train, which departs at 16 o'clock 45 minutes! " - "Of course, you can cut your way by passing through my meadow! And if you will notice my bull there, then you will have even time for the electric train, which is moving at 16 hours 15 minutes. "
This comical situation, meanwhile, is directly related to such a mathematical concept as the average speed of movement. After all, the potential passenger is trying to reduce his way for the simple reason that he knows the average speed of his movement, for example, 5 km per hour. And a pedestrian, knowing that the bypass path on the asphalt road is 7.5 km away, making mentally simple calculations, understands that it will be required for this road one and a half hours (7.5 km: 5 km / h \u003d 1.5 hours).
He, coming out of the house too late, is limited in time, so it decides to reduce your way.
And here we are faced with the first rule that dictates us how to find the average speed of movement: Given the direct distance between extreme dots The paths or exactly calculating the foregoing to everyone: it is necessary to conduct a calculation, taking into account the path of the path.
Reducing the path, but without changing its average speed, the object in the face of a pedestrian receives a time gain. The farmer, assuming the average speed of running away from the furious bull of the Sprinter, also makes simple calculations and gives its result.
Motorists often use the second, important, the rule for calculating the average speed, which concerns the time of staying along the way. This applies to the question of how to find an average speed in case the object has during the stop of the stop.
In this embodiment, usually, if there are no additional clarifications, it takes a full time for calculation, including stops. Therefore, the driver can say that its average speed of movement in the morning on a free road is much higher than the average speed of movement in an hour-peak, although the speedometer shows the same number in both options.
Knowing these numbers, an experienced driver never deals anywhere, in advance, as it will be its average speed of movement in the city at different times of the day.