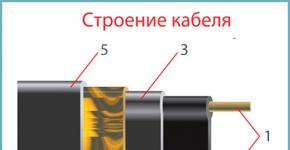
The better to insulate the foundation from the outside. Do-it-yourself foundation insulation with penoplex
Insulating the foundation of a house
One of the key elements of construction that is often overlooked is foundation insulation. At the same time, installation of foundation insulation is as important as for walls. These works are especially relevant for regions with harsh climates and in cases where the ground level freezes to a significant depth. The penetration of cold air leads to rapid destruction of the structure of building materials.
According to research, the foundation accounts for 15-20% of the heat loss of the entire structure. The warmth inside residential premises depends on the basement and the quality of its execution.
Why is it necessary to insulate the foundation?
Insulation for the foundation is calculated at the design stage of the future building. Based on the initial data (temperature and humidity of the region, load, groundwater), a specific material is selected and the required layer thickness is calculated.
Foundation waterproofing, as well as foundation thermal insulation, play an important role in maintaining its integrity. If the ground level rises, then deformation of the foundation is inevitable. Especially if the technology is violated during the work: the foundation slab must be insulated. And the foundation itself goes below the depth of soil freezing. This allows you to avoid the destructive effects of frost heaving mounds that occur in winter. Determining the seasonal level of soil subject to freezing lies with the designers.

Insulating the foundation is not only about installing additional insulation to protect against cold air. This process includes calculating the floor level.
Direct insulation of the foundation guarantees heat retention in the lower part of the house, and therefore throughout the entire structure. During the operation of the building, the owner saves significant money on heating.
Insulation of the foundation also serves to waterproof the structure.
If the work on insulating the base of a building is carried out correctly, you get:
- Reduce heat loss.
- Reduced heating costs.
- Elimination of the negative effects of frost heaving.
- Stabilization of the temperature inside the house.
- Minimizes condensation formation.
- Promotes strength under mechanical stress.
What is the best way to insulate the foundation - from the outside or from the inside?
The thickness of the foundation insulation is determined by many factors, including:
- Building class and future use.
- Atmospheric indicators of the region.
- The type of soil underlying it (including the level of soil freezing).
- Insulation material.

Thermal insulation of the foundation inside and outside the house,
Thermal insulation for the foundation can be done both externally and internally. Most builders claim that external insulation gives better results. Compared to external insulation, internal insulation does not provide protection against external freezing. Problems also arise with ground movement due to the expansion of freezing moisture.
The use of additional bitumen waterproofing helps preserve the structure of the material, but does not protect against frost heaving.
How and how to insulate the foundation from the outside
Insulation of the foundation determines the creation of a comfortable temperature regime in the premises. Also, the home owner will experience an impressive reduction in the cost of heating rooms - this is due to reduced heat loss. Depending on the level of soil freezing, the type of optimal insulation is determined.
Soil has a set of its own physical characteristics. It has been established that the freezing resistance of foundation walls should be one less than the thermal resistance of the external walls of the house.

Insulation of the foundation from the outside
The thickness of the insulation is determined by the formula:
δ ut = (R required -1.05-δ/λ)*λ ut
In the presented values
δ ut - thickness of foundation thermal insulation, m;
R required - normalized heat transfer resistance of the wall;
δ - thickness of the load-bearing foundation wall in meters;
λ - thermal conductivity coefficient of the material of the load-bearing part of the foundation;
λ ut - thermal conductivity coefficient of foundation thermal insulation.
Of course, not only the level of soil freezing affects the development of insulation for the foundation. Depending on the type of base structure, a project for strengthening and insulation is drawn up, as well as such measures as coating with bitumen waterproofing and much more.
Pile foundation

Insulation of a pile foundation
This type of foundation is gaining popularity due to its strength and reliability, speed of construction and low cost. If the piles are installed below the freezing depth of the soil, then there is no need to insulate the pile. But it is important to insulate the foundation around the perimeter - for this they use slabs of extruded polystyrene foam. This way it is possible to maintain the integrity and position of the blind area. These slabs should be laid 0.3-0.4 meters below the blind area. Recommended size 1.25 meters width and 50 mm height.
Columnar foundation
Insulation of the foundation, which is a system of columns, is most often done using extruded polystyrene foam. Sometimes foaming polyurethane foam is used.
Polystyrene foam is optimal for insulating a columnar foundation from the inside. But it has one clear advantage over other materials - low cost. Therefore, it is readily installed outside. Although this is not recommended.

Insulation of a columnar foundation
Expanded clay is also a cheap material. It is often poured into pre-installed formwork on the inside of the foundation.
TechnoNIKOL foundation insulation is classic mineral wool. It is also installed from the inside. The main advantage of foundation insulation with TechnoNIKOL is the absorption of moisture by the material.
Penoplex has better strength and durability. In all respects, it is among the leaders, but the cost of the material corresponds to the quality.
Strip foundation
For this type of foundation, insulation from the outside is much more important. To protect the walls of the basement, several layers of thermal insulation materials are used. To preserve the structure of the materials, it is important that the waterproofing of the foundation ensures the removal of moisture.
After preparing the trench, the soil must be compacted before pouring the foundation. Afterwards, a 10-15 cm layer of sand cushion is poured. Tamping is carried out again. Now a thin layer of “concrete” is poured, and in some cases insulating materials are applied to the sand bed. After waterproofing, the basement is additionally insulated.
Materials and methods of foundation insulation
The choice of thermal insulation materials on the modern construction market is incredibly diverse. It is best to start from what is proposed in the project (if there is none, contact the architect for revision).
After determining all the necessary indicators, including the depth of soil freezing, decide on the type of insulation. They may differ in structure and shape:
- Piece insulation.
- Flexible.
- Bulk, etc.
There are also fibrous, cellular and granular types. Raw materials for manufacturing are divided into organic, inorganic and artificial.
One of the most popular materials for insulation is polystyrene foam. It is cheap and has good performance characteristics. It can be foamed or extruded. Installation is also extremely simple and can be done on your own.
A popular type of foam is extruded polystyrene foam. It has a strong structure and is characterized by high hygroscopicity; polystyrene foam also retains heat well. Extruded polystyrene foam has its disadvantages:
- Low resistance to solvents.
- Susceptible to fire.
When working with expanded polystyrene there are certain mandatory rules:
- Solvents of organic origin must be used in fastening compositions. Mechanical destruction of the material structure reduces its protective properties.
- If the soil is susceptible to frost heaving, it should be additionally protected from mechanical damage. This is done using brickwork or a special polyethylene membrane.
- It is mandatory to lay a waterproof covering to protect against rainwater.
During work, polyurethane foam allows you to create a heat-insulating layer that does not have seams. This creates reliable protection against the penetration of low-temperature air. The coating is applied with a special pump in several layers.
The material has low thermal conductivity and provides excellent protection against noise and corrosion. It is fireproof, waterproof and durable.
Most modern projects provide for insulation, which uses extruded polystyrene foam boards, which are one of the types of penoplex. It has a number of advantages that make it a leader among insulation materials:
- The material is durable and has a long service life.
- It is absolutely harmless.
- Resistant to compression and tension.
- Extruded polystyrene foam boards are relatively inexpensive.
Which foundation insulation to choose?
Thermal insulation of the foundation cannot be universal. The best type of material can be selected for each specific home and for each condition.
Insulation of the foundation requires builders to pay attention at all stages, starting with the choice of insulation.
The main criteria for choosing material for the foundation of a house:
- Stability under changing pressure, under the influence of compression and tension forces that change throughout the year.
- Resistance to moisture penetration into the structure of the material.
- extruded polystyrene foam,
- spraying with polyurethane foam.

Insulation of the foundation with polyurethane foam
- This is a special material that is used for thermal insulation of the foundation. It successfully achieves high levels of insulation of heat, water and sound. It is applied to the surface in layers and using a special pump. This coating is about 0.5 cm and creates excellent insulation and protection for the foundation.
During the practical use of polyurethane foam, its following advantages were determined:
- There are no connecting seams, which are the weak point of the insulation design.
- High adhesive properties.
- Low thermal permeability.
- Reduced vapor permeability.
- Reliability.
- Durability of the material.
The disadvantages include:
- The need to use special equipment for installation.
- Destruction under the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
The well-known extruded polystyrene foam benefits only due to its low cost and simple installation. These slabs perfectly isolate the foundation from the destructive effects of moisture. They absolutely do not allow water to pass through and maintain the integrity of the foundation. This allows us to talk about a long service life of the slabs while maintaining the original characteristics.

Foundation insulation with polystyrene foam
Polystyrene foam, which is so readily used to protect the foundation, has low performance characteristics. Yes, it's cheap and convenient. But after several changes of seasons and going through cycles of freezing and thawing, it simply collapses and ceases to protect the foundation.
To complete buildings and vertical insulation of foundations, slabs with different degrees of compression (an indicator of the strength of the product) are used. So, when strengthening the foundation, slabs with a strength of 250 kPa are suitable. For the floor, it is necessary to select materials that have this indicator at the level of 500 kPa.
When choosing extruded polystyrene foam, the user must clearly understand its main advantages:
- Duration of operation – from 40 years or more. At the same time, all properties of the material are preserved in their original form for the entire period of use.
- High material performance in strength tests.
- Stable level of thermal insulation properties throughout the entire period of operation.
- Resistance under mechanical influence of rodents.
Every person who owns a private house or cottage or dacha faces the problem of heat loss, especially in winter. Approximately 1/5 of heat loss occurs through the foundation, and it is this foundation that is often forgotten to be insulated, especially in houses that do not have a basement. However, it is necessary to insulate the foundation, since this can significantly reduce heat loss, reduce humidity in the basement and extend the life of the structure as a whole. So how to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside? This will be discussed further.
There are several reasons that indicate that it is simply necessary to insulate the foundation:
- A common mistake made by building owners is to insulate the basement from the inside, not the outside, while the foundation itself is not protected from the harmful effects of moisture on it. Thus, under the influence of moisture, cracks form in the foundation at low temperatures, which over time can lead to partial or complete destruction of the foundation. That is why it is necessary to do insulation not inside, but outside the foundation.
- External insulation of the base also allows not only protection from high humidity, but also makes it possible to prevent freezing of the foundation in winter. When thermal insulation is performed correctly, insulation can reduce the impact of moisture on the foundation, since it is much more resistant to it.
Methods for insulating the foundation from the outside
How to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside with your own hands? Today, the building materials market offers a wide selection of insulation materials. The most commonly used insulation methods are:
- The classic and ancient method is to insulate the foundation with gravel, expanded clay or sand.
- Using sheet insulation (for example, polystyrene foam).
- Use of sprayed material (eg polyurethane foam).
Each of the materials has its own advantages and disadvantages, which will be discussed further.
This type of insulation for the foundation of a house is most often used in private construction, since polystyrene foam has the following advantages:
- The material has high strength and durability.
- Has high moisture resistance.
- The material is quite easy to install and secure to the base, which allows you to do the finishing yourself.
- Expanded polystyrene is inedible for rodents and is resistant to damage.
- Carrying out external decorative finishing is not particularly difficult.
- The cost of the material is affordable for almost everyone.
As for the technology of finishing the foundation from the outside, it is as follows:

- It is necessary to insulate the foundation of the house from the outside immediately after it has been erected and the rough floor of the first floor has been completed. However, it is also possible to insulate the foundation of an already finished house, but to do this you need to dig a trench around the foundation at least 1 m wide and with a depth equal to the depth of the foundation.
- Before proceeding with insulation, the foundation walls must be cleaned of all contaminants.
- If the groundwater level is elevated at the construction site, a drainage system must be installed. To do this, a layer of sand is poured into the bottom of the trench, a layer of geotextile is laid, then perforated pipes with a diameter of about 10 cm into which gravel is poured. The pipes are also wrapped in geotextile and covered with sand. They need to be taken to a special collector well.
- The next step is to coat the foundation walls with a latex-based primer. This primer will allow you to completely fill all the cracks and small cracks in the foundation, and will also ensure good adhesion to the waterproofing material.
- Then they make waterproofing (usually self-adhesive), which is smoothed with a roller, and the joints are sealed with a special sealant.
- Now you can start laying the insulation. It is fixed to the walls using special glue, which is applied to the polystyrene foam in a small strip at a distance of 1-2 cm from the edge of the sheet, as well as in small dots along the entire perimeter.
- Thus, continue along the entire perimeter of the foundation. If the foundation is high and one row of polystyrene foam is not enough, then the insulation is laid in a checkerboard pattern, like a brick, in several rows.
- Once all walls are insulated, large gaps are sealed with foam or sealant.
- Where the foundation will subsequently be covered with sand, there is no need to further strengthen the polystyrene foam, but on the protruding part it is secured using special dowels.
- Next, the insulation must be plastered, and a reinforcing mesh must be used to give strength (it must be buried in a layer of plaster).
Thus, by doing everything correctly, you can achieve high-quality insulation without leaving cold bridges. In addition, this finishing gives the house a full, complete look.

This method of foundation insulation differs from the previous one in that it does not need to be fixed; it is applied directly to the foundation walls using a special sprayer. Polyurethane foam is sprayed onto the surface of the foundation in liquid form, after which it hardens directly on the walls for some time. This finishing method allows you to avoid insulation joints and also ensures a tight fit to the walls.
According to the application technology, polyurethane foam can be applied to the wall without any effort, and there is no need to additionally prepare the surface (i.e., no need to cover it with a primer, treat it with glue, etc.), just clean it of dirt.
Usually the insulation layer is about 5 cm, and rarely more. This layer allows for high-quality insulation. It should also be noted that polyurethane foam is resistant to moisture, which indicates additional waterproofing of the foundation.
It must also be said that such material can only be applied using special installations with sprayers, so doing it yourself is practically impossible.

This method of insulating the foundation from the outside has been proven for decades. In fact, expanded clay is a porous material that is quite light in weight and has good thermal insulation properties. However, this method is not advisable to use if in an area with a sufficiently high groundwater level, since the material is hygroscopic, that is, it easily absorbs excess moisture.
In order to reduce the hygroscopicity of the material, it is necessary to shield expanded clay from the external environment using waterproofing materials.
Expanded clay insulation technology is as follows:
- Along the entire perimeter of the foundation along its walls, it is necessary to dig trenches, the depth of which is slightly greater than the freezing level of the soil.
- Next, the walls of the trench must be waterproofed using any waterproofing.
- After this, the trenches are filled with expanded clay, and a blind area is made on top of it.
The blind area is performed as follows:
- They install formwork from planed boards, just like for the foundation. The width of the blind area is usually at least 60 cm.
- To strengthen the blind area, reinforcing mesh is laid on top of the expanded clay.
- Next, the concrete solution is poured.
- After some time, when the blind area has gained strength, the formwork is dismantled.

Thus, to summarize, we can safely say that the most rational material for insulating the foundation is expanded polystyrene, which is popularly called polystyrene foam. It is budget-friendly and of high quality, and also allows you to perform insulation yourself, without the involvement of specialists. However, how and with what to insulate the foundation of a house from the outside is up to the owners of the house to decide.
A strip foundation is not just the basis of a building, the support of its structure, but can perform quite utilitarian functions, being the walls of inhabited basements, basements or semi-basements. In order for such rooms to be warm and cozy, the foundation should not be a simple concrete casting, but a structure that will provide reliable thermal insulation of the interior. To do this, not only horizontal, but vertical surfaces of the strip concrete foundation are subject to insulation.
Concrete itself, despite its high strength and great resistance to loads, is a rather poor heat insulator. It easily receives heat and gives it off just as easily. A bare concrete wall will not be a good barrier between the cold of the winter soil and the warmth of the inhabited room.
Note that the degree of cooling of the foundation is also affected by its depth. If the strip foundation is not buried in the ground below the soil freezing level, then areas of frozen soil may form under the house, which will negatively affect the climate in your home.
In what ways can you insulate the foundation?
There are two main ways to insulate foundations. They differ depending on the period during which the work is carried out. One option is to insulate the foundation at the stage of pouring it, and the second is subsequent insulation, carried out after the concrete casting has matured.
The most preferable is to insulate the foundation during the construction phase. This comprehensive approach allows you to get good results. In order to achieve reliable thermal insulation of the foundation, even in the conditions of central Russia with harsh winter periods, the insulation process must be carried out on both sides.
The most logical approach to insulating the foundation during construction is permanent formwork.
Insulation of the foundation with permanent formwork
Permanent formwork is a spatial structure into which concrete mortar is poured. At the stage of hardening of the solution, it acts as a regular wooden formwork, that is, it limits the spreading of the concrete solution. However, unlike wooden formwork, after the concrete has matured, permanent formwork is not removed, but remains on the thickness of the concrete as an insulation layer.

Permanent formwork can be made from various materials. Particularly popular is the construction of permanent formwork from polystyrene foam boards. These are plates made of foamed polymer material containing many tiny air bubbles.
At first glance, the disadvantage of such formwork is its high cost. The costs of its purchase and installation are several times higher than the costs of classic wooden formwork. However, such a foundation will not need to be subsequently insulated, so the final costs will be quite comparable.
Insulating the foundation after pouring it
It is best to begin work on insulating a poured foundation immediately during the process of its maturation. If you are not attentive to this stage of building a house and return to it later, then you will not be able to carry out insulation work efficiently.

The classic way to insulate a foundation after it has been built is to lay a layer of expanded clay on the basement floor, which is subsequently filled with a leveling screed. Expanded clay is clay baked in special ovens and its mass is an excellent heat insulator. Also, to increase the level of thermal insulation between the ground, basement and living rooms, thermal insulation of the floor of the first floor of the house is carried out.
We insulate the foundation with earth
This option for insulating the foundation is extremely economical on the one hand, but very labor-intensive and voluminous on the other hand.
The essence of this insulation is very simple - all foundation walls up to the level of the first floor are covered with earth. Thus, it turns out that under a layer of earth, inside a kind of mound, all the basement rooms are located. Earth or sand in themselves are good heat insulators, but in order for this insulation to be effective enough even for central Russia, the foundation will have to be sprinkled with a very substantial volume of sand. So, to fill a foundation with rather modest dimensions of 10 by 10 meters, you will have to spend about a hundred cubic meters of sand.

A significant advantage of this approach will be the elimination of the impact of heaving soils on your site on the foundation. In some cases, backfilling the outer foundation wall with sand is recommended not even for thermal insulation purposes, but in order to prevent soil movements from affecting the foundation.
When filling the foundation with soil or sand, it is necessary to provide channels for air ducts that will provide ventilation to the basement. Naturally, work on this method of insulation must begin immediately after dismantling the wooden formwork, even before erecting the walls of your future home.
We insulate the foundation with a layer of expanded clay
As already mentioned, this is also one of the classic ways to insulate the foundation. In principle, expanded clay insulation can be combined with earth insulation.

In addition to the usual backfill, expanded clay can also be used as a filler for concrete castings. Expanded clay is small lumps of clay fired in a specially rotating kiln. Inside each lump there are many air cavities, which determines the excellent thermal insulation properties of this material. Thus, expanded clay can be used as a filler in concrete mortar instead of crushed stone.
Thus, expanded clay filler can be used in the construction of low-depth strip foundations. In this case, expanded clay can be added not only to the concrete mortar for the foundation walls, but also when screeding the floor, thereby providing a completely closed thermal insulation circuit of the basement.
We insulate the foundation with expanded polystyrene
The development of chemical production has led to the widespread use of synthetic insulation materials. One such material is polystyrene foam, which is a board. Inside which there are many air bubbles.

Expanded polystyrene sheets can be glued to concrete castings and brick walls. When installing such slabs on a foundation consisting of concrete blocks, that is, having joints between individual parts, they must be positioned so that the joints of the slabs are not above the joints of the concrete blocks. This will prevent the formation of “cold bridges”.

Expanded polystyrene boards can be glued from the lowest level of the foundation base and right up to the roof - to the entire outer surface of the wall.
Insulation of the foundation with mastics
A certain insulation of the foundation can also be achieved during waterproofing work. Thus, to prevent the penetration of moisture from the soil, it is recommended to cover the vertical walls of the foundation with a layer of bitumen mastic. In addition to protection from moisture, several layers of such mastic will help you isolate cracks and tiny holes, joints of foundation slabs through which heat can leak from the room.

After applying several layers of bitumen mastic, a layer of rolled waterproofing material can also be applied to the side surfaces of the foundation. Just like mastic, it will serve as an additional layer of thermal insulation.
Video - do-it-yourself foundation insulation
In past times, no one even thought about such an energy-saving measure as insulating the foundations of private houses. In this regard, many owners of previously constructed buildings began to solve this problem as best they could. Moreover, this is often done after the walls and roof of the house have been insulated, but the desired result has not been achieved. This material offers detailed answers to the questions of why it is worth insulating foundations and with what materials you can do it correctly yourself.
Why do you need to insulate the foundation?
In an ordinary private house without thermal insulation, of which there are a great many built, in winter you almost always feel cool in the lower zone of the premises. No matter how well the heating system inside a residential building works, this coolness in the feet remains and causes discomfort for the people living in it. You will say - you just need to insulate the floors, and everything will be fine. But in fact, this is not enough, because there are several reasons why it is worth insulating the foundation:
- as noted above, heat loss through floors causes significant inconvenience to people;
- the amount of heat lost can be quite significant, which increases the cost of heating a private home;
- the foundation and its above-ground part - the base - without insulation are exposed to moisture and freezing, which contributes to the slow destruction of the structure;
- in areas with heaving soils saturated with moisture, the effect of frost heaving may occur. It puts additional stress on the base until it cracks.
If everything is clear with the first item on the list, then the rest require clarification. The fact is that the share of heat losses through cold floors reaches 20% of the total amount of heat lost by the building. Therefore, all attempts to save energy resources by thermally insulating all structures of the house except the base will not achieve their goal.
Imagine that the cold penetrates inside over the entire area, and insulating the floors from the inside does not fundamentally solve the issue; for this it is necessary to insulate the foundation from the outside.
Concrete, from which the vast majority of foundations are made, has very low resistance to heat transfer. During cold weather, the concrete wall freezes, causing condensation to form on its inside, which is absorbed into the thickness of the material. As frost intensifies, this moisture turns into ice crystals and leads to the destruction of the structure. That is why you should not insulate the foundations of private houses from the inside; this will help protect against the cold, but will not protect the structural elements from destruction.
The same freezing moisture with which loess soils are saturated causes them to swell when frozen, exerting shock loads on the base. As a result, cracks may appear in the concrete, which is at least unpleasant. All of the above reasons are equally relevant for all types of houses, including wooden ones, where it is also necessary to insulate the foundation. The exception is structures on screw piles, which will be discussed below.
Conclusion. If you analyze everything said above, the answer to the question of whether it is necessary to insulate the foundation or basement of a house without a basement will become clear. Definitely - yes, it is necessary, and the presence of a basement does not play any role, thermal insulation of the base is always necessary. Modern building codes also state this.
Insulation of the foundation with polystyrene foam and penoplex
In reality, there are not so many materials suitable for these purposes. A simple rule applies here: the service life of the heat-insulating layer should be close to the durability of the structure itself, otherwise the procedure will have to be repeated periodically. It is for this reason that it is better not to use such popular and cheap polystyrene foam as insulation for the foundation.
Judge for yourself: the durability of reinforced concrete is at least 100 years, and thermal insulation made of foam plastic will crumble after 20-25 years. Despite the fact that the material will be literally buried in the ground, it is not possible to control its condition. The deterioration of the properties of the insulating layer will become noticeable only in terms of sensations and heating costs. Also, one should not discount the difficulties and cost of re-insulating the foundation, even if it is done with your own hands and again with inexpensive polystyrene foam.
The decision to use foam plastic for covering the base has the right to life and is even often implemented. But this is a manifestation of short-sightedness and an unfounded approach to the matter. In extreme cases, polymer can be used to insulate the part of the foundation protruding above ground level from the outside - the base.

In modern construction, more suitable polymer materials are used for such work:
- penoplex (otherwise known as penoplex);
- extruded polystyrene foam.
There is no fundamental difference between these polymers, especially since they are made on the basis of the same material - polystyrene. There are differences in foaming technology, but for us they are not significant. It is important that penoplex and extruded polystyrene foam have high strength and low thermal conductivity, and therefore are well suited for insulating the foundation of a private house. In addition, they practically do not absorb moisture and are very durable.
For reference. These materials have higher thermal resistance than foam. Therefore, for thermal insulation of the base, you need a layer of penoplex of a smaller thickness (usually 50 mm), which is very convenient. And the strength of expanded polystyrene allows you not to hide it under a brick before filling it with soil in order to protect it from damage.
Thermal insulation during construction
The best way to properly and reliably insulate the entire foundation with penoplex is to do it yourself at the stage of building a house. In this case, special bitumen mastic is most often used to glue polystyrene foam boards to concrete. First, the surface is leveled with cement mortar, then cleaned and covered with the first layer of mastic (primer). Rolled waterproofing is glued onto it, and insulation is placed on top. The whole “pie” is shown in the diagram:

As can be seen in the diagram, an additional protective coating of geotextile can be laid on top of the thermal insulation layer, although often the penoplex is simply covered with soil. Additional protection will not require much expense, but will significantly extend the service life of the insulation. The technology for insulating foundations with expanded polystyrene using bitumen materials is shown in detail in the video:
Another interesting way to insulate the base of a house without a basement is used in cases where the foundation is a solid concrete slab. The essence of the method is that polystyrene foam is laid on a sand bed, and a monolithic concrete base is poured on top of it. In this case, it is possible to immediately install a heating circuit for heated floors inside the monolith. This design is called the Swedish stove; a diagram of its structure is shown in the figure:

Here you can see that the Swedish slab refers to shallow foundations, insulated not only from below, but also from the sides. In terms of energy efficiency, this technology is one of the best, but it requires a very scrupulous approach to the work. Failure to comply with technological requirements can lead to cracks in the slab and damage to the underfloor heating system.

The main disadvantage of the Swedish stove is the inability to carry out repairs in case of cracking. But if the insulation of the slab is laid correctly, then such a foundation will easily stand for several decades. At the same time, the use of a solid slab is possible on various subsidence soils. In practice, this insulated structure is often used to build wooden houses instead of a traditional strip foundation.

Insulation of the foundation of an already built house
In this case, dismantling work cannot be avoided. You will have to remove the basement cladding and open up the old blind area around the building. If the foundation of the house is a shallow strip foundation, then it makes sense to dig down to its bottom in order to cover the entire surface with thermal insulation material. Another, more popular option is to insulate the base and lay penoplex under the blind area in order to prevent freezing of the underground part of the base. The ideal option is to insulate the entire foundation and soil under the blind area, as shown in the diagram:

If you decide not to dig to the ground, you should still dig a hole at least 1 m wide along the entire wall to a depth of 200-300 mm, and compact the soil. The next steps are:
- clean the surface of the base, remove all sagging, and seal the depressions and cracks with mortar;
- Using the prepared adhesive mixture, attach the polystyrene boards to the base. Additionally, secure them with special dowels - umbrellas;
- pour a layer of sand at least 100 mm thick into the hole, level and compact;
- lay out slabs of penoplex or expanded polystyrene, laying geotextiles (as in the diagram);
- fill the blind area and line the base.
How the foundation of a built house is insulated in practice is shown in detail in the video:
Insulation with polyurethane foam
The thermal insulation properties of this material are not inferior to penoplex, but its application to the surface of a concrete foundation for insulation has its own characteristics. One of them is the need for special equipment, which automatically increases the cost of work. In this case, polyurethane foam is applied manually in layers up to 50 mm thick, which is why the surface is not perfectly flat.

This means that the method is good for the underground part of the base, but on the base the insulation layer will have to be leveled in order to make the cladding. What the base of a wooden house with polyurethane foam insulation looks like can be clearly seen in the photo:

Before applying thermal insulation to the foundation, waterproofing with coating or roll materials is still required. In addition, the width of the trench must be sufficient to carry out the work, that is, at least 0.7 m.
Despite the high efficiency of polyurethane foam as insulation, its application to the foundation is associated with higher financial costs. In addition, there is a question about the durability of the material.
Insulation with expanded clay
The main advantage of expanded clay over other materials is durability. The layer of this insulation will last as long as the concrete foundation itself. In addition, the insulation technology is quite simple: expanded clay is simply poured into the cavity between the base with waterproofing and the ground, and a blind area is placed on top. How to do this correctly is shown in the diagram:

The problem with expanded clay is its thermal conductivity; as a thermal insulation material, it is significantly inferior to any modern polymers in this indicator. To verify this, just look at the table, which shows the thermal conductivity values for different insulation materials:
Note. The lower the thermal conductivity value, the better the thermal insulation properties of the material.

It turns out that to create a layer with the same properties of expanded clay, you will need to pour several times more, which is reflected in the diagram. If you need to use it to insulate the base, you will have to build a retaining wall from facing bricks, which immediately complicates the whole process and leads to higher costs. In addition, a retaining wall also requires its own foundation or it must be erected on an existing one and, again, its underground part must be insulated.
Insulation of a pile-screw foundation
The fundamental difference between this type of foundation is that initially there is a gap between the ground level and the lower part of the building, which can be of different sizes. This is especially noticeable in situations where construction was carried out on an area with uneven terrain or simply on a slope. Accordingly, in most cases, insulation of a pile foundation as such is not carried out; the issue is resolved by thermal insulation of the floors of the first floor.

Under some conditions, thermal protection of the pile foundation is still carried out, for example:
- when the piles are interconnected by a single monolithic slab - a grillage;
- if the homeowner decided to build a false base and close the gap, thus constructing an underground technical floor with communications passing through it.
Since the grillage is the same concrete slab, it should be insulated using any of the methods described in the previous sections. At the stage of constructing such a foundation, insulating material can be laid under the grillage, as suggested in the illustration:

In the second case, the gap between the ground and the house is sewn up with any type of panels or filled with brick or granite, and a blind area is built outside. Now, in order to always have a positive temperature in the underground space, the false base must be insulated from the inside with any of the materials listed earlier.

Spraying polyurethane foam works well here, since you don’t need to dig anything and the appearance doesn’t really matter, which is reflected in the photo:

Conclusion
As it turned out, the process of insulating the foundation is not as simple as it might seem at first. An important point to remember: heat passes through the heavy concrete of the base very easily, so it only needs to be insulated from the outside. Otherwise, the formation of condensation is inevitable. Ideally, the soil under the blind area should also be protected from the cold, so your foundation will never freeze.
The foundation is an important load-bearing part of the building structure. It carries a vertical load - the weight of the entire house, and resists horizontal soil pressure. It also experiences the influence of groundwater and condensate. Moisture is absorbed by the foundation through the pores. In winter, all moisture that has penetrated into the pores of materials freezes. Ice crystals tear apart the material. The nearby soil masses are also in a state of seasonal movement. All these factors can lead to the destruction of the base.
Properly performed waterproofing and thermal insulation for the winter will help reduce these risks to a minimum. Insulation only from the inside is much less effective, because the foundation itself remains subject to temperature changes.
General scheme of foundation insulation
In addition, at the junction of the foundation, floors and walls, a “cold bridge” is formed; heat will flow through it into the external environment.
Thermal insulation of the foundation from the outside helps protect it and prevent heat loss.
Types of foundations and features of their insulation
Tape at the formwork stage
If you take care of thermal insulation in advance, during design, you will get a thoughtful, energy-efficient and economical solution.
After the trench has been dug, it should be filled with sand and formwork made of sheet polystyrene foam. Such formwork must be protected from expansion by pouring concrete mortar by installing supports made of boards or thick-walled plywood.
There are also special polystyrene foam blocks with cavities on sale. They are used for masonry, like bricks or foam blocks, joined together with glue. Reinforcement is installed in the cavity of such masonry, concrete is poured and vibration compaction is carried out.
 Permanent foundation formwork
Permanent foundation formwork Formwork of this kind will be permanent and, remaining on the foundation structures, will serve as excellent thermal insulation for it.
Belt made of concrete or stone
An insulated monolithic strip foundation will last significantly longer. First, the structure poured or built from foundation blocks should be waterproofed. For this purpose, special bitumen mastics are used. The waterproofing layer must be allowed to dry until the solvents have completely evaporated. This takes from three days to a week.
Foamed foam is glued to concrete using adhesives. Acetone-based glue should be avoided - it dissolves the foam.
 Thermal insulation of strip base
Thermal insulation of strip base Protective sheets of asbestos cement can be installed on top of the foam or a layer of plaster can be applied, reinforced with a pre-installed support mesh.
 Thermal insulation coated with a layer of plaster
Thermal insulation coated with a layer of plaster How to insulate a foundation made of rubble stone? Before thermal insulation, it should also be leveled with a layer of mesh plaster.
Columnar
How and why to insulate a columnar foundation? Its thermal insulation is more difficult than tape insulation, since there is no closed loop. Insulating each pillar will have less effect than insulating a closed external contour formed by tape. Most often, the insulated contour begins with joists and a subfloor.
To ensure that the columnar foundation does not act as a conductor of cold into the house, it is necessary to create a thermal break between the top of the column and the floor structures. The material for such a gasket should:
- have low thermal conductivity;
- be strong enough - through this gasket the weight load of the house will be transferred to the foundation.
Special finely granulated high-strength foams are suitable for this.
Slab
Foundation slabs are the most advanced type of supporting structure. The insulated Swedish stove, as it is popularly called, ensures maximum strength of the structure and its resistance to seasonal soil fluctuations. Thermal insulation is carried out before casting both from the bottom and from the ends of the slab in order to prevent the formation of the so-called. "cold bridges"
A layer of rolled waterproofing material is unrolled onto a leveled and compacted sand cushion, then expanded polystyrene slabs are laid out. A reinforcement system is installed on top of them, after which the slab can be poured. Sheets cut to the thickness of the slab are secured at the ends, which will serve as permanent formwork. They are secured against expansion with special squares.
 Insulation of Swedish stove
Insulation of Swedish stove Just in case, experienced builders place external supports for the end part of the formwork from boards and thrust beams for insurance.
The thickness of the plates in Russian sources ranges between 60 and 100 mm, Western recommendations say from 200-300 mm.
Pile-screw
The problems of insulating a pile-screw foundation of a house are the same as in the case of a columnar foundation. Theoretically, you can dig up the soil to the freezing depth and make an insulated contour around the external piles.
 Insulation of piles
Insulation of piles However, in this case, the entire main advantage of screw piles is lost - the almost complete absence of excavation work and installation of the foundation of a wooden house in one day.
Most experts agree that the piles themselves do not need insulation, and it is worth focusing your attention and efforts on insulating the walls, floors and points of contact between the joists and the tops of the piles and framing to prevent the transfer of cold through them. And the piles will have to freeze.
Materials
Traditionally, materials such as:
- Expanded clay, sand or slag. The oldest and least effective method.
- Foamed plastic sheets. Polystyrene foam and expanded polystyrene are much more effective than bulk materials.
- Mineral wool. High thermal efficiency and low moisture protection.
- Sprayed coatings. Maximum efficiency and very expensive equipment.
Bulk materials
The only advantage of traditional bulk materials is their low cost. They do not place high demands on the qualifications of workers and do not require complex and expensive equipment. Such materials are often used to insulate the foundation inexpensively and with your own hands.
A large volume of backfill is carried out in parallel with the functions of waterproofing the foundation, diverting groundwater from it. This is especially important in loamy and clayey soils with high groundwater levels and low levels of freezing.
 Scheme of foundation insulation with expanded clay
Scheme of foundation insulation with expanded clay Sequence of work:
- Select the soil around the foundation deeper than its base. The width is selected from 0.5 to 1.5 meters depending on the freezing depth and groundwater level.
- Waterproof the foundation walls.
- At the bottom of the resulting trench, lay geotextile waterproofing, cover with a layer of crushed stone about 10 cm and lay out drainage pipes.
- Fill the hole with the selected bulk material using layer-by-layer compaction.
A cubic meter of sand costs several hundred rubles, depending on the delivery distance.
Sheet foam plastics
Polystyrene foam is a modern and relatively inexpensive insulation material. It combines low thermal conductivity with high resistance to stress and damage resistance. Its installation is not difficult, does not require expensive equipment and is accessible to home craftsmen.
The disadvantages of the material are the need for additional waterproofing, requirements for surface preparation and low resistance to rodents.
Sequence of work:
- Clean the foundation walls up to the base from soil and bitumen and oil contaminants. Dry them.
- Lay drainage pipes along the bottom to drain groundwater.
- Perform waterproofing with materials that do not contain bitumen and acetone - they react with foam plastic and destroy it.
- Thermal insulation boards are glued with polymer glue. Gaps and cracks are filled with polyurethane foam to minimize heat loss.
- Thermal insulation is protected from rodents with fine-mesh reinforcement mesh.
- Fill the trench with sand.
A sheet of foam plastic measuring 1000*600*50 mm costs 80-100 rubles.
A sheet of polyurethane foam measuring 1200*600*50 mm will cost 120-140 rubles.
Mineral wool
Despite the availability of the material, mineral wool is rarely used for insulating foundations. This is due to the high labor intensity of the associated work, the need for additional waterproofing of the insulation and the installation of a protective screen made of asbestos cement sheets, protecting the material from mechanical damage by the soil. As a result, the cost per square meter of thermal insulation is approaching more modern materials. Mineral wool, or ecowool, is used mainly for insulating the above-ground part of the foundation.
 Insulation with mineral wool
Insulation with mineral wool Sequence of work:
- Clean and dry foundation walls. If necessary, repair defects.
- Secure the guides from slats or metal profiles.
- Lay mineral wool slabs. Perform steam and waterproofing using special films.
- Install a ventilated façade or plaster it.
A square meter of mineral wool 50 mm thick costs 100-110 rubles.
Sprayed insulation materials
This type of material provides extremely effective thermal insulation, since the sprayed layer of foamed plastic has no seams or joints. In addition, it also serves as waterproofing.
However, a significant disadvantage is the need to use expensive specialized equipment for spraying. The cost of professional installation reaches hundreds of thousands of rubles. Household devices are cheaper, but they can only pay for themselves with a large amount of work.
The minimum non-rechargeable set of equipment for spraying along with materials, containing 0.6 cubic meters of foam, costs from 20 thousand rubles.
Insulation process
The technological process depends on the material used for thermal insulation. Details are given above in the description of materials. The general requirements are:
- Cleaning the foundation wall from soil, unevenness and dirt.
- Drainage device at a level slightly below the sole
- The need for a blind area and its thermal insulation.
Some features of the process in particular situations are given below
Insulation from outside with close groundwater
If groundwater is high, foundation insulation loses its effectiveness. In addition, seasonal movements of freezing and thawing soil can damage or tear off thermal insulation.
 Disposal of nearby groundwater
Disposal of nearby groundwater How to properly protect yourself from groundwater? During construction the following operations are performed:
- Below the base, a drainage system is laid that drains groundwater from the foundation.
- A wedge-shaped filtering sand cushion is poured between the insulation and the ground, which removes moisture from the surface of the thermal insulation to the drainage pipes.
The sand cushion will also play the role of a damper, protecting the insulation from the pressure of the heaving soil.
In order for this method to work, the following conditions must be met:
- The foundation surface line should be as smooth as possible, without ledges or depressions.
- For backfilling, use large fractions of sand, possibly mixed with slag.
- The backfill must be sifted from stones that lead to sharp damage to the thermal insulation during seasonal movements.
Insulated blind area
An insulated blind area significantly increases the efficiency of thermal insulation of the foundation. For its device you should:
- Along the perimeter of the foundation, dig a recess about a meter to one and a half meters wide and up to half a meter deep.
- Lay drainage pipes along the outer contour, connected to the general drainage system.
- Place a cushion of sand 20 cm thick and compact it.
- Lay sheets of expanded polystyrene with a thickness of 30, or preferably 50 mm. The slabs are laid with the short side to the wall, the width of the insulation is thus 120 cm.
- Cover the top with a 10-15 cm layer of sand.
- Pour the concrete blind area.
Instead of foamed polystyrene, you can use a 20-centimeter layer of slag.
 Insulation of the blind area. The formwork was installed and the reinforcing mesh was laid for pouring the mortar.
Insulation of the blind area. The formwork was installed and the reinforcing mesh was laid for pouring the mortar. Biosecurity
Insulation for foundations made of foamed plastics needs protection from a number of biological factors:
- Rodents.
- Plant roots.
- Mold and fungi.
To prevent rodents from accessing the insulation, a layer of sand should be compacted tightly. The dug trench must be thoroughly cleaned of plant roots. Sheets of asbestos cement are installed on the end side to block access to biological objects. Modern heat-insulating materials contain additives that prevent the development of mold and fungi.
Most thermal insulation methods are not complicated and do not require expensive materials and equipment. However, if the work is carried out on a ready-made foundation, all of it is associated with significant volumes of excavation work. In this case, it is better to work with assistants. With the exception of spraying, all work is performed with conventional construction tools.