Methods for producing phosphorus and its compounds. Characterization of phosphorus: being in nature, especially physical and chemical properties, application. Allotropic modifications of phosphorus
Being in nature. Pure phosphorus in its pure form does not occur in nature, since it is a chemically active element. In the form of compounds, it is widespread, accounting for about 0.1% of the earth's crust by mass. Of the natural phosphorus compounds, calcium phosphate Ca3 (POj, - the main component of apatites and phosphorites, is of the greatest importance.
Allotropic modifications. Phosphorus forms several allotropic modifications. Of these, the most important are white, red and black phosphorus. The difference in the properties of allotropic modifications of phosphorus is explained by their structure.
Chemical properties. Of all allotropic modifications of phosphorus, white phosphorus has the highest activity. It oxidizes rapidly in air. Even with weak heating, phosphorus ignites and burns, releasing a large amount of heat: 4P + 502 \u003d 2P2Os.
Phosphorus combines with many simple substances: oxygen, halogens, sulfur and some metals.
For example: 2P + 3S \u003d P, S ,; 2P + 5C12 \u003d 2RS1 ,.
Application. In match production, in metallurgy, in the production of ammunition, for the production of certain semiconductors - gallium phosphide and indium phosphide, for the creation of drugs for the destruction of insect pests.
Phosphorus compounds
Phosphides. Compounds of phosphorus with metals. During the interaction of phosphides with water, phosphine PH is released: Ca, P, + 6H20 \u003d 3Ca (OH). + 2PH ,.
Phosphia. Very poisonous gas with the smell of garlic. It resembles ammonia in chemical properties, but is a more powerful reducing agent.
Phosphorus Oxide (U). Phosphorus oxide (V) has the appearance of a white snowy mass. The density of its vapor corresponds to the formula P4O10, this formula reflects the actual composition of the molecule. Phosphorus (V) oxide is easily combined with water, therefore it is used as a water-taking agent. In air, phosphorus oxide (V), attracting moisture, quickly turns into metaphosphoric acid: P40, „+ 2H, 0 \u003d 4NRO ,.
Orthophosphoric acid. It is a colorless, well soluble in water crystals. Not poisonous. It is an acid of medium strength.
Since it is tribasic, its dissociation in aqueous solutions proceeds in three stages. Phosphoric acid is not volatile and very stable: oxidative properties are not typical for it. Therefore, it interacts with metals in the row of standard electrode potentials to the left of hydrogen.
Phosphoric Acid Salts:
a) phosphates; in them all hydrogen atoms in phosphoric acid are replaced. For example. CajCPOJj, K3P04;
b) hydrophosphates; in these salts two hydrogen atoms of the acid are substituted. For example. K, HP04. CaHP04;
c) dihydrogen phosphates — one hydrogen atom in phosphoric acid is substituted. For example. KN, P04. Ca (H, P04).
All dihydrogen phosphates are readily soluble in water. Most medium phosphates are generally poorly soluble. Of the salts of this series, only sodium, potassium, and ammonium phosphates are soluble. In terms of solubility, hydrophosphates occupy an intermediate position: they are better soluble than phosphates, and worse than dihydrogen phosphates.
Phosphoric fertilizers
Simple superphosphate. A mixture of calcium sulfate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate. To obtain this fertilizer, crushed phosphorite is mixed with sulfuric acid. The reaction produces a mixture that is highly soluble in water. Such fertilizer is obtained in large quantities in the form of powder or granules.
Double superphosphate. Concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition Ca (H, GO4) ,. It is obtained by the decomposition of natural phosphate with phosphoric acid. In double superphosphate there is no calcium sulfate, which reduces the cost of its transportation and application to the soil.
Phosphorite flour. Natural ground mineral composition SaDRO ^ ,. It is a yellowish or brown powder. Slightly soluble in water. It is used on acid podzolic soils.
Precipitate. Concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition CaHP04 - 2H, 0. It is poorly soluble in water, but soluble in organic acids. Reduces soil acidity. It is obtained by neutralizing phosphoric acid with a solution of calcium hydroxide.
More on the topic Phosphorus:
- 1.1. Properties of elemental phosphorus. 1.1.1. Phosphorus allotropy.
- 3.3.1. Kinetics of the conversion of white phosphorus in the presence of A1Bp
- 1.1.4.1. The structure of red phosphorus is an inorganic polymer.
The structure of the phosphorus atom. The element of the VA group has the electronic formula 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3. Phosphorus - non-metal. The most characteristic oxidation states: +5, +3, 0, -3. Oxides E 2 O 5 and E 2 O 3 have acidic properties. The volatile hydrogen compound is phosphine PH 3.

Allotropic modifications of phosphorus White phosphorus has a molecular crystal lattice; it is a yellowish substance with a garlic odor. In vapors it has the composition P 4. In air it ignites at 18ºС. When stored in the light, it turns into red. It is insoluble in water, but it is soluble in carbon disulfide, benzene and other organic solvents. It is very toxic: 0.1 g of white phosphorus is a lethal dose for humans.

The antidote for phosphorus poisoning is a 2% solution of copper sulfate, which should be given to the patient after 5 minutes by teaspoon until vomiting occurs. Burning phosphorus not only causes very severe burns, but also causes poisoning of the tissues adjacent to the burn site, as a result of which healing is extremely slow. For burns with phosphorus, the antidote is a wet dressing soaked in 5% solution of copper sulfate. Due to the fact that white phosphorus is easily oxidized and ignited, it is stored under water.

Red phosphorus is a powder with a weakly pronounced crystalline structure and therefore called amorphous, dark red in color, has an atomic lattice, is very hygroscopic (easily absorbs water), but is insoluble in water; it is insoluble in carbon disulfide. Red phosphorus is obtained by prolonged heating of white phosphorus without air at 450ºС. Unlike white, it is not toxic, has no smell, ignites at ºС.

![]()
Finding in nature Phosphorus is an integral part of plant and animal proteins. In plants, phosphorus is concentrated in seeds, in animals, in nervous tissue, muscles, and skeleton. The human body contains about 1.5 kg of phosphorus: 1.4 kg in the bones, 130 g in the muscles and 13 g in the nervous tissue. The phosphorus content in the human body is approximately 1% of body weight. The daily intake of phosphorus by a person is about 2 g.


Chemical properties of phosphorus Chemically, white phosphorus is very different from red. White phosphorus is easily oxidized and self-igniting in air, therefore it is stored under water. Red phosphorus does not ignite in air, but ignites when heated above 240 ° C. During oxidation, white phosphorus glows in the dark - there is a direct conversion of chemical energy into light.

Phosphorus combines with many simple substances - oxygen, halogens, sulfur and some metals, exhibiting oxidizing and reducing properties. 1. With oxygen. When burning phosphorus, white dense smoke is formed. White phosphorus ignites spontaneously in air, and red burns when ignited. Phosphorus burns in oxygen with a blindingly bright flame. 4P + 3O 2 (lack) 2P 2 O 3 (P 4 O 6) 4P + 5O 2 (excess) 2P 2 O 5 (P 4 O 10)

2. With halogens. With elements having greater electronegativity than phosphorus, phosphorus reacts very energetically. If red phosphorus is added to a vessel with chlorine, then after a few seconds it spontaneously ignites in chlorine. This usually results in phosphorus (III) chloride. 4P + 6Cl 2 (deficient) 4PCl 3 4P + 10Cl 2 (excess) 4PCl 5


5. Red phosphorus is oxidized by water at a temperature of about 800 ° C in the presence of a catalyst - copper powder: 2P + 8H 2 O 2H 3 PO 4 + 5H 2 6. Concentrated sulfuric acid oxidizes phosphorus when heated: t 2P + 5H 2 SO 4 (к) 5SO 2 + 2H 3 PO 4 + 2H 2 O 7. Nitric acid oxidizes phosphorus when heated t P + 5HNO 3 (k) 5NO 2 + H 3 PO 4 + H 2 O 3P + 5HNO 3 (dec) + 2H 2 O 5NO + 3H 3 PO 4

Obtaining phosphorus Phosphorus can be obtained by heating a mixture of phosphorite, coal and sand in an electric furnace. The equation is easier to compose if one presents the course in two stages: 1) Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 + 3SiO 2 P 2 O 5 + 3CaSiO 3 2) P 2 O 5 + 5C 2P + 5CO ________________________________________ Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 + 5C + 3SiO 2 2P + 3CaSiO 3 + 5CO

Phosphine Phosphorus in oxidation state -3 forms the hydrogen compound phosphine PH 3, similar to ammonia. This oxidation state is less characteristic of phosphorus than nitrogen. Phosphine - a poisonous gas with a garlic odor, can be obtained from zinc phosphide by the action of acids or water: Zn 3 P 2 + 6HCl 2PH 3 + 3ZnCl 2 The main properties of phosphine are weaker than that of ammonia: PH 3 + HCl PH 4 Cl

Phosphonium salts in aqueous solutions are unstable: PH H 2 O PH 3 + H 3 O + Phosphine has reducing properties (the lowest oxidation state of phosphorus), burns in air (self-ignites): 2PH 3 + 4O 2 P 2 O 5 + 3H 2 O or PH 3 + 2O 2 H 3 PO 4 Phosphine is oxidized by many oxidizing agents PH 3 + 8HNO 3 (k) 8NO 2 + H 3 PO 4 + 4H 2 O Zinc phosphide is used as a zoocide for rodent control.

Phosphorus (V) oxide Phosphorus (V) oxide P 2 O 5 (or P 4 O 10) is formed when phosphorus is burned in air. 4P + 5O 2 2P 2 O 5 The solid crystalline substance P 2 O 5 is hygroscopic and is used as a dewatering agent. 1. When interacting with water, phosphorus (V) oxide forms metaphosphoric acid NRA 3 in the cold, having a polymer structure: P 2 O 5 + H 2 O 2HPO 3


Phosphoric acid In industry, phosphoric acid is produced by the action of sulfuric acid on phosphorite: Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 + 3H 2 SO 4 3CaSO 4 + 2H 3 PO 4 Orthophosphoric acid is a crystalline substance (apl \u003d 42 ° C), soluble in water. As a tribasic acid of medium strength, it dissociates stepwise. It enters into many reactions characteristic of acids.

Chemical properties of phosphoric acid 1. With metals in the series of metal stresses to hydrogen: 3Mg + 2H 3 PO 4 Mg 3 (PO 4) 2 + 3H 2 2. With basic oxides: 3CaO + 2H 3 PO 4 Ca 3 (PO 4 ) 2 + 3H 2 O 3. With bases and ammonia: H 3 PO 4 + NaOH NaH 2 PO 4 + H 2 OH 3 PO 4 + 2NaOH Na 2 HPO 4 + 2H 2 OH 3 PO 4 + 3NaOH Na 3 PO 4 + 3H 2 OH 3 PO 4 + NH 3 (NH 4) 2 HPO 4



Salts of phosphoric acid Medium salts are distinguished - phosphates (Na 3 PO 4) and acid salts - hydrophosphates (Na 2 HPO 4) and dihydrogen phosphates (NaH 2 PO 4). Water soluble phosphates and hydrophosphates of alkali metals and ammonium. All dihydrogen phosphates are soluble in water. Phosphoric acid is displaced by stronger acids from its salts: Ca 3 (PO 4) 2 + 3H 2 SO 4 3CaSO 4 + 2H 3 PO 4 conc.


It is open in the form of a mass that looks like wax, And in the dark it shone like the light of distant stars. The alchemist was in shock, but why not be here - try to get a philosopher's stone! But joy comes with chagrin next to it, Stone does not give Health and wealth. So was that stone that glowing wax? Think guys, the question is not so simple. Riddle

Phosphorus in its importance is not inferior to nitrogen. He participates in the great natural cycle of substances, and, had there not been phosphorus, the flora and fauna would have been completely different. However, phosphorus is not found very often in natural conditions, mainly in the form of minerals, and it accounts for 0.08% of the mass of the earth's crust. In terms of prevalence, it occupies the thirteenth place among other elements. It is interesting to note that in the human body, phosphorus accounts for approximately 1.16%. Of these, 0.75% goes to bone tissue, about 0.25% to muscle and about 0.15% to nervous tissue.
Phosphorus is rarely found in large quantities, and in general it should be attributed to scattered elements. It has not been found in free form in nature, since it has a very important property, it is easily oxidized, but is found in many minerals, the number of which is already 190. The most important of them are fluorapatite, hydroxylapatite, phosphorite. Vivianite, monazite, amblygonite, trifilite and, in very limited quantities, xenotite and torbernite are found somewhat less frequently.
As for the phosphorus minerals, they are divided into primary and secondary. Among the primary, the most common are apatites, which are mainly rocks of igneous origin. The chemical composition of apatite is calcium phosphate, which contains a certain amount of fluoride and calcium chloride. It is this that determines the existence of the minerals fluorapatite and chlorapatite. In addition, they contain from 5 to 36% P 2 0 5. Typically, these minerals in most cases are found in the magma zone, but they are often found in places where igneous rocks come into contact with sedimentary rocks. Of all the known phosphate deposits, the most significant are in Norway and Brazil. A large domestic apatite deposit was discovered by academician AE Fersman in Khibiny in 1925. “Apatite is mainly a combination of phosphoric acid and calcium,” wrote AE Fersman. “The appearance of this mineral is so diverse and strange that old mineralogists they called it apatite, which means “deceiver” in Greek. Either these are crystalline crystals, to the smallest detail resembling beryl or even quartz, then these are dense masses indistinguishable from simple limestone, these are radially radiant balls, or the rock is granular and shiny like coarse-grained marble. ”
Apatity as a result of weathering processes, bacterial activity, destruction by various soil acids pass into forms that are easily consumed by plants, and thus are involved in the biochemical cycle. It should be noted that phosphorus is absorbed only from the dissolved salts of phosphoric acid. However, phosphorus is partially washed out of the soil, and a large amount of it, absorbed by plants, does not return back to the soil and is carried away with the crop. All this leads to a gradual depletion of the soil. When phosphorus fertilizers are added to the soil, productivity increases.
Despite the significant demand for phosphate fertilizers, there are apparently no particular concerns associated with the depletion of raw materials reserves. These fertilizers can be obtained by complex processing of mineral raw materials, bottom marine sediments and various geological rocks rich in phosphorus.
The decomposition of phosphorus-rich compounds of organic origin often produces gaseous and liquid substances. Sometimes you can observe the evolution of gas with the smell of rotten fish, phosphorous hydrogen, or phosphine, PH3. At the same time as phosphine, another product is forming - diphosphine, P 2 H 4, which is a liquid. The diphosphine vapor spontaneously ignites and ignites phosphine gas. This explains the appearance of the so-called "wandering lights" in places such as cemeteries and swamps.
“Wandering lights” and other cases of luminescence of phosphorus and its compounds caused superstitious fear in many people who are not familiar with the essence of these phenomena. This is what Academician S.I. recalls working with gaseous phosphorus. Volfkovich: “Phosphorus was obtained in an electric furnace installed at Moscow University on Mokhovaya Street. Since these experiments were then conducted in our country for the first time, I did not take the precautions that are necessary when working with gaseous phosphorus - a poisonous, self-igniting and luminous bluish-colored element. For many hours of working at the electric furnace, part of the emitted gaseous phosphorus soaked my clothes and even my shoes, so that when I walked from the university at night along the dark streets of Moscow that were not illuminated then, my clothes radiated a bluish glow, but from under my boots (when rubbing them on the sidewalk) sparks were carved.
Every time a crowd gathered behind me, among which, despite my explanations, there were many people who saw in me a “newly appeared” representative of the other world. Soon among the residents of the Mokhovaya street district and throughout Moscow, fantastic stories about a luminous monk began to be passed from mouth to mouth ... "
Phosphine and diphosphine are quite rare in nature, and more often you have to deal with phosphorus compounds such as phosphorites. These are secondary minerals-phosphates of organic origin, play a particularly important role in agriculture. On the islands of the Pacific Ocean, in Chile and Peru, they were formed on the basis of bird droppings, guano, which in dry climates accumulates in powerful layers, often exceeding a hundred meters.
The formation of phosphorites can also be associated with geological disasters, for example, with the ice age, when the death of animals was massive. Similar processes are possible in the ocean during the mass death of marine fauna. A rapid change in hydrological conditions, which may be associated with various mountain building processes, in particular with the action of underwater volcanoes, undoubtedly, in some cases, leads to the death of marine animals. Phosphorus from organic residues is partially absorbed by plants, but mainly, dissolving in sea water, passes into mineral forms. Sea water contains phosphates in fairly large quantities - 100-200 mg / m3. In certain chemical processes in seawater, phosphates can precipitate and accumulate at the bottom. And when raising the seabed in various geological periods, phosphorite deposits are on land. Similarly, a large domestic phosphorite deposit could form near Kara-Tau in Kazakhstan. Phosphorites are also found in the suburbs.
| Phosphorus cycle in nature |
A good explanation of the most important stages of the phosphorus cycle in nature is the words of a famous scientist, one of the founders of the Russian science of the study of phosphorus fertilizers, Y. V. Samoilov: “Phosphorus of our phosphorite deposits is of biochemical origin. From apatite, a mineral in which almost all the phosphorus of the lithosphere was originally enclosed, this element passes into the body of plants, from plants into the body of animals, which are true concentrators of phosphorus. Having passed through a series of animal bodies, phosphorus finally drops out of the biochemical cycle and returns to the mineral one. Under certain physical and geographical conditions, mass death of animal organisms occurs in the sea.
| Phosphorus |
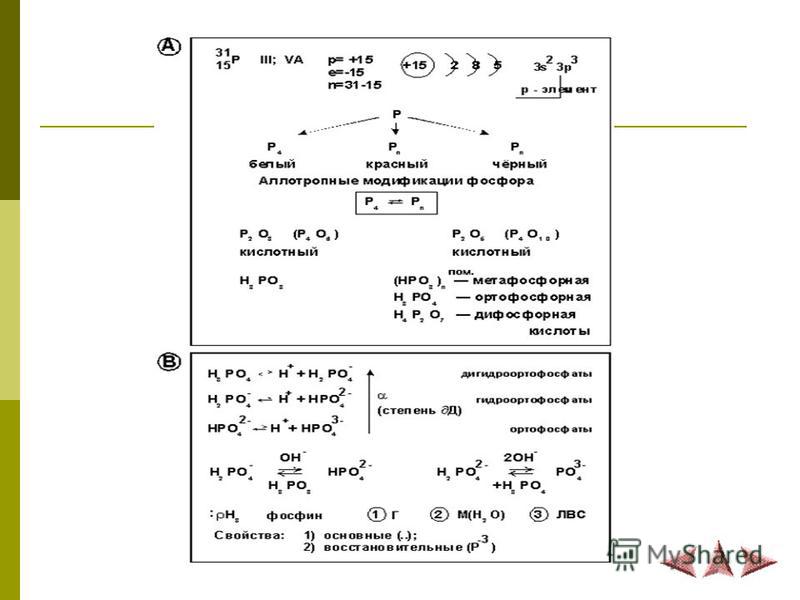
Being in nature. Pure phosphorus in its pure form does not occur in nature, since it is a chemically active element. In the form of compounds, it is widespread, accounting for about 0.1% of the earth's crust by mass. Of the natural phosphorus compounds, calcium phosphate Ca3 (POj, the main constituent of apatite and phosphorite, is the most important. Allotropic modifications. Phosphorus forms several allotropic modifications. Of these, white, red and black phosphorus are most important. The difference in the properties of allotropic modifications of phosphorus is explained by their structure . Chemical properties. Of all allotropic modifications of phosphorus, white phosphorus is the most active. It oxidizes rapidly in air. Even with weak heating, phosphorus ignites and burns. t, emitting a large amount of heat: 4P + 502 \u003d 2P2Os. Phosphorus combines with many simple substances: oxygen, halogens, sulfur and some metals. For example: 2P + 3S \u003d P, S ;; 2P + 5C12 \u003d 2PC1, .Application. B match production, in metallurgy, production of ammunition, for some semiconductors - gallium phosphide and indium phosphide, to create drugs for the destruction of insect pests. Compounds of phosphorus Phosphides. Compounds of phosphorus with metals. Phosphine PH is released during the interaction of phosphides with water: Ca, P, + 6H20 \u003d ЗСа (ОН). + 2РН,. Phosphines. Very poisonous gas with the smell of garlic. It resembles ammonia in chemical properties, but is a more powerful reducing agent. Phosphorus oxide (U). Phosphorus oxide (V) has the appearance of a white snowy mass. The density of its vapor corresponds to the formula P4O10, this formula reflects the actual composition of the molecule. Phosphorus (V) oxide is easily combined with water, therefore it is used as a water-taking agent. In air, phosphorus oxide (V), attracting moisture, quickly turns into metaphosphoric acid: P40, „+ 2H, 0 \u003d 4HPO, orthophosphoric acid. It is a colorless, well soluble in water crystals. Not poisonous. It is an acid of medium strength. Since it is tribasic, its dissociation in aqueous solutions proceeds in three stages. Phosphoric acid is not volatile and very stable: oxidative properties are not typical for it. Therefore, it interacts with metals in the row of standard electrode potentials to the left of hydrogen. Salts of phosphoric acid: a) phosphates; in them all hydrogen atoms in phosphoric acid are replaced. For example. CajCPOJj, K3P04; b) hydrophosphates; in these salts two hydrogen atoms of the acid are substituted. For example. K, HP04. CaHP04; c) dihydrogen phosphates — one hydrogen atom in phosphoric acid is substituted. For example. KN, P04. Ca (H, P04). All dihydrophosphates are highly soluble in water. Most medium phosphates are generally poorly soluble. Of the salts of this series, only sodium, potassium, and ammonium phosphates are soluble. According to their solubility, hydrophosphates occupy an intermediate position: they are better soluble than phosphates and worse than dihydrogen phosphates. Phosphate fertilizers Simple superphosphate. A mixture of calcium sulfate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate. To obtain this fertilizer, crushed phosphorite is mixed with sulfuric acid. The reaction produces a mixture that is highly soluble in water. Such fertilizer is obtained in large quantities in the form of powder or granules. Double superphosphate. Concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition Ca (H, GO4) ,. It is obtained by the decomposition of natural phosphate with phosphoric acid. In double superphosphate, there is no calcium sulfate, which reduces the cost of its transportation and application to the soil. Phosphate flour. Natural ground mineral composition SaDRO ^ ,. It is a yellowish or brown powder. Slightly soluble in water. It is used on acid podzolic soils. Precipitate. Concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition CaHP04 - 2H, 0. It is poorly soluble in water, but soluble in organic acids. Reduces soil acidity. It is obtained by neutralizing phosphoric acid with a solution of calcium hydroxide.
Being in nature. Pure phosphorus in its pure form does not occur in nature, since it is a chemically active element. In the form of compounds, it is widespread, accounting for about 0.1% of the earth's crust by mass. Of the natural compounds of phosphorus, calcium phosphate Ca3 (ROD) is of the greatest importance, which is the main component of apatites and phosphorites.
Allotropic modifications. Phosphorus forms several allotropic modifications. Of these, the most important are white, red and black phosphorus. The difference in the properties of allotropic modifications of phosphorus is explained by their structure.
Chemical properties. Of all allotropic modifications of phosphorus, white phosphorus has the highest activity. It oxidizes rapidly in air. Even with weak heating, phosphorus ignites and burns, releasing a large amount of heat: 4P + 502 \u003d 2P20).
Phosphorus combines with many simple substances: oxygen, halogens, sulfur and some metals.
For example: 2Р + ЗБ \u003d Р, 5); 2P + 5C12 \u003d 2RS15.
Application. In match production, in metallurgy, in the production of ammunition, for the production of certain semiconductors - gallium phosphide and indium phosphide, for the creation of drugs for the destruction of insect pests.
Phosphorus compounds
Phosphides. Compounds of phosphorus with metals. Phosphine PH is released during the interaction of phosphides with water: Ca, P, + 6H20 \u003d ЗСа (ОН), + 2РН ,.
Phosphip. Very poisonous gas with the smell of garlic. It resembles ammonia in chemical properties, but is a more powerful reducing agent.
Phosphorus Oxide (U). Phosphorus oxide (V) has the appearance of a white snowy mass. The density of its vapor corresponds to the formula P40 | (1, this formula reflects the actual composition of the molecule. Phosphorus (V) oxide is easily combined with water, therefore it is used as a water-taking agent. In air, phosphorus (V) oxide, attracting moisture, quickly turns into metaphosphoric acid: P40 „, + 2H, 0 \u003d 4HP03.
Phosphoric acid. It is a colorless, well soluble in water crystals. Non-toxic.
It is an acid of medium strength. Since it is tribasic, its dissociation in aqueous solutions proceeds in three stages. Phosphoric acid is non-volatile and very stable: oxidative properties are not characteristic of it. Therefore, it interacts with metals in the row of standard electrode potentials to the left of hydrogen.
Phosphoric Acid Salts:
a) phosphates: in them all hydrogen atoms in phosphoric acid are replaced. For example. Ca3 (PO ^ K3P04;
b) hydrophosphates; in these salts two hydrogen atoms of the acid are substituted. For example. K, HP04. CaNRO;
c) dihydrogen phosphates — one hydrogen atom in phosphoric acid is substituted. For example, KH, Rog Ca (H, P04) ,.
All dihydrogen phosphates are readily soluble in water. Most medium phosphates are generally poorly soluble. Of the salts of this series, only sodium, potassium, and ammonium phosphates are soluble. Hydrogen phosphates are intermediate in their solubility: they are better soluble than phosphates and worse than dihydrogen phosphates.
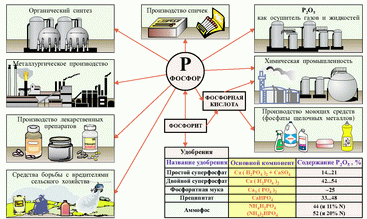
Phosphoric fertilizers
Downtime superphosphate. A mixture of calcium sulfate and calcium dihydrogen phosphate. To obtain this fertilizer, crushed phosphorite is mixed with sulfuric acid. The reaction produces a mixture that is highly soluble in water. Such fertilizer is obtained in large quantities in the form of powder or granules.
Double superphosphate. Concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition Ca (H, P04) g It is obtained by decomposition of natural phosphate with phosphoric acid. In double superphosphate there is no calcium sulfate, which reduces the cost of its transportation and application to the soil.
Phosphorite flour. Natural ground mineral composition SaDRO ^ ,. It is a yellowish or brown powder. Slightly soluble in water. It is used on acid podzolic soils.
Precipitate. Concentrated phosphorus fertilizer composition CaHP04 2H, 0. It is poorly soluble in water, but soluble in organic acids. Reduces soil acidity. It is obtained by neutralizing phosphoric acid with a solution of calcium hydroxide.
More on the topic Phosphorus:
- Bocharov V.V .. Investments. SPb .: - 176 p. (ser. "Tomorrow exam"), 2008


