Use of ashes as fertilizers. Wood ash as a fertilizer: how to apply in the garden
Article Content
Without a doubt, ash residues are the oldest type of fertilizer, proposed by nature to the once observant farmers. After all, the blackened forest and steppe conflagrations are invariably covered by lush green herbs by the spring, and seeds that fell from the trees hasten to hatch behind them. On the incinerated earth, after the first rains, all living things unite in growth. In this sense, only natural forest compost from fallen leaves and twigs can compete on equal terms with the beneficial product of fire.
Good old wood ash as a fertilizer will easily and naturally replace any artificial potash - phosphorus mixture with the same natural ingredients. It has a high calcium content. There is a rich palette of trace elements: magnesium, molybdenum, sulfur, copper, boron, iron. There is almost everything that cultivated plants need, there is only nitrogen. This is the uniqueness of ash as fertilizer.
This natural product is especially valuable in the complete absence of harmful chlorine.
Leave brand mineral mixtures created in chemical plants on the shelves of garden centers. The agricultural technology of the Stone Age in this case is not a regression vector. Today, in the 21st century, the use of ash as a fertilizer is once again universally practiced. This grandfather technology is now respectfully called organic farming.
Invisible differences
Interestingly, a curious young scientist Dmitry Mendeleev once compiled a complete description of the composition of ash remains. It was he who determined that organic substances during combustion form very different compositions of trace elements. For example, the incinerated clover and the ashes of burnt oak firewood vary greatly in structural content.
Agronomists still use this work of the great scientist.
Further research on the verge of organic chemistry and botany laid out information on the shelves - how to fertilize with ash, which plants are most useful for this or that species, and which plants do not accept it at all. Ashes can be harmful to them.
firewood used in stoves, fireplaces, barbecues; green and dry vegetation (weeds, shrubs, mowed grass, leaves).
It is such a treat that not only garden plantings will love, but also fruit trees.
The product is the richest in microelements from burnt vines of grapes, quinoa, and sunflowers. Ash such as fertilizer is most accessible to food-seeking roots. It has a unique structure resembling the finest dust.
In the product remaining on the fire after burning willow, pine, poplar, potassium poplar is several times less than in the ash from the wood of fruit trees.
The ash of burnt coal is also not rich in potassium, phosphorus and calcium. Some people consider this stove product useless and even able to do harm. This is a wrong judgment. After all, coal ash is not so poor. It is dominated by silicon oxides. It is well used as a nutritious and loosening additive in heavy soils, in which there is a lot of dense clay.
For some plants, wood ash may not be enough as a complete feeding. For example, raspberries also require nitrogen.
Ash dressing recipe

Here is the formulation of fertilizing some common plants in summer cottages:
Potatoes
When planting: one glass in the hole under the tuber. No need to mix. Just lay the material on the ash base and bury it.
After two weeks, when hilling, apply 2 kg per 1 sq. M. It is useful to repeat the procedure after a month. Powder leaves after every rain.
What is the result? Great benefit:
colorades will disappear or the damage caused by bugs will be minimal; potatoes will add a few record kilograms from the bush to the crop; the tubers will have a lot of starch.
Tomatoes and Cucumbers
Preplant treatment. For a couple of weeks before planting seedlings, loosen the beds, dig holes. In each, add half a glass of fertilizer, mix with the ground, pour. If the soil is heavy, add a glass of sand.
Superficial top dressing. During the growth period of the bushes, regularly free the root space from weeds. Once a month, feeding with ash is required (half a glass per bush). Loosen carefully (superficial roots), water the powder.
Basal watering. Prepare a solution of ash and water (1: 1). Leave the container in a sunny place in the garden, insist for two weeks. Then water the tomatoes and cucumbers under the root in the evening. Dilute the concentrate with warm water (1:10). After the “vitamin” watering, cover the beds with mulch from mowed grass.
Bow
Powder the groove for the seedling. Young onions love ash. Arrange the onions - seedlings, pour and sprinkle with earth 2-3 cm.
Peas, beans
A good idea is to use ash as a fertilizer for legumes. They adore ash feeding and gratefully respond to them. When planting seeds, add 100-150 g of ash to the wells, mix with the ground, water, mulch. In a few days, friendly shoots will appear. For curly varieties, install supports immediately so that subsequently you do not tear the roots.
Grape
Grapes are a child of the sun and ashes. The best varieties grow on the slopes of sleeping volcanoes, covered with a multi-meter ash layer formed by ancient eruptions. Feel free to add this substance to you (on a well-developed bush - three kilos).
This method is universal. Its use is not limited to nutrition of plantings. The soil becomes loose, unwanted fungi and other bacterial animals are suppressed. And also - planting resistance to frost and disease is noticeably increased.
Gardeners and gardeners use ashes and as an effective means of combating plant pests.
What is the soil on your site?
Any fertilizer serves, first of all, for enrichment and structural change of depleted soil from which the root system draws the necessary substances.
Therefore, for a competent, informed process of enriching the earth with ash, it is necessary to determine what soil in your garden and under garden trees, whether or not it is “liked” by certain plants. In various soils, ash fertilizer is effective from two to four years.
You can conduct a fairly accurate analysis on your own, without resorting to the services of specialists.
Koloboks, sausages and rings
Sandy and peaty soils are light, crumbly. They are easy to identify by touch and by eye.
Here is an easy way to identify other common soil structures.
Moisten a lump of earth, form a ball. Then, in your palms, roll the bun into a thin sausage (about a pencil thick or even thinner). Try to collapse it into a ring. Now compare with the determinant list. In parentheses indicate what your soil needs:
Sandy loam. The gingerbread man turned out, but the sausage fell apart. Root crops develop well, ground vegetables - poorly. (Enriched with peat, clay, compost).
Loam. The sausage is curled into a ring, but it is covered with cracks. This soil is heavy, it is quite productive, but requires constant replenishment with organic matter. (Add compost, coarse sand, coal ash, peat, humus).
Alumina. The ring curled up without cracks. The substance is dense, heavy. Water and air do not penetrate well to the roots. Root crops develop poorly, grow small. (Regularly dig up, add sand, peat, ash, other organic matter, cover with mulch).
Acidity
Few garden and garden plants (cranberries, sorrel, turnips, radishes, decorative heather, boxwood) develop well in acidic soils. Most vegetables are contraindicated. For example, cabbage under such conditions will certainly get sick keel. Knowing how to use ash can effectively reduce acidity. Peat ashes are especially good for these purposes. It is rich in lime, perfectly deoxidizes and alkalizes the soil. But there is little potassium in it.
There were clear rules for making wood ash.
If the site is heavy soil, it is applied in the fall, under digging. If it is light, work is carried out in the spring, so that snow and rains do not carry the trace elements into the porous layers lying below the surface root system of most vegetable crops.
Ash additives are often made when digging a garden. But it is better to fill them in already formed beds or holes for seedlings. In this case, the components must be mixed well with the ground.
These wonderful additives are suitable for all types of soils and for all types of vegetable and berry crops. But their overabundance can be harmful, observe the recommended proportions. Plants love measure.
Caution, dangerous poison!
Some summer residents are too lazy to take out the garbage and burn it directly on the sites. Plastic bottles, polystyrene packaging, plastic bags, construction and household waste are sent to the fire. Cardboard and newspapers are put there to make it better.
This barbaric practice does not only poison you and your neighbors with highly toxic smoke. Combustion products contain extremely hazardous substances - carcinogens. Once in the lungs, they are quite capable of provoking cancers.
Carcinogenic compounds at a relatively low temperature of the flame of the fire do not collapse, but only multiply when heated. It is not necessary to speak about useful substances in the charred remains of garbage.
Of course, nothing can be "fertilized" with such poison. It will cause irreparable damage to the crop.
How to harvest and store

Carefully collect the contents of the furnace ash pan or fireplace insert and store in a dry place with a draft. Moisture deprives valuable food for garden residents of many trace elements: they are either destroyed or washed away.
Use waterproof bags for storage. It is convenient to use large plastic large water bottles with screw caps for storage.
Ash is collected and stored separately for the garden: wood, grass, straw, grape, peat. Each package used is useful to sign, indicating the origin and composition of the ash.
A specially built brick hearth for burning wood residues will regularly replenish supplies. It is possible to adapt an iron barrel under a capacious "potbelly stove".
Avoid burning wood affected by fungi, mold. In general, low-quality wood is better not to use. Dried tree branches are often cut down in the city, but they should not be collected either: such firewood is thoroughly saturated with toxic exhausts from car engines.
Weight and volume
Finally, for the convenience of gardeners, here are some useful metric data. They will come in handy if you need to more accurately measure the amount (weight or volume) of an ingredient to “nourish” tender seedlings or to create complex fertilizers with your own hands.
So, how much dry ash is contained in common improvised measures:
in one tablespoon with top - 7 grams; in a 250-gram glass beaker - 100 grams; in a half-liter jar - 250 grams; in liter containers - exactly a pound.
The use of ash as fertilizer in large areas is conveniently planned in buckets. But now it’s very different in capacity.
Weigh the selected empty bucket on the steelyard, and then fill it and weigh it again. Subtract the first digit from the second. The result indicates the weight of the contents of your bucket. Now fertilizer with ash will be accurate and verified.
Wood ash as a fertilizer has been used for a long time. This substance is rich in various trace elements necessary for plant growth. Let's figure out how to properly apply ashes on the site.
Wood ash is a low-cost and affordable option for fertilizer, which contains about 30 minerals necessary for the proper development of plants. It neutralizes the acidity of the soil and makes garden crops unattractive to pests. In addition, ash positively affects the air permeability of the soil - makes the earth more loose, which contributes to the development of the root system of plants.
Wood ash is a natural mineral fertilizer based on organic matter.
Wood Ash Composition
Depending on the type and age of the plant that is burned, the composition of the ash varies. But there is a general formula derived by Mendeleev, from which you can find out the approximate percentage ratio of substances contained in 100 g of ash.
As you can see, the composition of the ash includes elements useful for plants, such as calcium, potassium, sodium and magnesium. Without them, our green pets will not be able to fully develop and bear fruit.
So, calcium carbonate improves metabolic processes and accelerates the growth of vegetative tissues. This substance is especially important for flowering plants, as it contributes to a more magnificent flowering.
Calcium silicate "sticks together" plant cells and helps the green body absorb vitamins. Onions react very sharply to the deficiency of this compound: the bulbs of such plants exfoliate and dry out.
Calcium sulphate - It is a calcium salt of sulfuric acid, which is part of such a popular fertilizer as superphosphate.


Calcium chloride - A necessary element for fruit and vegetable crops (especially cucumbers, pumpkins and zucchini). It promotes the formation of enzymes, participates in photosynthesis, helps transport nutrients, increases the winter hardiness of plants and their immunity to many dangerous diseases (in particular, to rot), and also maintains the uniformity of the soil.
Potassium Orthophosphate Helps regulate plant water balance. With a deficiency of this substance, ammonia accumulates in the leaves and roots, which inhibits the growth of plants. And this substance also helps to increase the winter hardiness of heat-loving crops and creates a favorable alkaline environment for roses, lilies and chrysanthemums.
Magnesium compounds Along with potassium, they participate in the production of energy by the plant, in the formation of carbohydrates, which become the building material for starch and cellulose.
Sodium compounds (sodium orthophosphate and sodium chloride) improve the water balance of plants and activate their enzymes. Sodium is especially needed for tomatoes.
Excess micronutrients in the soil are as harmful to plants as their deficiency. Therefore, wood ash should not be used if crops suffer from excess calcium or potassium. This can be determined by the excessive growth of leaf rosettes, the death of shoots along the entire length, browning of the fruit, premature fall of the leaves, as well as a change in their color (they turn white).
How to collect ash?
Ash happens stove (from burnt firewood) and vegetable. The first one is just gently taken out of the oven, and for cooking the second one needs a special device. You can use a metal box (preferably with a lid and a tray). At the same time, holes must be made in the bottom of the container through which ash will spill out into the pan.
Any plant debris is burned in a box: tree branches, hay, straw, tops, weeds. But for this purpose it is better not to use trees that have grown near highways: such ash will contain a lot of lead and other heavy metals. Also, ash cannot be used as a fertilizer after burning polymers, household waste, rubber, glossy magazines, colored paper and synthetic materials. Such ashes will not fertilize, but poison the soil in the garden.
The ash produced by burning hardwood contains more potassium. And ash from coniferous species - more phosphorus.


What plants and how to fertilize with wood ash?
Some plants especially like wood ash. Therefore, it is quite capable of replacing chemical fertilizers.
- Under cucumbers, zucchini and squash make 1 glass of ash during the digging of the soil, 1-2 tbsp. in each hole when planting seedlings, and on depleted soils during the growing season they additionally fertilize plants during irrigation: use 1 glass of ash per sq.m.
- Under tomatoes, peppers and eggplant during the digging of the soil, 3 glasses of ash per square meter are brought in, and when planting seedlings of these crops, a handful per hole.
- Under different types of cabbage when digging, they add 1-2 glasses of ash per square meter, when planting seedlings - also a handful in the hole.
- Under bow and winter garlic during autumn digging, 2 cups of ash per square meter are brought into the soil, and in the spring (as fertilizer) - 1 cup per square meter.
- Before sowing peas, beans, lettuce, watercress, radish, dill, carrots, parsley, radish and beetroot 1 glass of ash per 1 sq.m.
- When landing potato 2 matchboxes of ash are mixed with the ground and placed under the tuber in each well. In the spring during digging, apply 1 glass of ash per sq.m. During the growing season, wood ash is also used as top dressing: during the first hilling of potatoes, 1-2 tablespoons are made under each bush. ash, and at the second hilling (at the beginning of budding), the rate is increased to 1/2 cup under the bush.
In order for potatoes and garlic to be better stored in the winter, you can sprinkle them with sifted ash. So you provide them with additional protection against decay.
- Grape they are fed several times a season: in the evening, an infusion of ash is sprayed on the leaves of plants (1 kg of fertilizer is dissolved in 3 buckets of water, and before use it is additionally diluted with water in a ratio of 1: 5).
- When growing roses wood ash is introduced during the autumn digging to normalize the acidity of the soil. From the second year, roses are fed in the spring (100 g per 10 liters of water). Foliar top dressing is also used: infusion prepared from 200 g of ash and 10 l of water is sprayed on the leaves of plants.
- When landing seedlings in the pit, you can add up to 1 kg of ash mixed with earth (under fruit trees), up to 500 g - under berry shrubs.
- When growing seedlingsTo reduce soil acidity, ash can also be added. The amount is calculated individually, depending on what kind of land you used when preparing the soil, and what plants you plan to sow. But the average proportion is 1 glass of ash per bucket of earth.
- Some gardeners contribute ash to near-tree circles of trees and shrubs for digging every two to three years. And gardeners alternate the feeding of vegetables with the help of organic fertilizers and ash infusion under the root in the proportion of 1 glass of ash per bucket of water.
Some gardeners use ash infusion as an organic stimulant to help seeds germinate. For this, seeds are wrapped in a piece of cloth moistened with ash solution and left for several hours. In the future, they are dried and sown.


Ash slightly reduces the acidity of compost, creates favorable conditions for the development of beneficial microorganisms and the work of earthworms.
The use of ash on different types of soils
Wood ash does not fertilize soils with a high alkali content, as ash alkalizes the earth. In such a soil, plants cannot develop properly. And when wood ash is introduced into acidic soils, on the contrary, their reaction becomes neutral, which creates favorable conditions for crops.
The only exceptions are plants that initially prefer acidic soil (radishes, melons). Therefore, they need to be fed with ash with caution to prevent alkalization of the soil.
On sandy soils, ash is applied only in the spring, and on heavier soils it can also be used for autumn digging. On loamy and clay soils, it is enough to add only 300-500 g of ash per 1 sq. M - this will improve the fertility and structure of the earth. And even after a single application of such fertilizer, the positive effect can last up to 4 years.
Ash as a pest control
Wood ash is not only an excellent fertilizer, but also an effective means of combating fungal diseases (in particular) and insects that damage garden and garden crops.


When 2-3 real leaflets appear on cabbage, radish, radish and rutabaga, the plants are dusted with a mixture of ash and tobacco dust (in equal proportions). This will protect vegetables from cabbage flies and cruciferous fleas.
Before planting in the soil, potatoes are dusted at the rate of 1 kg of ash per 30-40 kg of tubers. After such a procedure, the potato becomes unattractive to. And many gardeners note that regular addition of ash to the earth helps to exterminate.
Powder dusting of carrots, feathers of onions and shoots of cabbage, radish and other cruciferous trees with wood ash helps to fight carrot and onion flies, as well as cruciferous flea. Treatment of cabbage leaves with sifted ash dissolved in water (1 glass of ash per bucket of warm water), according to some gardeners, also reduces damage from caterpillars.
Ash infusion is effective when used in the fight against. It is prepared simply: 12 l of cold water, 110 g of laundry soap and ash, 20 g of urea are thoroughly mixed and insisted for 2 days.
To protect strawberries (garden strawberries) from gray rot, during the ripening period of the berries, you can sprinkle plants with ash (2 tablespoons per bush).
Ash as a fertilizer contains many elements from the periodic table, the main ones are phosphorus, potassium, calcium, silicon, magnesium, iron, as well as trace elements: boron, manganese, copper, zinc, molybdenum and others. All these substances are necessary for the development and health of plants, so wood ash is considered the most complex mineral fertilizer. Many throw away dry grass, tops, branches after pruning the garden, dry leaves, but you can burn all plant debris and get valuable fertilizer for plant nutrition - ash.
The content in the ash of the main plant nutrients - phosphorus, potassium and calcium, depends on what plant residues were burned. For example, when burning hardwood firewood, ash contains about 5% phosphorus, potassium up to 10-15%, and calcium up to 40%. If we compare the ash obtained after burning the tops, straw and grass, then potassium can reach 30% in it, and calcium, on the contrary, is twice less than about 20%.
Another significant factor in favor of using ash as a fertilizer is that it does not contain chloride compounds, which many plants are sensitive to - potatoes, cucumbers, zucchini, cabbage, strawberries, raspberries, currants.
Ash has a beneficial effect on the composition and structure of the soil, it loosens it and neutralizes excess acidity. It is useful to bring ash into acidic and swampy soil, but to deoxidize clay or peat soil, it will be necessary to add ash twice as much as, for example, lime, about 1.5 kg of ash per 1 sq.m. As phosphorus-potassium fertilizer, it is enough to add 100-150 g of ash per 1 sq.m ..
Ashes contribute for digging in the fall or spring, you can also bring it into the holes, furrows, planting pits before planting, just mix the ash and soil thoroughly so as not to burn the roots of the plants.
Do not add ash together with mullein or nitrogen-containing mineral fertilizers, since nitrogen enters into a reaction, turns into ammonia and volatilizes. Also, phosphorus fertilizers do not work together with ash, since ash creates an alkaline environment in which phosphorus compounds are inaccessible to plants.
For plants loving acidic soil - heather, hydrangea, conifers, ashes as fertilizers and top dressing should not be made. However, ash is recommended to feed potatoes. When dusting seed tubers with ash, they germinate better. Effectively add ash when planting potatoes in each well. For potatoes, ash is the best potash fertilizer, in which the yield is increased, and the starch content in the tubers is increased.
Ash as a fertilizer weighing 1 kg will replace about 220 grams of superphosphate or 240 grams of potassium chloride or 500 grams of lime. To fertilize 10 acres you will need about 10-12 kg of ash.
During the period of plant growth and harvesting, it is possible to carry out liquid top dressing with ash, for this, 50-100 grams of ash are bred in a bucket of water, about half a glass - a glass and watered with a plant solution.
Still ash is an effective tool for controlling pests and plant diseases.
When sowing vegetable seeds for seedlings, soak them in water with ash, then the seedlings will be friendly and strong. Ash is an excellent protective agent against the "black leg", a common disease of seedlings. Sprinkle the surface of the earth in crates with seedlings of ash and the "black leg" will recede.
Very often gardeners use ash-soap solution to combat aphids, flea, scoop, whitewash. To make an ash-soap solution for spraying plants, pour 300 g of ash with 10 liters of hot water. After a day, strain the solution through cheesecloth and dissolve 30 g of laundry soap in it. With a soapy soap solution, spray the plants in the morning, evening or in cloudy weather so as not to burn the leaves. Repeat spraying in 10-14 days.
There is an easy way to control pests with ash. For example, dusting cabbage, radish, radish with ash, you can frighten off the cruciferous flea and cabbage fly, and dusting with onion ash will protect it from the onion fly. Sprinkling soil around the plants with ash creates an obstacle to the movement of slugs and snails.
Topping perennial plants with ash should also be done in autumn to increase their cold resistance in the coming winter.
You can store ash for a long time, it does not lose its properties. The main thing is to keep it in a hermetically sealed container or plastic bag in a dry place to protect it from moisture.
Wood ash as a fertilizer has been used since ancient times. She is one of the most valuable sources. calcium, potassium, magnesium and sodium, as well as other substances necessary for the full growth and development of plants.
The exact chemical composition of this substance of natural origin cannot be determined, since it varies depending on the type and age of the plant that was burned. However, even Mendeleev derived a general formula, which indicates the approximate percentage of elements in 100 grams of ash.
Ash formula
This organic fertilizer is rich in various trace elements. Some of them catalyze growth and development, others help fight various diseases. The concentration may be higher or lower than stated. You can focus on the formula below to understand what substances in an approximate ratio are contained in this organic fertilizer.
The composition of wood ash:
- CaCO3 (calcium carbonate) - 17%
- CaSiO3 (calcium silicate) - 16.5%
- CaSO4 (calcium sulfate) - 14%
- CaCl2 (calcium chloride) - 12%
- K3PO4 (potassium orthophosphate) - 13%
- MgCO3 (magnesium carbonate) - 4%
- MgSiO3 (magnesium silicate) - 4%
- MgSO4 (magnesium sulfate) - 4%
- NaPO4 (sodium orthophosphate) -15%
- NaCl (sodium chloride) - 0.5%
From the presented formula it can be seen that wood ash as a fertilizer contains one of the most important elements of plant nutrition - calcium. It is necessary for the normal growth of green mass at the initial stage of development, and provides a balanced diet throughout the growing season. This is especially important for garden crops, which form a large aerial part, for example, tomatoes, pumpkins,.
Table: ash composition variations, depending on type:

Calcium carbonate
When ash is used as a fertilizer, active growth is observed, and more compact (in terms of) maturation of such members of the nightshade family as tomatoes. Calcium Carbonate (CaCO3) affects the activity of metabolic processes. It enhances the speed of movement of substances through the cells of the plant body, and normalizes the flow of biochemical processes. This property allows it to be used as fertilizer. This element is especially useful for flowers, as it affects the size and splendor of the buds.
Fertilizing cucumbers with ash, which contains a large amount of calcium carbonate compounds, helps them to fully develop. This plant is characterized by the continuous growth of vegetative tissues, and Ca serves as a link in the transport of nutrients to cells.
Calcium silicate
Calcium silicate (CaSiO3) - a substance that, when combined with pectin components, glues cells, holding them together. Helps to actively absorb vitamins.For example, it reacts very sharply to CaSiO3 deficiency. Bulb is dried and stratified. This situation can be corrected by watering the plant with infusion of ash.
Calcium sulphate
Calcium Sulphate (CaSO4) is a calcium salt of sulfuric acid. It is part of one of the most popular mineral fertilizers. When used in the composition of the ash, it has a less powerful, but longer-lasting effect on plants than in the composition of mineral top dressing.
Calcium is especially important for seedling growth., during the formation of green mass, for example, for flowers and herbs, onions and parsley. With age, this element accumulates in the stems and leaves, and after its death returns to the soil.
Calcium chloride
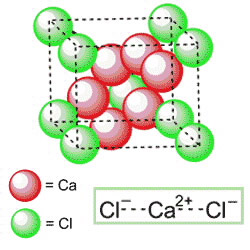 Calcium Chloride (CaCl2). Many sources claim that wood ash does not contain chlorine. But, in accordance with the formula, we see that its composition includes calcium chloride. Is it dangerous for plants? It is safe to say that no. The two ionic elements that make up this compound, in contrast, are of great importance for the healthy nutrition of fruit and vegetable crops.
Calcium Chloride (CaCl2). Many sources claim that wood ash does not contain chlorine. But, in accordance with the formula, we see that its composition includes calcium chloride. Is it dangerous for plants? It is safe to say that no. The two ionic elements that make up this compound, in contrast, are of great importance for the healthy nutrition of fruit and vegetable crops.
Almost all flora known to science uses chlorine to stimulate growth throughout the growing season. It is constantly contained in the green mass of fruit and vegetable crops in the amount of up to 1% of their total weight. In grapes and tomatoes, its content is slightly higher.
Calcium chloride activates the formation of enzymes, as well as photosynthesis, helps to transfer nutrients. Rock salt helps to fully utilize a small supply of these substances if wood ash is used as a fertilizer.
Another useful property of this chloride is that it increases the winter hardiness of fruit trees and grapevines, which makes it possible to grow this heat-loving crop even in rather cold regions (Pskov and Leningrad regions). It helps maintain the uniformity of the soil, avoiding swelling, which helps protect the roots from the penetration of cold air to them.
CaCl2 helps to cope with the following plant diseases:
- Rotting apples stored.
- Blackening of fruits in tomatoes.
- Cracking.
- Blackening and rot, both during growth and during storage.
- Premature fall of grapes.
- Re-harvesting mold.
- The appearance of the "black legs" in roses.
Due to its “draining” property, CaCl2 helps to defeat many diseases of crops caused by horse and stem rot. It is very useful for roses. Thanks to this element, ash infusion can be used not only for garden, but also for indoor plants, to improve the earth and prevent the growth of harmful microorganisms.
The presence of CaCl2 in the soil allows the conversion of ammonium nitrate into a salt of nitric acid, which is very useful for plant life. This is a very important aspect when fertilizing cucumbers with ash, as they are sensitive to a lack of nitrogen.
Rock salt
Rock salt, which is part of the ash, is a catalyst for growthfor plants such as cucumbers, pumpkins, squash, as it allows cells to retain water, accumulating and applying it in case of drought.
Potassium Orthophosphate
Potassium Orthophosphate (K3PO4). This substance Helps regulate plant water balance. With a lack of this substance, ammonia accumulates in the leaves and roots, which inhibits growth. Also, potassium salt of phosphoric acid helps to increase the winter hardiness of heat-loving plants, for example, grapes. Potassium also creates a favorable alkaline environment for garden flowers such as roses, lilies and chrysanthemums.
Magnesium
Ash refers to fertilizers, which include three magnesium compounds that act together on various metabolic processes in fruit and vegetable crops, as well as in cereals. This element, in some way, is a "partner" of potassium, they are together participate in the production of energy by the plant body.
Magnesium sulfate is involved in the formation of carbohydrates, which become the building material for starch and cellulose. For a rooted root system (for a rose, for example), the presence of magnesium in fertilizer is very important, since it consumes it in a larger volume compared to the ground part.
Sodium
The last item on the list, but not the last in importance. It activates a number of enzymes that do not react with other substances from the chemical composition of the ash. For example, tomatoes relate to natriefil, plants that respond positively to sodium, especially when not adequately provided with potassium. is he improves their water balance.
When should ash be used?
Various chemical trace elements that must be part of healthy plants are contained in this organic compound. Their deficiency negatively affects development and growth, leading to the occurrence of diseases.

As we found out above, the main element that is contained in ash in various compounds is calcium.
Signs calcium deficiency:
- Depigmentation of leaves in indoor plants (they acquire a white color).
- Deformation of the leaves (the tips are bent down, the edges are twisted up).
- Peduncles fall on nightshade.
- Dark spots appear on the fruits of tomatoes.
- The upper parts of the shoots die off, the taste of the fruits worsens.
- On tubers and stalks of potatoes and onions, patches of dead tissue form.
The second most important substance that must be used for normal plant life is potassium. It is contained in ash in a much smaller volume than calcium, but in sufficient quantity to normalize metabolic processes in the plant body. If it is not enough, then this can be understood by certain changes in appearance.
Signs potassium deficiency:
- On fruit trees, leaves prematurely fade, but stay firmly on the branches.
- Roses stop smelling.
- The edges of the leaf begin to dry on potatoes and nightshade, then it is folded into a tube.
Another element from the composition is magnesium. It is a forming element that allows the production of carbons. With its deficiency, the plant is inhibited, and its active development stops. With its deficiency, the same symptoms appear as with a lack of potassium. Sodium is a conditionally useful substance, therefore, you can ignore its small amount in the fraction when using wood ash as a fertilizer.
A few examples where the use of ash is contraindicated
Excess fertilizers, even organic ones, can lead to no less negative consequences than their lack. The use of wood ash as a fertilizer should be excluded in soils with high alkalinity. The following plant changes can indicate an increased pH factor:
Signs excess calcium:
- Excessive growth of leaf rosettes in grapes and apple trees.
- Dying off of shoots along the entire length of the whip of tomatoes.
- Fallen leaves in garden flowers.
- Inter-vein chlorosis with whitish spots in rose bushes.
- Depigmentation of leaves (they acquire a white color).
Signs excess potassium:
- Browning the pulp of apples and pears.
- Bitter pit of fruits.
- Premature fall of leaves of garden and indoor plants.
Video: a film for gardeners about wood ash
Ash in the garden - what, when and how to feed her?
Let us dwell on plants, which most of all show the use of ash as a top dressing.
Cucumbers
This gourd, successfully zoned in the middle lane, consumes many different nutrients throughout its growth and development. Calcium and potassium, which help to use ash as a fertilizer, are responsible for the formation of lashes and ovaries. It is these substances that help retain water in the cells. Fertilizing cucumbers with ash is necessary, since it is a plant that constantly needs a normal water balance.

How to fertilize cucumbers?
The first way to make fertilizer from ash is to sprinkle a bed with a thin layer of this substance before watering. All useful substances are absorbed subsequently with water. The second method is more time-consuming, but allows you to create a composition in which there will be more nutrients. This is an infusion of ash, which is done like this: 3 tablespoons of powder is poured with a liter of water and insisted for a week. After that, they are applied under the plant, followed by abundant watering. The rate of consumption of the solution when fertilizing cucumbers with ash is 0.5 liters per bush.
Bow
This culture is prone to root rot. Ash refers specifically to those fertilizers that prevent the growth of putrefactive bacteria in the soil. Onions can be fertilized in the same way as cucumbers, pollinating the ground before watering, or using an ash infusion (prepared in the same proportion as for feeding cucumbers).
Top dressing should be applied no more than three times per season. You can also make this fertilizer before the spring digging of the beds. This will protect the onion from diseases at the initial stage of growth, and will help it stock up with trace elements necessary for further development.
There is another way to make this top dressing. It is very convenient to use it on onion beds. These are grooves that are made with a hoe along the rows with a bow. An infusion of ash is poured into them, and it is immediately sealed with soil.
Tomatoes
If wood ash as a fertilizer is used to feed the bushes, then a week after application, you can observe the activation of their growth. These plants love calcium and potassium. They need them for the formation of moisture reserves in fleshy stems, and the formation of full-fledged juicy fruits.
How to fertilize tomatoes with ash?
Pre-landing method
This organic fertilizer is applied to the soil in the spring, a couple of weeks before planting tomatoes. The consumption rate is 1 glass per well. It is advisable to fertilize when the earth warms up to at least 15 degrees of heat.

We feed tomatoes in the process of growth
Ash refers to fertilizers that can be applied throughout the growing season. Therefore, tomatoes can be fed and superficially. To do this, pretend the earth in the hole, before watering, followed by loosening.
From ash, the taste of tomatoes improves, they become juicy and sweet. Potassium, which is part of it, enters into a series of chemical reactions, due to which fruit sugar, fructose, is formed.
Grape
Foliar grape top dressing
It is carried out several times during the season, in the evening. The liquid is directly sprayed onto the leaves using a grass broom, or through a specialized spray gun with an increased nozzle size. If there is no such equipment, then you can do it yourself.
How to make a device for spraying the infusion of ash?
To do this, take a standard atomizer and a medium-sized knitting needle. We heat the spoke in an open flame (a gas stove will do), and pierce new holes with a larger radius. Do not forget to shake the container before spraying, then the suspension will be evenly distributed over the leaves of the grapes.
In the autumn, a large number of old vines accumulate in the vineyard. They are ideal for burning. This ash is used for the preparation of specific top dressing, which takes into account the seasonal need of grapes for various nutrients.
For the full dissolution of all nutrients in water, it takes about three days, this is the approximate dissolution time of magnesium. About 1 kg of ash is poured with 3 buckets of water, and this suspension is mixed several times daily. The resulting composition can be stored in a cool place for a month.
For use, it is diluted with water in a proportion of 1 part of the working solution to five parts of water. For better adhesion to the leaves of the grapes, you can add shavings of laundry soap to the resulting suspension.
Roses
In the first year of her stay in a new place, the queen of the garden does not need additional nutrition. But the soil before planting can be prepared in advance by introducing wood ash as fertilizer during the autumn digging, to normalize the acidity of the soil.

Starting from the second year, they successfully feed the overwintered rose. This is mainly done by making ready-made organic fertilizers. But you can also make fertilizer from ash.
For roses, both root and non-root top dressing is used. For the first, the concentration of the substance in the aqueous solution is lower - 100 g. powder per 10 liters of water. When foliar feeding, when the liquid is sprayed on the leaves of the plant, apply a concentration of 200 gr. on 10 l of water.
It is better to feed roses in the evening, during the day you can burn leaves and flowers under the rays of the scorching sun. For spraying, a grass broom is used.
The infusion of ash, during application it is necessary to constantly stir. The fact is that phosphorus, which is part of this organic fertilizer, has a tendency to quickly precipitate at the bottom of the tank. If this happens, the plants will not receive it, but this is the most important trace element.
Houseplants
 Wood ash as a fertilizer, is used for both garden and indoor plants. For example, it helps fight root rot in tuberous begonias.
Wood ash as a fertilizer, is used for both garden and indoor plants. For example, it helps fight root rot in tuberous begonias.
Cyclamens, geraniums and fuchsia respond well to the substances that make up its composition. It must be added when transplanting these plants, based on their proportion of 2 tbsp. tablespoons per 1 liter of finished soil.
You can also make fertilizer from ash for indoor plants with the help of sleeping tea. It activates growth in the winter, helps maintain leaf color, and maintain flowering. Following this recipe, it is necessary to mix 1 part ash with 1 part squeezed tea leaves.
The use of ash as a fertilizer is useful for most horticultural crops. The set of microelements included in its composition provides the growth and nutrition of the plant.
But this substance can be used not only as a top dressing. It helps fight a lot of pests. When dusting or spraying crops with ash, one can observe the rapid death of garden antagonists such as larvae of the Colorado potato beetle (2 days), slugs, cruciferous fleas.
Another weighty argument for using ash is its availability. Every autumn on the garden plot there is something to burn from plant debris (tree branches, hay, straw, tops). Some amateur gardeners fit old barrels under the oven, then production occurs without loss of ash fraction.
This fertilizer has an organic origin, which is very important for many gardeners. Using it, you can not be afraid for your health, and the health of your loved ones. Perhaps this is one of the main arguments when choosing wood ash as a fertilizer.
Video: the use of ash as a fertilizer
Ash is an absolutely affordable and highly effective phosphorus-potash fertilizer that contains a lot of substances and microelements necessary for the development and growth of plants. You don’t need to buy it, you don’t need to use transport for transportation - this fertilizer can be done independently. The availability and benefit of ash is undeniable! Although it should be noted that the qualitative characteristics and the mass fraction of certain trace elements may vary depending on the raw materials used to produce the ash.
Important! When using ash as a fertilizer, it should be remembered that when the raw material is burnt, nitrogen escapes, so its lack must be compensated by any nitrogen-containing additives.
Averaged indicators of the main elements in the ash after burning:

Potassium
- Wood:
- coniferous - about 8%;
- deciduous - 14%;
- grapevine - 40%.
- Herbal raw materials:
- straw - about 20%;
- potato tops - 40%;
- sunflower (stem, leaves and head) - 40%;
- dried grass (nettle, quinoa, sow thistle, etc.) - 30%.
- Buckwheat, sunflower husk - 35%.
- Peat - 10%.
- Slates - no more than 2%.
Phosphorus
- Wood:
- coniferous - 6%;
- deciduous - not more than 10%.
- Herbal raw materials - 1%.
- Peat - 1%.
- Shales - 1.5%.
Calcium
- Wood - 45%.
- Herbal raw materials - 10–20%.
- Peat - 20-50%.
- Shales - about 70%.
Important! In no case can ash be used as fertilizer after burning: polymers, household waste, rubber, colorful glossy magazines, colored paper and synthetic materials. When using such “fertilizer”, you can generally forget about the crop - the land will be poisoned for many years.
Use of ash on different types of soil
- Agrotechnicians do not recommend using ash as fertilizer on soils with high alkalinity. This is due to the chemical characteristics of ash prepared from any raw material - it additionally alkalizes the soil, which can significantly complicate plant nutrition.
- Loamy and clayey soils - adding only 300-500 g / m² of ash, significantly improves the fertility and structure of the earth. Even after a single fertilizer application, the beneficial effect can last up to 4 years.
- Acidic soils - when wood ash is applied as fertilizer, a certain balance is created between the natural reaction of the earth (acidic) and the alkaline component (ash), which has a beneficial effect on the growth and development of plants. The exception is crops that initially prefer acidic soil: potatoes, radishes, melons and some others, as a result of which these plants need to be fertilized with ash very carefully, after weighing the possible benefits and possible harm.
Ways to use ash as a fertilizer
In practice, ash as a fertilizer is used in 3 ways:
- Dry scattering in near-tree circles of trees, under bushes, between rows of garden crops and in holes before planting seedlings.
- Spraying or watering plants with a concentrated solution and / or infusion prepared from ordinary water and ash.
- Bookmark in a compost pile (2 kg / m³). Subsequently, compost is used traditionally.
 How to use ash as a fertilizer?
How to use ash as a fertilizer?
How much ash is needed for a particular crop?
How to properly prepare a solution of ash for watering and spraying?
Familiar questions? Well, experienced gardeners and agronomists recommend:
Advice! Ashes diluted in water, when watering, it is necessary to constantly shake slightly or stir, in order to exclude its subsidence to the bottom.
- Before planting seedlings of tomatoes, peppers and eggplant, you need to add 5 dessert spoons of ash to each well and mix it lightly with the ground or add it when digging at the rate of three 200-gram glasses per 1 m².
- Lawn grass - before sowing seeds, add fertilizing to the selected area, 300 gr. on 1 m². It is not recommended to sprinkle already sprouted seeds.
- Fertilization with ash from cucumbers, tomatoes and cabbage during the growth period can be carried out with a pre-prepared solution: 100 g / 10 l (ash / water), after mixing the ingredients, the infusion is ready in 24 hours. Pour 500 ml of infusion under each plant or make longitudinal grooves and shed evenly.
- For a good cabbage crop, fertilizer is recommended to be applied repeatedly, and every 10-12 days. The procedure should be carried out during the entire growth period.
- For trees, it is useful to fertilize at least 1 time in 3 years:
- adults - 2 kg under each tree, bring in the area of \u200b\u200bthe trunk circle in a pure form, you can make a special groove (10 cm deep) around the circumference and feed there. In dry weather, subsequent heavy watering is required;
- seedlings - Pour 1 kg of ash into a hole prepared for planting, where to mix it with the ground, then planting is done traditionally.
- Fertilizer with indoor plants ash is also widely used. To do this, the product is poured into a flower pot (1 tbsp. L. To 5 liters of land) or an infusion is prepared (2 tbsp. L. To 6 liters of water), which is used for irrigation.
Advice! Feeding trees and rooted seedlings can be done with infusion prepared from 1.5 kg of ash and 12 liters of water. The resulting composition, simply, evenly spills around the plant, no further than 0.5 m from the trunk.
The use of ash for plants as a protection against diseases and pests
 The use of ash for plants comes down not only to fertilizing the soil, it is also an excellent tool against many pests and diseases:
The use of ash for plants comes down not only to fertilizing the soil, it is also an excellent tool against many pests and diseases:
- Processing from a cruciferous flea - mix ash and tobacco dust in equal proportions and pollinate the resulting composition of the plant.
- Ash infusion is very effective when used in the fight against powdery mildew, as well as aphids. It is prepared very simply, for this they are mixed: 12 liters. cold water, 110 g of laundry soap and ash, 20 g of urea. All ingredients are thoroughly mixed and infused for 2 days.
- It is believed that the regular addition of ash to the land of the garden contributes to the extermination of wireworms.
- As a prevention of various fungal diseases, plants are also pollinated with ash.
Advice! Spray the ashes only when the street is completely calm, this will guarantee that the product will reach exactly those plants for which it was planned. The best results are given by pollination in the early hours, when the dew has not yet slept.
Wood ash as fertilizer - video
glav-dacha.ru
Feeding cucumbers with ash

Cucumbers are almost entirely composed of water. They contain a very small amount of proteins, fats and carbohydrates and many useful enzymes and minerals for the body. In particular, vitamins C, B1, B2, P and A. Eating fresh cucumbers has a beneficial effect on the health of the human body. But in order to get a good harvest, you need to properly care for the plant and fertilize in time. Especially useful is the feeding of cucumbers with ash. Let us consider in more detail how often and in what quantities it is necessary to feed the plant.
How to feed cucumbers with ash?
Pursuing the desire to collect a rich crop of cucumbers, the main thing is not to overdo it. Throughout the entire growth period, the plant needs to be fertilized only 5-6 times. Let's talk in more detail about how to feed cucumbers with ash. The first stage can be performed even at the stage of plant formation, when a second leaf appears on the stem. The second stage of soil treatment with fertilizer must be carried out at the beginning of flowering. Then, when the plant begins to bear fruit, fertilizer ash cucumbers produce about once every two weeks. It is only necessary to feed plants during warm weather and after heavy watering. Otherwise, when processing dry soil, fertilizers can harm the root system of the plant.
Processing cucumbers with ash is not the only way to fertilize. You can also feed plants with various complexes of mineral or organic fertilizers, dissolving them well in water in advance. However, wood ash for cucumbers is one of the best and priceless fertilizers. It contains all the necessary mineral elements that the plant needs during its formation and growth.
If we talk about how to fertilize cucumbers with ash, then there are several possible options. You can cultivate the soil with dry ash immediately before watering. And you can pre-prepare a special infusion of ash and fertilize the earth with it. To prepare such an infusion is very simple. 2 tablespoons must be put on 1 liter of water  tablespoons of wood ash and insist for a week, stirring occasionally.
tablespoons of wood ash and insist for a week, stirring occasionally.
If you are wondering if it is possible to feed cucumbers with ash, then the answer will definitely be yes. One of the main advantages of this fertilizer is the absence of chlorine in the composition, which is found in many other mineral fertilizers. It is also worth remembering that the composition of the ash directly depends on the combustion of which plant it is received. Hardwood contains a lot of calcium, ash bark and straw is rich in phosphorus, and when burning meadow grass you can get ash with a high content of potassium.
womanadvice.ru
that fertilize with ash from trees
Kostenko Sergey
wood ash is a universal fertilizer that contains the main ash macroelements (P, K), many trace elements, as well as calcium and magnesium. the aqueous solution has an alkaline reaction. it can be used on any crops like phosphorus-potassium fertilizer with a high content of trace elements. mainly introduced in the fall or spring when digging. it is possible to use infusion of wood ash in the second half of the growing season for watering and spraying on a leaf.
I repeat - it’s possible to use any kind of crop on the floor, but not on any soil - on alkaline, it is necessary in combination with lime
Hedgehog
Everything _ is an excellent potash fertilizer
Tatyana Vedenina
Everything can be fertilized with ash, sprayed, or diluted in water.
And it destroys pests on radishes, turnips, radishes well !!!
margarita brown
This is a conventional potash fertilizer, no chemistry. In order for root crops (carrots, beets, etc.) to be sweet, it directly depends on the potassium content in the soil.
Natalya Belousova
Any ash that is formed when burning wood, dry leaves and grass is the most useful fertilizer for plants at any stage of their development.
Sergey
acidic soils. on alkaline even alkalizes ... potassium-loving cultures. type of potato
Lady in a hat
This is a very good fertilizer for stone fruits - plums, cherries, peaches, cherries .... To bring in the trunk circle in the autumn, since the fruit buds are laid in the winter
Can you fertilize the earth with ash?
Lucy Lucyao
Ash is called a non-combustible residue from mineral impurities of herbaceous plants or wood during their complete combustion. Ash (wood, vegetable) contains potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, calcium and a large set of trace elements, therefore it is considered a good alkaline potassium-phosphorus complex fertilizer. It is important to remember that ash retains its properties only when stored dry. Ash is added to the substrate before planting houseplants, mixing well with the soil, at the rate of 1 part ash to 40-50 parts of soil. In addition to applying dry ash to the soil, ash ash is used to fertilize plants. To get the infusion, the ash is poured with water (25 g of ash per liter of water) and insisted for about a week, stirring occasionally so that the soluble substances from the ash go into water, and then use the resulting infusion for fertilizing plants.
A very valuable thing for a gardener is charcoal (preferably birch, aspen), small pieces of which (0.8-1 cm in diameter) are a desirable part of the substrate for orchids, aroid, cacti and succulents (3-8% of the substrate volume). Charcoal makes the substrate loose and permeable, and also works as an antiseptic in the substrate, protecting the roots from decay. Charcoal powder is used to treat plant wounds - the result of treatment or vegetative propagation.
Many gardeners in autumn scatter the ash obtained from burning plant debris over the entire area (application rate of 100-150 g of ash per square meter), and along with the rain, nutrients from the ash fall into the ground. The soil sprinkled with ash warms up faster in the spring. In the spring, ash is brought under all garden crops into holes or rows.
Ash also helps to drive pests (cruciferous fleas) from plants of the cruciferous family (cabbage, watercress, radish and others, as well as flowers: alissum, lunaria, vespers, and others), which especially annoy the plants in spring and are able to completely destroy seedlings. The beds and leaves of the attacked plant pests are dusted with ash (for better adhesion of the ash, you can pre-sprinkle the leaves with water). For ease of dusting the plants with ashes, they take an empty can or plastic can, make many holes at the bottom, pour ash into the can and, gently shaking the can over the plants, uniformly cover them with fine fly ash.
Rustam _
of course yes)
musya
yes it is very good.
lor1 888
not possible, but necessary. just don't overdo it.
nina Vandium
If this was fertilized with manure, then very good.
Black wolf
it is even necessary
Galina Guseva
It is possible and necessary ..
Leon
of course, especially trees should be fertilized with ash from worms helps !!


