Explanation of 01 invoice sample. How are leased fixed assets accounted for off-balance sheet and at what cost?
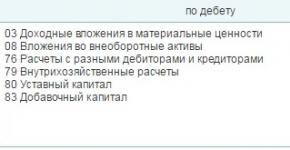
By debit
* receipt (purchased, created, received free of charge) of fixed assets credited to the balance sheet of the enterprise;
* amounts of expenses associated with improving the facility (modernization, modification, completion, additional equipment, reconstruction, etc.), which lead to an increase in future economic benefits initially expected from the use of the facility;
* the amount of revaluation of the value of the fixed asset.
By loan Account 01 “Fixed Assets” reflects:
* disposal of fixed assets as a result of sale, liquidation, free transfer to other enterprises;
* partial liquidations;
* the amount of depreciation of fixed assets.
Analytical accounting of fixed assets is carried out for each object separately,
Analytical accounting of non-current tangible assets is carried out for each object of these assets.
Under capital investments understand the costs of an enterprise for the acquisition or creation of fixed assets, other non-current tangible or intangible assets, as well as the costs of reconstruction, expansion and technical re-equipment of existing enterprises.
Synthetic accounting of costs for capital investments is carried out on account 08 “Investments in non-current assets” according to subaccounts:
08-1 "Acquisition of land";
08-2 "Purchase of natural resources";
08-3 "Construction of fixed assets";
08-4 "Acquisition of fixed assets";
08-5 "Acquisition of intangible assets";
08-6 "Transfer of young animals to the main herd";
08-7 "Acquisition of adult animals."
The debit of account 08 "Investments in non-current assets" and its subaccounts reflects the costs of acquiring or creating tangible and intangible non-current assets, and the credit - their write-off to the cost of objects put into operation.
Analytical accounting of capital investments is carried out accordingly by type of fixed assets, other tangible non-current assets, intangible assets, as well as by individual objects of capital investment (inventory items).
The organization of accounting for capital investments is influenced by the method of performing work: contracting (that is, by specialized organizations on a contractual basis) or economically (that is, by the forces and means of the enterprise itself).
At contracting the method of performing the work, accounting for material, labor and financial costs for the work performed is carried out by the contractor himself. The customer company, in this case, only accounts for the costs of capital investments and makes payments to the contractor for the work performed and accepted according to the certificates. Based on this, the developer makes an entry in the accounting records for the cost of construction and installation work completed and accepted according to the acts: D08 K60
The same record is used to record the cost of purchased fixed assets that do not require installation (free-standing machines, vehicles, measuring instruments, production and household equipment, etc.).
According to account 08 "Investments in non-current assets" the actual cost of completed construction projects (reconstruction, modernization, acquisition) is calculated. Commissioning of each facility is formalized act of acceptance and transfer of fixed assets, which serves as the basis for writing off the cost of capital investments in completed objects, as well as crediting them to the balance sheet as part of fixed assets.
The crediting of commissioned fixed assets to the balance sheet at the actual cost of their construction (manufacturing, acquisition) is reflected in accounting by the entry: D01 K08.
The entry into the balance sheet of fixed assets contributed by the founders (participants) to the authorized capital of the enterprise, at fair value agreed upon by the parties, before January 1, 2000, was formalized as D01 K75. From January 1, 2000, the amount of accounts receivable is reflected as D75/1 K80. The cost of fixed assets received as a contribution is D08 K75, and then D01 K08.
Fixed assets received through free transfer from other legal entities, as well as as subsidies from the Government of the Russian Federation until January 1, 2000 were reflected as D01 K83 “Additional capital”, for fixed assets for production purposes, or D01 K88 “Retained earnings”. Since January 1, 2000, such transactions are classified as profit - D08 K99 "Profit and Loss". In this case, the value of gratuitously received fixed assets can be reflected in the financial result in two ways:
1. At the time of acceptance of fixed assets for accounting at their original cost;
2. As depreciation accrues on accepted fixed assets.
In the second method, the following entries are made for fixed assets accepted free of charge:
D08 K98 – at the original cost;
D01 K08 – at the original cost;
D20,25,26,44 K02 – for the amount of accrued depreciation;
D98 K99 – for the amount of depreciation.
In the first method, gratuitously transferred fixed assets are formalized by postings: D08 K99 and D01 K08.
1.5 Synthetic and analytical accounting of depreciation of fixed assets.
During operation, fixed assets, while maintaining their original physical form, gradually wear out (physically, morally), transferring their value in parts to the cost of the newly created product. In order to accumulate funds for the complete restoration of worn-out objects, the cost of the worn-out part of fixed assets, in the form of depreciation charges, is included in the costs of production or circulation.
Accounting Regulation (Standard) 6/97 “Fixed Assets” defines depreciation as the systematic distribution of the cost of an item of fixed assets subject to depreciation over its useful life.
The cost of fixed assets subject to depreciation is determined as the difference between the cost of the object and its liquidation value. Liquidation value is understood as the amount that an enterprise expects to receive from the sale (liquidation) of an object after the end of its useful life (operation) minus the expected costs associated with the sale (liquidation) of the object.
The object of depreciation is fixed assets that have a limited useful life (land, for example, whose useful life is unlimited, is not subject to depreciation).
The useful life of fixed assets is the period during which the enterprise plans to use the corresponding object, or the number of units of products (services) that the enterprise expects to receive from its use. The useful life of fixed assets is determined by the enterprise itself.
To calculate depreciation, enterprises can use:
* method of uniform write-off of the cost of fixed assets (linear method);
Accounting account 01 is the active account “Fixed Assets”, it reflects information about the organization’s fixed assets (Fixed Assets), their value and movement. The account belongs to the non-current assets section of the approved Chart of Accounts.
Fixed assets of an enterprise are the material assets of an enterprise used in economic activities and transferring their value to the cost of production.
Fixed assets
The OS includes:
- production equipment and machinery;
- buildings and constructions;
- roads;
- transmission networks (heating networks, electrical networks, etc.);
- means of transport;
- power machines and equipment;
- various equipment and tools;
- working and breeding livestock;
- other OS.
In addition, fixed assets include capital investments in leased fixed assets, in land improvement, and the land plots themselves. Fixed assets, as non-current assets, participate in the production process as a means, not an object.
Conditions for recognizing an object as a fixed asset
To recognize an OS object, the following conditions must be present simultaneously:
- purpose - use in the production activities of the organization;
- expected SPI over 12 months;
- promising economic benefits;
- not intended for resale.
OS costing less than 40,000 rubles. can be taken into account as part of inventories and immediately written off as expenses.
Account 01 in accounting
The fixed assets accounting account is active, its structure is displayed in the form of a table:
In the standard version, synthetic account 01 includes subaccounts for breakdown by type of fixed assets.
To reflect disposals, a sub-account for the disposal of fixed assets is also often opened, into which the initial and written-off costs are collected, and the write-off is carried out from this account. If the disposal account is not used, then transactions Dt 02 - Kt 01 arise.
For the correctness of analytical accounting, a breakdown is carried out by objects. Items in the account are stated at their original cost, which may include shipping costs, fees, etc.
Get 267 video lessons on 1C for free:
If an asset is owned by several organizations, then in the accounting of each of them its value is reflected in proportion to the share of ownership.
Main correspondence of account 01
Typical correspondence of the fixed assets accounting account is presented in the table:

OS upgrade
Modernization of fixed assets is the transformation of the operating system, which led to an improvement in its characteristics.
An increase in the cost of fixed assets due to the modernization or reconstruction of an object is reflected by standard posting:
Increase in value after revaluation:
| Dt | CT | Operation description |
| 01 | 83 | Revaluation amount |
Depreciation of fixed assets
Depreciation of fixed assets in accounting refers to the gradual transfer of their value to the cost of manufactured products.
- land;
- environmental management facilities;
- livestock;
- non-production housing facilities;
- forestry, road management;
- external landscaping.
If repairs last more than one year, and conservation of objects lasts more than three months, then depreciation is suspended.
In the balance sheet, fixed assets are reflected at their residual value: original cost minus accumulated depreciation. Non-depreciable property is reflected in the balance sheet at historical cost.
Depreciation starts from the month following the commissioning date. The accrual will stop in the next month after the cost has been completely written off.
After the book value of the asset becomes zero, the asset is not reflected in the balance sheet.
Examples of accounting entries for account 01 “Fixed assets”
Example 1. Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting
In April 2016, Karuna LLC purchased from the OS supplier the contract price of 110,000 rubles, excluding VAT. Delivery services - 10,000 rubles. The term of the fixed assets is 36 months, the method of calculating depreciation is linear. The OS will be used in the main production activities.
To reflect the acquisition and acceptance of fixed assets for accounting, the Karuna accountant makes the following entries in April:
The monthly depreciation amount will be: 120,000 / 36 = 3,333 rubles)
Depreciation calculation in May:
Example 2: OS upgrade
In September 2014, Fortuna LLC put into operation an operating system worth RUB 960,000, SPI was set for 5 years, depreciation is calculated using the straight-line method. In December 2016, the organization modernized the facility in the amount of 96,000 rubles. As a result of modernization, the SPI increased by 1 year.
Let's do the calculations:
- monthly depreciation: 960,000 / (12*5) = 16,000 rubles;
- the amount of accumulated depreciation until December 2016: 16,000 * 27 (months) = 432,000 rubles.
- residual value at the date of modernization: 960,000 - 432,000 = 528,000 rubles.
Postings for OS upgrade:
- the residual value of the fixed assets will be 528,000 + 96,000 = 624,000 rubles;
- the new SPI is: 6*12 = 72 months;
- remaining term: 72 - 27 = 45 months;
- monthly depreciation amount: 624,000 / 45 = 13,867 rubles.
Reflection of depreciation in January 2017.
Account 01 “Fixed Assets” is intended to summarize information about the availability and movement of the organization’s fixed assets that are in operation, in reserve, on conservation, in lease, in trust management.
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting under account 01 “Fixed assets” at their original cost. An item of fixed assets owned by two or more organizations is reflected by each organization in account 01 “Fixed Assets” in the corresponding share.
Acceptance of fixed assets for accounting, as well as changes in their initial cost during completion, retrofitting and reconstruction are reflected in the debit of account 01 “Fixed assets” in correspondence with score 08"Investments in non-current assets."
Changes in the initial value during the revaluation of the corresponding objects are reflected in account 01 “Fixed assets” in correspondence with score 83"Extra capital".
To account for the disposal of fixed assets (sale, write-off, partial liquidation, transfer free of charge, etc.), a subaccount “Retirement of fixed assets” can be opened to account 01 “Fixed Assets”. The cost of the disposed object is transferred to the debit of this subaccount, and the amount of accumulated depreciation is transferred to the credit. Upon completion of the disposal procedure, the residual value of the object is written off from account 01 "Fixed assets" to score 91"Other income and expenses."
Analytical accounting for account 01 “Fixed Assets” is carried out for individual inventory items of fixed assets. At the same time, the construction of analytical accounting should provide the ability to obtain data on the availability and movement of fixed assets necessary for the preparation of financial statements (by type, location, etc.).
Account 01 "Fixed assets"
corresponds with accounts
| by debit | on loan |
|
03 Profitable investments in material assets 08 Investments in non-current assets 80 Authorized capital 83 Additional capital |
02 Depreciation of fixed assets 11 Animals for growing and fattening 76 Settlements with various debtors and creditors 79 On-farm settlements 80 Authorized capital 83 Additional capital 91 Other income and expenses 94 Shortages and losses from damage to valuables 99 Profit and loss |
Application of the chart of accounts: account 01
- Transition to the application of the standard for fixed assets
Let's compare them. To fixed assets accounted for on the corresponding analytical accounts of account 0 101 00 ... accounts From January 1, 2018, the composition of the groups of fixed assets that form the analytics of the synthetic account... groups of individual fixed asset objects reflected on the balance sheet accounts before January 1, 2018 changes ... write off fixed assets worth from 3,000 to... from the balance sheet to an off-balance sheet account
- New in fixed asset accounting in 2018
8 of the GHS “Fixed Assets”, fixed assets are recognized as material assets that meet the following criteria: 1) have a period of... years). Groups of fixed assets provided for by the GHS “Fixed Assets” in 2018 Account number* Groups of fixed assets provided for... “Fixed Assets” depreciation on fixed assets is accrued in the following order: 1) for an object of fixed assets worth...
- Conservation of fixed assets. Accounting and taxation
To account 01 "Fixed assets" subaccount "Fixed assets for conservation". Depreciation of a fixed asset... 2012 fixed asset. Its initial cost was 1,600,000 rubles. The fixed asset was... "Disposal of fixed assets" 01 "Fixed assets on conservation" 1,600,000 ...;Disposal of fixed assets" 1,000,000 Act on acceptance and transfer of fixed assets, Accounting...
- Is it possible to transfer fixed assets with a residual value of less than 40 thousand rubles? as part of the MPZ?
By virtue of this Federal Law *(1). In the accounting of the organization, current... reporting of the organization", appendices No. 1 and No. 4 to the Order... .2007 N 03-03-06/1/879, arbitration practice (resolution... value of assets from the credit of accounts 01 " Fixed assets", 03 "Income... within the framework of the Legal Consulting service. *(1) At the same time, before the approval of the federal... Federal Law (second sentence of paragraph 1 of Article 30 of Law No. 402 ... 2017 N 03-03 -06/1/7342): if the original cost of the property...
- Federal standard "Fixed assets"
When disclosing information about fixed assets. In Instruction No. 157n, which is currently... the result). Depreciation begins to accrue on the 1st day of the month following... accounting. Accrual stops on the 1st day of the month following... is reflected in the credit of the corresponding balance sheet accounts for accounting for fixed assets. When reflecting in accounting... disposal of fixed assets, the following criteria must be observed: 1... apply when maintaining records from January 1, 2018.
- New classifiers of fixed assets: OKOF and depreciation groups
How do analytical accounts for fixed assets relate to the groupings of fixed assets in the new... it is necessary to group fixed assets accepted for accounting from January 1, 2017... in relation to fixed assets put into operation from January 1, 2017... for accounting ) after January 1, 2017. Fixed assets accepted for... accounting before January 1, 2017... are not committed. Instructions for using the Unified Chart of Accounts...
- VAT deduction before commissioning of a fixed asset
Fixed assets is “acceptance of these fixed assets for registration” (paragraph 3, paragraph 1... paragraph 1 of Article 172 of the Code does not directly say in which account... registration as fixed assets objects in account 01 “Fixed assets” (or... that reflecting an object on account 01 “Fixed Assets” is legal only after... rights (in accordance with clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation,... 2 of Article 171 and clause 1 of Article 172 of the Code, in accordance with. .. 1 of Article 172 of the Code regarding the deduction of “input” VAT on fixed assets...
- Repair of fixed assets taking into account the provisions of the federal standard
Are formed on account 1 106 31 000 “Increase in investments in fixed assets - other movable... dismantling of fixed assets by debit of the corresponding analytical accounts of account 0 101 00 000 “Fixed assets... major repairs of fixed assets, changing their value, are formed on account 1 106 31 ... 000 “Increase in investments in fixed assets – other movable...
- Guidelines of the Ministry of Finance on the application of the GHS “Fixed Assets”
Objects of fixed assets recognized upon the first application of the GHS "Fixed Assets" are carried out on the corresponding balance sheet accounts: 1 ...) at their cadastral value on the date of the first application of the GHS "Fixed Assets... upon the first application of the GHS "Fixed Assets" on the corresponding balance sheet accounts, accounting subjects... fixed assets; features of accounting for individual fixed assets recorded on balance sheet accounts outside...
-
The following algorithm of actions. When mothballing fixed assets: 1. The manager’s order is approved to carry out... more than three months. When reactivating fixed assets: 1. The manager’s order to carry out... a period of more than three months is approved. Example 1. An object of fixed assets (equipment) was mothballed with... conservation (re-mothballing) of fixed assets, then they are also produced at the expense of targeted financing and...
- Measures for the transition to the application of the federal standard “Fixed Assets”
When accounting for fixed assets, you must keep in mind the following changes. 1. Fixed assets include... clause 35 of the GHS “Fixed Assets” provides for the following methods of depreciation of fixed assets: 1) linear method. This...accounting for fixed assets must provide for: 1) methods of depreciation regarding groups of fixed assets; 2...) fixed assets; 8) features of accounting for individual fixed assets reflected on balance sheet accounts outside...
- Air conditioners as fixed assets: accounting and reflection of expenses
2.2.4.3359-16. The specified norms have been in effect since... dated 01.01.2002 No. 1 (hereinafter referred to as Classification), in depreciation... should be taken into account as part of fixed assets in accounts 0 101 ... produced in equal parts (1,500 rubles each) per.. . 25 730 1 500 Payment made... (KVR 244, KOSGU 225) 1 500 * * * To ensure... consider the following: 1) for accounting purposes, air conditioners are recognized as fixed assets; 2) ... and article 340 of KOSGU. SanPiN 2.2.4.3359 ...
- Accounting for fixed assets in an institution since 2018
Fixed assets after the start of application of the Federal standard "Fixed Assets" are reflected on the corresponding balance sheet accounts... as of January 1, 2018, account 0 101 00 000 "Fixed Assets" is taken into account... of the property (account 0 101 10 000 "Fixed Assets" – real estate... fixed assets that form the analytics of the synthetic account (0 101 0X 000), individual fixed assets... reflected on balance sheet accounts before January 1, 2018...
- Mothballing of fixed assets in 2018
No entries are made in the corresponding analytical accounts of account 101 00 “Fixed Assets”, ... rub. The object was preserved for 1 year (12 months). During this... the object's stay on conservation is equal to 1 year (12 months), and... the following correspondence: Dt 1 401.20 271 – Kt 1 104.34 411 ... reflect the correspondence indicated in table 1. Table 1 “Conservation expenses OS... of transport in the amount of the cost of 1,302.25,830 1,206.25,660 ... The previously transferred prepayment was offset 1,302.25,830 1,304.05,225 ...
- Application of off-balance sheet accounts
Clause 333 of Instruction No. 157n, in addition to movable and immovable objects... is taken into account as part of fixed assets on the balance sheet account 0 101 00... by shipping documents executed properly: 1) invoices confirming the delivery of material... (clause 4 Order No. 538): 1) movable property, the book value of which... the founder writes off from the off-balance sheet account 21 fixed assets that are classified as special... for storage). Instructions for using the Unified Chart of Accounts...
Account 01 is used to reflect information about the organization’s fixed assets and their movement. Let us recall the procedure for working with this account and give examples of postings.
Accounting for fixed assets is carried out in accordance with PBU 6/01 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n).
Fixed assets include equipment, land, buildings, and premises. Objects can be in operation, reserve, conservation, lease, or in trust management.
Reflection of fixed assets on account 01 in accounting
All information about fixed assets is reflected in account 01 in accounting and is important for management and taxation. In order for objects to be taken into account, they must be owned by the organization.
Fixed assets are accepted for accounting at original cost. The initial cost is all the organization's expenses for putting the facility into operation. Moreover, the initial cost for different organizations for the same object may differ.
If the property is owned by two or more organizations, then each of them reflects it on account 01 depending on the share.
In the debit of account 01 Fixed assets in correspondence with account 08 Investments in non-current assets are reflected:
- acceptance of fixed assets for accounting;
- change in the initial cost during completion, retrofitting and reconstruction.
Debit 01 in correspondence with account 83 Additional capital reflects the change in the initial value of objects during revaluation.
If fixed assets are disposed of (sold, written off or partially liquidated, transferred free of charge), then you can open subaccount"Disposal of fixed assets." The cost of the disposed object is transferred to the debit of the subaccount, and the amount of accumulated depreciation is transferred to the credit. After disposal, the residual value of the object is debited from account 01 to account 91 Other income and expenses.
Analytical accounting for account 01 Fixed assets must be maintained for individual inventory items. Such accounting must be structured in such a way that it is possible to obtain data on the availability and movement of fixed assets for the preparation of financial statements. This is, for example, information on species, locations, etc.
Objects that are classified as fixed assets. Criteria:
- period of use - more than 12 months;
- purchased NOT for sale;
- may generate income for the organization in the future;
- the cost per unit is not less than the cost limit of 40 thousand rubles. (without VAT)
Features of accounting on account 01:
- account is active;
- objects are accounted for at their original cost;
- if a fixed asset belongs to two or more organizations at once, then it is reflected in each of them in the corresponding shares;
- during revaluation, the change in the original value is reflected in account 01
Let us remind you that the limit on fixed assets, which is now equal to 40 thousand rubles, will disappear in accounting. The new accounting standard “Fixed Assets” will replace PBU 6/01 (see. Accounting changes in 2017).
| by debit | on loan | ||
| 03 | Profitable investments in material assets | 02 | Depreciation of fixed assets |
| 08 | Investments in non-current assets | 11 | Animals being raised and fattened |
| 76 | 76 | Settlements with various debtors and creditors | |
| 79 | On-farm settlements | ||
| 79 | On-farm settlements | 80 | Authorized capital |
| 80 | Authorized capital | 83 | Extra capital |
| 83 | Extra capital | 91 | Other income and expenses |
| 94 | Shortages and losses from damage to valuables | ||
| 99 | Profit and loss | ||
Transfer of assets to account 01
A company has the right to claim a VAT deduction if it has taken into account the costs of purchasing fixed assets for account 08 "Investments in non-current assets". There is no need to wait until the asset is transferred to account 01 “Fixed assets” (letter of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated July 4, 2016 No. 03-07-11/38824).
The company accepts VAT for deduction on fixed assets when it registers it (paragraph 3, paragraph 1, article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). The Tax Code does not specify in which account the object should be located. Only the Instructions for the chart of accounts mention that the company accounts for fixed assets in account 01 (Order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated October 31, 2000 No. 94n).
Tax officials and the Ministry of Finance previously believed that a deduction was possible when a company registered an object as a fixed asset. That is, it will put the asset into operation and show the cost on account 01.
In letter No. 03-07-11/38824, the Ministry of Finance came to the conclusion that the account number does not matter for the deduction. If the company has assets in account 08, then they can now be deducted. To do this, submit an amendment or show the deduction in your current reporting.
Submit a declaration with deductions no later than three years from the date when the company took into account the purchase in accounting (clause 1.1 of Article 172 of the Tax Code of the Russian Federation). Otherwise, it will not be possible to protect the deductions even in court (resolution of the Arbitration Court of the Moscow District dated 09.09.2015 No. A40-158139/14).
Example
On April 7, 2014, the company acquired a building that requires renovation. On the same day, the object was registered under account 08 “Investments in non-current assets”. The company has three years to claim VAT as a deduction. The right to deduction arose on April 7, 2014, that is, in the second quarter of 2014. The three-year term will expire in the second quarter of 2017 - June 30. Hurry up to submit your declaration before this date (clause 2.2 of the Constitutional Court ruling dated March 24, 2015 No. 540-O). To avoid missing the deadline, declare the deduction in your financial statements for the first quarter of 2017 or earlier.
Posting account 01
Typically, account 01 Fixed assets does not have subaccounts. To account for the disposal of objects (when they are written off, sold, etc.), you can open a subaccount “Retirement of fixed assets”.
Debit 01
| Debit | Credit | Operation |
|---|---|---|
| 01 | 01 | The object is transferred from one division to another |
| 01 | 01 | The initial cost of the disposed object is written off to a separate subaccount "Retirement of fixed assets" |
| 01 | 03 | Property intended for rental was transferred to fixed assets |
| 01 | 08-1 | The land plot has been registered |
| 01 | 08-2 | Natural resource management object has been registered |
| 01 | 08-3 | The fixed asset facility built by the organization was put into operation |
| 01 | 08-4 | A fixed asset item that does not require installation has been put into operation |
| 01 | 08 | The cost of the facility increased as a result of completion, retrofitting or modernization |
| 01 | 08 | Material exploration assets were transferred to fixed assets |
| 01 | 83 | The cost of the object increased as a result of revaluation |
| 01 | 79-1 | The head office of the organization received an object of fixed assets from the branch, allocated to a separate balance sheet (in the accounting of the head office) |
| 01 | 79-1 | The branch, allocated to a separate balance sheet, received an object from the head office of the organization (in the accounting of the branch) |
| 01 | 79-3 | The object was received for trust management (on a separate trust management balance sheet) |
| 01 | 79-3 | An object previously transferred to trust management was returned (in the accounting of the management founder) |
| 01 | 91-1 | The revaluation of fixed assets is reflected within the amount of the previous depreciation |
Credit 01
| Debit | Credit | Operation |
|---|---|---|
| 02 | 01 | Depreciation on an item disposed of as a result of sale, gratuitous transfer or liquidation is written off to reduce its original cost |
| 76-1 | 01 | The residual value of the insured object as a result of its damage or destruction is written off at the expense of insurance compensation |
| 79-1 | 01 | The fixed asset object was transferred to a branch allocated to a separate balance sheet (in the accounting of the head office of the organization) |
| 79-1 | 01 | The fixed assets object was transferred to the head office of the organization (in the accounting of the branch) |
| 79-3 | 01 | The fixed asset object was transferred to trust management (on a separate trust management balance sheet) |
| 79-3 | 01 | An object of fixed assets previously received for trust management was returned (on a separate balance sheet of trust management) |
| 91-2 | 01 | The residual value of an object disposed of as a result of sale, write-off or partial liquidation is included in other expenses |
| 91-2 | 01 | The value of an object has been reduced as a result of its revaluation |
| 91-2 | 01 | The residual value of fixed assets lost due to emergency circumstances (natural disaster, fire, accident, etc.) is written off as other expenses. |
| 94 | 01 | The shortage of fixed assets is reflected (at residual value) |
An important place when a business entity carries out its activities is occupied by movable and immovable assets, which are called fixed assets in accounting. They are used for a long time and are quite expensive. Therefore, there are some features of their reflection and taxation. Account 01 in accounting is used to reflect information about this type of object.
It is established by law that fixed assets can be called property that is used in business activities for a long time and its value exceeds a given limit.
For accounting purposes, the limit is limited to the cost of 40,000 rubles. That is, an enterprise or individual entrepreneur can consider property a fixed asset if it is used for more than one year and its price is more than 40,000 rubles.
Tax legislation sets a higher limit for the division of objects between fixed assets and materials. It is determined by the amount of 100,000 rubles and above.
Conditions for recognition of OS
In addition to the cost delineation of objects, there are a number of criteria defined in the PBU. These include:
- Objects must be used in the entrepreneurial activity of the subject to manufacture products, perform work, perform services, or manage a company.
- The useful life of an asset must be more than 1 year for it to be called a fixed asset.
- Such objects are not intended for further implementation.
- The use of the object will create income for the enterprise.
Attention! From the classification it follows that the main assets are buildings, structures, equipment, vehicles, tools, inventory, etc., the cost of which exceeds 40 thousand rubles.
Which accounts does it correspond with?
To account for fixed assets, the Chart of Accounts provides for account 01. On it, funds are recorded at their original cost. The account is active, so an increase (receipt of fixed assets) is recorded as a debit, and a decrease (disposal) is recorded as a credit. Analytical accounting is carried out by types of OS objects.
By debit, account 01 can correspond with the credit of accounts:
- - shows the return of a fixed asset from an income-generating investment (for example, a return from a tenant).
- sch. 08 – reflects the arrival of fixed assets, an increase in their price as a result of re-equipment, completion and reconstruction.
- sch. 76 - receipt of fixed assets from other debtors, when its installation and modification are not required.
- sch. 79 - receipt of fixed assets for internal business settlements (for example, from the parent company)
- sch. 83 - increase in the cost of fixed assets due to revaluation.
For a loan, account 01 can correspond with the debit of the following accounts:
- - the disposal of fixed assets is reflected
- sch. 11 - transfer of fattening animals to the main herd
- sch. 76 - write-off of the cost of fixed assets due to other settlements (for example, due to insurance payments)
- sch. 79 - transfer of fixed assets through the system of intra-business settlements (between branches, parent company, etc.)
- sch. 83 - decrease in the cost of fixed assets as a result of their revaluation
- sch. 91 - disposal of fixed assets
- sch. 94 - the cost of missing OS is shown
- sch. 99 - write-off of fixed assets as a result of emergency circumstances.
You might be interested in:
Account 02 in accounting: Depreciation of fixed assets
Postings to account 01 in accounting
Receipt of fixed assets
The receipt of an object can occur in different ways - as a result of a purchase, a contribution to the authorized capital, under a donation agreement, etc.
When purchasing an operating system, all costs for its acquisition and preparation for use are collected on account 08, after which the entire amount is transferred to account 01, where accounting is performed. The receipt of fixed assets is accounted for using the following transactions:
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 08 | 60 | The purchase of an asset has been completed (the amount is indicated excluding VAT) |
| 19 | 60 | Registered for VAT on the purchased OS |
| 08 | 60, 76 | Work to prepare the object for use, transportation, etc. is taken into account (the amount is indicated excluding VAT) |
| 19 | 60, 76 | VAT on preparation for use is taken into account |
| 01 | 08 | The OS object is registered |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
OS construction
The object can be obtained as a result of capital construction. Moreover, its initial price includes payment for the contractor’s services and the cost of materials for construction.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 08 | 60, 76 | The price of contract work is shown in the accounting |
| 08 | 10 | Raw materials and supplies given for work on the facility are shown in the accounting |
| 08 | 60, 76, 23, 25, 26 | Other costs for building the OS are shown in accounting |
| 19 | 60, 76, 23, 25, 26 | Input VAT on construction work has been taken into account |
| 01 | 08 | The completed OS object has been accepted for operation |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
OS upgrade
The main feature of modernization is that its result changes the original characteristics of the OS object. As a result, its cost, period of use, etc. change. When accounting for expenses, it is advisable to open a sub-account on account 08, in which to collect all costs incurred for modernization.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 08 | 10 | Material costs written off for modernization |
| 08 | 23 | Auxiliary production costs written off |
| 08 | 60, 76 | A third-party contractor was involved in the modernization |
| 08 | 70 | The salaries of employees involved in the work were written off for modernization |
| 08 | 69 | Social contributions of employees were written off for modernization |
| 01 | 08 | Increased OS cost due to modernization costs |
Sale
When selling, proceeds are recorded in the amount established by the contract. In this case, expenses must include sales costs, as well as accrued depreciation. All transactions are shown in account 91.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 62 | 91 | Reflected revenue from the sale of operating systems |
| 91 | 68 | Determined VAT on the sale of fixed assets |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Depreciation calculated over the operating period is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | The residual value is transferred to other expenses |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Costs for preparation for sale, dismantling, delivery, etc. are indicated. |
| 19 | 60, 76 | The amount of VAT for delivery, dismantling, etc. services has been determined. |
| 68 | 19 | VAT credited |
| 91 | 99 | The financial result of the sale of the OS is reflected |
You might be interested in:
Accounting policies of organizations: why they are needed, approval deadlines, samples for 2019
Liquidation
Liquidation of an asset can be carried out in a situation where it is no longer profitable to use it and it is not possible to sell it. In this case, the decommissioned OS can be disassembled, and the resulting materials can be used for other purposes.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The original cost of the object is transferred |
| 02 | 01/Disposal | Accrued depreciation is transferred |
| 91 | 01/Disposal | Residual value is transferred |
| 19 | 68 | The tax amount was restored based on the residual value |
| 91 | 60, 76 | Expenses include the costs of hiring a third party for the disassembly operation |
| 19 | 60 | VAT charged by the contractor has been taken into account |
| 10 | 91 | Materials received during disassembly of the OS object were capitalized |
Revaluation
This operation is not considered mandatory. However, if its necessity is established by local acts, the revaluation must be performed on the last day of the year. At the same time, the revaluation itself can be of two types - revaluation or markdown
Unaccounted assets based on inventory results
In order to ensure the reliability of accounting, a business entity must periodically make an inventory of its property, which includes fixed assets. If, as a result of the procedure, unaccounted for objects were discovered, they must be accepted for accounting in the same month. This is done at the current market value of a similar object.
OS shortage based on inventory results
Another result of the inventory may be the identification of the absence of some OS object. In such a situation, the damage from its absence should be written off to the responsible person, or, if there is no such person, to losses. This happens in the amount of the actual residual value.
| Debit | Credit | Content |
| 01/Disposal | 01 | The cost of the asset is written off |
| 01/Disposal | Accrued depreciation is written off | |
| 94 | 01/Disposal | The residual value of the operating system is written off for shortages. |
| 83 | 94 | The amount of the revaluation carried out is written off |
| If the culprit is identified | ||
| 73/2 | 94 | The total amount of the shortfall is written off to the guilty person |
| 73/2 | 98/4 | The difference between the residual value and the current market value of a similar object is reflected |
| 50, 51, 70 | 73/2 | The deficiency is repaid by the person at fault |
| 98/4 | 91 | The difference between the residual value and the market value is written off to other income. |
| If the culprit is not identified | ||
| 91 | 94 | The amount of the shortage on the fixed asset item is written off as other expenses |