Accounting for workwear: from purchase to write-off. Income tax: gradual write-off of workwear (Ignatieva A.R.) Terms of wear and tear of workwear for construction
At enterprises with hazardous and harmful production conditions, it is periodically purchased workwear. Write-off deadlines PPE depends on how it is provided to employees, as well as on the service life of the products. The cost of items is included in production costs. Accounting for workwear is carried out in accordance with data obtained from primary documentation.
Providing PPE
Occupational safety and health protection of personnel is one of the key tasks of an enterprise manager. In accordance with Article 210 of the Labor Code, employees of some enterprises are required to receive special clothing. It is necessary to prevent the influence of negative production factors. PPE is used when the safety of activities cannot be ensured only by existing equipment and production organization.
Classification
Remedies are divided into:
- Spacesuits, insulating suits.
- Respiratory protection equipment. These include pneumatic helmets.
- Overalls.
- Means that provide protection for legs, arms, head, eyes, face, and hearing organs. Among them, in particular, are boots, shoe covers, canvas mittens, glasses, shields, berets, helmets, and headphones.
- Fall protection products.
- Dermatological preparations.
Safety precautions
The legislation establishes the procedure according to which workers are provided with protective equipment. The employer is obliged to provide PPE to persons operating in contaminated areas and hazardous industries. In addition, the employer must ensure the preservation, washing, drying, decontamination, disinfection, and repair of workwear. According to the provisions of Article 215 of the Labor Code, personal protective equipment, including foreign-made ones, must comply with Russian standards and have a certificate. Otherwise, the use of funds is prohibited.
by profession
As a rule, they are provided for by regulations adopted by executive bodies. For example, the relevant provisions are present in the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development dated October 1. 2008 No. 541n. It approves the standards for the issuance of protective clothing to employees employed in enterprises with harmful, dangerous conditions, operating at elevated temperatures, in through production areas. The Order provides for types and limits of PPE for the year. The names of professions included in the regulatory document are taken from qualification reference books.

Submission procedure
The rules for issuing PPE establish that specialists in the professions provided for in the Model Standards receive protective clothing, regardless of whether their positions are included in qualification reference books or other acts. The Ministry of Health and Social Development has the right to adopt other provisions regulating these issues. For example, orders may be issued regulating the issuance of special clothing to workers in the water sector, housing and communal services, metallurgy, construction, mining or oil and gas enterprises.
Production conditions
They are considered the determining criterion in regulating the issuance of workwear. For example, at a chemical enterprise, in any case, limits are set on the provision of PPE to drivers, mechanics, welders, crane operators, and laboratory technicians. Legislation may define certain types of workwear for use by employees of specific positions. For example, such provisions are provided for drivers of food enterprises. These employees are provided with hats, winter workwear, leather boots, etc. Drivers of electric power complex enterprises must also receive PPE. However, things must meet the requirements established for this field of activity. For example, winter workwear must be protected from water and electric current.
Providing PPE in excess of limits
The employer has the right to exceed the established issuance standards. This need is determined by the characteristics of production activities. The right to exceed the limits is provided for in Article 221 of the Labor Code. When making an appropriate decision, the employer coordinates it with representatives of the trade union. The determining factors in this case are the financial capabilities of production and priorities in the organization of personnel management policies. The employer can provide employees with types of personal protective equipment not provided for in legal acts. For example, it could be a special summer workwear. However, in this case, certification is required at the areas where employees perform their production activities.

Documenting
At the stage of signing the contract, the employee must be familiar with the rules governing the issuance of workwear. The enterprise is forming a special register for specialties and positions for which PPE is provided. Such statements may include sections by season, which indicate the quantity and duration of operation of the kits. Eg, summer workwear can be provided in the amount of 1 set per employee. Duration of operation - from May to September. The statement may indicate individual means of protection, their quantity, and the frequency of provision. Such a register is usually compiled at enterprises engaged in construction, processing, mining, and chemical production. The issuance standards provide for regular replacement of protective clothing. As a general rule, new PPE is provided at least once a year. Issuance standards may be reflected in a collective agreement or formalized in a separate act. Information about which PPE the employee received is indicated in his personal card.
Important point
If the employer approves improved standards for the issuance of workwear, then the relevant information is reflected in the collective agreement. At the same time, standard criteria recommended by law, modified at the enterprise, are given. The fact that PPE is provided to the employee is confirmed by his signature. The issuance of workwear is carried out by an authorized employee of the enterprise. PPE is provided to staff on a rental basis. When an employee is fired or transferred to another position that does not require the use of special clothing, the products are returned to the employer.
Specifics of replacing PPE
In a number of cases, the employer, after agreement with the State Inspectorate for Labor Protection and the trade union, purchases workwear that differs from that provided for in the Standard Standards. Such actions are usually driven by management's desire to provide better protection to personnel. For example, a robe can be replaced with a cotton suit. The worker may receive rubber boots instead of leather ones. Low boots made of artificial material can be replaced with tarpaulin ones. Particular attention is paid to the material from which the workwear is made. An apron with a rubberized base can be replaced with a polymer one, if in this case it will better protect the employee. The situation is similar with means that provide hand protection. For example, if the production process requires it, canvas mittens can replace polymer ones.

Nuances
Some PPE may be provided to employees after preliminary certification of production areas. The list of such equipment includes, in particular, plugs, light filters, glasses, PVC gloves, galoshes, gas mask, mat, respirator, etc. As part of the certification, the nature of professional activity is studied. In accordance with the results, . The PPE that employees receive must match their gender, height, size, and operating conditions. Emergency equipment is provided to personnel for the duration of the technological operations for which they are provided. The transfer of such PPE is carried out between shifts. Site foremen are responsible for the application of the products. With the onset of cold weather, warm clothes are issued: jackets, sheepskin coats, felt boots, earflaps, etc. With the arrival of the warm season, they are put into storage until the next season.
Number of sets
There is one standard for each employee. However, from 2014 it may be increased. For example, if 5 pairs of gloves are required for a year, then an employee can receive 10 pairs for 2 years. According to legislators, this procedure will allow staff to look neater. It should also be noted that it is currently possible to provide different PPE to employees combining several types of activities. For example, if a citizen is registered as a battery operator and a driver at the same time, he receives two corresponding sets. Staff going to work without PPE is regarded as a violation of discipline. If employees are inappropriately dressed at work, the law provides for penalties for the management of the enterprise.
Hand protection
The most inexpensive and common means are gloves. They provide protection for hands from contamination, scratches, abrasions, and minor mechanical impacts. The cotton glove is made from natural cotton yarn. This ensures free air exchange and prevents excessive sweating of the hands. The cotton glove protects hands when performing carpentry, mechanical assembly, painting, construction, warehouse, and auto repair operations. This type of PPE is used in enterprises engaged in cargo transportation, car servicing, and service stations. Additional durability is provided by the polymer coating. The PVC glove protects your fingers from slipping on parts and creates a stable grip on objects.

Financial statements
Accounting for workwear is carried out based on actual acquisition costs. The company can produce PPE on its own. In this case, the costs of producing products are first grouped in accounts that summarize information about production costs. Based on the fact of production, the cost is calculated. It includes all expenses. When sending finished products, a certificate of completion of work is drawn up. In this case, the following is recorded in the documents:
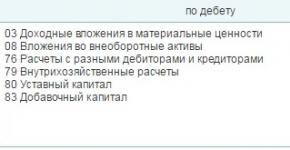
db sch. 23 CD. Account 10 for the amount of production costs.
Analytics is carried out in detail, indicating the quantity, name, date of receipt and return, as well as financially responsible employees.
Standards for writing off workwear
The procedure for disposal of personal protective equipment depends on whether the funds are classified as fixed assets or included in production inventories. Typically, workwear falls into the latter category. However, if its cost is more than 40 thousand rubles, and the period of operation is more than a year, it is included in fixed assets. When generating accounting documents, they are used. Disposal in this case can be formalized in a linear manner over the period of useful operation or directly upon provision to the employee. The first method is used if the period of use is more than a year, the second, accordingly, less than a year. It should be noted that some workplaces provide uniforms that are not designed to protect employees from the adverse effects of the work environment. It is not workwear; therefore, its accounting has its own specifics. A uniform, as a rule, indicates that an employee belongs to a specific company. Standards for writing off workwear established by law may be changed upward. This is permitted in the following cases:
- Reducing the lifespan of things. The rules provide for a maximum period of use of clothing. It cannot be increased, but it can be decreased.
- Replacing a certain type of PPE with another. As stated above, the relevant decision must be agreed upon in writing with the State Inspectorate.
- Providing personal protective equipment to employees for whom it is not provided for in the standard standards. In these cases, a preliminary certification of production activity areas is carried out.
Reduction is not allowed. If, in accordance with the law, an employee must receive two pairs of pants per year, then he cannot be provided with one. Otherwise, the manager may receive a fine. If such a violation is committed again, it may lead to the suspension of the enterprise’s activities for up to 3 months. From the above it follows that if an employer sets his own, they should increase the protection of personnel, improve the provision of PPE for employees, and not worsen them.

Main methods of disposal
Workwear is written off based on the costs that were actually incurred for its production or purchase. Management decides which method to use to include costs in production costs. This can be done:
- Completely at the time of release of products into operation.
- Partially for a certain period from the start of use.
Workwear whose service life does not exceed 3 months is subject to complete write-off.
Features of taxation
Workwear is accounted for without VAT. PPE is provided to employees for a certain time, that is, ownership of it does not pass to the staff, but remains with the enterprise. In some cases, however, difficulties may arise. They are due to the fact that at some enterprises employees pay for special clothing. For example, such a situation is possible upon dismissal. When terminating the contract, the employee pays the remaining cost of the personal protective equipment to the cash desk. In this case, you need to either charge VAT or be guided by FAS Resolution No. 2901/2008. According to its provisions, the employee did not purchase workwear, but merely paid compensation to the company. Insurance premiums for personal protective equipment are not charged if they are not transferred to the ownership of the personnel.
Additionally
It should be said that tax accounting for writing off personal protective equipment differs from accounting. Funds whose cost is less than 10 thousand rubles. with a period of operation of less than a year, are included in material costs. The costs of their purchase are considered indirect. They are written off at the time the workwear is provided. If the cost is more than 10 thousand rubles, and the period of operation exceeds a year, PPE is included in the Write-off in this case using the straight-line method.
1C
Decommissioning of workwear is carried out using a document. It can be entered in two ways. In the first case, the operation is carried out on the basis of “Transfer of Funds”. The introduction can be done separately. In this case, the fields are entered using the “Select” button or manually. Additionally, in the “Location” column, you should indicate the workshop from which the PPE is being removed. “Write-off of expenses” must be filled out if the cost of workwear has not been paid in full. Costs are by default credited to the debit of the account indicated in the main part.
Acquisition
The purchase of workwear is registered using the document "Receipt of goods" with the corresponding type of operation. To add a product item, you must enter a new item in the appropriate tab, in the “Workwear” group. The number of products and the count (10) are also indicated here. At the next stage, the transfer of materials is formalized. For this, a document of the same name is used. It should indicate the employee who receives PPE.

Conclusion
The procedure for writing off the cost of workwear depends on the operational period. If it is more than a year old, then it is classified as PPE. The peculiarity of PPE is that it cannot be included in the operating system if the cost is less than 40 thousand rubles. In this case, workwear is written off either linearly or in proportion to the volume of operations performed. In the latter situation, you need to generate a production document every month and register the quantity of products produced in it. The debit of the entry for which work clothes are written off is filled in with the indicators specified in the “Reflection of expenses” field. This is an account (20 or 25), a cost item, a division, for off-balance sheet accounts. 10.10, 10.11 the amount is received after the documents are processed. If the cost is written off during the entire operational period, transactions are indicated at the end of the period when closing the month. An appropriate register is provided to reflect these transactions. It creates a record Dt sch. 20.01 Kd count. 10.11.
- The employer is obliged to purchase and issue workwear that has passed certification or declaration of conformity.
- Until December 31, 2013, workwear was purchased and issued based on the results of certification of workplaces for working conditions. From January 1, 2014, instead of certifying workplaces based on working conditions, a special assessment of working conditions is carried out. Therefore, if the organization additionally creates new jobs, which, according to the results of the assessment and safety assessment, contain harmful or dangerous factors, and the necessary protective clothing is not available, a contract for its supply should be concluded again.
- Working clothes are purchased at the expense of the employer. This means that purchasing such clothing at the expense of employees is unacceptable. In practice, similar situations often arise.
- The protective clothing issued to employees must correspond to their gender, height and size, the nature and conditions of the work performed. Thus, the law obliges the employer to provide workwear of the required size. Therefore, when concluding an agreement with a supplier, you should indicate the entire size range in the application. When delivering materials, monitor its implementation.
What sources of financing can be used to purchase workwear?
This question most often interests accountants of budgetary institutions. This type of expenditure can be financed both from budget subsidies allocated for the implementation of state (municipal) tasks, and from funds received from the provision of paid services.
In addition, a budgetary institution has the right to purchase special clothing using insurance contributions for compulsory social insurance against industrial accidents and occupational diseases. The basis for the acquisition is the results of the SOUT.
The amount of funds allocated by the policyholder to finance preventive measures cannot exceed 20% of the amount of insurance premiums accrued for the previous calendar year, minus the costs of paying security for the specified type of insurance, made by the policyholder in the previous calendar year.
Let us note that in order to make expenses from insurance premiums for injuries, a budgetary organization must submit an application to the executive body of the Social Insurance Fund at the place of its registration before August 1 of the current calendar year.
How to account for workwear costs
Workwear owned by the organization is accounted for in the accounts/sub-accounts for materials accounting before being put into operation. Like other materials, it is taken into account at the cost of actual acquisition costs. The procedure for accounting for workwear is fixed as an element of the company’s accounting policy. The purchased workwear arrives at the warehouse on the basis of a receipt order.
There is another way. As can be seen from paragraph 9 of the Guidelines, an organization can keep records of special tools, fixtures, and equipment in the manner prescribed for accounting for fixed assets. This method has a number of disadvantages. Firstly, the cost of workwear will have to be subject to property tax. Secondly, it is necessary to monitor the condition of the workwear so that it can be written off on time.
Issuance of protective clothing to employees
When transferring workwear from a warehouse to other divisions of the company, it is necessary to draw up a primary document on the basis of which the workwear is kept accountable. Such paper will be enough to write off the cost of workwear as an expense both in accounting and tax accounting.
If you choose a unified primary, you can use one of these forms:
- demand-invoice;
- invoice for materials release.
If you decide to develop your own form, then you can take the invoice for the release of materials as a basis, removing unnecessary things from it.
The employee responsible for receiving workwear issues it to employees. His actions also need to be recorded somewhere. It is advisable to create a special statement for each person in all departments for a year or month, so as not to fill it out every time you issue special clothing.
Records can also be kept on a special card, which is filled out for each employee of the organization who has received special clothing.
Accounting for the disposal of workwear
If workwear is retired before the end of the established service life (damaged, physically worn out and unsuitable for further use), its cost should be written off as a lump sum and included in other expenses.
How to retain the cost of workwear from a resigning employee?
When you issue workwear to an employee, you must conclude an agreement with him on the transfer of soft equipment for use or a one-time document on acceptance and transfer.
The employee’s obligation to compensate for direct actual damage caused to the employer is provided for in Article 238 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, therefore termination of the employment contract does not entail the release of the employee from financial liability for non-return of workwear.
Thus, in the case of correct registration of the issue of special clothing if it is not returned by an employee leaving the organization, the employer has the right to demand reimbursement of the cost of the special clothing (the useful life of which has not expired) taking into account the degree of wear and tear (Article 246 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Yulia Volkhina, Project Manager
Each profession has its own period for wearing workwear, the standards are approved by the Ministry of Labor Resolution No. 63. You will learn from the article how the service life in 2018 is determined, how to extend it and how to draw up an extension certificate.
Read our article:
Overalls (OC) are one of the types of personal protective equipment. Speaking about workwear, we mean not only protective suits, vests, overalls and short fur coats, but also special shoes, gloves and mittens, helmets and caps, etc., which are needed by people working in conditions of possible threat to their health or life.
Establishing the service life of workwear is an important part. According to current legislation, monitoring the service life of certified workwear in accordance with accepted standards is the direct responsibility of the employer.
Service life of workwear – norms
The period of use of workwear depends on two main factors:
- the type of production in which the employee is involved and, accordingly, the presence and nature of the workplace;
- climatic conditions of the environment in which production activities are carried out.
Various combinations of these factors give rise to a variety of types of CO and safety footwear, as well as requirements for the timing of their use.
A suitable size is a prerequisite for the operation of any CO. It should not restrict the employee’s movement, and the employer is obliged to take care of this.
The lifespan of workwear is 2018 standards (by profession)
The employer must promptly provide its employees with overalls and other personal protective equipment. This process is regulated. According to this article, for a specific workplace where the presence of harmful and (or) dangerous factors or special temperature conditions has been established, CO is selected based on approved industry standard standards ().
It should be noted that the employer has the right to independently establish standards for the consumption of special clothing in production, but on the condition that this does not worsen the degree of protection of workers when performing labor functions in comparison with the requirements of the law.
Rules for the issuance and use of protective clothing, as well as responsibility for providing employees with protective equipment and other personal protective equipment are established.
Service life of workwear - standards according to GOST
The production of workwear is regulated by numerous GOSTs, applied depending on the type and purpose of protective equipment. GOSTs contain requirements for dimensions, ergonomics, materials and fittings, markings, control and testing methods, transportation, storage and operation. As such, GOSTs do not establish service life.
Labeling requirements state that the product must be marked with a production date, and operating instructions state that the operational documentation should indicate the warranty period, which cannot be less than the time of use corresponding to standard standards.
How standards for wearing workwear depend on the type of production
Each industry has its own requirements for the service life of workwear, its materials and configuration. The shelf life of workwear according to the law depends on sanitary standards, the presence of pollution factors, exposure to electric current, elevated temperatures, toxic substances, the risk of injury to body parts and much more.
For example, a library employee is given a suit or robe for protection from dirt and mechanical influences for a period of 1 year. The battery operator is entitled to another set: a suit with acid-proof impregnation (for 1 year), rubber boots (1 pair for 2 years), a rubberized apron with a bib (1 for 2 years), 6 pairs of rubber gloves, as well as duty dielectric gloves, galoshes and goggles for protection against chemical influences.
Workers in certain industries must be provided with additional personal protective equipment, which are listed in current regulations.
How does the service life of workwear depend on the climate zone and time of year?
Depending on the average annual temperature, each of which has its own expiration dates:
- Belt 1 (-1 C). The insulated jacket and trousers are replaced every 3 years, and boots are replaced every 4 years.
- Belt 2 (-9.7 C). The jacket and trousers are changed every 2.5 years, boots - every 3 years.
- Belt 3 (-18 C). New clothes are issued every 2 years, shoes - every 2.5 years.
- Belt 4 (-41 C). New jackets and trousers are issued every 1.5 years, shoes - once every 2 years.
- Special belt (-25 C). The service life is the same as in the 4th belt, but the employee is additionally given a sheepskin coat (4 years), mittens (4 years), and a hat (3 years).
At a number of enterprises, employees are issued summer CO. This could be a cotton or mixed fabric suit, light shoes and gloves. Such clothing is considered seasonal and is issued only in the warm season.
Extending the wearing period of workwear
Protective equipment tends to run out, wear out or break. And it happens that they live long and are suitable for use even after the end of their wear period. What if the used protective equipment is still wearable?
From what day are the terms of use of workwear calculated?
Since compliance with the service life of workwear is the direct responsibility of the employer and responsible persons, it is important to understand from what day the calculation of these terms begins. In general, the countdown begins from the day the CO kit is actually issued to the employee. If we are talking about the terms of wearing insulated clothing and shoes, then they also include the time of their storage in the warm season.
Time to wear out
Certain types of workwear (glasses, sleeves, etc.) are used until they wear out, that is, the employee uses such clothing until it becomes unusable, after which he receives a new one.
For example, in accordance with the Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of Russia dated December 14, 2010, for PPE that is not included in the standard standards, such as signal vests, gloves, shoulder pads, elbow pads, etc., a “wear-out” period can be established based on the SOUT and with taking into account the specifics of the work for which they are used.
For protective equipment with a wear-out period, regular checks must be carried out to determine suitability for further use. The frequency of these checks is set by the employer and can be, for example, 1 year. To record inspections, a log should be kept to record suitability and indicate the date of the next inspection.
For some SZ issued “before wear”, the regulations set a maximum service life, which cannot be exceeded. For example, for safety glasses it cannot be more than one year according to clause 7.
What are the consequences of violating the established service life of CO?
Violation of the service life of workwear threatens the employer with liability depending on the severity of the violation. Thus, for a violation, the organization can be fined in the amount of 30,000 to 50,000 rubles, and the manager and responsible persons - from 1,000 to 5,000 rubles (for a repeated violation - disqualification for a period of 1 to 3 years).
Sanctions for failure to issue CO and PPE may be more serious:
- officials - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- entrepreneurs - from 20,000 to 30,000 rubles;
- legal entities – from 130,000 to 150,000 rubles.
Although the responsibility for issuing and observing the service life of workwear falls on the shoulders of the employer, the employee is obliged to treat his set of protective equipment with care, and if it is damaged, immediately notify the enterprise administration about it ().
Real situation
At an enterprise in the Nizhny Novgorod region, numerous violations were discovered during an inspection of the GIT. In particular, work clothing and safety footwear with expired expiration dates were not replaced within the required time frame, records of the issuance of personal protective equipment were not properly kept, and the issued personal protective equipment did not comply with industry standard standards. As a result, the legal entity was fined under Part 1 of Art. 5.27.1 Code of Administrative Offenses for 50 thousand rubles.
Working clothes are the property of the employer, and the employee does not have the right to use his set of protective clothing during non-working hours and for personal needs. If an employee deliberately damaged his workwear or it became unusable due to his violation of labor discipline (being intoxicated, etc.), then the employer can deduct the cost from him. In other cases, it is prohibited to deduct the cost of equipment and personal protective equipment from employees.
Under no circumstances should you begin work without special clothing or if the CO is damaged. Depending on the type of production, this can lead to frostbite, burns, fractures, illnesses, can lead to death, and also endanger the life and health of other people.
The cost of purchasing special tools, devices, inventory and workwear from January 1, 2015 is written off over more than one tax period. Let's consider the procedure for writing off workwear and special equipment
24.08.2015The write-off of special clothing and equipment for more than one tax period is provided for by amendments to subparagraph 3 of paragraph 1 of Article 254 (Federal Law No. 81-FZ of April 20, 2014). A proposal has been added to this paragraph regarding the possibility, starting next year, of writing off the value of so-called low-value property over more than one reporting (tax) period, depending on the accounting policy chosen by the taxpayer.
Note that this is allowed in accounting.
The purpose of the changes is to bring accounting and tax accounting of material costs closer together.
The procedure for writing off workwear and special equipment
Accounting and tax legislation divides the material assets entering the organization according to cost and service life (useful life). Assets with a useful life of less than one year, regardless of cost, are usually taken into account as inventories. Assets with a useful life of more than one year are accounted for differently depending on their cost. As a general rule, material assets worth more than 40,000 rubles are taken into account as part of fixed assets, while those worth less than 40,000 rubles are included in inventories.
We know that the cost of fixed assets is depreciated and transferred to costs gradually, and the cost of inventories is included in costs immediately upon transfer to production or operation.
These general rules apply to both accounting and tax accounting.
Until January 1, 2015, taxpayers were not given the right to make independent decisions regarding the procedure for accounting for special-purpose material assets.
In accounting, these types of assets are allowed to be taken into account both as part of inventories and as part of fixed assets according to the rules of PBU 6/01 (approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated March 30, 2001 No. 26n). Thus, special-purpose material assets worth more than 40,000 rubles and a useful life of more than one year can be accounted for both in account 10 “Materials” and in account 01 “Fixed Assets”. The choice of accounting method is indicated in the accounting policy.
Special tools, special devices and special equipment in order to determine the accounting procedure for their receipt, release and disposal are combined into one category - special equipment (Guidelines for accounting of special tools, special devices, special equipment and special clothing, approved by order of the Ministry of Finance of Russia dated December 26, 2002 No. 135n). Thus, there are two main groups of special-purpose assets - special equipment and special clothing.
If special equipment is taken into account as part of materials and its service life exceeds 12 months, then its cost can be written off gradually and included in costs in two ways - linear or proportional to the volume of production. The choice of accounting method is fixed in the accounting policy.
At the same time, the cost of special equipment for individual orders or in mass production is allowed to be repaid in full at the time of transfer to production or operation. Moreover, the service life is not limited to a minimum limit.
If special clothing is taken into account as part of materials and its service life exceeds 12 months, then its cost is written off gradually and included in costs in one way - linearly.
The cost of special-purpose materials does not affect the accounting procedure. The service life of special equipment or special clothing is important.
Let us present in the form of a table the options for accounting for special-purpose material assets (according to accounting policies, they are reflected in accounting as part of materials) (see tables 1-3).
Table 1. 1st option. The service life of workwear and special equipment does not exceed 12 months, regardless of cost
Table 2. 2nd option. The service life of workwear and special equipment exceeds 12 months, the cost is less than 40,000 rubles.
Table 3. 3rd option. The service life of workwear and special equipment exceeds 12 months, the cost is more than 40,000 rubles.
When choosing a procedure for accounting for special-purpose material assets as part of fixed assets, the method of including the value of assets in costs may be the same in accounting and tax accounting. Accounting differences will not arise with the straight-line method of calculating depreciation. The non-linear method of calculating depreciation in tax accounting does not coincide with the method of writing off value in proportion to the volume of production used in accounting.
Disposal of workwear and special equipment in practice
Let us give an example of determining the costs of writing off the cost of special-purpose items in accounting and tax accounting.
The organization produces and sells machines. In January 2015, for the production of machine tools, it is planned to purchase a tool worth 10,000 rubles. (without VAT). The tool will also be handed over to the workshop in January. The useful life of the tool is 10 months. According to the accounting policy, for accounting and tax purposes, special tools are taken into account as part of materials and written off evenly over their service life. We begin write-off in the month following the month the tool was transferred to the workshop. Let's determine the amount of material expenses in accounting and tax accounting for the first quarter of 2015 by writing off the instrument.
Accounting
DEBIT 20 CREDIT 10
2000 rub. (RUB 10,000: 10 months x 2 months) - reflects the direct costs of producing the machine in terms of the cost of the tool.
The total amount of material expenses for the first quarter of 2015 will be 2000 rubles.
Tax accounting
The tax register reflects direct costs for the production of the machine in terms of the cost of the tool in the amount of 2000 rubles. (RUB 10,000: 10 months x 2 months).
The total amount of material expenses for the first quarter of 2015 amounted to 2,000 rubles.
The terms for wearing workwear and the conditions for issuing them are regulated by Article 221 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The provisions differ depending on the temperature and pollution conditions in which the work processes take place. For various professions, there is a specific one provided by the employer.

Workwear for different professions
The management of the organization has the right to replace personal protective equipment provided for by labor protection with equivalent ones. It is mandatory to provide similar protection to employees
Terms of use of workwear in different climatic zones
The period of use of workwear may vary depending on the climate zone in which it is used. According to the issuance standards regulated by the state, for all industries the use of PPE occurs within different time frames. This can be seen in the summary table below.

Summary table of service life in years
For special climate zones, winter special clothing is provided, the service life of which is also limited. The additional kit includes:
- Short fur coat - 4 years.
- Ushanka hat – 3 years.
- Mittens with fur - 2 years.
The service life of workwear issuance standards are regulated for each element separately. To avoid violations, all items must be recorded on the employee’s personal protective equipment card. By contacting us, you can choose the best option, taking into account the specific working conditions.

Employee's workwear registration card
Service life of workwear for certain professions
The service life of workwear largely depends on the categories of professions. Work may be performed in outdoor or indoor areas and may involve exposure to hazardous or contaminant substances.
The service life of workwear for working personnel is as follows:
1. Workwear for the fitter
A canvas suit and hard-toed leather boots can be used throughout the year. Mittens will need to be changed at least once a month.

Norm for issuing workwear for fitters per year
2. Asphalt worker's overalls
Jackets and overalls made of cotton fabric, leather boots and ankle boots are issued for a year. Shoes with wooden soles are used for up to six months. Combined mittens are used for no more than three months.

Change house for storing workwear
Separate rooms must be equipped for storing workwear. The norms and rules for overalls used in various fields are prescribed in the instructions of the State Sanitary and Epidemiological Supervision
3. Gas welder’s overalls
The period of use of special clothing and standards for operators of resistance welding installations are as follows:
- Suit with fire retardant impregnation - 12 months.
- Boots – 12 months.
- Gloves – 1 month.
How much can be used for such a specialty must be looked at by climate zones.

Workwear set for gas welder
4. Road worker overalls
To perform all kinds of tasks on the roads, in addition to a waterproof raincoat (36 months), the following protective elements are required with a maximum service life of up to 12 months:
- Cotton suit.
- Leather boots.
- Signal vest.
The useful life of some types of workwear may be limited by actual wear and tear. Such products include canvas knee pads. As for protective gloves or mittens, they must be issued quite often, since they are subject to maximum stress.

Workwear for road workers
5. Roofer's overalls
The wear life of protective clothing for working on roofs also has its limitations. Regardless of what material the roof is made of, personnel must have PPE used for no more than 12 months:
- Trousers.
- Overalls.
- Jackets.
- Boots.
Felted galoshes can be used for no more than six months, while canvas mittens can be used for no longer than two months. also regulate the procedure for providing employees with appropriate protection.

Comfortable overalls for roofing work
6. Boilermaker’s overalls
What period of protective clothing is allowed for certain professions is determined by representatives of the labor protection department, based on the materials used and the design features of the protective devices.
Boiler house workers must be provided with overalls and shoes, replaced with new ones once a year. Canvas mittens are issued every two months. Headphones and earbuds that protect against noise are used until they are physically worn out.

Noise-protective headphones for work in boiler rooms and enterprises with high noise generation
Overalls for line personnel
The service life of workwear according to GOST for engineering and technical workers (area mechanics, foremen, foremen) in months is:
- Cotton suit – 18.
- Waterproof raincoat – 24.
In winter, an insulated jacket and felt boots are additionally used, whose operational period depends on the climatic zones.