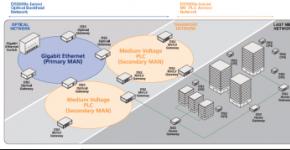
Educational and methodical material on the topic: Reception of a cluster in the lesson. What is it and how to use it? What is a cluster in economics
Cluster: types and benefits
Most enterprises today are modernized with the participation of the state. The state determines the main priorities for the development of enterprises in all areas of activity - from industry to tourism. Structural modernization is developed by the state on the basis of clustering.
What is a cluster?
Although the cluster is an economic term, its exact definition cannot be found in economic dictionaries. A cluster can be considered an industrial group. In a broader sense, a cluster is a group consisting of several companies united by a common activity or on a territorial basis. Based on this definition, we can conclude that not only qualitative characteristics determine the competitiveness of an enterprise, but also its economic environment, that is, the cluster develops not due to external influences, but due to internal influences.
What is a cluster for?
What is a cluster, now it has become clear, it remains to find out what it is for. Clusters are aimed, first of all, at developing the competitive advantages of the national industry at the expense of domestic enterprises without the involvement of foreign companies. Organizations united in a cluster "grind" to each other, work harmoniously in one direction of activity, thus developing the domestic market and entering the world level.
What are clusters?
There are three main types of clusters:
Regional;
Vertical;
Industry.
What is a computing cluster?

There is such a thing as a supercomputer. It is also called a computing cluster. What is a computing cluster? The subject is a computer with several processors connected by a communication network. In other words, these are several computers (but with higher performance than usual), united by one "backbone". Such a system allows solving one task in parallel (simultaneously) on all computers.
Cluster in tourism
Tourism has a great impact on the country's economy, in connection with this, its importance is increasing. The rapid growth of tourism activities, as well as the increase in the well-being of the inhabitants of a particular country and its economy as a whole, made it possible to make the development of tourism one of the priority areas. So, the governments of different countries, including Russia, have introduced the concept of "tourist cluster". It includes a group of travel companies localized in one region to develop infrastructure and use modern technologies to conduct business. The main task of the tourism cluster is to provide tourism services with high competitiveness.
The composition of the tourism cluster

The management of the tourism cluster is carried out by a management company - this is a legal entity (usually a JSC) that operates on the basis of the principles of public-private partnership, to which the state transfers some powers in managing certain economic zones of the tourism cluster. The management company of the tourism cluster regulates the activities of the following companies related to tourism:
Tour operators;
travel agencies;
Organizations providing tourism services (hotels, hotels, holiday homes, etc.).
Secondary components of the tourism cluster:
Public catering enterprises (restaurants, cafe-bars, etc.);
Enterprises providing transport services (airlines, railway and trucking);
Places of trade in goods for tourists;
Leisure places (parks, venues for concerts, cinemas);
Objects providing services for the maintenance of tourist transport.
The purpose of the tourism cluster
The article answered the question of what a cluster is and what types of it exist in our time. The turn has come to say a few words about the purpose of the tourism cluster. All his work on the development of tourism activities is aimed at becoming a separate country as the center of world tourism. In any case, such goals are set by the government for tourism clusters.
In less than a couple of weeks, new words appear in our daily life, the meaning of which we cannot explain. The reason for this is the information age, which constantly “accelerates” time and brings many interesting discoveries. Terms are constantly changing, losing their old meanings and acquiring new meanings. Probably, each of you heard how the word cluster slips in this or that context. What is it, and in what areas is this expression used? Let's take a closer look in this article.
Dictionary about the meaning of the word
As it was not difficult to guess, the word cluster comes from English " cluster» - group, swarm, pack, accumulation, clot, bundle.
This term is used in economics, computer engineering, music, astronomy and means a set of objects that are functionally similar to each other and assembled into one bundle.
- Computer engineering. Servers are collected in one cluster, which increases the stability of the system and its performance. The second value that can be found in information technology is the hard disk sector.
- Economy and industry. Production units that are interconnected and concentrated in one place.
The above descriptions of the term "cluster" are most often found in our language. Although, recently, this expressive means can be heard in management, medicine, pedagogy and even in sports.

Cluster in industry
Innovative processes of recent decades have led to a technological breakthrough in the fields of telecommunications, mobile devices, microelectronics, computer and economic cybernetics. All these branches are interconnected, and therefore, not only at industrial enterprises, but also within individual countries, the so-called cluster analysis began to take shape. The accumulation of production potential in one place provides an effective implementation of investment investments.
Consider concrete examples:
- Cluster approach in the national economy. In Germany, clusters have been established in the chemical industry and mechanical engineering, in France, the food industry has been formed, and in Japan, computer engineering.
- Cluster approach within industrial concerns. The American automobile cluster in Detroit has gathered around itself such giants as Ford Motor Company, Chrysler Group LLC and General Motors. The cooperation of automotive corporations promotes the exchange of innovative technologies and to increase jobs.

Qualitative successes in the development of world industry, gave a scientific and technological revolution in the field of information technology. Inventions in this area, almost instantly become publicly available to any person.
New technologies make it possible to create, process and store huge amounts of information, and computerization has become an integral part of the success of any enterprise.
Cluster in Information Technology has three main meanings:
- . The hard drive of a computer is designed to work with data (writing, reading and saving), and consists of their minimum logical units - clusters. The cluster size that is created during disk formatting is user-selectable. For a computer designed for work (the presence of a huge number of small files), create clusters no more than 4Kb. For a home system designed for gaming or watching videos, this value can reach 32 KB or more.
- Computer group cluster. Two or more computers are assembled into a single system (cluster) designed for a large amount of computing. The main advantages obtained with such a connection:
- System unification.
- Fault tolerance.
- Flexibility of management.
- Multitasking.
- Cluster in programming. Along with object-oriented programming, there is the concept of abstraction of data types, based on the functionality of program components (clusters). Clusters allow you to hide the details of the implementation of algorithms.

Cluster strategy for the development of medicine
Recently, in many countries, for the development and modernization of promising sectors of the economy, it has been successfully used cluster strategy. Medical organizations are no exception in this list. At the state level, there is support for competitive medical centers, and clusters are being created from organizations that have not previously collaborated with each other.
Such medical enterprises are located on the same territory, and, exchanging the scientific base collected over decades, significantly improve the quality of medical services for the population.

Little known meanings of the term "cluster"
- Music. A chord with an interval between notes of one second is also called a cluster. The term was first used in music by the American composer Henry Cowell.
- Education. In the learning process, information is systematized and divided into semantic units (clusters). This technique stimulates the intellectual development of each member of the team.
- Biology. In biology, there is such a thing as a "cluster of genes" - related genes located on a chromosome that are part of one multigene family.
- Logistics. In logistics, this strategy provides an effective territorial construction of transport and warehouse clusters that optimize the process of delivery and storage of goods.
- Economy. United by any signs (logistics, commodity) financial or trading activities.
Now you know the meaning of the term "cluster": what it is, and in what areas of modern life it is used. Ignoring the specific meanings of this expressive expression (such as a cluster chord or hard drive sector), a cluster is a set of enterprises that specialize in performing similar functions.

The exchange of tangible and intangible assets gives a huge breakthrough in the development of both individual industries and the state itself as a whole.
Video about the cluster
In this video, Rick Tyson talks about the application of the cluster method in sports when benching:
Elena Minaeva
Technology "Clusters" and its modification
cluster came to us from information technologies and denotes the union of several homogeneous elements, which can be considered as independent units with a certain property.
A significant contribution to the formation of understanding cluster clustering approach introduced by Michael Eugene Porter, Professor of Business Administration at Harvard Business School, a recognized expert in the study of economic competition.
Method clusters universal - it helps to work with a large amount of information that needs to be mastered, highlighted, systematized and presented in a certain way.
The essence of the method is to highlight the topic, semantic units and graphic design in a certain order of the scheme.
In work on clusters the following must be observed regulations:
1. Don't be afraid to write down everything that comes to mind. Unleash your imagination and intuition.
2. Keep working until time runs out or ideas run out.
3. Try to build as many connections as possible. Don't follow a predetermined plan.
DRAFTING CLUSTER:
Stage 1 - a keyword is written in the middle of a blank sheet "STORY", which is "heart" ideas, themes.
Stage 2 - everything that they remembered about this topic is written around the word - expressing ideas, facts, images ( "brainstorm" appropriate for the topic (model "chaos")
Stage 3 - systematization is carried out. Chaotic records are combined into groups, depending on which side of the content this or that recorded concept, fact (model) reflects. "planet and its moons").
Stage 4 - as you write, the words that appear are connected by straight lines with the key concept. Each of "satellites" also appear in turn. "satellites", new logical connections are established.
The result is a structure that graphically reflects our thoughts, defines the information field of this topic.
cluster in education can be used in three aspects:
In the representation of the system of work and social partnership of the institution (administrative);
In summarizing the experience of the teacher (self-education);
In the organization of the educational activities of the teacher (educational).
Clustering subject educational areas is not limited, the use clusters possible in the study of a wide variety of topics.
Pedagogical technology implemented directly by the teacher.
Therefore, from how much he understands the meaning technology, its scientific foundations, how it can adapt them to specific conditions or develop individual technology, depends not only on the effectiveness of the educational process, but also on the formation of pedagogical technology as a way of professional thinking of the teacher and his activities.
Only on the activity of the teacher, the focus on finding, mastering and implementing educational innovations in practice depends on how quickly changes in his pedagogical activity will occur.
The readiness of the teacher to change himself and change the situation is the main condition for the effective implementation of active teaching methods in the educational process.
Related publications:
Interactive technology "Kaleidoscope of hints" Dear parents! We present to your attention the interactive technology "Kaleidoscope of hints", which we have been developing for three years.
Case technology - interactive technology for short-term learning based on real or fictional situations For the first time, work with cases as part of the educational process was implemented at the Harvard Business School in 1908. In Russia, this technology has become.
Consultation for parents "Technology of self-massage" In our practical work on the correction of children's speech, we often use elements of self-massage using a special ball. That's what it's called.
Finger gymnastics as a health-saving technology There is such an opinion of early development teachers that the entire intelligence of the baby is concentrated on the tips of the fingers. And this is true, because they are developed.
Pedagogical technology for creating a portfolio of a preschooler PRESENTATION "Pedagogical technology of a preschooler's portfolio" Technology of a preschooler's portfolio: A portfolio is a piggy bank of a child's personal achievements.
Technology "Song" Purpose: Development of singing skills of children of senior preschool age. Technology objectives: - Development of positive dynamics in singing skills;
A cluster is a graphical form of information organization, when the main semantic units are singled out, which are fixed in the form of a diagram with the designation of all the links between them. It is an image that contributes to the systematization and generalization of educational material.
Download:
Preview:
Reception cluster at the lesson. What is it and how to use it?
Cluster as one of the methods of critical thinking
The modern education system is focused on the formation of independent thinking in students. Critical thinking is a pedagogical technology that stimulates the intellectual development of students. Cluster is one of his methods (techniques).
The features of critical thinking include the presence of three stages:
- call,
- comprehension,
- reflection.
At the first stage, activation takes place, involving all members of the team in the process. The goal is to reproduce the already existing knowledge on this topic, form an associative series and raise questions that you want to find answers to. At the comprehension phase, work with information is organized: reading the text, thinking and analyzing the facts obtained. At the stage of reflection, the acquired knowledge is processed as a result of creative activity and conclusions are drawn.
Cluster reception can be applied at any of the stages.
- At the challenge stage, children express and record all available knowledge on the topic, their assumptions and associations. It serves to stimulate the cognitive activity of schoolchildren, motivate them to think before starting to study the topic.
- At the stage of reflection, the use of a cluster allows you to structure the educational material.
- At the reflection stage, the cluster method performs the function of systematizing the acquired knowledge.
It is possible to use the cluster throughout the lesson, in the form of a general strategy for the lesson, at all its stages. So, at the very beginning, children record all the information that they have. Gradually, during the lesson, new data is added to the schema. It is advisable to highlight them in a different color. This technique develops the ability to assume and predict, supplement and analyze, highlighting the main thing.
Basic principles of clustering
The cluster is made in the form of a cluster or a model of a planet with satellites. The main concept, thought, is located in the center, large semantic units are indicated on the sides, connected to the central concept by straight lines. These can be words, phrases, sentences expressing ideas, thoughts, facts, images, associations related to this topic. And already around the “satellites” of the central planet there may be less significant semantic units that more fully reveal the topic and expand logical connections. It is important to be able to specify the categories, substantiating them with the help of the opinions and facts contained in the material being studied.
Rules for designing a cluster in a lesson
Depending on the way the lesson is organized, the cluster can be drawn up on the board, on a separate sheet or in a notebook for each student when completing an individual task. When composing a cluster, it is advisable to use multi-colored crayons, pencils, pens, felt-tip pens. This will allow you to highlight some specific points and more clearly display the big picture, simplifying the process of systematizing all the information.
There are several recommendations for clustering. When creating it, you should not be afraid to state and record everything that comes to mind, even if these are just associations or assumptions. In the course of work, incorrect or inaccurate statements can be corrected or supplemented. Students can safely use their imagination and intuition by continuing to work until they run out of ideas. You should not be afraid of a significant number of semantic units, you should try to make as many connections between them as possible. In the process of analysis, everything is systematized and will fall into place.
Application of the cluster method
The cluster method can be used in almost all lessons, when studying a variety of topics.
The form of work when using this method can be absolutely any: individual, group and collective. It is determined depending on the goals and objectives, the capabilities of the teacher and the team. It is possible to flow from one form to another. For example, at the challenge stage, it will be individual work, where each student creates his own cluster in a notebook. As new knowledge becomes available, as a joint discussion of the material covered, on the basis of personal drawings and taking into account the knowledge gained in the lesson, a general graphic scheme is drawn up. The cluster can be used as a way to organize work in the classroom, and as homework. In the latter case, it is important that students have some experience in its preparation.
Advantages and results of the application of the reception
The use of a cluster has the following advantages:
- it allows you to cover a large amount of information;
- involves all team members in the learning process, they are interested in it;
- children are active and open, because they do not have a fear of making a mistake, making an incorrect judgment.
During this work, the following skills are formed and developed:
- the ability to ask questions;
- highlight the main
- establish cause-and-effect relationships and build inferences;
- move from particulars to the general, understanding the problem as a whole;
- compare and analyze;
- draw analogies.
What gives the use of the cluster method in the classroom for children?The cluster reception develops systemic thinking, teaches children to systematize not only educational material, but also their value judgments, teaches children to develop and express their opinion, formed on the basis of observations, experience and new knowledge gained, develops the skills of simultaneously considering several positions, the ability for creative processing information.
findings . Lessons using the cluster method give the children the opportunity to express themselves, express their vision of the issue, give freedom of creative activity. In general, non-traditional technologies used in the educational process increase the motivation of students, create an environment of cooperation and educate children in self-esteem, give them a sense of creative freedom.
April 6th, 2013 06:38 pm
Publisher's Preface
Recently, the editors of our site http://www.smdp.ru/ received a letter from Irina Kovalchuk from the Galician Innovation Cluster. It shows that over the 6 years that have passed since the first publication of the article, its relevance has only increased. In 2007, it was immediately reprinted by half a dozen online publications, from Russian archipelago to KER-Holding, an engineering energy corporation from Tatarstan. In all lists of literature on the topic, it is in the first place. Everyone has already learned the word. Practice, unfortunately, lags behind.
What are clusters and how to create them? Epistemotechnological approach
Yuri GROMYKO
Director of the E.L. Schiffers Institute for Advanced Research, Doctor of Psychology. Sciences, Professor of the British School of Social and Economic Research, full member of the Russian Academy of Natural Sciences
When last year I came to a high-ranking official in the government on a credible recommendation and offered to participate in the design of clusters and the creation of new types of production, he, with a wry smile, answered me: “Clusters - x-yasters! one ".
(Case of life!)
1. Is the sectoral form of organization adequate for industrial production in the 21st century?
2. The price of the epistemotechnological challenge
3. Epistemotechnological ideas about clusters
4. Types of clusters
5. Clusters and the All-Russian vertical of projects (GDP rate)
6. Clusters as reserve development systems
7. Epistemotechnological hierarchy of clusters
8. Clusters as multi-scenarios
9. Clusters - a springboard for a new organization of people's consciousness and thinking.
10 Benedict Spinoza's Warning
1. Is the sectoral form of organization adequate for industrial production in the 21st century?
The problem of forming industrial development clusters is an attempt to answer a question that is well understood by any practical industrialist: why fundamentally new technologies are not being introduced in our country. Some high-ranking politician brought a group of "businesses" to a branch of the Academy of Sciences, where scientists presented their developments. After numerous many hours of presentations, confirmed by the opinions of foreign experts, he asked the captains of the domestic business if they were ready to buy the proposed solutions and implement them in their enterprises. None of the businessmen expressed a desire to make the scientist happy with the purchase of his development. Does this mean that Russian business is greedy and not curious? I think that the main reason for the lack of interest in the results of research and development is not in this.
The problem lies elsewhere. From the point of view of the proposed development, it is absolutely not clear to the financial decision maker whether this new technology can be introduced (squeezed) into the existing type of production, or whether it is necessary to form a completely new type of production on the basis of this technology. The introduction of new technology into an industrial enterprise of the old formation, the old way of life, can cause very serious dysfunctions, which will entail a decrease in the efficiency, reliability and, ultimately, profitability of this production. The creation of a fundamentally new production that has no analogues anywhere in the world causes various concerns, since it is associated with numerous risks. But really, how to calculate the marketing "guaranteed" demand for a product that does not yet exist? As a rule, the various developments of our scientists involve the creation of not just separate industries, but new industries. Another thing is whether the form of sectoral organization is adequate for industrial production in the 21st century.
Is there a scientific answer to this question? It turns out there is. It was developed by one of our teachers in the field of development economics of super-complex systems and megaprojects, Professor Mark Davidovich Dvortsin. This, unfortunately, two years ago, the deceased scientist developed a special discipline - "Technodynamics", which describes the patterns of evolution and changes in full-scale production systems, including institutions of education, industry, and science. Technodynamics is a theory of institutional dynamics focused on the analysis of changing technologies that determine the conditions for the creation of new industrial systems in changing institutional conditions. This practical discipline shows the futility of the ideas of the so-called "innovation economy", which can analyze only one problem - to "squeeze" or not "squeeze" new technological solutions into old organizational systems. But to figure out whether we are talking about updating the old techno-industrial way, or the task is to create industrial production of a fundamentally new techno-industrial way - the "innovative economy" is not capable. Therefore, a much more successful term than the innovation economy is the concept introduced by Yu.V. Krupnov - "development economics", with only one amendment that development is initially a non-economic category. First, it is necessary to organize development, and only then capitalize it.
2. The price of the epistemotechnological challenge.
What is the main trend of the transition to a new techno-industrial order connected with? With a radical change in the institutional conditions of people's activities, which is based on a change in the main type of ownership. The new type of way of life is associated with the emerging type of transfer ownership, with the transfer of technologies from one area and the use of these technologies in another area. Ownership of the transfer and the dynamics of technology presupposes the development of the institution of intellectual property. The threatening state of this institution in Russia is evidenced by the lawsuit filed by Microsoft against the director of a rural school, Ponosov, as well as the purchase and implementation of the company's system products at Russian nuclear power plants and nuclear submarines. The thing is that technology transfer is carried out in a special “aura” that envelops an asset or an industrial platform. This aura is formed not by information technologies in the form of the notorious IT, but by epistemic technologies that provide the ability to isolate technological solutions based on new physical principles and effects and determine the conditions for their transfer to other practical industrial zones. Within the framework of the new techno-industrial structure that is being formed all over the world, 90 percent of the added value will be formed precisely in this aura. Therefore, as in other areas, the problem sounds very simple: either we will form our own epistemic “aura” and asset analysis system, or it will all be appropriated through someone else’s “aura” of billionaire Bill Gates.
But in order for technologies and new technological solutions to be transferred from one area of industrial production to another on the basis of epistemic (knowledge) practices, special platforms must be prepared to ensure such a transfer. It is actually with the construction of such platforms that the formation of clusters is connected for us, since on the basis of such platforms it is supposed to combine fundamental practice-oriented science, design developments and new high-tech industries. From this point of view, clusters are not just a manic obsession after 15 years of stupidity to start doing something and bring production processes to fruition with all your might - to create satellites, planes, cars, etc. This very important task of raising production discipline and mobilization has nothing to do with clusters, development economics, or even an innovative economy. That is, clusters, in the language of Schopenhauer, are not only will (obsession), but also a representation.
3. Epistemotechnological ideas about clusters.
Building a cluster is associated with the need to unite, within one special zone, production business projects in a specific technological area, fundamental developments and modern systems for designing new products and preparing for the production of these products.
Actually, the unification within the framework of a single management system of knowledge and technology exchange cycles will allow building the supporting institutional structures (core and backbone) of the future cluster, which unites several fundamentally new, today non-existent industries. The transition to the cluster is associated with the organization of the processes of technodynamics of the same type of technological systems within the framework of the new techno-industrial structure that is being formed in Russia, based on the transformation and replacement of significant arrays of Russian industrial production with new technological solutions. The epistemotechnological approach allows us to expand the idea of a cluster introduced by the Nobel Prize winner Michael Porter. As you know, today's fashionable economist gave the following definition of a cluster: "A cluster or an industrial group is a group of neighboring interconnected companies and related organizations operating in a certain area and characterized by a common activity and complementary to each other"2.
The central point in the formation of a cluster in our approach is not just territorial and geographical convergence, a residential association of industries from several different industries, between which synergy and mutually functional relationships are possible (supplier-consumer type, development of related solutions, etc.). The task is to bring a number of fundamentally new laboratory technologies, the operation of which is based on new physical principles and effects, to new systems of activity and practice. On the basis of the formed new systems of activity and practice, it is possible to re-equip the entire array of branches of the previous techno-industrial order. From this point of view, every cluster integrates several different activity schemes in its device:
A scheme for organizing a full-scale productive system that combines fundamental practice-oriented science (physical, mathematical and humanitarian), innovative industry and developing education in its structure.
Scheme of spheral organization of the industrial production platform in the form of processes of production, reproduction, sustainable functioning, development, disposal of technologies of the previous techno-industrial order, leadership, organization, management.
A scheme of multisectoral and polyspheric organization of practice, which implies the organization of technodynamics and technological diffusion of new solutions not along the boundaries of industries and redistributions, but in accordance with the principle of innovative susceptibility of various groups of the trans-Russian innovation infrastructure.
The scheme of co-organization and simultaneous use of the knowledge and logistics (post-industrial) level of redistribution and the modernized industrial platform (neo-industrial level of redistribution), which ensures the formation of new generation devices.
The scheme of co-organization of a breakthrough centrally organized core and a competitive market environment, at different speeds and on different principles, perceiving and implementing technologies and products of a new techno-industrial order.
A scheme for the formation of dual-use products based on serial production, providing proven quality of products.
The scheme of a double “marketing ring” (from marketing a product to marketing a new lifestyle, and from marketing a person using a given product and service to marketing a thing), providing marketing of a new type of devices and technological services for their implementation with marketing of a new lifestyle in Russia , with the fashion for life in Russia of a creative, creatively thinking person.
A scheme for investment design and construction of a financial and engineering company that ensures the implementation of megaprojects based on tracking the entire alternative set of promising project products and taking into account risks, rather than discounting the financial flow.
The idea of creating clusters from an epistemotechnological position includes the following major organizational principles.
The clusters being created are a zone of income outside the hydrocarbon industry. The main idea of forming a cluster is to create conditions based on science-based and technologically feasible integrated solutions, as well as commercial mechanisms for the re-equipment of the high value added industry (development of new generation devices, mechanical engineering, new materials - polymers, ultrapure materials, nanotechnologies) and thereby preparing comprehensive production and technological packages for profitable investment. Such decisions, which form the basis of investment projects, are a condition for the formation in Russia for the first time of a zone of profitable financial investments outside the resource-extracting sector of industry, in accordance with the decisions of the President of the Russian Federation and the mission of Russian industry.
Clusters are a zone for growing new standard solutions for regional development. These technological packages created in clusters can be replicated in different territories of the country, forming regional platforms for strategic employment, including through attracting specialists who have previously left it to the country.
Clusters are an adapter between fundamental science and complex developments. The formation of complex technological solutions is a key advantage of the cluster, which provides the translation of knowledge about new physical principles and effects obtained in the laboratories of the country's academic institutions into industrial production technologies, as well as into the technological know-how of devices and instrumental systems of a new class for various industries.
Knowledge management as a condition for the formation of a development economy. The ongoing circulation of knowledge (fundamental, technological, technical, natural sciences, humanitarian, economic) forms the basis of complex technological solutions and new forms of industrial production systems management. From this point of view, the cluster is a factory of complex practice-oriented knowledge, which makes it possible to determine the zones of priority investment investments.
Innovative infrastructure and financial and engineering schemes for the implementation of the megaproject. To implement the mega-projects of industrial re-equipment developed at the sites of the formed clusters, it is planned to develop special financial and investment schemes and innovative strategies supported by consumers of large infrastructure solutions (such as Russian Railways). The principles of knowledge circulation, financial and engineering schemes, innovation and network strategies should be developed on the basis of special humanitarian theories. From this point of view, the creation of clusters involves the co-organization of technical, natural-science and humanitarian knowledge.
Clusters as a learning organization. The most important condition for the creation of a new generation of pilot industries is the constant process of retraining managers and developers of the emerging cluster, which allows us to consider it as a training organization that masters new institutional schemes of activity.
4. Types of clusters.
And what is the representation behind the clusters? This idea should be connected with the answer to the question: what do we actually want to achieve by creating a cluster - organized in the form of a cluster - production system, with what practical necessity is such clustering3? From our point of view, this "clustering" as a strategic process can be associated with at least four of the following circumstances:
1) Technological re-reproduction and re-development of some existing infrastructure platform based on fundamentally new technological solutions for the next technological and industrial and socio-cultural order. For example, on the basis of fundamentally new materials, we are beginning to re-equip the entire infrastructure of Russian Railways. In this case, a cluster or multicluster begins to form around the joined zones of new technological solutions. It becomes clear that one technological transformation will soon lead to the next, and so on. This type of cluster should be called infrastructural-innovative. The main advantage of this cluster is due to the fact that it is formed around a system of guaranteed consumption of products. It is worth including fundamentally new materials in the design of infrastructure units and now the manufacturers of this range will have a guaranteed consumer. The main difficulty in the formation of this cluster lies in the docking, organization and aggregation of different technological solutions in order for the re-equipped infrastructure to function stably.
2) The next type of cluster is associated with the creation of infrastructures that do not currently exist on the basis of fundamentally new physical principles and effects. For example, such a new infrastructure could be the launch of a constellation of satellites of different sizes - large satellites, small satellites, nanosatellites, which provide the creation of multi-level surveillance systems. Such a fundamentally new infrastructure can be the creation of a laser machine tool industry, in which small-sized lasers can replace the functions of many machine tools that exist today. Finally, such an infrastructure can be a system for maintaining health and providing a person with “live food”, the energy effect of which is not reduced by aromatic additives and dyes, based on biophotonics technologies that allow detecting ultraweak radiation and diagnosing the state of human cellular tissues. The main advantage in the formation of this cluster is that it does not need to fit into existing production systems. It is formed in a new free space. The main disadvantage of this cluster is that it is never possible to calculate the guaranteed demand for the products of this cluster in advance. Therefore, the formation of this cluster can only be carried out under serious guarantees from the state.
3) The third type of cluster should be called ultrastructural (as opposed to infrastructural), meta-industrial cluster. On its basis, an industry is being created to transform existing types of industry. The industry for the re-equipment of existing industry is what we call meta-industry. A typical type of ultrastructural meta-industrial cluster can be a nanoelectronic cluster. The proposed scientific solutions for creating devices of a new type based on nanoelectronic technologies can be used to re-equip instrument-making enterprises of the previous techno-industrial order. The main advantage of this cluster is the ability to form around a new class of advanced technology a whole bunch of enterprises where it will be implemented. The main difficulty in building this cluster lies in the most complex system of coordination of scientific and technological, financial and organizational and industrial and production decisions.
4) The fourth type of cluster can be called a cluster of "borrowing a frontier technology platform". Progress towards the formation of a new techno-industrial order implies the creation of conditions for the development of technologies that form the cutting edge of technological development in the world today. Therefore, the borrowing and remastering of advanced technological platforms in the system of Russian industry is a prerequisite for its competitiveness. In this case, we are not talking about the simple development of technological lines that produce finished products. The task is to, based on the connection to the analysis of technological solutions embedded in this platform of fundamental practice-oriented science, after some time to propose the next step in the development of this technological platform. The advantage of building this cluster is that it is based on import-substituting technologies. The operation and use of these technologies involves entering the domestic market and offering lower prices for the production of products already mastered by the consumer. The main difficulties in the formation of this cluster are connected, first of all, with the domestic culture of industrial and production labor. Very often, the cost and production costs on a borrowed technological platform are higher than on similar foreign productions.
It should be noted that the four types of clusters that we have identified are ideal types according to Max Weber, that is, they represent a certain coordinate system within which decisions to build a particular cluster can be analyzed and understood. Moreover, a particular cluster often involves a combination and combinations of the listed types: one, two, three, or all four. It is very important to understand that the obligatory general moment of building each of the listed types of clusters is the co-organization of practice-oriented fundamental science, design development and innovative industry.