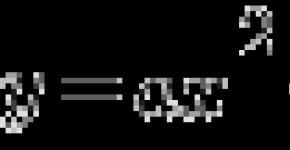Therapeutic business What professions at the institute. Medical professions: list, features and requirements
About the specialty:
The description of the specialty therapeutic case, in which universities teach, admission, exams, what subjects are in the specialty.
Therapeutic case is a very popular specialty, both in universities and in the colleges of Moscow. A huge number of schoolchildren seek to get a secondary special education. Most view medical colleges as the first step in a long educational staircase. Therapeutic case is quite complex specialty and requires complete dedication. Many of the students here are already understood here that they will not be able to learn to the doctor, but they want to devote their lives medicine. Having received secondary special education in the specialty therapeutic case, they become medsens and brothers in hospitals, clinic doctors and occupy other younger medical positions.
What do the medical care been taught?
This specialty is trained by the basics of medicine and pharmacology, physiology and many practical medical skills: to make injections, dressing, put droppers, take care of seriously ill, prescribe treatment, to diagnoses, conduct first medical care, conduct various procedures. Even if after obtaining secondary special education in the specialty therapeutic caseYou do not want to continue learning in medical universities, you will have a huge baggage of medical skills that will allow working in this area.
Prospects for learning therapeutic case
The doctor has a choice: work in a state hospital or private clinic. Some doctors combine the service in the State Medical Institute with private practice. In this case, the main thing is to choose a sought-after direction. Dentistry is very popular, but because of this, a surplus of specialists in the market has been created, and the young dentist will be hard to find a good place. But pediatricians, obstetricians and general practitioners give up, and this position can be made to a decent medical institution. For most destinations you can always enjoy private medical activities and open your business. The specialty medical case opens a lot of doors and gives a bunch of opportunities. In the end, medical knowledge will help both in everyday life and family life.
Earlier, this state standard had a number 040100
(according to the classifier of directions and specialties of higher professional education) Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation State educational standard higher professional education Specialty 040100 - Medical Case Qualification doctor Introduced from the moment of approval
Appendix N 3 to order
Moscow 2000.
1. General characteristics of the specialty
040100 - Medical Case1.1. The specialty is approved by the Order of the Ministry of Education of the Russian
Federation (Order of the State Committee for RF dated 05.03.94 No. 180).
1.2. The qualification of a graduate is a doctor.
The normative term for the development of the main educational training program in the specialty 040100 - therapeutic case with full-time education - six years, with an interconnect (evening) form of training - six and a half years.
1.3. The qualification characteristic of the graduate.
The object of professional activities of graduates is the patient.
The doctor - a graduate in the specialty 040100 Therapeutic business has the right to conduct medical and preventive activities only under the control of certified specialists. He has the right to occupy medical positions that are not related to independent management of patients. A graduate can engage in research activities on theoretical and fundamental areas of medicine.
Graduates in the specialty 040100 - therapeutic case can be prepared for the following types of professional activities:
- prophylactic
- diagnostic
- therapeutic
- educationally educational
- organizational and managerial,
- research.
The doctor - a graduate in the specialty 040100 Therapeutic case was prepared for solving the following tasks:
- conducting primary, secondary and tertiary prevention of diseases of the population (healthy, patients, members of their family and teams);
- diagnosis of diseases, primarily early and typical manifestations of disease, as well as low-impact and atypical variants of the disease of the disease based on propaedeutic and laboratory and instrumental methods of research;
- diagnosis and first aid for emergency conditions;
- treatment with the use of therapeutic and surgical methods;
- diagnosis and maintenance of physiological pregnancy, receiving childbirth;
- examination of patients's working capacity;
- forensic examination;
- hygienic education of patients and their families;
- organization of labor in medical facilities and medical records;
- medical care to the population in extreme conditions of epidemics, in the foci of mass lesion;
- independent work with information (educational, scientific, regulatory reference literature and other sources).
The doctor should be able to:
- carry out the individual and population prevention of diseases, dispensarization of healthy and patients;
- diagnose and treat patients when providing planned and emergency medical care with diseases and pathological conditions, the study of which is provided for by the curriculum and training plans in a medical university;
- conduct medical documentation;
- conduct forensic medical examination;
- provide medical care in the foci of mass destruction of the population;
- organize the work of the subordinate medical personnel in the branches of health institutions, taking into account the safety requirements and in accordance with the regulatory documents of the Health Service;
- effectively work on medical enlightenment of healthy and patients.
1.4. The possibility of continuing the formation of a doctor who has mastered the main educational program of higher professional education in the specialty 040100 - therapeutic case:
The doctor was prepared for the continuation of education in the internship, the ordict, graduate school (on theoretical departments) on the programs of postgraduate vocational education.
2. Requirements for the training level of applicant
2.1. The preceding level of formation of the applicant is average (full) general education.
2.2. The applicant must have a state-owned document document on the average (full) general education or secondary vocational education, if it has an entry on obtaining an average (full) general education presenter, or higher vocational education.
3. General requirements for the main educational
Graduate training program in the specialty
040100 - Medical Case
3.1. The main educational doctor's training program is developed on the basis of this State Educational Standard and includes a curriculum, training disciplines, training and work practices programs.
3.2. Requirements for a compulsory minimum of the content of the main educational program of training a doctor, to the conditions for its implementation and the timing of its development are determined by this State Educational Standard.
3.3. The main educational program of training a doctor consists of the disciplines of the federal component, the disciplines of the national-regional (university) component, disciplines for the choice of student, as well as optional disciplines. Disciplines and student selection courses in each cycle must consistently complement the disciplines specified in the federal component of the cycle.
3.4. The main educational program of training a doctor should include a student of the following disciplines and outcome state certification:
gSE cycle - humanitarian and socio-economic disciplines;
cycle EN - Mathematical, Natural Science and Medical Biological
disciplines;
cGC CYCLE - professional disciplines;
dS cycle - discipline specialty;
FTD - elective.
4. Requirements for a mandatory minimum content
Main educational program
Preparation of the doctor
By specialty
040100 - Medical Case|
Name of disciplines and their main sections |
Just hours ( total labor intensity) |
|
|
Humanitarian and socio-economic disciplines |
||
|
Federal Component: |
||
|
Foreign language Securing high school program, studying a new lexico-grammatical material necessary to read and transfer the original foreign language literature in the specialty. Various types of speech activities, reading, etc., allowing to use a foreign language as a means of professional communication (written and oral). Text processing skills in the specialty to use received information on professional purposes: translation, annotation, referencing (in native and foreign languages). Oral communication skills (listening, dialogic and monologic speech), allowing to participate in professional communication with foreign colleagues in the volume of those listed in the program on the "Foreign language" discipline for students of medical and pharmaceutical universities |
||
|
Physical education. |
||
|
Domestic history. History of Russia as an integral part of the history of mankind. The main patterns and peculiarities of world history through the prism of the National Russian history. The impact of Russian history to the global process. Representation on the history of mankind and its basic stages as an important factor in the formation of value orientation and determining the civil position of the modern person. Problemshistory methodology; the ratio of political, economic, spiritual factors in history; The role of religion and religious representations. Criteria for knowledge of history; Types and forms of civilizations. New approaches to the problem of "man in history"; The history of everyday life, lifestyle and morals; Political leaders, commander and reformers in history. Social history, the interaction of revolutions and reforms. The place and role of Russia, Russian civilization and culture inhistory of mankind. Characteristic features of European and eastern civilizations. The main stages of world history. Ancient World: Role antique heritage for European culture; Contribution of Eastern Civilizations (China, India, Arab East, etc.); Russia I. nomadic world. Middle Ages: the formation of national states; authoritarian power and the emergence of a class representative office; Humanism and Reformation; The role of Christianity B. european civilization; The formation of Orthodoxy in Russia. New history: History of geographical discoveries that expanded borderspeace; Industrial revolution and its consequences; Hush century and century of enlightenment and humanism; Russia opens a window to Europe; Russian reforms and reformers in the XIX century; The contribution of Russian culture to world culture. The newest history (XX century): the role of the XX century in world history; globalization of social processes; The problem of economic growth and modernization; Social transformation societies; The collision of internationalism and nationalism, integration and separatism, democracy and authoritarianism. World and local war; The role of the Soviet Union in the victory over fascism; History of the Cold War. Scientific and technical revolution and its effect on the move social development; Integration of science and education. Russian factor in the political, social and spiritual history of the XX century. Geopolitical changes in the world at the turn of the 1800-90s. |
||
|
Culturalology. Structure and composition of modern cultural knowledge. Cultural and cultural philosophy, cultural sociology, cultural anthropology. Cultural and cultural history. Theoretical and applied culturaology. Methods of cultural research. The basic concepts of cultural studies: culture, civilization, morphology of culture, cultural functions, subject of culture, culturegenesis, cultural dynamics, language and symbols of culture, cultural codes, intercultural communications, cultural values \u200b\u200band norms, cultural traditions, cultural picture of the world, social institutions of culture, cultural self-identity, cultural modernization. Typology of cultures. Ethnic and national, elitar and mass culture. Eastern and Western types of cultures. Specific and "middle" cultures. Local cultures. The place and role of Russia in world culture. The trends of cultural universalization in the global modern process. Culture and nature. Culture I. society. Culture and global problems of modernity. Culture and personality. Inultation and socialization. |
||
|
Political science. Object, subject and method of political science. Functions of political science. Political life and power relations. Role and place of politics inlife of modern societies. Social policies. History of political teachings. Russian political tradition: origins, sociocultural bases, historical dynamics. Modern political schools. Civil society, its origin and features. Features of the formation of civil society in Russia. Institutional aspects of policies. Political power. Political system. Political regimes, political parties, electoral systems. Political relations and processes.Political conflicts and ways of their permission. Political technologies. Political management. Political upgrades. Political organizations and movements. Political elites. Political leadership. Socio-cultural aspects of politics. World Politics and international relations. Features of world Political process. National and state interests of Russia in a new geopolitical situation. Methodology of knowledge of political reality. Paradigms of political knowledge. Expert political knowledge; Political analytics and prognostics. |
||
|
Jurisprudence. Medical law, bioethics and deontology are important regulatory systems in the field of health health. State and law. Their role in the life of society. Rights of law and regulatory acts. Omlustration and legal culture of the doctor. The main legal systems of modernity. International law as a special system of law.Sources of Russian law. Law and regulatory acts. System of Russian law. Branches of law, as guarantors to ensure the rights of citizens in health. Office and legal responsibility. The value of legality and law enforcement in modern society. Constitutional state. The Constitution of the Russian Federation is the main law of the state. Constitutional rights of citizens to health and medical care. Features of the federal device of Russia. The system of state authorities in the Russian Federation. Legal basis for health management. Medical law. Fundamentals of the Russian legislation on the protection of citizens' health. Rights of patients and medical workers. The concept of civil legal relationship. Individuals and legal entities. Ownership. Liabilities in civil law and responsibility for their violation. Compensation of harm caused by improper medical care. Hereditary law. Marriage family relationship. Mutual rights and obligations of spouses, parents and children. Responsibility for family law. Mystery adoptionchild. Family planning concept. Labor contract (contract). Labor discipline and responsibility for its violation. Features of regulating the labor of medical workers. Administrative offenses and administrative responsibility. The concept of a crime. Criminal liability for committing crimes. Professional and official offenses of medical personnel and their prevention. Environmental law. Features of legal regulation of future professional activities. Legal basis for the protection of state secrets. Medical secrecy. Legislative and regulatory acts in the field of information protection and state secrets. Actual problems of medicine and law. |
||
|
Psychology. Item, object and methods of psychology. The role of psychological knowledge in the work of the doctor. The main scientific schools of modern psychology. Individual, personality, individuality. The influence of the patient's personality on the emergence, the course of the disease and the possibility of the influence of the disease on his psyche. The identity of the doctor as a factor of confidence in a patient him. The structure of the psyche. The ratio of consciousness and unconscious. Levels of behavior. Modern ideas about learning. Behavioral approach to understanding abnormal behavior. Modification of behavior from the subjects of learning. Research and identity. Psychological characteristics of activity as a purely human behavior. Conscious and automated components of activity. Will as a conscious organization and self-regulation of the personality of their activities. The concept of frustration. Mechanisms of intrapsihical protection. Personality development in activities and health. Doctor and patient as partners in managing activities aimed at the patient's health. Motivation of behavior. Conscious and unconscious motifs. Motives and meaning. Motivation and health. Motivation and illness. Psychological meaning of the disease. Perception of the world. Properties of perception as a subjective image of the world. Podpong perception. Perception in the medical and diagnostic process. Inner health painting. Inner painting of the disease. Therapeutic effects. Cognitive processes. Emotional processes. Emotional provision of behavior. Emotion factors. Psychology grief. Prevention of fear and anxiety. Psychology of communication. Features professional medical communication. Transfer and counter -Transfer. Communication channels, psychology groups. The structure of the group and its measurement. Group dynamics. Doctor as a memberprofessional group. Therapeutic groups. Family as a small group. Pedagogy. Object, subject, tasks, functions, pedagogy methods. Main categories Pedagogy: education, education, training, pedagogical activities, pedagogical interaction, pedagogical technology, pedagogical task. Medical pedagogy. Pedagogical aspects of the professional activity of the doctor. Training of patients, medical personnel. Training programs in working with the patient's family. |
||
|
Russian language and culture of speech. Stirring modern Russian. Lexica, grammar, syntax, functional and stylistic composition of the book speech. Conditions the functioning of the conversational speech and the role of non-language factors. Linguistic and extrallinguistic public speech factors. Sphere of functioning, species diversity, language features of formal business style. Interpenetration of styles of specifics elements of all linguistic levels in scientific speech. Genre differentiation, selection of language products in a journalistic style. Features of oral public speech. Orator and his audience. Maintenance types of arguments. Speech preparation: The choice of the topic, the purpose of speech, the search for material, the beginning, deployment and completion of speech. Major techniques search for material and types of auxiliary materials. Verbal registration of a public speech. Understandability, informativeness and expressive public speech. Language formulas of official documents. Receptions for unifying the language of service documents. International Properties of Russian Official Business Writtenspeech. Language and style of administrative documents. Language and, commercial correspondence style. Language and style of instructive methodical documents. Advertising in business speech. Regulations documents. Speech etiquette in the document. The main units of communication (speech event, speech situation, speech interaction). Regulatory, communicative, ethical aspects of oral and written speech. Culture of speech and improving competent letters and speaking (literary pronunciation, semantic emphasis, word order function, collective). Non-verbal means of communication. Speechnorms of educational and scientific fields of activity. |
||
|
Sociology. Background and socio-philosophical prerequisites of sociology as science. Sociological proof O.Konta. Classic sociological Theories. Modern sociological theories. Russian sociological thought. Society and social institutions. World system and processes globalization. Social groups and community. Types of communities Community and personality. Small groups and teams. Social organization. Social movements. Social inequality, stratification and social mobility. The concept of social status. Social interaction and social relations. Public opinion as a civil society institution. Culture as a factorsocial change. The interaction of the economy, social relations and culture. Personality as a social type. Social control and deviation. Personality as an active entity. Social changes. Social revolutions and reforms. Social concept progress. Formation of the global system. Place of Russia in the worldcommunity. Methods of sociological research. |
||
|
Philosophy. The subject of philosophy. Place and role of philosophy in culture (medicine). Historical types and directions in philosophy. The main stages of the historical development of philosophical thought. Philosophy in the development of Russian spirituality. The structure of the philosophical knowledge of being. The concept of spirit, matter and consciousness, space, time and movement. Life as a specific form of motion of matter. Scientific, philosophical and religious paintings of the world. Dialectics, its principles and universal laws. Development, its models and laws. Organic evolution on Earth. Ontological status of earthly life. Man, society, culture. Human and nature. Production and its role in human life. Society and its structure. Man in social relationship system. Man as a creator and culture creation. Love and creativity in human vital activity. Man and historical process, personality and mass, freedom and necessity. The meaning of life and human activity. Cognition. The ratio of opinion, faith, understanding, interpretation and knowledge. Rational and empirical knowledge. Irrational knowledge: intuition in medicine. Reflection of the world in consciousness as knowledge. Creative "Designing" Knowledge. Practice. The science. Scientific and adverse knowledge. Truth and its criteria. The structure of scientific knowledge, its methods and forms. Scientific revolutions and change of types of rationality. Union of philosophy and medicine. Philosophical and methodological foundations of medicine. Philosophical and ethical problems in medicine (bioethics) ² . |
||
|
Economy. The subject of economic science, its sections. Economic systems. Economic institutions. Macroeconomics. Demand. Individual and market demand. Sentence. Market mechanism. The role of prices in the economy. Markets of interrelated goods and services. Firm. Accounting and economic costs and profits. Performance. Competition and market structure. Antimonopoly regulation. Labor market. The demand and supply of labor. Human capital. Revenues. Inequality and redistribution of income. Functions and types of money. Inflation and its causes. GDP and GNP. Pp. National income. Personal income. Cumulative demand and proposal. Macroeconomic equilibrium. Types and unemployment levels. Measures to combat unemployment. The economic growth. Growth models. Economic cycles. Fiscal policy. The main articles of income and expenditures of the state budget. Banking system. International economy. Development of economic science. Basics of an applied economy. Entrepreneurship. Types of enterprises. Types of securities. Basics of accounting. Evaluation of the results of economic activity. The concept of bankruptcy. Marketing basics. Types of advertising. Taxes. Tax system. Financial institutions. The mechanism of action of stock exchanges, insurance and investment companies. Basics of consumer knowledge. Transition economy. Characteristics and structure of Russian economy. |
||
|
Bioethics. Moral and ethical norms, rules and principles of professional medical behavior. Patient and doctor's right. Ethical foundations of modern medical legislation. Application of ethical principles when using new biomedical technologies |
||
|
History of medicine and pharmacy. The impact of the habitat on human health, finding effective means of treatment and prevention, diagnosis, doctor's relationship and patient, a doctor's place in society; idea of \u200b\u200bmedical systems and medical schools; The doctrine of a healthy lifestyle. Folk and traditional medicine. Magic and demonological medicine. Medical education. First medical institutions. The influence of world religions on medicine. Outstanding medicine and pharmacy figures. Outstanding medical discoveries, the influence of humanistic ideas on medicine. The influence of the scientific revolution and technical program on the development of medicine. Features of the domestic history of medicine. Problems of medical ethics and deontology in the history of domestic medicine and at the present stage. |
||
|
Latin and Terminology Basics |
||
|
Disciplines and courses on the selection of a student installed by the university: |
||
|
Naturally scientific, mathematical and biomedical disciplines |
||
|
Federal Component: |
||
|
Mathematics. Mathematical methods for solving intellectual tasks and their use in medicine. |
||
|
Computer science. Theoretical basis of computer science. Collection, storage, search, processing, transformation, dissemination of information in medical and biological systems. Using computer in health care. |
||
|
Basic laws of physics. Physical phenomena and processes. The physical foundations of the functioning of medical equipment. Device and appointment of medical equipment. |
||
|
Chemistry: general and bioorganic. Chemical nature substances. Chemical phenomena and processes. Basic laws and concepts. Chemistry and medicine. |
||
|
Biology with ecology. |
||
|
Medico-biological disciplines |
||
|
Biological chemistry .Chemical nature of substances and chemical phenomena and processes in the body. Clinical biochemistry |
||
|
Human anatomy. The structure of the human body is in relationship with the function and topography of systems and organs. Development and Individual Features . |
||
|
Histology, embryology, cytology. The main patterns of the development and vital activity of the body based on the structural organization of cells, tissues and organs. Rastofunctional features of tissue elements. Methods of their research |
||
|
Normal physiology. Functional systems of the human body, their regulation and self-regulation when exposed to the external environment. The patterns of functioning of individual organs and systems |
||
|
Microbiology, virology, immunology. Classification, morphology and physiology of microorganisms and their identification. The role and properties of microorganisms. Spread and influence on human health. Methods of microbiological diagnostics. The use of basic antibacterial, antiviral and biological preparations. |
||
|
Pharmacology. Classification and main characteristics of medicines. Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics. Indications and counterparts for the use of medicines, use and side effects. |
||
|
Pathological anatomy. Structural foundations of diseases and pathological processes. Morphological changes of organs and tissues in pathological processes. |
||
|
Pathophysiology. Causes, main mechanisms for the development and outcomes of typical pathological processes. The patterns of violations of the functions of organs and systems |
||
|
National-regional (university component): |
up to 15% of the total cycle volume |
|
|
Professional disciplines |
||
|
Federal Component: |
||
|
Medical and preventive disciplines |
||
|
Hygiene with the basics of human ecology. Wg. Preventive medicine. Diseases associated with the adverse effects of climatic and social factors. Hygienic aspects of nutrition. Hygiene medical and preventive institutions. Hygiene children and adolescents. Hygienic problems of medicine assistance working in industry. Organization and conduct of preventive measures. Ecology and rational environmental management . |
||
|
Subject, place and role of public health and health, health care systems. Medical statistics. Public health indicators. The most important diseases and their socio-hygienic significance. Financing a health care system. Health insurance. Social insurance and social security. Planning, financing institutions of health care. Organization of medical care to various groups of the population. |
||
|
Epidemiology. . |
||
|
National-regional (university component): |
up to 15% of the total cycle volume |
|
|
Clinical disciplines Collection and analysis of information on the state of health of the patient, training a professional algorithm for solving practical problems of diagnosis, treatment of patients and prevention of diseases, professional medical behavior skills. Maintaining medical records. |
||
|
Infectious diseases. |
||
|
Clinical pharmacology. |
||
|
Dermatovenerology. |
||
|
Medical physical culture and medical control. |
||
|
Radiation diagnosis and therapy. |
||
|
Section course. |
||
|
Neurology, neurosurgery. |
||
|
Medical genetics. |
||
|
Otorinolarningology. |
||
|
Ophthalmology. |
||
|
Psychiatry and narcology. |
||
|
Forensic Medicine. |
||
|
Extreme and military medicine. |
||
|
Obstetrics and gynecology. |
||
|
Pediatrics. |
||
|
Common care for patients. |
||
|
Propaedeutics of internal diseases. |
||
|
Domestic diseases, general physiotherapy, HPT. |
||
|
Endocrinology. |
||
|
Phthisiopulmonology . |
||
|
Surgery: |
||
|
Common care for patients. |
||
|
General surgery, anesthesiology. |
||
|
Resuscitation and intensive therapy. |
||
|
Operational surgery and topographic anatomy. |
||
|
Surgical diseases. |
||
|
Stomatology . |
||
|
Traumatology and orthopedics. VPX. |
||
|
Urology. |
||
|
Oncology. |
||
|
National-regional (university component): |
up to 15% of the total cycle volume |
|
|
Disciplines specialty |
||
|
Internal illnesses. |
||
|
Surgical diseases. |
||
|
obstetrics and gynecology . |
||
|
Polyclinic therapy. |
||
|
Professional diseases . |
||
|
Infectious diseases, epidemiology. |
||
|
Public health and health. |
||
|
Disciplines and courses on the selection of a student installed by the university: |
||
|
Total hours of theoretical training: |
||
|
Practices: |
||
5. Terms of development of the main educational
Graduate programs
By specialty
040100 - Medical Case5.1. The term of mastering the main educational program
the training of a doctor with full-time learning is
303 weeks, including:|
Theoretical training, including research work of students, workshops, including laboratory as well as exam sessions |
220 weeks |
|
Practices: Educational - P. about all clinical disciplines to25% Production |
18 weeks |
|
Complete state |
4 weeks |
|
vacation (including 4 (8) posts of postgraduate leave) |
41(46) a week |
5.2. For persons having a secondary (full) general education, the deadlines for the development of the main educational program of training a doctor in part-in-country (evening) form of training -
6,5 years.5.3. The maximum learning load (total labor intensity) of the student is established
54 An hour per week, including all kinds of its audit and extracurricular (independent) study work.5.4. The volume of student's audit classes in full-time education should not exceed the average for the period of theoretical training.
36 hours a week. At the same time, the specified volume does not include classes on optional disciplines.When forming the main educational program, the university is obliged to allocate
on audit classes with students
2/3 from the volume of total labor intensity,on laboratory, practical classes - no less
30% from audit time.Independent work of students in the study of all disciplines of this educational program should be at least
1/3 The volume of the total labor intensity.5.5. With part-time (evening) form of training, the volume of audit classes should be at least
20 hours a week.5.7. The total volume of vacation times in the school year should be
6-11 Weeks, including at least two weeks in winter.6. Requirements for the development and conditions of implementation
The main educational training program
Graduate in specialty
040100 - Medical Case6.1. Requirements for the development of the main educational
medical training programs
6.1.1. The Higher Educational Institution independently develops and approves the main educational program of the university to prepare a physician on the basis of this State Educational Standard.
The disciplines for the choice of student are mandatory, and the optional disciplines envisaged by the study plan of the highest educational institution are not mandatory for study by the student.
Couchers (projects) are considered as a type of learning work on discipline and are carried out within the watches assigned to study.
For all disciplines and practitioners included in the high school curriculum the establishment should be put up with a final assessment (excellent, well, satisfactory, unsatisfactory or credited, not credited).
6.1.2. When implementing the basic educational program, higher education
the institution has the right:
change the volume of hours drawn to the development of educational material for cycles of disciplines, within
15%;To form a cycle of humanitarian and socio-economic disciplines, which should include from eleven basic disciplines given in this State Educational Standard, as required by the following 4 disciplines: a foreign language (in a volume of at least 340 hours), physical culture (in the amount of at least 408 hours ), philosophy, domestic history. The remaining basic disciplines can be implemented at the discretion of the university. UMO recommends including such disciplines such as psychology and pedagogy, lawwork, bioethics, medical history, Latin language and the basis of terminology. At the same time, they can be associated with interdisciplinary courses while maintaining a mandatory minimum content. If disciplines are part of the general professional or special training (for humanitarian and socio-economic areas of preparation (specialties), the clocks allocated to study them can redistribute within the cycle;
to teach humanitarian and socio-economic disciplines in the form of copyright lecturers and various types of collective and individual practical training, tasks and seminars on programs developed in the university itself and taking into account regional, national-ethnic, professional specifics, as well as research preferences of teachers providing qualified coverage of the subject of the cycle disciplines;
establish the necessary level of teaching certain sections of disciplines included in the cycles of humanitarian and socio-economic, natural-scientific disciplines;
providing classes on the discipline "Physical Culture" with an internally-correspondence (evening) form of training, taking into account the wishes of the student;
in medical and pharmaceutical universities, teaching questions of anatomy, physiology, medical physical education and medical controls provided for in the Physical Culture program for students of the Russian Federation, only on profile departments;
introduce to the 6th year reading of problematic complex lectures on sections ending the preparation in accordance with the State Educational Standard.
6.2. Requirements for personnel support of the educational process
The implementation of the main educational program for the preparation of a graduate specialist should be provided by pedagogical personnel having a basic education that corresponds to the profile of the discipline taught, and systematically engaged in scientific and / or scientific and methodological activities (at least 3 years); Teachers for all medical and biological, clinical and disciplines of the specialty, as a rule, should have a degree (not less than 60% of candidates and 10% of the catalog of sciences) and experience in the relevant professional field (at least 3 years);
To pedagogical activities, in the field of medical and pharmaceutical profile, persons who are prohibited by the verdict of the court or medical contraindications are not allowed.
6.3. Requirements for educational and methodical support of the educational process
The implementation of the main educational training program of the graduate specialist should be provided by the access of each student to library funds and databases, on the maintenance of the compliant disciplines of the main educational program, the presence of methodological benefits and recommendations on all disciplines and for all types of practicing workshops, course design, practitioners, as well as visual manuals, multimedia, audio, video materials.
Laboratory Workshops There should be disciplines: Physics, Mathematics, Informatics, General Chemistry, Bioorganic Chemistry, Biology, Biological Chemistry, Human Anatomy, Histology, Embryology, Cytology, Normal Physiology, Microbiology, Virology and Immunology, Pharmacology, Pathological Anatomy, Pathophysiology, Hygiene , Military Hygiene, Public Health and Health, Epidemiology, Military Epidemiology.
Practical classes should be provided and provided for in the study of disciplines: physical culture, foreign language, Latin and the basis of terminology, physics, mathematics, computer science, computer science.
Clinical practical classes should be provided and provided for in the study of all clinical disciplines and epidemiology, military epidemiology.
The library fund must contain the following logs (2 sets):
obstetrics and gynecology
Allergology
Angiology and vascular surgery
Anesthesiology and resuscitation
Annala Surgery
Antibiotics and chemotherapy
Archive of pathology
Bulletin of experimental biology and medicine
Bulletin of regulatory acts
Vestnik dermatology and venereology
Herald of intensive therapy
Herald of otolaryngology
Herald of ophthalmology
Herald of radiology and radiology
Herald surgery. I.I. Grekova
Military Medical Journal
Questions of virology
Questions of resortology, physiotherapy and medical physical education
Questions of medical chemistry
Questions of biological, medical and pharmaceutical chemistry
Questions oncology
Nutrition issues
Higher education in Russia
Hematology and transfusiology
Hygiene and Sanitation
Breast and Cardiovascular Surgery
Magazine issues of neurosurgery
Journal of Higher Nervous Activities
Magazine microbiology and epidemiology
Journal of Neurology and Psychiatry
Health of the Russian Federation
Immunology
Immunology. Allergology
Sexually transmitted infections
Cardiology
Clinical gerontology
Clinical and laboratory diagnostics
Clinical medicine
Clinical Pharmacology and Therapy
Medical and social expertise
Medicine of labor and industry
Medical newspaper
Medical radiology
Medical equipment
Medical Bulletin
International Medical Journal
Molecular genetics, microbiology and virology
Morphology
Nephrology
Oncology
Ophthalmoshurgery
Pathological physiology and experimental therapy
Pediatrics
Problems of hematology and blood transfusion
Social hygiene problems and medicine history
Problems of tuberculosis
Problems of endocrinology
Psychological magazine
Pulmonology
Russian Bulletin of Perinatology and Pediatrics
Radiation biology
Russian Bulletin Gastroenterology, hepatology and coloproctology
Russian journal of skin and venereal diseases
Russian medical journal
Russian oncological journal
Russian Medical Journal
Nursing
Social and Clinical Psychiatry
Stomatology
Forensic-medical examination
Traumatology and orthopedics
Therapeutic archive
Toxicological messenger
Ultrasound diagnostics
Urology
Successes of modern biology
Successes of physiological sciences
Pharmacology. Toxicology
Pharmacy
Physiology and morphology
Physiology of man
Chemical Pharmaceutical Journal
Surgery. Magazine them. N.I. Pirogov
Cytology
Experimental and clinical pharmacology
Endoscopic Surgery
Epidemiology and infectious diseases
The security of the students's mandatory (with the vulture of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation) educational literature for each discipline of the state educational standard of the licensed specialty should be 0.5 copies, and the library foundation is at least 125 units per student full-time form of preparation.
6.4. Requirements for the material and technical support of the educational process.
The highest educational institution that implements the main educational program for the preparation of a graduate specialist should be the material and technical base that meets the current sanitary and technical standards and ensures all types of laboratory, practical, clinical disciplinary, interdisciplinary training and research work of students stipulated by the approximate curriculum (the number of premises for deploying the department is determined at the rate of at least 18 square meters of training and educational and laboratory premises for 1 student).
6.5. Requirements for organization practices
1. From all clinical disciplines to
25% The clock is allocated to practical classes in outpatient polyclinic institutions.2. The complex of the steamed and procedural medical sister -
4 weeks on the fourth semester.3. The complex of the paramedic ambulance and emergency care -
4 weeks on the sixth semester.4. The hospital's medical doctor -
6 Weeks on the eighth semester.5. The perplexer of the doctor of emergency and emergency care -
4 Weeks on the tenth semester.Production practice after 2 courses
- Studying the work of junior medical personnel and performing manipulations for patient care.Industrial practice after 3 courses - the study of the work of secondary medical personnel and the implementation of manipulations and procedures of medium medical personnel.
Industrial practice after 4 courses - the study of the work of the doctor in the hospital of therapeutic, surgical and obstetrician-gynecological profile.
To be able to: examine patients with the most frequent therapeutic, surgical and obstetric and gynecological diseases, evaluate the examination and survey of the patient, to formulate a preliminary diagnosis, to draw up a survey plan, give the nearest and long-term forecast, recommendations for outpatient treatment, carry out treatment of patients under the guidance of the doctor, correctly make medical records, participate in the reception of physiological genera and produce primary processing of newborns.
The student must be familiar with:
Procedure, storage, accounting and appointment of medicines
(Especially: potent, narcotic, expensive),
Work of the physiotherapy office, technique procedures,
Work of the pathologist department,
Organization and conduct of anti-epidemic work.
Industrial practice after 5 courses - study of the work of the doctor in the primary health element in the outpatient polyclinic institution
Get skills:
To provide medical and prophylactic assistance to the majority of the population in the conditions of polyclinic,
On the formation of clinical thinking in the early diagnosis of the most common diseases, taking into account the peculiarities of their flow, treatment, prevention, clinical examination, disability examination,
To provide emergency care at the prehospital stage in acute diseases and urgent states.
7. Requirements for graduate preparation
By specialty
040100 - Medical Case7.1. Requirements for the professional training of a specialist.
The graduate should be able to solve the tasks corresponding to its qualifications specified in paragraph 1.2 of this State Educational Standard.
As a result of clinical training on therapeutic and surgical disciplines, obstetrics and gynecology, pediatrics, as well as for other clinical disciplines and courses, a specialist must have a medical behavior and basics of clinical thinking, as well as the ability to ensure the solution of professional tasks and applying a medical algorithm to them Activities for medical care for emergency and threatening life of states, prevention, diagnosis, treatment and rehabilitation of patients.
The specialist should be able to:
Carry out preventive, hygienic and anti-epidemic activities;
Provide medical and preventive assistance to the population;
Analyze and evaluate the health of the population, the impact on it factors of the surrounding and production environment, the quality of medical care;
apply modern methods of scientific knowledge, means and methods of pedagogical impact on the identity, knowledge of the general and individual features of the psyche of man;
Deciding using mathematical methods professional tasks and work with computer;
Promotion healthy image and lifestyle, the value of physical education for health.
Specialist in his professional activity should apply knowledge
:Major physical, chemical, biological and physiological patterns, processes and phenomena in the norm and pathology, as well as work with medical and diagnostic equipment;
Buildings, topography and development of cells, tissues, organs and organism systems in relationships with their function in normal and pathology;
common patterns of origin and development of life, the life of the body and the laws of genetics;
The main characteristics of drugs and forms, their classification, pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics, indications and contraindications to the appointment and use for prevention and treatment, recipes;
Foreign language for professional communication (oral and written) and work with original literature in the specialty.
7.2. Requirements for the final state certification of the graduate
.7.2.1. The final certification tests are intended to determine the practical and theoretical preparedness of the doctor to fulfill the professional tasks established by this State Educational Standard, and the continuation of education in the internship, redeference or in graduate school on theoretical areas of medicine. Certification tests that are part of the final state certification of the graduate must fully comply with the main educational program of higher professional education, which he mastered during the training. The final state certification of the doctor includes a three-stage state exam.
7.2.2.Order of conduct,the main stages and certification program.
Stage 1 - Practical training. The practical training of a graduate is evaluated.
It is carried out on the relevant clinical databases that make up the basis of the Dodiplome training system in the specialty 040100 therapeutic matter.
The duration of the stage should be possible to give a graduate to successively perform the entire required volume of skills and skills for professional activities.
The results of practical skills and skills are evaluated as "executed" or "not executed."
11 Stage - Attestation Testing. Test material covers the content of humanitarian, mathematical, natural-scientific, biomedical and professional disciplines. Different types of test tasks are used to establish and evaluate various sides of clinical thinking logic: comparison, comparison and opposition of medical data, analysis and synthesis of the proposed information, establishing causal relationships.
The composition of the test tasks of the final interdisciplinary exam is subject to annual renewal in a single bank of interdisciplinary certification tasks approved by the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation.
Test results are estimated as "handed over" or "not handed over."
111 Stage - Final interview. Check the integrity of the vocational training of a graduate, i.e. The level of its competence in the use of the theoretical base to solve professional situations. The interview is carried out on the basis of solving situational problems of a generalized nature - clinical, ethical-deontological, analysis of patients, etc. An assessment in this case is subject to the degree of graduate ability to develop and implement the optimal solutions to such situations based on the integration of the content of disciplines included in the certification test.
The results of the interview are estimated on a five-point system.
According to the results of the three stages, a final assessment on the interdisciplinary exam is exhibited.
Compilers
:Educational and methodical association of medical and pharmaceutical universities
The State Educational Standard of Higher Professional Education is approved at a meeting of the educational and methodological council on the specialty 040100 therapeutic case (September 16, 1999 Protocol No. 3)
.Chairman of the UMO Council __________________________________ Finger MA
Deputy Chairman of the Council of the UMO ______________________ Denisov I.N.
Head of the Department of UMO ________________________________________________________
Agreed:
Head of the Department of Educational Medical Institutions and Personnel Policy of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation ___________________________________ Volodin N.N.
Management of educational programs and standards of higher and secondary vocational education of the Ministry of Education of the Russian Federation
Head of Department ____________________________________ Shestakov GK
Deputy Head of Office _____________________ Senashenko V.S.
Chief Specialist of the Office ____________________________ Senatorova N.R.
The most common exams when admission:
- Russian language
- Mathematics (base level)
- Chemistry - profile subject, by selection of university
- Biology - by choosing a university
- Physics - on the selection of the university
- Foreign language - by choosing a university
"Therapeutic business" is one of the most popular specialties in medical universities and at the faculties of medicine. Most doctors first study at the "medical case", and then receive postgraduate education to become narrow specialists.
Professions
The graduate of the specialty "Therapeutic Business" can get a specialization and become:
- therapist
- pediatrician
- gynecologist (obstetrician-gynecologist),
- surgeon
- cardiologist
- endocrinologist
- neuropathologist and others.
Specialists of more rare professions, for example, hematologist, nutritionist, beautician, nephrologist, oncologist, etc. Also receive basic education in the specialty "Therapeutic case". A total of more than 100 narrow specializations available to graduates!
Currently, the market especially needs qualified gynecological obstecologists, pediatricians, "family" doctors (general practitioners), cardiologists.
Possible jobs
- state and commercial medical institutions,
- state health authorities,
- institutions of social protection of citizens
- research institutes,
- medical cabinets in educational institutions and enterprises,
- institutions of secondary vocational and higher education (medical faculties, universities, colleges).
A graduate can work as a doctor, a department department, a teacher, can be a scientist or open a private account (own business). For further career growth in institutions, as a rule, it is required to continue their education in the field of medicine.
Description of specialty
A graduate in the specialty "Therapeutic case" has no right to independently conduct patients, prescribe and conduct treatment. He can only be performed by patients with patients under the control of more experienced specialists. At the same time, he can engage in scientific activities, can occupy various positions in medical institutions.
To work by a doctor, a graduate in the specialty "Therapeutic case" at the end of the university it is necessary to get postgraduate education. This is an internature (1 year) or the residency (2 years) for the selected specialization, such as therapist, an obstetrician-gynecologist, resuscitative, etc. After that, he becomes a doctor who has the right and qualifications to work independently with patients. You can choose the residency and after it go to the doctor.
The passage of the internship (without the choice of the ordinance) is required for all graduates of the medical school or the faculty. During the year, INTERN operates under the guidance of experienced doctors. They check its activities and protect patients from medical errors that an inexperienced specialist may admit.
Basic subjects in high school
The first three years of study are studied by the humanitarian (economy, sociology, history of Russia, etc.), natural science (physics, chemistry, etc.) and medical and biological disciplines, among the latest human anatomy, physiology, microbiology, pharmacology, etc.
Some humanitarian and socio-economic disciplines are studied in direct connection with medicine and are aimed at the comprehensive development of specialists. For example, psychology for working with patients, lawwork for the knowledge of the legislation in the field of medicine, the history of medicine and pharmacy.
From the fourth year, the focus is on professional disciplines. Students of the specialty "Therapeutic business" are studying many areas of medicine without a certain slope in one of them. The most deeply studied items:
- obstetrics and gynecology,
- pediatrics,
- internal illnesses,
- infectious diseases
- surgical diseases
- general surgery and anesthesiology,
- extreme and military medicine.
Training time
The educational standard of the specialty establishes a six-year term of study under full-time and a period of 6.5 years - with part-time form. In practice, the internally, only the first 2 years of study operates, from 3 to 7 course, training is conducted. In correspondence form, it is impossible to get a specialty doctor.
It turns out, taking into account the mandatory internship or the order, the duration of the doctor's training is 7-8 years.
In total, in full-time learning, the future doctor learns 303 weeks, of which 222 weeks are given to direct training at the university (lectures, workshops, seminars, laboratory work) and passing exams and tests. At least 41 weeks allocated for vacation, not less than 18 weeks - for production practices.
Skills and skills purchased during the preparation
The graduate in the specialty "Therapeutic Case" can:
- diagnose patients and assign them treatment, adequate diagnosis and health status,
- provide medical care in a variety of situations, including emergency,
- carry out the prevention of disease
- carry out rehabilitation and medical measures for diseases of any organism systems, as well as after injury, surgical operations,
- conduct various medical examinations, including assessing the working capacity of people, forensic examination,
- work with medical preparations
- work with medical equipment, equipment, tools that are used to diagnose and treat patients,
- main medical documentation and much more.
The choice of profession is a very important thing. The fate, the content of each day, the implementation of abilities and interests, the circle of communication depends on the solution. By making a choice, it is recommended to pay attention to professions related to medicine. They are suitable for people who dream to devote themselves to care for other people, their health. Medical professions, a list and reviews of all specialties - this is what we have to consider.
Professions that can be obtained in university
Many people seek to receive higher education. In medical universities, applicants are offered 9 specialties. It:
- "Therapeutic case."
- "Pediatrics".
- "Medical and prophylactic matter."
- "Dentistry".
- "Pharmacy".
- "Surnery".
- "Medical biochemistry".
- "Medical Biophysics".
- "Medical Cybernetics".
The first four specialties are assigned a doctor's qualifications. The "pharmacy" become pharmacists, and on the "nursing case" - medical sisters. The last specialties are assigned the qualifications of a biochemistry doctor, a biophysics doctor and a Cybernetic doctor. Let's analyze the presented list of medical professions, specialties.
"Therapeutic case" and "Pediatrics"
"Therapeutic case" is the most multifaceted specialty. That is why many statements are always served on her in universities. People who have this specialty can deal with treatment, diagnosis, prevention, exercise educational, organizational and management and research activities.
"Pediatrics" is a specialty, the essence of which is the treatment of children, diagnosing and preventing childhood diseases. Doctors watch the development of babies, starting from birth, send them when identifying any problems with specialists who have highly specialized medical professions.
"Medical and prophylactic business" and "Dentistry"
At "dentistry", students study disciplines associated with diseases of the oral mucosa, implantology, cariesology, etc. Later with such a specialty, people become dentists-therapists, orthopedes, hygienists. They are engaged in the diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the oral cavity, eliminate caries, set implants, removable and non-removed prostheses, perform the prevention of diseases.

"Pharmacy" and "Nursing"
An interesting specialty is "pharmacy". It suits people who love chemistry and dismantling in it. The "pharmacy" are prepared by specialists who will continue to engage in the manufacture of drugs, work in research niche, develop new medicines, study the effectiveness of drugs. After graduating from studying this specialty, many people work in pharmacies - sell drugs, provide consulting services to visitors.
"Nursing business" is an important specialty, the necessary profession. The nurse is required in all sectors of medicine. This specialist carries for sick people, performs the directions of the doctor. After graduating from the university, you can get a job in any clinic or hospital for the post of a private medical sister. In the future, due to the presence of higher education, it will be possible to become an older medical sister.

Medical biochemistry, biophysics and cybernetics
The specialty "Medical biochemistry" is associated with laboratory diagnostics, biochemical, clinical, immunological and medical and genetic studies. The direction "Medical Biophysics" involves working with modern medical equipment. Those people who come here in the future become radar, ultrasound diagnostic doctors.
"Medical Cybernetics" - a young specialty. It combines various sciences: both biology and physics, and computer science, and medicine. People who have this specialty can work with computing equipment, apply the latest equipment in surveys of patients people, eliminate malfunctions from devices. Future profession of students studying at the "Medical Cybernetics" - Cybernetics doctor, a laboratory manner of sound and radiation diagnostics, immunologist, etc.
Medical Contraindications for Professions
Not all people can have professions associated with medicine, because they have contraindications:
- nervous and mental illness;
- pronounced diseases of hearing and vision;
- skin and infectious diseases;
- diseases of the musculoskeletal system;
- violation of coordination of the movements of hands of hands.
With serious diseases of the danger to others, do not succeed on the list of professions presented above. Medical examination is what every applicant passes upon admission to any medical university. Results are provided in the Reception Commission.

Features of the receipt of medical specialties in the university
Our country has long been transferred to the training of specialists in a two-level education system. However, medical universities decided not to abandon the traditions of the Russian higher education. All specialties (except "nursing business") refer to the specialty. To become a doctor or pharmacist, it takes from 5 to 6 years of study in a university on full-time. "Nursing business" refers to undergraduate. The duration of training in this specialty is 4 years in the day office.
The correspondence form of training is allowed only in the direction of "Pharmacy" and "Nursing". The rest of the medical professions can be obtained only in full-time compartment. The fact is that learn to treat sick people and carry out various medical manipulations only in the university, working out all the skills on phantom and mannequins, and in the hospital in the patient's bed when practicing practices.
Postgraduate education for doctors
In the highest school, the duration of the doctor's preparation is the biggest. Students who learn in universities that are not related to medical, are entitled to conduct activities after receiving a diploma. With medical specialties, everything is completely different. The doctor's diploma does not give the right to conduct an independent medical activity. For his receipt, future specialists undergo primary postgraduate specialization.
The following prospects for further education are opening up before graduates of medical universities:
- acquisition of primary medical specialization in the internship (after receiving a diploma) within 1 year;
- acquisition of medical specialization with in-depth training in the ordinature for 2 or 3 years;
- the maintenance of research activities in the field of theoretical biological sciences.

Acquisition of specialization in the internship
In the internship, as mentioned above, primary medical specializations acquire. These include: Therapy, Gynecology and Obstetrics, Surgery, Infectious Diseases, Pediatrics, Psychiatry, Ambulance and Others. Who can be happening after the internship? For example, a graduate of the university after the completion of studies in the specialty "therapeutic matter", appreciating all medical professions, chose a surgeon. In order for them to become, when entering the internship, you will need to choose the specialization of "Surgery".
After the end of the internet, the graduate receives 2 documents: a certificate attached to the diploma, to obtain postgraduate education and a certificate of a specialist, giving the right to independent medical activities.

Receipt of specialization in the ordinature and training in graduate school
Specialization requiring in-depth training includes cardiology, hematology, clinical pharmacology, ultrasound diagnostics, childish oncology, surgical dentistry, etc. For example, a doctor who has received specialization in the internship in the direction of "Surgery", in the ordainture can learn to the doctor Neurosurgea or on a doctor-oncologist-surgeon.
After 2 or 3 years of study, the doctor also receives 2 documents: a certificate and certificate. Thanks to them, you can work on the selected specialization. Thus, the path to the profession of a narrow specialist in medicine can be 9 years old. People interested in some kind of specific subject and science, open the way to graduate school. Training duration is 3 years. The purpose of graduate school is to prepare highly qualified scientific personnel.
Middle and primary medical education
Medical professions receive not only in universities, but also in dsces - colleges, colleges. Middle service specialists are prepared here. These include:
- feldshera;
- obstetrics;
- medical sisters;
- assistants of sanitary doctors;
- epidemiologists;
- medical laboratory technicians;
- dental techniques;
- pharmacists.
There is also the profession "Junior Medical Sister". This is the primary professional medical education. Junior medical sisters begin to earn up students I-II courses. Their obligations include a change of linen on a sick person, his beds, feeding seriously ill patients, assisting in transportation.

In conclusion, it is worth noting that before entering a medical school, in order to obtain any profession, it is worth assessing his personal qualities. In future work, care, emotional sustainability, accuracy, observation, responsibility, compassion, conscientiousness are important.
Specialty 31.02.01 "Therapeutic business" - Feldsher.
Workplace
Profession of paramedics is quite multifaceted. This is a medical specialization. It combines both therapeutic and surgical, obstetric and resuscitation skills. If the Feldsher is busy at the medical and obstetric items of assistance, then its range of responsibilities includes the primary reception, formulation of accurate diagnosis, treatment, the purpose of drugs and observing the patient during the period of illness and recovery. In addition, Feldsher takes birth. . If the Feldsher is part of the paramedic brigade, then it performs the functional responsibilities of the doctor, but if the medical team is only his assistant. Often, paramedics work in ambulance. They measure pressure and perform the functions of nurse and sanitary in one person.
Establishment
Feldscher profession is quite highly in demand. These specialists are constantly required in medical institutions and in the village, where there are no doctors. How many people who work under this work profession are directly dependent on the place of work.
Important qualities
Medicine is a very responsible and stressful sphere of activity. First of all, a person must have a steady psyche and ability to focus on emergency situations. Feldscher is necessarily well developed long-term memory. He must keep in the head a lot of information about diseases, their symptoms, treatment and methods for providing emergency care. Also, the Feldsher is a good psychologist who knows how to calm the patient, especially if it comes to generic activities.
Practice

Official duties.
It provides the provision of medical and preventive and sanitary and preventive care, first emergency medical care in acute diseases and accidents. Diagnoses typical cases of the most common diseases and assigns treatment, while using modern methods of therapy and prevention of diseases, prescriptions. Provides trial assistance, assisters a doctor during operations and complex procedures, takes normal childbirth. Carries out the current sanitary supervision, organizes and conducts anti-epidemic measures. Organizes and conducts dispensary monitoring of various groups of the population (children; teenagers; pregnant women; participants and disabled wings; patients who have suffered acute diseases; patients suffering from chronic diseases). Organizes and conducts preventive vaccinations to children and adults. Experts temporary disability. Provides storage, accounting and write-off of drugs, compliance with drug reception rules by patients. He has medical accounting and reporting documentation. Sanitary and educational work among patients and their relatives to strengthen the health and prevention of diseases, promoting a healthy lifestyle.
Must know:
laws and other regulatory legal acts of the Russian Federation in the health sector; structure, main aspects of medical organizations; statistics of the health status of the serviced population; rules of operation of medical instrument and equipment; medical ethics; psychology of professional communication; the basis of the clinic; Basics of medicine disasters; Basics of labor legislation; The rules of the internal labor regulation; Rules for labor protection and fire safety.
Requirements for qualifications.
Secondary vocational education in the specialty "Therapeutic Case" and a specialist certificate of a specialty "Therapeutic business" without the presentation of the work on experience.