Where red phosphorus is used. Physical properties of phosphorus
Phosphorus exists in three main forms. allotropic modifications (there are about 11 of them in phosphorus):
1. White phosphorus -white crystalline substance with a peculiar smell.
t pl \u003d 44 ° C, t bale \u003d 280 ° C. Exists in the form of molecules P 4.
Insoluble in water. Soft. Volatile. Flammable (already at 40 ° C). Oxidation in the air is accompanied by a glow. VERY POISONOUS (even through the skin)! It is able to accumulate in the body and cause necrosis of bone tissue (especially the jaw). The lethal dose is 0.05 ... 0.15 g.
It is very active chemically, therefore it is stored under water and in the dark.
Obtained by rapid cooling of the red phosphorus vapor.
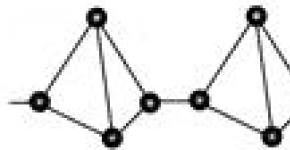
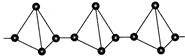 2. Red phosphorus -red-violet crystalline substance, insoluble in water. Not toxic, does not glow. Less reactive. Flammable only at 210 ° C. It has a polymer structure P n.
2. Red phosphorus -red-violet crystalline substance, insoluble in water. Not toxic, does not glow. Less reactive. Flammable only at 210 ° C. It has a polymer structure P n.
 Obtained by prolonged (50 h) heating of white phosphorus ("280 ° C).
Obtained by prolonged (50 h) heating of white phosphorus ("280 ° C).
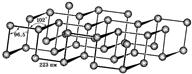
3. Black phosphorus -the most stable form of the element is a black substance with a metallic luster, greasy to the touch and very similar to graphite, and with a completely absent solubility in water or organic solvents. It is possible to set black phosphorus on fire only by first preliminarily burning hot oxygen in the atmosphere of pure oxygen up to 400 ° С. Black phosphorus conducts electric current and has the properties of a semiconductor. The melting point of black phosphorus is 1000 ° C under a pressure of 18 · 10 5 Pa. Ignites at a temperature of 500 ° C. Not toxic, inactive.
It is obtained from white phosphorus at 220 ° C and a pressure of 1.2 GPa (13000 atm)
Definition
White phosphorus represents one of the allotropic modifications of the chemical element of phosphorus (Fig. 1). It consists of P 4 molecules.
Metastable, at room temperature soft as wax (cut with a knife), fragile in the cold. Melts and boils without decomposition, volatile with mild heating, distilled with water vapor. It is slowly oxidized in air (a chain reaction with the participation of radicals, chemiluminescence), with weak heating it ignites in the presence of oxygen. It is well soluble in carbon disulfide, ammonia, sulfur oxide (IV), poorly in carbon tetrachloride. It does not dissolve in water, is well preserved under a layer of water.
Fig. 1. White phosphorus. Appearance.
The chemical formula of white phosphorus
The chemical formula of white phosphorus - P 4. It shows that the molecule of this substance contains four phosphorus atoms (Ar \u003d 31 amu). Using the chemical formula, you can calculate the molecular weight of white phosphorus:
Mr (P 4) \u003d 2 × Ar (P) \u003d 4 × 31 \u003d 124
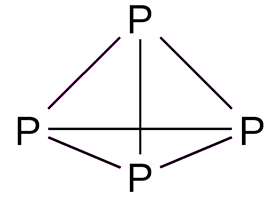
Structural (graphic) formula of white phosphorus
More visual is structural (graphic) formula of white phosphorus. It shows how atoms are interconnected within a molecule. The structural formula of white phosphorus is:
Electronic formula
Electronic formulashowing the distribution of electrons in an atom over energy sublevels is shown below:
15 P 1s 2 2s 2 2p 6 3s 2 3p 3
It also shows that phosphorus belongs to the elements of the p-family, as well as the number of valence electrons - at the external energy level there are 5 electrons (3s 2 3p 3).
Examples of solving problems
EXAMPLE 1
| The task | Set the mass formula of a substance containing 55.2% potassium, 14.6% phosphorus, and 30.2% oxygen. |
| Decision |
Let us denote the number of moles of elements that make up the compound by “x” (potassium), “y” (phosphorus), and “z” (oxygen). Then, the molar ratio will look as follows (the values \u200b\u200bof the relative atomic masses taken from the Periodic Table of D.I. Mendeleev are rounded to integers): x: y: z \u003d ω (K) / Ar (K): ω (P) / Ar (P): ω (O) / Ar (O); x: y: z \u003d 55.2 / 39: 14.6 / 31: 30.2 / 16; x: y: z \u003d 1.4: 0.5: 1.9 \u003d 3: 1: 4 So the formula for the compound of potassium, phosphorus and oxygen will have the form K 3 PO 4. This is potassium phosphate. |
| Answer | K 3 PO 4 |
EXAMPLE 2
| The task | Nitric oxide contains 63.2% oxygen. What is the formula of oxide. |
| Decision | The mass fraction of element X in a molecule of HX composition is calculated by the following formula: ω (X) \u003d n × Ar (X) / M (HX) × 100% We calculate the mass fraction of nitrogen in the oxide: ω (N) \u003d 100% - ω (O) \u003d 100% - 63.2% \u003d 36.8% Let us denote the number of moles of elements that make up the compound by “x” (nitrogen) and “y” (oxygen). Then, the molar ratio will look as follows (the values \u200b\u200bof the relative atomic masses taken from the Periodic Table of D.I. Mendeleev are rounded to integers): x: y \u003d ω (N) / Ar (N): ω (O) / Ar (O); x: y \u003d 36.8 / 14: 63.2 / 16; x: y \u003d 2.6: 3.95 \u003d 1: 2 So the formula of the compound of nitrogen and oxygen will have the form NO 2. This is nitric oxide (IV). |
| Answer | NO 2 |
Phosphorus
PHOSPHORUS -but; m [from Greek phōsphoros - luminiferous] A chemical element (P) that plays an important role in the life of animals and plants (found in some minerals, in animal bones, in animal and plant tissues). Red f. Black f. Fish has a lot of phosphorus. F. is needed to strengthen bones. White f. (flammable and glowing in the dark substance). The sea shines, shines with phosphorus (glows at night with a greenish light due to the abundance of microorganisms).
◁ Phosphoric (see).
phosphorus(lat. Phosphorus), a chemical element of group V of the periodic system. Named from Greek. phōsphóros - luminiferous. It forms several modifications - white phosphorus (density 1.828 g / cm 3, t pl 44.14 ° C), red phosphorus (density 2.31 g / cm 3, t pl 593 ° C), etc. White phosphorus is easily self-igniting, glows in the dark (hence the name), poisonous; red is less chemically active, poisonous. Extracted from apatite and phosphorite. The main consumer is agriculture (phosphate fertilizers); used in match production, metallurgy (deoxidizing agent and component of certain alloys), in organic synthesis, etc. It is present in living cells in the form of ortho- and pyrophosphoric acids and their derivatives.
PHOSPHORUSPHOSPHORUS (lat. - Phosphopus), P (read "pe"), a chemical element with atomic number 15, atomic mass 30.973762. Located in the VA group in the 3rd period of the periodic system. It has one stable nuclide 31 P. The configuration of the outer electronic layer 3 s 2
r 3
. It exhibits oxidation states from –3 to +5 in compounds. Valencies from III to V. The most stable oxidation state in compounds is +5.
The radius of the neutral atom is P 0.134 nm, the radius of ions: P 3 - 0.186 nm, P 3+ 0.044 nm (coordination number 6) and P 5+ - 0.017 nm (coordination number 4) and 0.038 nm (coordination number 6). The sequential ionization energies of the neutral P atom are 10.486, 19.76, 30.16, 51.4, and 65 eV. The electron affinity is 0.6 eV. Pauling Electronegativity (cm. Pauling Linus) 2.10. Non-metal.
Discovery story
In 1669, the first free phosphorus state was received by the Hamburg alchemist H. Brand (there is evidence that a substance similar in properties was obtained back in the 12th century by the Arab alchemist Behil). Finding the Sorcerer's Stone (cm. ELIXIR) he calcined in a closed vessel the dry residue from the evaporation of urine with river sand and charcoal. After calcination, the vessel with the reagents began to glow in the dark with white light (this was phosphorus, which was recovered from its compounds contained in urine).
In 1680, phosphorus glowing in the dark (from the Greek "phosphorus" - luminiferous) was received by the Englishman R. Boyle. (cm. BOULE Robert) In subsequent years, it was found that phosphorus is found not only in urine, but also in brain tissue, in the bones of the skeleton. The simplest method for producing phosphorus by calcining bone ash with coal was proposed in 1771 by C. Scheele (cm. SHEELE Carl Wilhelm). The elementary nature of phosphorus was established at the end of the 18th century by A. L. Lavoisier. (cm. LAVOISIER Antoine Laurent)
Being in nature
The content in the earth's crust is 0.105% by mass, which significantly exceeds the content, for example, of nitrogen (cm. NITROGEN). In sea water, 0.07 mg / l. In its free form, phosphorus does not occur in nature, but it is part of 200 different minerals. The most famous phosphorite (cm. PHOSPHORITES) calcium Ca 3 (PO 4) 3, apatites (cm. Apatity) (fluorapatite 3Ca 3 (PO 4) 3 · CaF 2, or, Ca 5 (PO 4) 3 F), monazite (cm. MONACYT),
turquoise (cm. TURQUOISE). Phosphorus is part of all living organisms.
Getting
Phosphorus production is carried out by electrothermal reduction of it from phosphorites and apatites at 1400-1600 ° C with coke in the presence of silica:
2Са 3 (РО 4) 2 + 6SiO 2 + 10C \u003d P 4 + 6CaSiO 3 + 10CO
4Са 5 (РО 4) 3 F + 21SiO 2 + 30C \u003d 3P 4 + 20CaSiO 3 + 30CO + SiF 4
The released P 4 vapors are then treated with superheated water vapor to obtain thermal phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4:
P 4 + 14H 2 O \u003d 4H 3 PO 4 + 8H 2
Upon desublimation of P 4 vapor, white phosphorus is formed. It is processed into red phosphorus by heating without air at a temperature of 200-300 ° C in reactors equipped with a screw shredder for the reaction mixture.
Structural features of allotropic modifications and their physical properties
Elementary phosphorus exists in several allotropic modifications, the main of which are white (phosphorus III), red (phosphorus II) and black (phosphorus I).
White phosphorus is a waxy, transparent substance with a characteristic odor. It consists of tetrahedral P 4 molecules that can rotate freely. White phosphorus has a molecular type cubic crystal lattice, the cell parameter but \u003d 1.851 nm. The density of 1.828 kg / DM 3. Melting point 44.14 ° C, boiling point 287 ° C. There are two forms of white phosphorus: the a-modification, with a cubic crystal lattice, at –76.9 ° C changes to the b-modification, the crystal lattice of which is not installed and there is no free rotation of P 4 molecules. Dielectric. It is soluble in ethanol, benzene, carbon disulfide CS 2.
By heating white phosphorus without air at 250-300 ° C, red phosphorus is obtained. Admixtures of sodium, iodine and selenium and UV rays accelerate the transition of one modification to another.
Red phosphorus is amorphous, has a color from scarlet to dark brown and purple. There are several crystalline forms with various properties. Crystalline red phosphorus (Hittorf phosphorus) is obtained by cooling a solution of red phosphorus in molten lead saturated at a temperature of 600 ° C. It has a monoclinic lattice, unit cell parameters but \u003d 1.02 nm, at\u003d 0.936 nm, with \u003d 2.51 nm, angle b 118.8 °. The density of red phosphorus is 2.0-2.4 kg / dm 3. Dielectric. When heated, red phosphorus evaporates in the form of P 4 molecules, the condensation of which leads to the formation of white phosphorus.
When white phosphorus is heated to 200-220 ° C under a pressure of 1.2 GPa, crystalline black phosphorus is formed. The lattice is built of fibrous layers with a pyramidal arrangement of atoms. The most stable variety of black phosphorus has an orthorhombic lattice, parameters but \u003d 0.3314 nm, at\u003d 0.4376 nm, s \u003d 1.0478 nm. The density of black phosphorus is 2.702 kg / dm 3. It looks like graphite; semiconductor, diamagnetic. When heated to 560-580 ° C, it turns into red phosphorus. Black phosphorus is inactive, hardly ignites.
Chemical properties
Phosphorus in the compounds is mainly covalent. Phosphorus has free 3d orbitals, which leads to the formation of donor-acceptor bonds. The most active is white phosphorus. It is oxidized in air. Oxidation occurs by the mechanism of chain reactions and is accompanied by chemoluminescence. When phosphorus is burned in excess of oxygen, P 2 O 5 is obtained, which forms P 4 O 10 dimers and P 8 O 20 tetramers. With a lack of oxygen, P 2 O 3 is obtained. It spontaneously ignites in air due to the heat released during oxidation. Red phosphorus in the air oxidizes slowly, does not ignite spontaneously. Black phosphorus does not oxidize in air.
Phosphorus (V) oxide is an acid oxide. It reacts with water with the release of a large amount of heat. In this case, first a polymer metaphosphoric acid (NRA 3) n is formed. When treated with hot water, it turns into tribasic orthophosphoric acid of medium strength N 3 PO 4:
P 4 O 10 + 2H 2 O \u003d (NRA 3) 4; (NRA 3) 4 + 4H 2 O \u003d 4H 3 PO 4
or P 2 O 5 + 3H 2 O \u003d 2H 3 PO 4
Phosphorus interacts with halogens with the release of a large amount of heat. With F, Cl, Br forms trihalides and pentahalides, with I - only tri triide PI 3. All phosphorus halides are easily hydrolyzed to orthophosphoric H 3 PO 4, phosphorous H 3 PO 3 and hydrohalic acids:
PCl 5 + 4H 2 O \u003d H 3 PO 4 + 5CH
PI 3 + 3H 2 O \u003d H 3 PO 3 + 3HI
Phosphorus trihalides are a trihedral pyramid with halogen atoms at the base and a phosphorus atom at the top. The pentahalide molecule is two trihedral pyramids with a common face. The phosphorus oxyhalides of POF 3, POCl 3, and POBr 3 were obtained.
With sulfur, phosphorus forms sulfides P 4 S 3, P 4 S 5, P 4 S 7, P 4 S 10. Known phosphorus oxysulfides: P 2 O 3 S 2, P 2 O 2 S 3, P 4 O 4 S 3, P 6 O 10 S 5, P 4 O 4 S 3. Phosphorus reacts with Se and Te, forms compounds with Si and C (PC 3).
It does not directly react with hydrogen. When interacting with a dilute solution of potassium hydroxide KOH, gaseous phosphine PH 3 is formed:
4P + 3KOH + 3H 2 O \u003d 3KN 2 PO 2 + PH 3
As an impurity, diphosphine P 2 H 4 is also formed. Both phosphines have a characteristic smell of rotten fish.
Phosphine PH 3 in chemical properties resembles ammonia NH 3, but is less stable.
Phosphorus during fusion reacts with metals. With alkaline earth forms M 3 P 2 ionic phosphides, decomposing upon contact with water:
Mg 3 P 2 + 6H 2 O \u003d 3Mg (OH) 2 + 2PH 3,
Ca 3 P 2 + 6H 2 O \u003d 3Ca (OH) 2 + 2PH 3
With transition metals, phosphorus forms metal-like phosphides Mn 3 P, FeP, Ni 2 P.
Phosphorus is part of inorganic acids. This is orthophosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 (its salts are orthophosphates, monohydrophosphates, Na 2 HPO 4 and dihydrophosphates, Ca (H 2 PO 4) 2); metaphosphoric acid (NRA 3) n (its salts are metaphosphates), hypophosphorous acid H 3 PO 2 (its salts are hypophosphites, NaH 2 PO 2), dibasic phosphorous acid H 3 PO 3 (its salts are phosphites, Na 2 HPO 3).
Phosphorus is a part of organic esters, alcohols and acids: phosphinic RRP (O) OH, phosphonous RH 2 PO 2 and phosphonic RP (O) (OH) 2, where R and R are organic radicals.
Application
White phosphorus is used in the manufacture of phosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 (for the production of food phosphates and synthetic detergents). It is used in the manufacture of incendiary and smoke shells, bombs.
Red phosphorus is used in the manufacture of mineral fertilizers, match production. Phosphorus is used in the production of non-ferrous metal alloys as a deoxidizer and serves as an alloying additive. It is used in the production of soft magnetic alloys, in the preparation of semiconductor phosphides. Phosphorus compounds serve as starting materials for the production of medicines.
Body content
Phosphorus is present in living cells in the form of ortho- and pyrophosphoric acids, it is part of nucleotides, nucleic acids, phosphoproteins, phospholipids, coenzymes, enzymes. Human bones are composed of hydroxylapatite 3Ca 3 (PO 4) 3 · CaF 2. The composition of tooth enamel includes fluorapatite. The main role in the conversion of phosphorus compounds in humans and animals is played by the liver. The exchange of phosphorus compounds is regulated by hormones and vitamin D. The daily human need for phosphorus is 1-2 g. With a lack of phosphorus, various bone diseases develop in the body.
Physiological effect
Phosphorus compounds are toxic. The lethal dose of white phosphorus is 50-150 mg. Getting on the skin, white phosphorus gives severe burns. The chemical warfare agents sarin, soman, and herd are phosphorus compounds. Acute phosphorus poisoning is manifested by burning in the mouth and stomach, headache, weakness, vomiting. After 2-3 days, jaundice develops. Chronic forms are characterized by a violation of calcium metabolism, damage to the cardiovascular and nervous systems. First aid for acute poisoning - gastric lavage, laxative, cleansing enemas, intravenous glucose solutions. In case of skin burns, treat the affected areas with solutions of copper sulfate or soda. MAC of phosphorus vapor in the air 0.03 mg / m 3. Dust of red phosphorus, entering the lungs, causes pneumonia.
encyclopedic Dictionary. 2009 .
Synonyms:See what "phosphorus" is in other dictionaries:
- (Greek, from phos light, and phoros bearing). A simple body, yellowish, flammable and luminous in the dark. Dictionary of foreign words included in the Russian language. Chudinov AN, 1910. Phosphorus Greek. phosphoros, from phos, genus. pad. ... ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
PHOSPHORUS - PHOSPHOR, chem. element (symbol P) with at. at. 31.02, belonging to the V group and the 3rd row of the periodic table of Mendeleev (serial number 15). F. is widespread in nature, but only in the form of oxygen compounds: the soil contains it in the form of salts ... ... Big Medical Encyclopedia
Phosphorus - is a solid substance, soft and plastic in consistency, obtained by processing natural phosphates mixed with sand and carbon in an electric furnace. There are two main varieties of phosphorus: a) white phosphorus, ... ... Official terminology
- (symbol P), a chemical element of the fifth group of the periodic table, first discovered in 1669. Found in the form of PHOSPHATES in minerals, the main source of phosphorus is APATIT. This element is used for the manufacture of PHOSPHORIC ACID, ... ... Scientific and technical encyclopedic dictionary
- (Phosphorus), P, chemical element of group V of the periodic system, atomic number 15, atomic mass 30.97376; non-metal white (glows in air, mp 44.14 ° C), red (mp 593 ° C) or black (mp 1000 ° C). Phosphorus is used in ... ... Modern Encyclopedia
- (Latin Phosphorus) P, a chemical element of group V of the Mendeleev’s periodic system, atomic number 15, atomic mass 30.97376. The name is from Greek. phosphoros luminiferous. It forms several modifications of White phosphorus (density 1.828 g / cm & sup3, mp ... ... Big Encyclopedic Dictionary
Phosphorus - (Phosphorus), P, chemical element of group V of the periodic system, atomic number 15, atomic mass 30.97376; non-metal white (glows in air, mp 44.14 ° C), red (mp 593 ° C) or black (mp 1000 ° C). Phosphorus is used in ... ... Illustrated Encyclopedic Dictionary
phosphorus - a, m. phosphore m. & LT; gr. phos light + phoros carrier. A common chemical element that plays a large role in the life of animals and plants. White, red, black phosphorus. BAS 1. There are natural and art-produced phosphors ... Historical Dictionary of Gallicisms of the Russian Language
P (Latin Phosphorus * a. Phosphorus; N. Phosphor; f. Phosphore; and. Fosforo), chem. Group V element periodic Mendeleev systems, at.n. 15, at. m. 30.97376. Natural F. is represented by one stable isotope 31P. Known for 6 arts. ... ... Geological Encyclopedia
PHOSPHORUS, phosphorus, pl. no husband. (Greek phosphoros luminiferous) (chemical). A chemical element that is highly flammable and glows in the dark, a substance found in some minerals, in animal bones, in animal and plant tissues. ... ... Explanatory Dictionary of Ushakov
Ipi Lucifer Prosphorus, Lucifer), i.e., a light carrier. The name of the planet Venus as a morning star. As an evening star, she was called Hesperus, or Vesper, and was considered the son of Astrea and Eos, the father of Hesperides. (