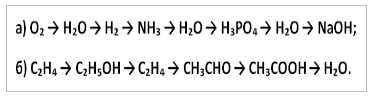
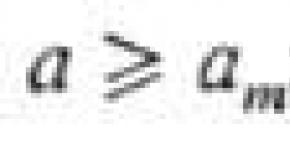The role of water in chemical processes. Presentation on the topic: “The role of water in chemical reactions
High crests uplifting Raging sea water
And drowns, as if playing, Big sea vessels
The vast expanse of the ocean And the quiet backwater of the pond, Waterfall cascade and fountain spray, And all this is just water.
In lace as if dressed Trees, bushes, wires. And it seems like a fairy tale, And in essence - only water.
How fluff winter clothes Snow white native fields, But the time will come, everything will melt, And there will be simple water.

Chemistry lesson in grade 11 on
« The role of water in chemical reactions »
Presentation prepared by:
chemistry teacher
MBOUSOSH №1 S. Aleksandrov - Guy
Belova Svetlana Sergeevna

The role of water in chemical reactions
Environments of aqueous solutions of electrolytes

Water dissociates into ions: H 2 ABOUT ↔ H + + HE - ,
its constant at 25 ° WITH equals
[ H + ] · [ HE - ]
[ H 2 ABOUT ]
Hence the product of constant values
K d ∙ \u003d \u003d const.
The numerical value of the product of ions, on
which water dissociates, is called ionic product of water KH2O it is equal
KH2O \u003d [ H + ]·[ HE - ] \u003d CD ·[ H2O ] = 10 -14
= 1,8 · 10 -16
TO D =
 1 ∙ 10 –7 - acidic, at –7 - alkaline medium. "width \u003d" 640 "
1 ∙ 10 –7 - acidic, at –7 - alkaline medium. "width \u003d" 640 " If within 15–25 ° C ion
water work K H 2 ABOUT = 10 –14 ,
that equality and corresponds to
neutral environment = = 1 ∙ 10 –7 ,
at 1 ∙ 10 –7 - sour,
at –7 - alkaline medium.
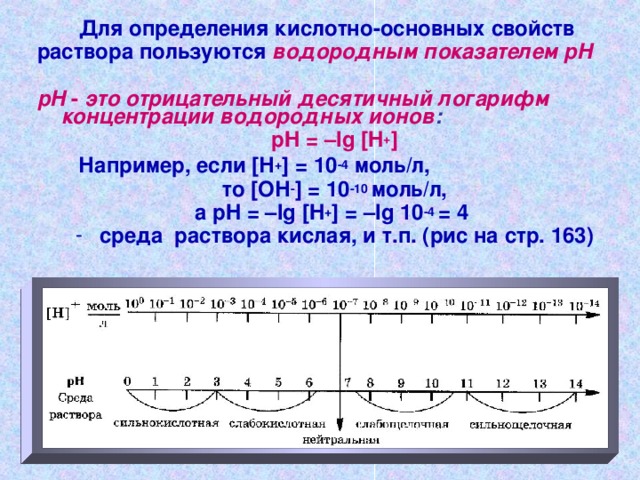
To determine the acid-base properties
mortar enjoy pH
pH - this is the negative decimal logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration :
pH \u003d –lg
For example, if [ H + ] = 10 -4 mol / l,
that [ HE - ] = 10 -10 mol / l,
but pH \u003d –lg \u003d –lg 10 -4 = 4
- wednesday acidic solution, etc. (Figure on page 163)
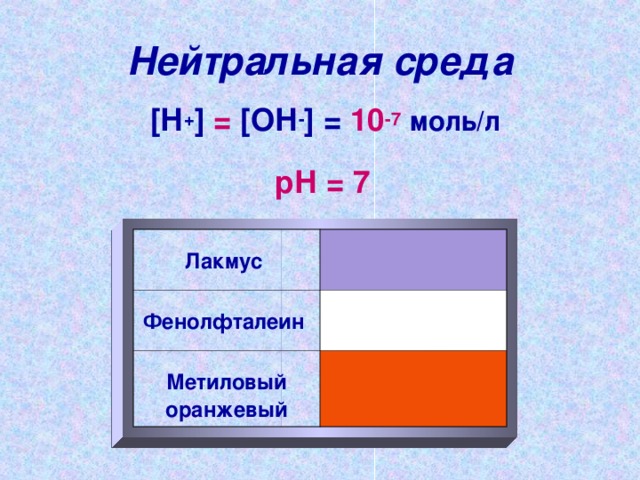
Neutral environment
[ H + ] = [ HE - ] = 10 -7 mol / l
pH \u003d 7
Litmus
Phenolphthalein
Methyl Orange
 [OH -] 10 -7 mol / l pH 7 Litmus Phenolphthalein Methyl orange "width \u003d" 640 "
[OH -] 10 -7 mol / l pH 7 Litmus Phenolphthalein Methyl orange "width \u003d" 640 " Acid environment
[ H + ] [ HE - ] 10 -7 mol / l
pH 7
Litmus
Phenolphthalein
Methyl Orange
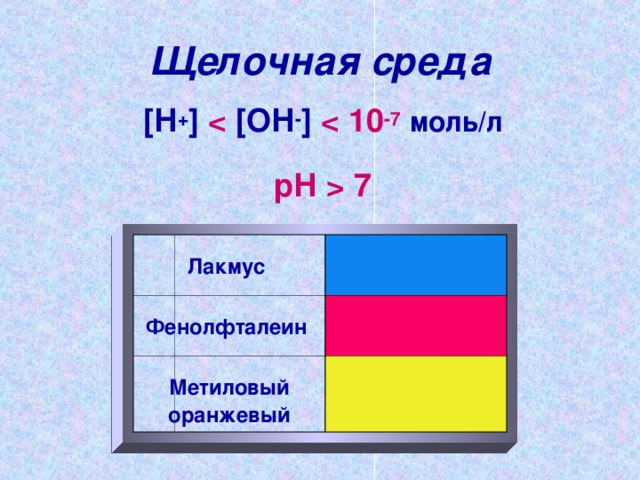 7 Litmus Phenolphthalein Methyl Orange "width \u003d" 640 "
7 Litmus Phenolphthalein Methyl Orange "width \u003d" 640 " Alkaline environment
[ H + ] [ HE - ] 10 -7 mol / l
pH 7
Litmus
Phenolphthalein
Methyl Orange
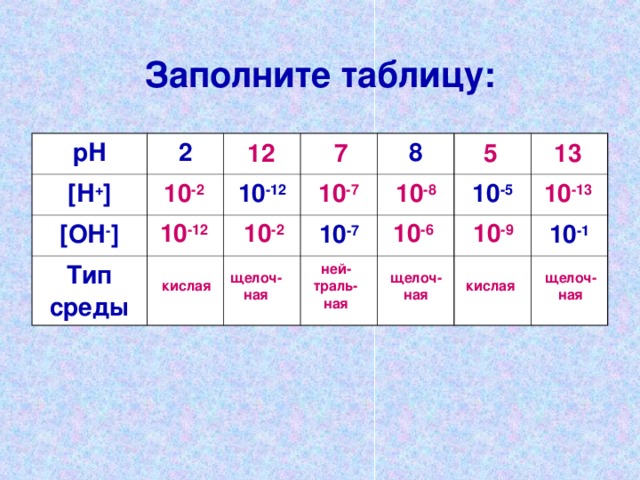
Fill the table:
[ H + ]
[ HE - ]
10 -12
Medium type
10 -7
10 -5
10 -1
10 -13
10 -8
10 -7
10 -2
10 -2
10 -6
10 -9
10 -12
sour
alkaline
her- trawl
alkaline
sour
alkaline

pH of some liquids
Hydrochloric acid
industrial -1.1
diluted 0,0
Rechargeable
acid (sulfuric) 0.15
Gastric juice 1.4
Lemon Juice 2.1
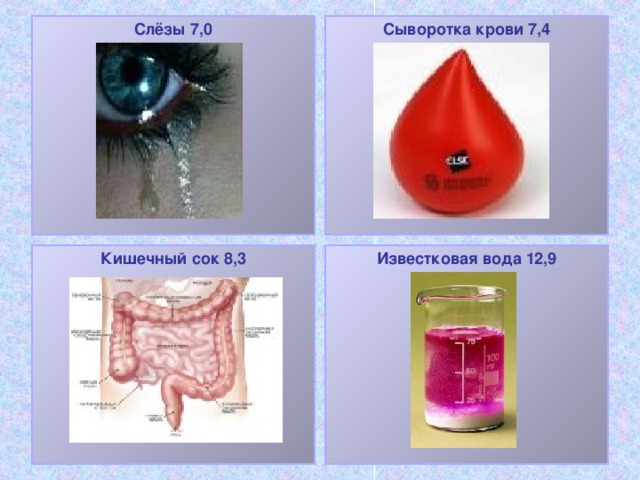
Tears 7.0
Blood serum 7.4
Intestinal juice 8.3
Lime water 12.9
Group work
- Analysts
- Theorists

Experimentally determine the approximate pH value and the concentration of hydrogen ions in the following liquids:
Tomato juice
Coffee
Washing powder solution
Toilet soap solution
Shampoo solution

Homework
1. Prepare messages:
- about the role of pH in practical human activity, biochemical processes of the hydrosphere;
- the pH value of physiological fluids of the human body (blood, saliva, urine, etc.)
- The message "Changing the pH of the blood is dangerous"
2. Solve the problem:
Determine the content of H ions + in a tear
child (0.03 ml, pH \u003d 7.3).
To watch a presentation with artwork and slides, download its file and open it in PowerPoint on your computer.
Slides text content:
Well, quickly take your hat off! I am the daughter of a space dad. And it is omnipresent and light, - I am ice, I sweat, I am clouds. I have frost, tea, broth, fog, River, stream and ocean. When I get angry, I boil; And I freeze from the cold. Water “The role of water in chemical reactions” 11th class Presenter: teacher of the 1st qualification category of Municipal Autonomous Establishment “Gymnasium No. 1” of SyktyvkaraYurina Alexandra Viktorovna The Earth's surface is 71% water 1. The multifaceted role of water in the transformation of H2O substances as a reaction medium Reactions proceed in solutions Solubility in water Soluble (more than 1 g of substance dissolves in 100 g of water) Alkali hydroxides Me; Almost all nitrates; All monosaccharides; Lower alcohols Carboxylic acids Slightly soluble (100 g of water dissolves from 0.01 to 1 g of substance) Ca (OH) 2; BaF2 and AlF3; Silver and lead sulfate; Aniline and phenol. Virtually insoluble (100 g of water dissolves less than 0.01 g of the substance) Almost all phosphates and carbonates; All hydrocarbons; Higher alcohols Aldehydes Carboxylic acids H2O as a reagent. Necessary reagent in the decomposition reactions of complex biopolymers (hydrolysis reactions). During the formation of biopolymers, polymerization, H2O water is released as a dissociation factor. Water molecules are polar, therefore electrolytes easily dissociate in water. H2O as a H2O catalyst * If you just mix them, the reaction does not go - if you add a drop of water, the reaction will immediately start and go wildly The interaction of dry powders of aluminum and iodine. 2Al + 3J2 \u003d 2AlJ3 + Q H2O as a transporter of substances All liquid media consist of more than 90 - 98% of water. It carries O2, nutrients, hormones, etc. to the body. Blood Delivers CO2 and decomposition products to the places of their removal from the body 2. Dissolution processes of the crystal lattice; Diffusion of dissolved substances; Chemical process - hydration (interaction of molecules of the dissolved substance with H2O) a) hydration reaction acetylene) CuSO4 + 5H2O \u003d CuSO4 * 5H2O blue crystals white 3. Electrolytic dissociation Electrolytes are substances that break down into ions in solutions (dissociate) The degree of electrolytic dissociation is the ratio of the number of moles of a substance decomposed on the ions to total solute electrolytes STRONG WEAK (degree of dissociation tend to unity) (degree of dissociation tend to zero) All alkali; All salts; Acids: HCl, HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4, HBr, HJ, CF3COOH, etc. Many inorganic acids (H2S, H2CO3, HCN); Almost all organic acids. Acids These are electrolytes dissociating to hydrogen cations and acid residue anions These are electrolytes dissociating to hydrogen cations and acid residue anions HCl \u003d H + Cl HCOOH H + HCOO + - + - Bases These are electrolytes dissociating to metal cations (ammonium or organic base) and hydroxide - anions KOH \u003d K + OH CH3NH2 * H2O CH3NH2 + OH + - + - Salts These are electrolytes dissociating to metal cations (ammonium or organic base) and anions of acid residue Al2 (SO4) 3 \u003d 2Al + 3SO4 NH4NO3 \u003d NH4 + NO3 CH3COONa \u003d Na + CH3COO 3+ 2- - + + - Homework 1. p.17 - read. Study notes in notebook 2. Ion exchange reactions (write out the complete and abbreviated ionic equations): A) K2S + 2HCl \u003d B) K2S + NaNO3 \u003d B) K2SO4 + Pb (NO3) 2 \u003d 3. Recover molecular equations: A) Fe + 3OH \u003d Fe (OH) 3B) 2H + S \u003d H2SB) 3Ca + 2PO4 \u003d Ca3 (PO4) 2 + 2- 3+ - References Chemistry. Grade 11. Basic level: studies. for general education. institutions / OS Gabrielyan. http://kozlenkoa.narod.ru/indexlessons.htmhttp://yandex.ru/images/searchhttp://forum.xumuk.ru/index.php?showtopic\u003d97449
Attached Files
MBOU "Molodkovskaya SOSH"
Mglinsky district, Bryansk region
Chemistry teacher: Shtyrkhunova Tatyana Aleksandrovna
Abstract chemistry lesson in grade 11 on the topic: "The role of water in chemical reactions."
The purpose of the lesson: Systematize knowledge about the composition, structure, properties of water, meaning, being in nature, about the problems of fresh water.
Objectives of the lesson: 1. Consider the different areas of the role of water in chemical reactions.
2. Develop logical thinking, skills to obtain information from various sources. To develop skills of self-organization and self-esteem.
3. To educate the attitude to water as an irreplaceable substance in the life of all living organisms.
Lesson type: Combined lesson.
Used equipment:computer, multimedia projector, cards, solubility table, a number of active metals.
Used POR: computer presentation.
Formed chemical knowledge, skills and abilities of students: systematization of students 'knowledge about the prevalence of water in nature, physical and chemical properties, areas of water use, expanding students' knowledge about the role of water, about the environmental problems of fresh water.
Formed competencies:
educational and cognitive competence: development of skills to compare, analyze, prove, be able to solve the following practical tasks: the ability to assess the state of the environment, the promotion of their ideas for the protection of water resources of the native land;informational competence: development of the ability to analyze and select the necessary information, the ability to prepare and make messages, the ability to use the Internet to search for educational information.
During the classes.
1.Orization moment.
Check d.
Answer a series of questions on the topic: Reversible and irreversible reactions. Chemical equilibrium.
2. Introductory word of the teacher.
Teacher. Guys, in today's lesson we will get acquainted with an amazing substance, its physical properties, anomalies, being in nature, value and natural reserves. I invite you to make a trip to the Country of miraculous transformations and hold our lesson under the motto "The joy of seeing and understanding is the greatest gift of nature."
Slide1. I read verses on water.
So, what substance will we talk about in class?
I formulate the topic of the lesson, familiar with the purpose of the lesson.
“Water ... You have neither taste, nor color, nor smell, it is impossible to describe you — you enjoy without knowing what you are.
You are not just necessary for life, you are life itself. You are a deity, you are perfection, youthe greatest wealth in the world "
French writer wrote such words about water.Antoine de Saint-Exupery.
And our lesson is dedicatedmost familiar and at the same time most mysterioussubstance - water.
We write in the notebooks the topic of the lesson: « The role of water in chemical reactions. "
Introductory remarks of the teacher about water:
Water is familiar and incomprehensible, amazing, paradoxical, mysterious, unpredictable. There is no number of epithets that could fully characterize this unique substance. It was and remains a muse, a source of inspiration for poets, artists, composers, scientists, who for many years unravel the secrets of this great creation of nature and never cease to be surprised at what they learn.
Getting to know the slides 2-6.
Teacher. From the geography course you know that water is the most common substance on earth.
Message 1. "Water on Earth"
Water is the most important, the most important substance in the world around us. She is both familiar and unfamiliar, and known and mysterious ... Natural water! Look at the sky and you will see clouds or clouds stretching for miles. How easy they are! But do not imagine that they are weightless. The mass of 1 km3 of clouds is about 2000 tons, and in the atmosphere of the Earth water vapor is about 12,300 km3, and this is also natural water. Everyone knows the currentoverland streams: streams, streams, rivers. Sometimes they spread widely and freely across the plain, sometimes form powerful rapids, fall from dozens and hundreds of meters high by waterfalls, carrying their waters into the oceans and seas. About 71% of the surface of our Earth is covered by the World Ocean, constituting about 97% of all surface water and half of lithospheric.
So much or little water on Earth? Very little! Of the total volume of the Earth, water accounts for about 2.5 billion km3.
The water shell of the Earth is 1.5 billion km3, and the rest is in the deep layers of the earth's crust. Most of the water is salty, and suitable for life, fresh, only about 5 million km3. Every year a person needs more and more fresh, clean water. Humanity faces a crisis of water pollution. Some countries are already experiencing a shortage of clean fresh water and are forced to import it from abroad. Water must be protected.
Teacher. From the course of biology, you know that water is inseparably connected with the existence of life on Earth.
How much water is in the human body?(65%- 75%)
Did you know that the brain contains80% water.6 slide
Message 3. “Water in a living organism”
All living things on our planet for 2/3 consists of water. Microorganisms are in the first place in terms of water content in a living organism, microorganisms in the second, animals in the second, and humans in the last.
Bacteria are 81% water, spores are 50%, animal tissue is 70% on average, and lymph is 90%. The most water-rich tissue is the vitreous body of the eye, which contains up to 99% moisture.
The water in the body performs several functions: the substances dissolved in it react with each other, water helps remove metabolic wastes, serves as a temperature regulator, being a good carrier of heat, as well as a lubricant.
In living organisms, water can be synthesized in tissues. For example, a camel's fat in a hump, when oxidized, can give up to40 liters of water. A person, drinking 2.5 liters of water per day, washes the stomach daily with 10 liters of liquid and evaporates 0.7 liters of water.
2 . The structure of the water molecule andphysical properties (7 slide and 8).
(frontal survey)
Slide 9. Find chemical errors in the text (we perform the work frontally).
Teacher.Your answers have shown that you are ready for further travel.
Yes, the role of water in chemical reactions is multifaceted. Slide 11.
12 slides. Water – reaction medium.
Water is the best solvent in the world; it dissolves many solid, liquid and gaseous substances. The water of the seas and oceans contains almost all elements of the periodic system, billions of tons of metal ores. Ocean water is therefore called "liquid ore", sodium, chlorine, gold, uranium, and various salts are extracted from it.This property of water is of paramount importance for nature, almost all chemical transformations on Earth, including in living organisms, occur in water, in its presence, or with its participation.
Due to the high polarity of the molecules, water is capable of dissolving many substances with ionic and covalent polar bonds.
In relation to water, substances are divided into:
1) soluble2) insoluble3) poorly soluble Slide13.
Consider the solubility table of substances.
Using the solubility table,write on the board examples of substances.
Ba (OH) 2,KCl,BaSO4, CaSO4,NaNO3, CuSO4, HNO3, AgCl,FeS, Ca (OH) 2
Slide14. Water dissociation factor.
Slide 15. Water catalyst.
Recall, what is a catalyst?
Slide 16. Water transporter of substances.
Message.
Literally every process in the body takes place with the help of water. Every cell is saturated with water, every chemical reaction takes place with the help of water. This includes those chemical reactions that take place in your body and produce energy, helping you stay active and have an effective metabolism. Since water is a component of the blood that supplies your body with nutrients, there must be enough water in the blood to deliver nutrients to each cell. Lack of water slows down the metabolic rate.
Slide 17. Water - reagent. Remember what water reacts with?
Water is one of the most reactive substances.
Student: From the material we have learned, we know that oxides, hydrides, alkali metals, and other substances (called them) interact with water.
Answer a series of questions.
What is formed by the interaction of the basic oxide with water? Acid oxide? .....
Write the reaction equations in the notebook.
Control over the learning of the lesson material.
Teacher: So, we sailed to the final station. Let's do several tasks.
Slide 19. What substances does water react with? Write down the reaction equations. (Work in pairs) Then we check the execution of the task.
Slide18. Specify the role of water in the listed processes.
Write in a notebook, then check.
Slide 20. What is this passage about? What role does water play?
Summing up the lesson. Slide21. Christina reads a verse about water.
We conclude: What is water?
Slide22. Take care of the water.
Teacher : Remember that clean water reserves are constantly declining, andwe must save water.
10. Reflection.
On the students' tables there are three colored cards with which we will evaluate the lesson.
The blue card is “3”, the yellow card is “4”, the red card is “5”.
How do you assess your knowledge gained in today's lesson?
How do you rate the work of your classmates in class?
How do you rate the lesson as a whole?
Scoring a lesson.
11. Homework: paragraph 17, № 3,4,5.
Olga Golikova
The presentation reflects the physical properties of water; given the classification of substances by solubility in water; determination of aqueous solutions and electrolytes. The main provisions of the theory of electrolytic dissociation (TED) are presented. The definitions of acids, bases and salts are given from the position of the TED. The role of water as a vehicle and as a participant in chemical reactions is shown.
Download:
Preview:
To use the presentation preview, create a Google account (account) for yourself and log in: https://accounts.google.com
Captions for slides:
Performed by the student of grade 11 Olga Golikova Presentation in chemistry on the topic: The role of water in chemical reactions
Water is the most common solvent on Earth, which largely determines the nature of terrestrial chemistry, as a science. Most of chemistry, when it was born as a science, began precisely as the chemistry of aqueous solutions of substances. Systematic name: hydrogen oxide Traditional names: water Chemical formula: H 2 O Molar mass: 18.01528 g / mol
Water is a liquid without color, odor and taste, t Kip \u003d 100 ° C, t PL \u003d 0 ° C, p \u003d 1 g / cm 3 (at 4 ° С). Water does not conduct electric current, conducts heat poorly, the specific heat of water is very high. Water is the only substance that shrinks when hardened. Therefore, the density of ice is less than the density of liquid water. That is why ice floats on the surface of the water. Water
Water is a unique chemical whose role in chemical reactions is difficult to overestimate water. Reaction medium Dissociation factor Transport of substances reagent catalyst
A huge number of chemical reactions takes place in the aquatic environment. By solubility in water, all substances are conventionally divided into three groups. Solubility of substances in water
These are homogeneous systems consisting of water molecules, solute particles and products of their interaction. The hydration process is the result of the interaction of water with solute molecules. Aqueous solutions -
Substances that break down into ions in solutions dissociate. The ratio of the number of moles of a substance disintegrating into ions to the total amount of solute is called the degree of electrolytic dissociation. All electrolytes are divided into: - strong (degree of dissociation tends to unity) - weak (dissociate very little in solutions) Electrolytes
Svante August Arrhenius (1859-1927) Swedish chemist and physicist. In 1887 he finally formulated the theory of electrolytic dissociation, in 1887 explained the retreat of electrolyte solutions from the laws of Vant-Hoff and the Raoult law (showed the physical meaning of the correction factor i). He created the theory of isohydricity, developed the theory of salt hydrolysis. Established the exothermic nature of most of the processes of dissociation of electrolytes and the dependence of the speed and completeness of these processes on temperature. Theory of Electrolytic Dissociation
Acids are electrolytes that dissociate into hydrogen cations and anions of an acid residue; Bases are electrolytes dissociating into metal cations (ammonium or organic base) and hydroxide anions. Salts are electrolytes dissociating into metal cations (ammonium or organic base) and acid residue anions. Three types of electrolytes
All liquid media are more than 90-98% water; The blood carries oxygen, nutrients, hormones and other compounds throughout the body, while removing carbon dioxide and decomposition products. The role of water as a vehicle
Hydration reaction (addition reaction) hydration reaction of acetylene compounds with the formation of carbonyl compounds. When acetylene is hydrated, acetaldehyde is formed, in the case of substituted acetylenes, mainly ketones. Water as a participant in chemical reactions
It is a source of pure hydrogen and oxygen. The interaction of hydrogen and oxygen serves as the reaction that allows spacecraft to be injected into orbit. Water participates in electrolysis processes.
Thanks for attention
1. What is the structure of the water molecule? What are its physical properties?
2. Expand the integrating role of water in the natural sciences - between chemistry, biology, physics and geography. Is it possible to do this fully enough without structuring and updating integration problems? 
3. Tell us about the role of water in solving the economic problems of society. 
4. Expand the global problem of humanity - the problem of fresh water on Earth and suggest a way to solve it. 
5. Tell us about the role of water in chemical reactions. 
6. Prove that electrolyte dissociation is the result of the hydration process. What role did Russian chemists play in studying this aspect of the theory of electrolytic dissociation? 
7. What is the degree of electrolytic dissociation? What groups divide electrolytes according to the degree of electrolytic dissociation? Give examples of representatives of each group. 
8. List the chemical properties of water. Which of these properties are of practical use? 
9. What are crystalline hydrates? What process underlies the application of gypsum dressings or the manufacture of products from alabaster? 
10. Write down the reaction equations, with the help of which the following transformations can be carried out: