Requirements for water from the well. Key indicators of drinking water quality
Most people believe that water coming from wells, a priori is clean and cannot contain harmful impurities. Of course, in most cases it is, but the opposite also happens. Often, drinking liquid is contaminated, and a large amount of toxins, impurities, bacteria is present in its composition. In this regard, a logical question arises: where and how to analyze the water from the well and how much does it cost? If you doubt the quality of your drinking water, do not hesitate to conduct a special analysis.

When is verification necessary?
This is a voluntary event, but in life there are times when its implementation is absolutely necessary.
- Acquisition / sale of real estate.
In the first case, you can make sure that you will drink clean water. In the second - increase the value and value of real estate offers in the eyes of a potential buyer.

- The presence of health problems.
If you or your loved ones have health problems, drinking clean water is the key to recovery. Indeed, many ailments come because of dirty water - indigestion, colds, allergic reactions.

- Preparing for the opening of institutions. If you plan to open a DDU or a health center, clinic, sanatorium, checking the liquid for any kind of impurities is strictly required.
- Carrying out calculations of the system data. In the event that a decision has been made acquiring an appropriate filtration unit, you will need to find out the degree of water pollution.
- Conclusion of an agreement with a selected laboratory.
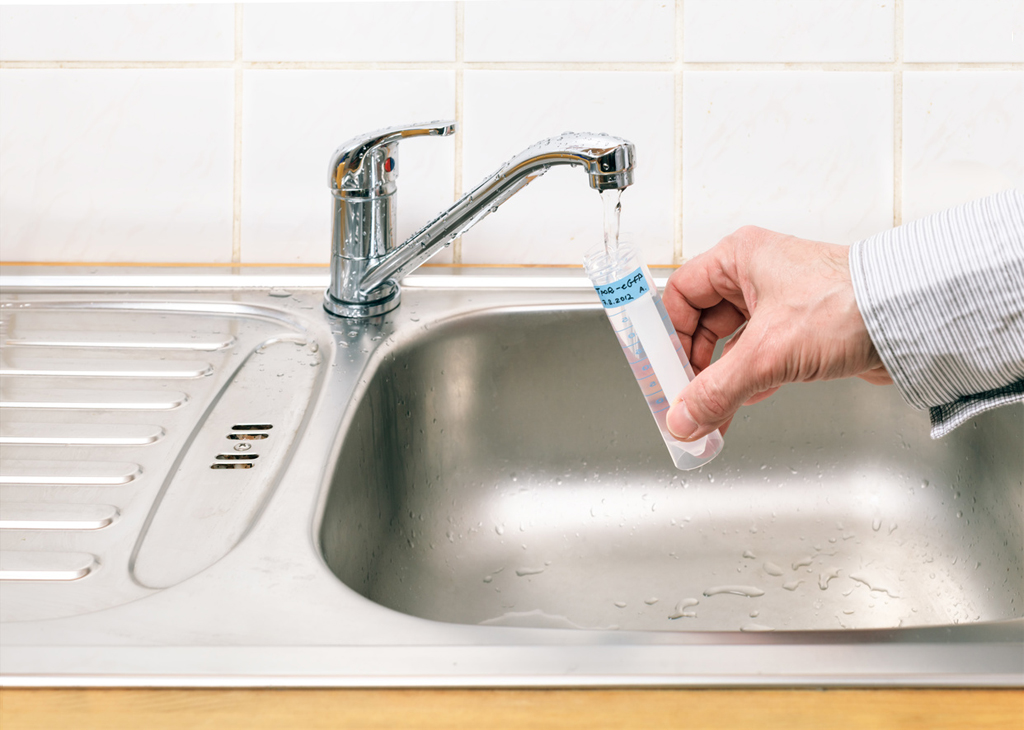
- Arrival of a specialist at home in order to take water. This is done in special containers. They put down the place and time of the fence. Usually two containers are used - one for chemical research, the other for microbiological analysis.
- Delivery of samples to laboratory conditions.


- Directly research. First of all, verification of organoleptic factors is carried out. After that, specialized chemist analysts are involved in the work, which determine the presence of certain chemicals in the water. Further, microbiologists who determine the number of bacteria help them.

- At the end of the period of work, conclusions are made, which are in a documentary form issued to the customers of the audit. They receive a protocol with the results of all tests, as well as basic recommendations for eliminating problems.
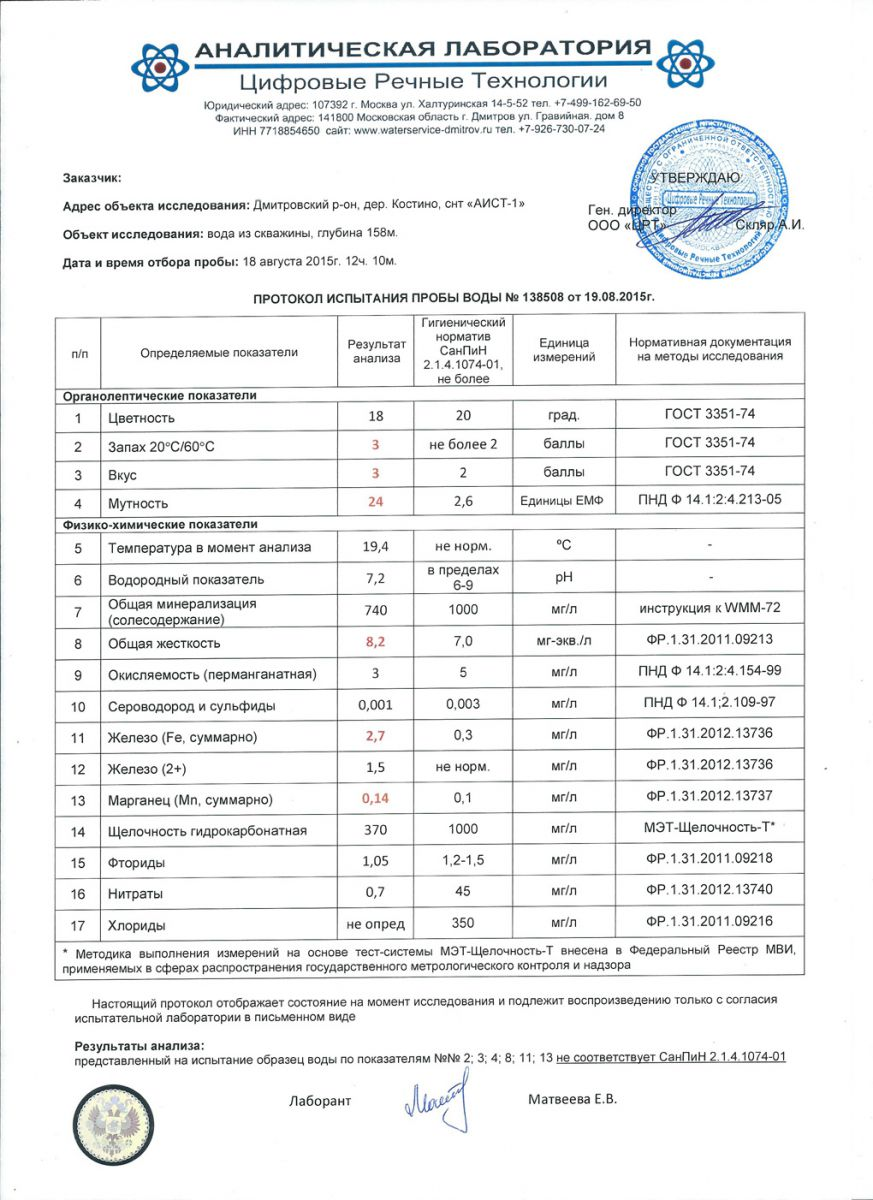
An example of a competent chemical analysis of water from an accredited SES laboratory
Important! The timing of measures is most often determined by the size of the selected institution. Small companies conduct an examination in a couple of weeks, while large laboratories cope with the task in 3-7 days of work.
How much does water analysis from a well cost?
In fact, research is not as expensive as it might seem at first glance. In return, the customer receives tremendous benefits. The price range for services may vary. But we will consider the average.
On a note! In total, analysis together with sampling costs from 3,000 to 5,000 rubles. If we are talking about an expanded survey, then it comes at a price of up to 6,000 rubles. As for the full examination, you will have to pay about 9,000 rubles for it. The total amount depends on the list of parameters that are checked, as well as on the list of additional services.
So, we examined the features of the analysis and made specific conclusions. It is important to choose the laboratory correctly, based on the experience of its work, the professionalism of the staff, the quality of the equipment used, and reviews. Only experts will be able to conduct the event as competently and efficiently as possible.

Checking the quality of the aquatic environment before installing cleaning systems
It is worthwhile to carry out these events on a regular basis, repeating them every few years, because under the influence of natural factors the composition of the water can change.
Important! It is worth carrying out the analysis of drinking fluid a month after drilling. After all, the impurities that were formed as a result of mounting are leveled at this time.

Where can I analyze?
There are plenty of laboratories involved in such analyzes. Their differences lie in the cost of services, as well as in the direct quality of work. It is best to give preference to large companies that have worked in the market for a long time. Before the final decision, you should familiarize yourself with the list of tests that are conducted.
Advice! It is also worth clarifying whether the company has its own laboratory and state accreditation. Any institution undertakes to conclude a contract, within the framework of which any analyzes and tests will be designated.
Types of indicators to measure
To analyze the general condition of the fluid, various tests must be performed. They include organoleptic, microbiological, chemical measures, as well as a comprehensive assessment, which is designed to give the most complete picture of the overall quality of the water. Traditionally, the lion's share of laboratories carries out verification activities for several indicators.
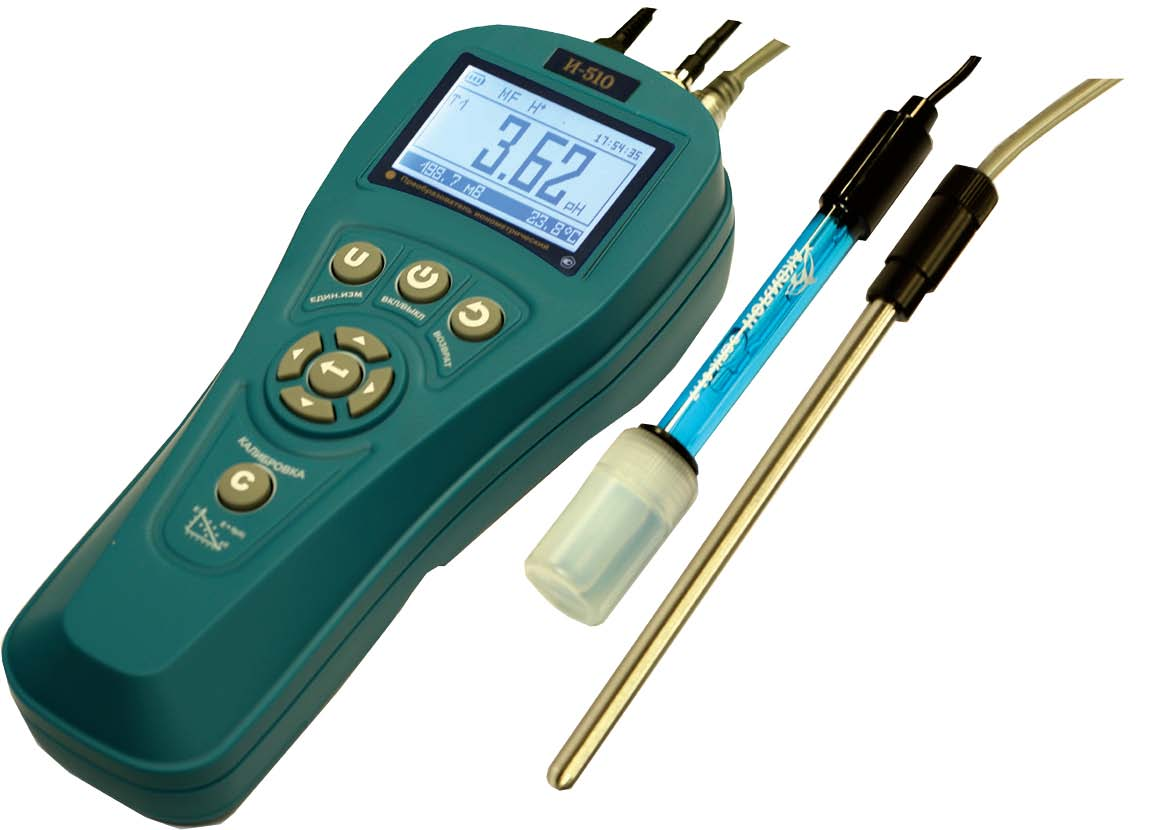

I-510 ionomer for determining the activity of hydrogen ions in aqueous solutions
| Indicator | What does he mean? |
|---|---|
| The activity of hydrogen ions | The normal value is in the range of 6-9 units. If the level is exceeded, the water becomes unpleasant and acquires as if soap properties. This degrades her aroma. |
| Rigidity | This is a critical indicator because it displays the content of calcium and magnesium ions in the drinking fluid. If the water is excessively hard, it harms not only equipment and utensils, but also human health. |
| Dry residue | This parameter reflects the content in water of various dissolved substances of an organic or inorganic nature. |
| The presence of nitrates | The concentration of these harmful elements should not be greater than 45 mg / l. If the parameter is greater, this may indicate that the soil is contaminated with nitrates. |
| Sulphates and Chlorides | According to regulatory standards, the concentration of the first elements should be no more than 500 mg / l, the second - 350. |
| Oxidizability | This indicator indicates the presence of an acidic medium in water. It should not exceed 5-7 mg / l. |
| Microbiological examination | It involves calculating how much microorganisms are contained per 1 ml of liquid. GOST suggests that water from a well should not contain them at all. |
| Organoleptic research | These indicators allow you to evaluate parameters such as taste characteristics, transparency factor, color, aroma. |

Event Stages
According to the normative indicators of the standards, there are several stages of water analysis.
According to sanitary standards, drinking water must be safe in epidemiological and radiation terms, harmless in chemical composition, and have pleasant organoleptic properties. Therefore, it is advisable to comply with the requirements of sanitary norms and rules. To select a water treatment system from a well or well, it is important to check the water.
The requirements (standards) that water must comply with are set out in the sanitary norms and rules of the Russian Federation (SanPiN) and international standards of the World Health Organization (WHO), the main provisions of which are given in the table below . And so, consider key indicators of water quality.
Organoleptic properties of water
The organoleptic properties of water include the following characteristics: smell, taste, color and turbidity.
Smell
The smell and taste of water are explained by the presence of natural or artificial contaminants in it. The nature of odors and tastes is very different, and can be due to the presence of certain dissolved salts in water, as well as the content of various chemical and organic compounds.
In addition, it should be noted that the smell and taste can appear in water at several stages: from the source of natural water, during water treatment (including in a water heater), during transportation through pipelines. The correct determination of the source of odors and tastes is the key to the success of their elimination.
The magnitude (intensity) of the smell is determined on a 6-point scale. For example, the smell of rotten eggs is caused by the presence of hydrogen sulfide (H 2 S) in water, as well as the presence of sulfate-reducing bacteria that produce this gas, and the putrefactive smell is caused by the presence of natural organic compounds in water. Chemical odors (e.g. gasoline, phenolic) indicate the anthropogenic nature of the pollution.
The taste and taste of water
The taste of water is due to natural substances dissolved in water, each of which gives a certain taste to water:
- brackish - with sodium chloride;
- bitter - magnesium sulfate;
- acidic - with dissolved carbon dioxide or dissolved acids.
The pleasant or unpleasant taste of water is provided both by the presence and concentration of impurities in it.
Color
Under the color refers to the natural color of natural and drinking water. Chromaticity indirectly characterizes the presence in water of some organic and inorganic dissolved substances and is one of the important indicators that allow you to choose the right water treatment system.
The color of water is determined by comparison with solutions of a specially prepared color scale (based on certain concentrations of the chromium-cobalt solution) and is expressed in degrees of color of this scale. According to the requirements for drinking water, this indicator should not exceed 20 degrees.
The main "culprits" of the color of water are organic substances washed out of the soil (mainly humic and fulvic acids). The increased color of water can also indicate its possible industrial pollution. The presence of humic acids can lead to a certain biological activity of water, increases the permeability in the intestines of metal ions: iron, manganese, etc.
Turbidity
An indicator characterizing the presence in water of suspended substances of inorganic origin (for example, carbonates of various metals, iron hydroxide), organic origin (colloidal iron, etc.), mineral origin (sand, clay, silt), as well as microbiological origin (bacteriological phyto- or zooplankton). Turbidity is expressed in mg / dm3.
Turbidity can also be due to the presence on the surface and inside the suspended particles of various microorganisms that protect them from both chemical and ultraviolet disinfection of water. Therefore, the reduction of turbidity in the process of water purification also contributes to a significant reduction in the level of microbiological contamination.
Chemical indicators of water quality
Chemical indicators characterize the chemical composition of water. These indicators include the pH of the water, pH, hardness and alkalinity, mineralization (dry residue), anionic and cationic composition (inorganic substances), and the content of organic substances.
Oxidation.
The indicator characterizing the integral pollution of water, i.e. the content of oxidizing organic and inorganic impurities in water, which under certain conditions are capable of being oxidized by a strong chemical oxidizing agent. The pollutants mentioned above mainly include organic substances - for water from surface sources, and inorganic ions (Fe 2+, Mn 2+, etc.) - for water from artesian wells.
There are several types of water oxidizability: permanganate (PMO), dichromate, iodate. As can be seen from the names - in this case, the corresponding oxidizing agents are used to conduct a chemical analysis of water. The oxidation index, mgO / L, is the number of milligrams of oxygen equivalent to the amount of reagent (oxidizing agent) used to oxidize the substances contained in 1 liter of water.
The value of bichromate oxidation is usually used to determine such an important indicator of water as COD - the chemical need for oxygen. COD is used to characterize polluted natural surface waters, as well as for wastewater. This indicator indicates the degree of nutrient pollution of water.
Bichromate oxidation allows one to obtain a value that most fully characterizes the presence of organic pollutants, with the exception of chemically inert substances such as gasoline, kerosene, benzene, toluene, etc. It is believed that when determining this indicator, up to 90% of organic impurities are oxidized.
In practice, to characterize drinking water, the permanganate oxidability index (PMO) or the permanganate index (PMI) is usually used. The higher the PMO value, the higher the concentration of pollutants. Note that the magnitude of permanganate oxidation is lower than the value obtained for dichromate by about 3 times.
PH value
Hydrogen indicator or pHis the logarithm of the concentration of hydrogen ions taken with the opposite sign, i.e. pH \u003d -logH + 1. The pH value is determined by the quantitative ratio in water of H + and OH - ions formed during dissociation of water. If OH - ions prevail in water, which corresponds to a pH value\u003e 7, then water will have an alkaline reaction, and with an increased content of H + ions, which corresponds to pH<7, вода имеет кислую реакцию. В очищенной дистиллированной воде эти ионы уравновешивают друг друга и ее рН приблизительно равен 7.
When any substances are dissolved in water, the balance of these ions is disturbed, and therefore a pH change occurs. For example, even when stored in an open container, purified water due to the absorption of carbon dioxide from the air will have an acid reaction:
СО 2 (gas) + Н 2 О ---\u003e + + HCO 3 -
Depending on the pH value, the rate of chemical reactions, the degree of corrosiveness of water, the toxicity of pollutants and many of its other characteristics can vary.
Typically, the pH level for water used for domestic and drinking purposes is normalized within the range of 6..9.
Dry residue.
This value characterizes the amount of dissolved inorganic and organic substances. This primarily affects the organoleptic properties of water. It has been established that up to 1000 mg / l water can be used for water consumption.
The value of solids affects the taste of drinking water. A person can use water with a dry residue of up to 1000 mg / l without risk to his health. With a larger value, the taste of water most often becomes unpleasant bitter-salty. It should also be noted that in water with a low level of solids, taste may be absent and it is also not very pleasant to use it.
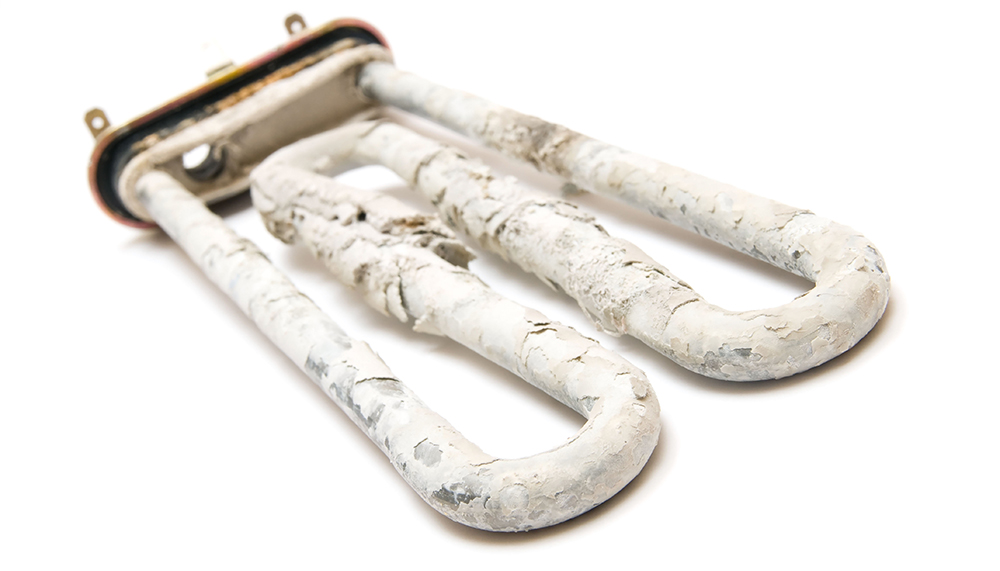
Rigidity
This indicator characterizes the property of water associated with the content in it of dissolved salts of alkaline earth metals, mainly calcium and magnesium (the so-called "hardness salts").
Water with a high content of such salts is called hard water, with a low content - soft.
The numerical expression of water hardness is the concentration of calcium and magnesium cations in it. According to GOST R 52029-2003, stiffness is expressed in degrees of hardness (° W), which corresponds to the concentration of an alkaline earth element, numerically equal to 1/2 of its mole, expressed in mg / dm³ (g / m³) (1 ° W \u003d 1 mEq / l).
Distinguish temporary (carbonate) stiffnessdue to calcium and magnesium bicarbonates (Ca 2+ and Mg 2+ cations and HCO 3 - anions).
When boiling water, bicarbonate anions react with these cations and form poorly soluble carbonate salts with them, which precipitate on the heating elements in the form of a white scale, called lime in common people.
Ca 2+ + 2HCO 3 - \u003d CaCO 3 ↓ + H 2 O + CO 2
Temporary hardness can be eliminated by boiling - hence its name.
Permanent (non-carbonate) water hardnesscaused by the presence of salts that do not precipitate upon boiling. Basically, these are sulfates and chlorides of calcium and magnesium (CaSO 4, CaCl 2, MgSO 4, MgCl 2). It should be noted that it is the presence of CaSO 4 salt, whose solubility decreases with increasing water temperature, leads to the formation of a dense scale.
Water with high hardness causes great harm to household electric heating appliances, forming scale and thereby causing them to overheat and destroy, forming unpleasant matte deposits on plumbing; soap and shampoos foam poorly in it, and therefore their consumption increases.
Hard water dries the skin and harms the hair; negatively affects the quality of cooked food, the useful substances of which can form compounds poorly absorbed by the body with hardness salts.
Hard water is also harmful to the human body: the risk of developing urolithiasis increases, water-salt metabolism is disturbed.
Sometimes as a characteristic metric "Full rigidity"water equal to the sum of constant and variable (carbonate) hardness.
Iron
Its toxic effect on the human body is negligible, but still drinking drinking water with a high iron content can lead to the deposition of its compounds in human organs and tissues.
In general, iron can occur in water in free form in the form of divalent and trivalent ions:
Fe 2+- usually in artesian wells in the absence of dissolved oxygen. Water with a high content of such iron may be initially transparent (Fe 2+), but upon standing or heating it acquires a yellowish-brown color. This occurs as a result of the oxidation of dissolved iron to Fe 3+ with the formation of insoluble salts of ferric iron:
Fe 3+- contained in surface water supplies in the so-called oxidized state, and, as a rule, in an insoluble form.
Organic iron
There is another form of the presence of iron in natural water - this is organic iron. It occurs in water in various forms and in the composition of various complex compounds of ferric iron ions with dissolved inorganic and organic compounds, and mainly with humic salts - humates. An increased content of such iron is observed in bog waters and the water has brown or brownish staining.
Organic iron compounds are generally soluble or have a colloidal structure ( colloidal iron) and it is very difficult to remove. Colloidal particles, due to their small size and high surface charge, which does not allow the particles to come together and prevents their coarsening, preventing the formation of conglomerates, create suspensions in water and do not precipitate when they are in suspension and, thereby, cause turbidity of the initial water.
On the palate, such water has a characteristic unpleasant metallic aftertaste and forms rusty smudges. The presence of colloidal iron in water promotes the development of glandular bacteria, which further affects the taste of water and causes sedimentation on the inner surface of pipelines and sanitary equipment until they become completely clogged.
Manganese
Manganese is part of many enzymes, hormones and vitamins that affect growth processes, blood formation, and the formation of immunity. However, its increased content in water can have a toxic and mutagenic effect on the human body.
Water with a high content of manganese has a metallic taste. Its presence leads to a much faster deterioration of household appliances and heating systems, since it can accumulate in the form of black deposits on the inner surfaces of pipes, followed by peeling and the formation of a black precipitate suspended in water. In addition, the increased content of manganese leads to the formation of black spots on dishes, white laundry when washing, stains nails and teeth in a grayish-black color.
There are also "manganese" bacteria, which, like "glandular" bacteria, can develop in such water and become the cause of overgrowth and blockage of pipelines.
Ammonium Nitrogen (NH 3 and NH 4 +)
The indicator most often characterizing the presence in water of organic substances of animal or industrial origin. Sources of ammonia nitrogen are: livestock farms, domestic wastewater, wastewater from agricultural land, food and chemical industries.
These compounds are mainly the decay products of urea and proteins. The limiting value of the indicator "ammonium nitrogen" is toxicological. According to SanPiN standards, the ammonium content in water should not exceed 2.0 mg / l.
Microbiological indicators of water quality
Microbiological safety indicators of drinking water include the total microbial number, the content of bacteria of the Escherichia coli group (common coliform bacteria and coliphages), spores of sulfite-reducing clostridia and Giardia cysts.
Checking the quality of drinking water is carried out on the basis of the standards for the requirements of regulatory documents of the states.
The table shows the standards of the main quality indicators for sanitary standards SanPiN of the Russian Federation, indicated in column 3 - SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01“Hygienic requirements for water quality of centralized drinking water supply systems” and column 4 - SanPiN 2.1.4.1175-02“Hygienic requirements for water quality in non-centralized water supply. Sanitary protection of sources. "
It is for these indicators that you should check the quality of the water from your source and assess the need to install additional equipment for water treatment.
For comparison, the standards of the World Health Organization (WHO) are given.
The norms of the main indicators of water quality according to the requirements of sanitary standards of the Russian Federation and WHO
| Indicator | Units rev. | SanPiN 2.1.4. 1074-01 | SanPiN 2.1.4. 1175-02 | WHO |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Organoleptic indicators |
||||
|
no more than 2..3 |
||||
|
no more than 2..3 |
||||
|
Color |
no more than 30 |
|||
|
Turbidity |
||||
|
or mg / l kaolin |
||||
|
Chemical indicators |
||||
|
Hydrogen indicator |
||||
|
Dry residue |
||||
|
Total hardness |
||||
|
Oil products |
||||
|
Phenolic index |
||||
|
Alkalinity |
mg HCO 3 - / l |
|||
|
Inorganic substances |
||||
|
Aluminum (Al 3+) |
||||
|
Ammonia nitrogen |
||||
|
Iron (Fe, total) |
||||
|
Manganese (Mn, total) |
||||
|
Nitrates (NO 3 -) |
||||
|
Nitrite (NO 2 -) |
||||
|
Sulphates (SO 4 2-) |
||||
|
Fluoride (F) |
||||
|
Chlorides (Cl-) |
||||
|
Zinc (Zn 2+) |
||||
|
microbiological indicators |
||||
|
Thermo Toler. if bacteria |
The number of bacteria in 100 ml |
|||
|
Common bacteria |
The number of bacteria in 100 ml |
|||
|
Coliphages |
The number of units in 100 ml |
|||
|
Total microbial number |
The number of microbes in 1 ml |
|||
* - as directed by the Chief State Sanitary Doctor
The list of mandatory indicators of water quality for the selection of filters and water treatment systems
For the right choice of a water treatment system, it is necessary to analyze the source water in an accredited laboratory. If it is convenient territorially, bring a water sample. The cost of the analysis for 15 physical and chemical indicators is 2500 rubles, the analysis will take 5-7 business days (in the summer a little more).
In most cases, to select filters, a shortened chemical analysis of water is enough for 15 main indicators:
- smack
- smell
- turbidity
- color
- hydrogen indicator (pH)
- permanganate oxidizability (PMO)
- total stiffness
- total iron
- sulfates
- chlorides
- manganese
- ammonia and NH 4 +
- nitrites
- nitrates
- fluorides
In cases where a shallow well (up to 10-15 meters) or a well fed with surface water is used as a source of water intake, additional indicators such as:
- oil products
- surfactants
- phenolic index
And if there is a specific smell in the water, you should additionally check the water for the presence of such impurities as:
- hydrogen sulfide
- total nitrogen
We do not perform water analysis by microbiological indicators. To do this, contact the nearest SES.
Water sampling for analysis
For analysis organoleptic and chemical indicatorsenough water samples of 1.5 liters. As a container, a plastic bottle from drinking or mineral water is suitable (but in no case from soft drinks, beer, etc., which are quite difficult to completely wash). When taking a sample, turn on the water supply, let the water flow for 5..10 minutes, rinse the container and cork thoroughly 2..3 times, draw water under the very neck of the bottle and seal it tightly with a cork. Deliver a water sample to the laboratory as soon as possible for quality control.
In order for you to quickly and conveniently get to the nearest laboratory and be sure of the correctness of the obtained analysis results, please contact an accredited laboratory, for example, an SES laboratory.
Attention!
- The selected sample must be delivered to the laboratory within 4 hours, and if fast delivery is not possible, keep the water sample in the refrigerator at 2..6 ° C, but not more than 48 hours.
- It is advisable to preliminarily clarify the time of receiving samples in your chosen laboratory and the conditions for payment for water analysis.
Sampling for microbiologicalanalysis is carried out in sterile containers, which must be taken in advance in the laboratory. In this case, taking a water sample is necessary under conditions that exclude extraneous microbiological contamination, for example, from air.


