Phosphoric anhydride
The phosphorus element forms a number of oxides, the most important of which are phosphorus (III) oxide. P2O3 and phosphorus oxide (V) P2O5 .
Phosphorus (III) oxide, or phosphorous anhydride (P2O3) obtained by slow oxidation of phosphorus, burning it in a lack of oxygen. It is a waxy crystalline white mass with a melting point of 22.5 ° C. Toxic.
Chemical properties:
1) reacts with cold water, forming phosphorous acid H3PO3;
2) interacting with alkalis, forms salts - phosphites;
3) is a strong reducing agent.
Interacting with oxygen, it is oxidized to phosphorus oxide (V) P2O5.
Phosphorus (V) Oxide, or Phosphoric Anhydride (P2O5) obtained by burning phosphorus in air or in oxygen. It is a white crystalline powder, with a melting point of 36 ° C.
Chemical properties:
1) interacting with water, forms orthophosphoric acid H3PO4;
2) having the properties of an acid oxide, it reacts with basic oxides and hydroxides;
3) capable of absorbing water vapor.
Phosphoric acid.
Phosphoric anhydride corresponds to several acids. The main one is phosphoric acid H3PO4 . Dehydrated phosphoric acid is presented in the form of colorless transparent crystals having a melting point of 42.35 ° C and dissolving well in water.
It forms three types of salts:
1) medium salts - orthophosphates;
2) acid salts with one hydrogen atom;
3) acid salts with two hydrogen atoms.
Getting phosphoric acid:
1) in the laboratory: 3P + 5HNO3 + 2H2O \u003d 3H3PO4 + 5NO ?;
2) in industry: a) thermal method; b) extraction method: Ca3 (PO4) 2 + 3H2SO4 \u003d CaSO4? + 2 H3PO4.
Natural phosphates are reduced to free phosphorus, which is burned in air or in oxygen. The reaction product is dissolved in water.
The remaining phosphoric acids, depending on the method of joining PO4 groups, form 2 types of acids: polyphosphoric acids, which consist of chains - PO3-O-PO3 -... and metaphosphoric acids, which consist of rings formed by PO4.
Application: phosphoric acid is used in the production of fertilizers, chemicals, organic compounds, for the preparation of protective coatings on metals. Phosphates are used in the manufacture of enamels and pharmaceuticals. Metaphosphates are part of detergents.
- NH4H2PO4 or (NH4) 2H2PO4.
Nitrophoska It is obtained by fusing ammonium hydrogen phosphate, ammonium nitrate and sodium chloride (sulfate).
38. Carbon and its properties
Carbon (C) - typical non-metal; in the periodic system is in the 2nd period of group IV, the main subgroup. Sequence number 6, Ar \u003d 12.011 amu, nuclear charge +6. Physical properties: carbon forms many allotropic modifications: diamond - one of the hardest substances graphite, coal, soot .
Chemical properties: electronic configuration: 1s22 s22p2 . On the electron shell of an atom - 6 electrons; at the external valence level - 4 electrons. The most characteristic oxidation states: +4, +2 - in inorganic compounds, - 4, -2 - in organic ones. Carbon in any hybrid state is able to use all its valence electrons and orbitals. 4-valent carbon has no lone electron pairs and no free orbitals - carbon is chemically relatively stable. Several types of hybridization are characteristic: sp, sp2 , s p3. At low temperatures, carbon is inert, but when heated, its activity increases. Carbon is a good reducing agent, but combining with metals and forming carbides , it acts as an oxidizing agent:
Carbon (coke) reacts with metal oxides:
Thus, the metal is smelted from the ore. At very high temperatures, carbon reacts with many non-metals. It forms a huge amount of organic compounds with hydrogen - hydrocarbons. In the presence of nickel (Ni), carbon, reacting with hydrogen, forms a saturated hydrocarbon - methane: С + Н2 \u003d СН4.
When interacting with sulfur, it forms carbon disulfide: С + 2S2 \u003d СS2.
At an electric arc temperature, carbon combines with nitrogen to form a poisonous gas. tizian : 2С + N2 \u003d С2N2 ?.
In conjunction with hydrogen, dicyan forms hydrocyanic acid - HCN. Carbon reacts with halogens depending on their chemical activity, forming halides. In cold weather it reacts with fluorine: С + 2F2 \u003d СF2.
At 2000 ° C, in an electric furnace, carbon combines with silicon, forming carborundum: Si + C \u003d SiC.
Being in the nature: free carbon is found in the form of diamond and graphite. In the form of compounds, carbon is in the composition of minerals: chalk, marble, limestone - CaCO3, dolomite - MgCO3? CaCO3; bicarbonates - Mg (НCO3) 2 and Ca (НCO3) 2, СО2 is a part of air; carbon is the main component of natural organic compounds - gas, oil, coal, peat, is a part of organic substances, proteins, fats, carbohydrates, amino acids that make up living organisms.
Phosphoric anhydride
| Phosphorus Oxide (V) | |
 |
|
| Are common | |
|---|---|
| Systematic name | Phosphorus Oxide (V) |
| Chemical formula | P 2 O 5 |
| Rel molecule weight | 283.889 a. eat. |
| Molar mass | 283.889 g / mol |
| Physical properties | |
| Substance density | 2.39 g / cm³ |
| Condition (Art. Conv.) | white powder |
| Thermal properties | |
| Melting temperature | 420 о С (Н-form), 569 (О-form) ° C |
| Boiling temperature | sublimates at 359 (H-form) ° C |
| Enthalpy (Art. | -3010.1 kJ / mol |
| Chemical properties | |
| Solubility in water | reacts g / 100 ml |
| Classification | |
| cAS number | (P 2 O 5) (P 4 O 10) |
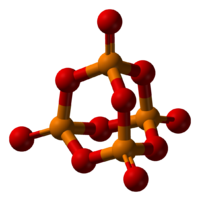
Phosphorus pentaoxide (phosphoric anhydride, phosphorus pentoxide, phosphorus oxide (V) - P 2 O 5, acid oxide.
Structure
Pairs of phosphorus oxide (V) have a composition of P 4 O 10. Solid oxide is prone to polymorphism. Exists in an amorphous vitreous and crystalline state. For the crystalline state, two metastable modifications of phosphorus pentoxide are known - the hexagonal H-form (a \u003d 0.744 nm, \u003d 87 °, spaces, gr. R3C) and the orthorhombic O-form (a \u003d 0.923 nm, b - 0.718 nm, s \u003d 0.494 nm , spaces, group Rpat), as well as one stable orthorhombic O-form (a \u003d 1.63 nm, b \u003d 0.814 nm, c \u003d 0.526 nm, space. group Fdd2). Molecules P 4 O 10 (H-form) are built of 4 groups of PO 4 in the form of a tetrahedron, the vertices of which are occupied by phosphorus atoms, 6 oxygen atoms are located along the edges, and 4 - along the third-order axis of the tetrahedron. This modification is easily sublimated (360 о С) and actively interacts with water.
Other modifications have a layered polymer structure, also constructed from PO 4 tetrahedra, combined into 10-membered (O-form) and 6-membered (O "-form) rings. These modifications have a higher sublimation temperature (~ 580 о С) and less chemically active.The H-form goes into the O-form at 300-360 about C.
Properties
P 4 O 10 interacts very actively with water (the H-form absorbs water even with an explosion), forming mixtures of phosphoric acids, the composition of which depends on the amount of water and other conditions:
P 4 O 10 + 6H 2 O (W) → 4H 3 PO 4 (-177 kJ)
It is also able to extract water from other compounds, representing a strong dehydrating agent:
2HNO 3 + P 2 O 5 → 2HPO 3 + N 2 O 5; 4HClO 4 + P 4 O 10 → (NPO 3) 4 + 2Cl 2 O 7.
Phosphorus (V) oxide is widely used in organic synthesis. It reacts with amides, turning them into nitriles:
P 4 O 10 + RC (O) NH 2 → P 4 O 9 (OH) 2 + RCN P 4 O 10 + RCO 2 H → P 4 O 9 (OH) 2 + 2 O
Also interacts with alcohols, esters, phenols and other organic compounds. In this case, P — O — P bonds are broken and organophosphorus compounds are formed. Reacts with NH3 and with hydrogen halides, forming ammonium phosphates and phosphorus oxyhalides:
P 4 O 10 + 8PCl 3 + O 2 → 12Cl 3 PO
Upon fusion of P 4 O 10 with basic oxides, it forms various solid phosphates, the nature of which depends on the reaction conditions.
Getting
Phosphorus (V) oxide is obtained by burning phosphorus. The technological process takes place in the combustion chamber and includes the oxidation of elemental P by pre-dried air, the deposition of P 4 O 10 and the purification of exhaust gases. Purify the resulting pentoxide by distillation.
P 4 + 5O 2 → P 4 O 10 + 2984 kJ.
The technical product has the form of a snowy white mass, consisting of a mixture of different forms of P 4 O 10.
Application
P 4 O 10 is used as a dehumidifier for gases and liquids. It is also an intermediate product in the production of orthophosphoric acid H 3 PO 4 in a thermal manner.
It is widely used in organic synthesis in dehydration and condensation reactions.
Literature
- Akhmetov N. S. "General and inorganic chemistry" M.: Higher school, 2001
- Remy G. “The course of inorganic chemistry” M.: Foreign literature, 1963
- F. Cotton, J. Wilkinson, “Modern Inorganic Chemistry,” Moscow: Mir, 1969
Wikimedia Foundation. 2010.
See what is "Phosphoric anhydride" in other dictionaries:
PHOSPHORIC ANHYDRID - (p2o5) phosphorus oxide V (see); white powder, very hygroscopic, forms phosphorus with water (see); It is used as a powerful desiccant for gases and liquids. In case of contact with skin and attempt to wash it off with water, a strong thermochem is guaranteed. burn. When ... ... Big Polytechnical Encyclopedia


