Warm floors in your own home. Warm floors are water: types, features, as well as how to make a water-heated floor in an apartment with your own hands, step-by-step actions
Today, many owners of private houses install warm water floors for additional or main heating. They have a lot of advantages: they evenly warm up the room, increase comfort, do not require additional energy consumption, since they operate from one boiler with radiators. In this article, we will consider the question of how to install a warm floor in a private house with our own hands, water, even without experience in carrying out such work.
Preparation and calculation of materials
Such responsible work should begin with the planning and preparation of all the necessary materials. Strictly speaking, an accurate calculation can only be carried out by specialists who have information about the level of heat leakage in a particular room. But for individual needs, as a rule, approximate calculations are used, which fully satisfy the requirements.
To begin with, you should draw a plan for the location of pipes for a warm water floor in a private house. The diagram drawn on a sheet in a cage, on which the system can be calculated based on the quadrature of the room, will be clearest and clearest of all. Each cell will correspond to one step, that is, the distance between the pipes of the system. For a temperate climate zone:
- With sufficiently good insulation of windows and a house, the distance between adjacent turns of the pipe can be made about 15-20 cm.
- If the walls are well insulated - 10-15 cm.
- In spacious rooms, where some of the walls are cold and some are warm, an alternating step is made: near cold walls, the distance between adjacent pipe coils is not too large, and as it approaches warm walls, it increases.
Choosing a floor covering for a warm floor:
- A serious mistake is made by those who are going to lay a thick wooden covering or parquet on a warm water floor. Wood conducts heat poorly, which is why it will greatly impede the heating of the room. The efficiency of such heating may be even worse than that of a radiator, in turn, heating costs are quite large.
- The ideal coating for warm floors is ceramic, stone or porcelain stoneware tiles. When heated, it will keep warm remarkably, and this is the best option for a bathroom or kitchen. Children love to play in rooms with warm floors, and just walking barefoot is much more pleasant than on wooden parquet.
- A slightly worse option for flooring, more appropriate for a bedroom or guest room, is laminate or linoleum. Such materials transmit heat well without lowering the efficiency of water heat supply. In this case, the laminate must be chosen with a minimum thickness, and linoleum - without a substrate with insulation.
Important! When heated, many artificial materials can release harmful fumes into the air. That is why floor coverings with chemical additives must have a mark from the manufacturer of the product about the possibility of their use in residential premises on warm floors.
Underfloor heating base
If we are talking about housing with concrete floors, then the best option for a base under a warm water floor with your own hands in a private house is a concrete screed with water heating.
Important! The same method is used for the first floors (basement) of private cottages, if the base of the floor is on a sand cushion, which is located directly on the ground.
In houses with wooden floors, this option will not work. Wooden floor beams simply cannot withstand the large weight of a concrete screed, no matter how thin it is. In this case, a lightweight version of warm floors is used, which we will talk about a little later.
Do-it-yourself installation of warm floors begins with a thorough preparation of the base, which should be even, without any depressions and protrusions. The maximum allowable drop can be 5 mm.
Important! If the depth of surface defects is 1-2 cm, then you will have to pour and then level a thin layer of fine gravel (granite screening) with a grain size of up to 5 mm. On top of the leveling layer, it will be necessary to lay a film and walk on wooden boards during the installation of thermal insulation. Otherwise, the leveling layer itself will serve as a source of irregularities.
Layout schemes for water-heated floors
The most common schemes for laying water-heated floors are spiral and snail:
- The snail warms up the entire floor area evenly.
- But with a spiral, you can provide a greater level of heating in the coldest area of \u200b\u200bthe room. For this, the first branches of the pipe, through which hot water will be supplied, are laid there.
The exact length of the pipe is determined according to a pre-prepared plan.
Important! For underfloor heating, only a single piece of pipe must be used. If the area of \u200b\u200bthe room is large, then several heating circuits should be planned. Moreover, the length of the pipe of each of these circuits should not exceed 100 m. Otherwise, too much pressure will be required, which is needed for the normal flow rate of hot water. In terms of area, this is approximately 15 square meters.
It is better to make a warm water floor with your own hands in a private house from a metal-plastic pipe, the diameter of which is 16 mm. It bends easily with a fairly small radius, and it is much more convenient to work with it than with a cross-linked polyethylene pipe. It is undesirable to use pipes with a diameter of 20 mm, because a large diameter will require an increase in the thickness of the concrete, which will negatively affect the efficiency of the heating system.
As a rule, the pipe consumption per 1 square meter of area is:
- 10 meters at a step of 10 cm.
- 6.75 meters at 15 cm steps.
Selection of insulation and fasteners
To prevent the heat from going down, a layer of dense foam must be laid on the base.
Important! The density of the insulation should be chosen at least 25, and preferably 35 kg / m3. Lighter types of foam will simply crumple under the weight of the concrete layer.
Insulation and heat reflector
The optimal insulation thickness is 5 cm.When laying on the ground or if you need higher protection from the cold, when there is a poorly or unheated room on the floor below, the thickness of the thermal insulation layer can be increased to 10 cm.
To reduce heat loss, it is recommended to lay a heat-reflecting screen, consisting of a metallized film, over the insulation. This could be:
- Reflective foam screen that is glued behind the radiators.
- Penofol (metallized polyethylene foam).
- Plain food grade aluminum foil.
The metallized layer quickly becomes unusable due to the aggressive effect of concrete, so the screen itself must also be protected. Such a protective layer will serve as a plastic film, which is often used for greenhouses in greenhouses. The thickness of this film should be about 75-100 microns.
Moreover, it provides the necessary moisture for the maturing concrete screed throughout the entire period of its hardening. Pieces of film should be overlapped, and the joints should be carefully glued with tape.

Pipe fittings
Pipe fittings are installed on top of the thermal insulation. Their purpose is to fix the adjacent branches of the pipe and place it on the floor in strict accordance with the preliminary diagram. Fasteners hold the pipe until the concrete screed is hard enough. The use of fasteners facilitates the installation of a warm water floor with your own hands in a private house and guarantees the correct location of the pipe in the thickness of the concrete cushion.
Fasteners can be special metal strips, welded metal mesh, plastic brackets that fix the pipe to the foam base:
- Metal strips are used with increased thickness of the concrete pad. They raise the pipe slightly in relation to the thermal insulation, so that it is slightly closer to the upper surface of the concrete pad. The pipe simply snaps into the curly grooves of the strips.
- The metal mesh not only anchors the pipe, but also reinforces the concrete pad layer. The pipe is fixed to the mesh with pieces of wire or plastic clamps. In this case, the consumption of fasteners is 2 pieces per 1 running meter. Additional fasteners can be used in places of curvature.
- Plastic brackets are assembled by hand. They pin the pipe to the foam as it is laid. Semi-industrial floor heating is made using a special stapler. However, its purchase is justified only with intensive professional use.
Recently, manufacturers of underfloor heating systems have begun to offer another rather convenient solution - special sheets of dense polystyrene foam with a profiled surface. As a rule, the surface of such sheets is the intersection of grooves or rows of protruding elements between which the heating pipes are laid.
The surface of such sheets is smooth, extruded, all pores are closed, and an additional waterproofing film is not needed for it. Having at your disposal a special thermal cutter, the grooves in the expanded polystyrene can be made independently. However, to carry out such work, at least minimal experience is required.
Important! Reinforced-plastic pipes are supplied in coils. During the laying process, the coil is rolled along the pipe placement path. Do not pull pipes out of a lying bay, as this will cause it to twist and can lead to incandescence of the inner layers.
Preparation and pouring of concrete
It is possible to fill pipes with concrete when installing a water-heated floor with your own hands in a private house in stages only after they are completely laid, correctly connected to the collectors, and also filled with a coolant under a pressure of 4 bar.
Important! Before pouring, the pipe must be kept under pressure for at least a couple of days. If a leak is found, it must be repaired immediately. If the system itself has not yet been installed, then instead of water, air should be pumped into the pipes using a compressor and the pressure should be fixed with ball valves.
Immediately after the injection, the pressure may decrease slightly due to the straightening of the pipes. During the pouring and hardening of the concrete, the pressure is monitored using a connected pressure gauge.
In order to compensate for thermal expansion, a damper tape is attached along the walls. The thermal expansion of a concrete cushion should be 0.5 mm per linear meter, with a temperature increase of 40 degrees. In the event that the heating is only 20 degrees, then the expansion will accordingly be half as much. It is necessary to multiply the expansion by the length of the longest section of the concrete floor and compare this value with the thickness of the damper tape.
As a rule, for ordinary houses, it is sufficient to lay the tape only along the walls and at the doorway. Also, the damper tape plays the role of thermal insulation of the warm floor and walls. In this way, cold bridges that cause unnecessary heat leakage are eliminated.

In some cases, expansion joints are additionally made:
- If the length of either side of the room is more than 8 meters.
- The floor area is over 30 square meters.
- The length and width of a room differ by more than two times.
- The shape of the room has several curves.
For an extended underfloor heating, an expansion joint with a damper tape is fitted every ten meters. To prevent the movement of concrete cushions in these places from breaking through the pipe, a rigid plastic corrugation or a large-diameter pipe should be put on it. The entry of the protective pipe into the concrete cushions is at least 0.5 m on each side.
If, according to the placement plan, an accumulation of warm pipes occurs in one place, for example, near a collector, then a heat insulator sleeve must be put on some of the pipes. This will make it possible to avoid local overheating, as well as better retain heat for the desired areas of the floor.
Warm water floor concreting
If concrete for pouring a warm floor is not brought in, but is made on site, then the following components will be required:
- Washed river sand - 1.9 c. h.
- Cement grade 300 (400) - 1 part by weight.
- Crushed stone 5-20 mm in size - 3.7 in. h.
Important! This is a composition of heavy concrete, the weight of which is 2.5 tons per 1 cubic meter. m of finished material.
But many refuse sand in concrete for underfloor heating. This is due to its low thermal conductivity. Therefore, in practice, cement-gravel mixtures are often used, the composition of which is as follows:
- Cement - 1 bucket.
- Granite crushed stone - 5-20 mm - 2 buckets.
- Water - 7 liters (if the solution is very thick, you can add another 1 liter).
- Fine granite screening - 4 buckets.
Granite conducts heat remarkably, and such concrete has a significantly lower thermal resistance. In addition, it is worth introducing reinforcing fiber, which is a small plastic fiber.
Important! Any self-leveling floor must include a plasticizer. Its amount depends on the brand and purpose of the drug. Moreover, the plasticizer should not be any, but intended specifically for the warm floor.

General rules for filling:
- If the pipe is fixed on strips or brackets, then a reinforcing mesh must be laid on top of it. And the height of the concrete screed should be chosen 5-10 cm.
- In this case, it is necessary to provide at least 3 cm of concrete above the pipe. A smaller spacer can lead to cracking, and a too thick concrete pad will increase heat transfer losses.
- With the right choice of concrete and an acceptable temperature, it begins to set after 4 hours. To maintain normal humidity, it must be covered with a waterproof film, and during the drying process, the surface must be sprinkled with water.
- After 12 hours, the hardened concrete will be able to support the weight of one person. However, its full maturation occurs no earlier than 28 days. All this time, it is necessary to take care of its humidity, as well as maintain a sufficiently high pressure in the laid pipes. Only after the specified time has passed, the first thermal tests of such a floor can be carried out.
Important! As during the first test of a warm water floor with your own hands in a private house, you cannot quickly heat it up to high temperatures afterwards.
Flooring
Ceramic tiles or other types of floor coverings can be glued onto the finished, completely dried concrete base. In this case, you should use glue that is intended for warm floors.
Important! If the tile falls just on the expansion joint, then one of its parts should be glued, and the other should be placed on silicone glue. Silicone absorbs thermal movements of the substrate, so that the tiles will not crack from overvoltage.
A lightweight version of a warm floor for wooden floors
As mentioned above, for wooden floors it is necessary to make a light warm floor without a concrete cushion. In this case, the sequence of work may differ slightly, depending on the structure of the floor and the condition of the old floor:
- To prevent the heat from going down, you need to put insulation under the pipes. It can be placed between the overlap lags, and then it is better to use mineral wool. Or it can be laid on an old rough floor - here you will already need expanded polystyrene with a density of 25-35 kg / m3.
Important! To prevent the formation of condensation, a vapor barrier membrane should be laid under the mineral wool, and the first rough floor should be filled on top of the logs.
- As well as for a concrete floor, it is recommended to lay a heat-reflecting screen made of foam or foil on the insulation. At the same time, all seams and joints must be carefully glued with tape.
- It is necessary to lay logs directly on the expanded polystyrene, to which the boards of the subfloor should be nailed. In this case, there should be approximately 2 cm gaps between the boards for laying the pipe.
Important! The same gaps should be provided at the ends of the floor boards. Otherwise, you will have to choose transverse grooves for the pipe, and this can cause the boards to break.
- In order for the heat to be more evenly distributed over the floor, the pipe must be laid not just in grooves, but in specially designed metal gutters that are designed for this purpose. The metal transfers heat well over the entire surface and evenly heats the finish coat. Tips for choosing it were given a little higher - it can be a laminate that can work with heating, or a rigid polymer coating. Thick parquet flooring is the least suitable for warm floors.
Important! In comparison with a concrete warm floor, a lightweight structure is equipped much faster and is cheaper. Another advantage is the ability to repair pipes in the event of an accident. Pipe problems in a concrete floor can only be eliminated by completely replacing it. But a wooden floor also has a drawback - it is a significantly lower heat output.
A competently equipped step-by-step do-it-yourself heated water floor in a private house is another step towards convenient and comfortable living conditions for the whole family. But, even if for some reason you cannot do this work on your own and are forced to invite specialists, the knowledge gained will help you take an active part in this process and control the quality of the system being assembled.
Warm floors are, in our understanding, a more modern heating system than radiator heating. However, this is far from the case - they appeared much earlier. Stubborn historical facts show that underfloor heating was successfully used in the days of Ancient Rome, on the territory of Korea, and in Russia too. True, only stove heating was used then, since the system for transporting hydrocarbons through pipes did not yet exist. In the modern world, the most economically successful countries widely use underfloor heating, and this is done not only for reasons of obvious comfort, but also taking into account the fact that such heating saves energy resources, the demand for which is growing every year.
This type of heating is not a cheap pleasure. Components and labor are very expensive. That is why any zealous owner may have the idea of \u200b\u200bmaking a water-heated floor with his own hands. Why not? Moreover, the experience of both successful and unsuccessful implementations has already been accumulated enough to give specific recommendations. The purpose of our article is to give specific advice to those owners who are going to make a warm water floor, but at the same time so that they save their money and end up getting what they wanted - comfortable and economical heating.
Why exactly a water-heated floor?
Of course, they are easier to implement, they are easier to manage, but the cost of energy resources makes its own adjustments - this type of heating is much more expensive in operation than a water-heated floor. It will take only 4-5 years and a warm water floor will pay off with interest, but only on the condition that it is done correctly and correctly. This is what the authors of the article want to tell our readers about. Sweeping aside colorful catalogs with expensive equipment, but based only on the experience of people who were able to implement a warm water floor in their home.
Most heating systems currently use natural gas as a heat source - and this is completely logical, since this type of fuel is cheaper than others. And this trend will continue for at least several more decades. Therefore, it is best to implement warm floors with water, the heat carrier in which is heated by the energy of natural gas combustion. But for this, a number of conditions must be met.
Water underfloor heating device
A warm water floor is a complex multi-component system, each part of which performs its own function. Consider its structure in the following figure.
 Typical construction of a "pie" of warm water floor
Typical construction of a "pie" of warm water floor This type of underfloor heating is called "wet" because it uses "wet" construction processes, namely the pouring of a cement-sand screed. There are also so-called dry warm floors, but they are mainly made. Within the framework of this article, we will consider precisely "wet" warm water floors, since they are much better, although their installation is more complicated.
A warm water floor is mounted on a stable and solid base, which can be a concrete slab or soil. A vapor barrier made of polyethylene film with a thickness of at least 0.1 mm is laid on the base. The next layer of the "pie" is insulation, as it is best to use extruded, which has a very low coefficient of thermal conductivity, high mechanical strength and reasonable cost. A cement-sand screed is equipped on top of the insulation, to which a plasticizer must be added - for the mobility of the mixture, ease of installation and reduction of the water-cement ratio. It is advisable to reinforce the tie with a metal wire mesh with a cell pitch of 50 * 50 mm or 100 * 100 mm. There, inside the screed, there are underfloor heating pipes with a coolant circulating in them. It is recommended to make the height of the screed above the pipes at least 3 cm, however, practice suggests that 5 cm is better, so the strength will be higher and the distribution of heat over the floor will be more even.
At the place where the walls adjoin to the screed, as well as at the boundaries of the warm water heating circuits, a damper tape is laid, which compensates for the thermal expansion of the screed when it is heated. The final floor covering should be designed specifically for working with warm floors. The best way out is ceramic or porcelain stoneware, but some other types of coverings - laminate, carpet, or can also be used with warm floors, but there must be a special sign in their marking.

Such coatings, however, require strict adherence to the thermal regime of the floor, which is achieved by the use of automation - special mixing units.
Requirements for rooms where heating with warm water floors will be implemented
The smartest move in construction is when the underfloor heating pipeline is laid even at the stage of erecting floors. This is very successfully used in Germany, Sweden, Norway, Canada, and yes, and in other economically successful countries where energy resources are very expensive and therefore they use floor heating, which is 30-40% more economical than radiator heating. It is quite possible already in a finished room, but it must meet certain requirements. Let's list them.
 The most correct underfloor heating pipeline is the one that was laid even at the stage of building a house
The most correct underfloor heating pipeline is the one that was laid even at the stage of building a house - Given the significant thickness of the warm water floor - from 8 to 20 cm, the ceiling height in the room should allow such a heating system to be mounted. It is also necessary to take into account the size of the doorways, which should be at least 210 cm high.
- The sub-floor must be strong enough to withstand the heavy cement-sand screed.
- The base for the warm floor must be clean and even. Irregularities should not exceed 5 mm, since the drops strongly affect the flow of the coolant in the pipes, they can lead to airing of the circuits and an increase in hydraulic resistance.
- In the room where a warm water floor is planned, all plastering work must be completed, windows inserted.
- Heat loss in the premises should not exceed 100 W / m 2. If they are larger, then you should think about insulation, and not heat the environment.
How to choose a good floor heating pipe
About pipes of a warm water floor is written in sufficient detail in our portal. Obviously, for a warm floor, it is better to choose pipes made of cross-linked polyethylene - PEX or PERT. Among PEX pipes, preference should be given to PE-Xa pipes, since they have a maximum crosslink density - about 85% and therefore have the best "memory effect", that is, pipes after stretching it always tend to return to their original position. This allows the use of slip-ring axial fittings, which can be embedded in building structures without fear. In addition, when the pipe is broken, you can restore its shape by heating the problem area with a construction hairdryer.

PERT pipes have no memory effect, so only push-in fittings are used with them, which must not be bricked up. But if all the contours of the underfloor heating are made with solid pipe sections, then all connections will be only on the collector and it is quite possible to use PERT pipes.
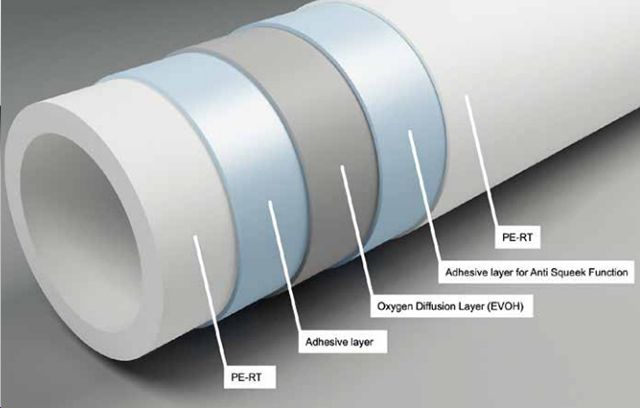
In addition, manufacturers produce composite pipes, when aluminum foil is placed between two layers of cross-linked polyethylene, which is a reliable oxygen barrier. But the heterogeneity of the material, the difference in the coefficients of thermal expansion of aluminum and polyethylene, can provoke pipe delamination. Therefore, it is better to choose PE-Xa or PERT pipes with a polyvinylethylene (EVOH) barrier, which significantly reduces the diffusion of oxygen into the coolant through the pipe wall. This barrier can be located in the outer layer of the pipe, or inside, surrounded by layers of PE-Xa or PERT. Of course, the best pipe is the one with the EVOH layer inside.
There are three main pipe sizes for underfloor heating circuits: 16 * 2 mm, 17 * 2 mm and 20 * 2 mm. Most often they use 16 * 2 and 20 * 2 mm. How to choose the “right” pipe.
- First, the brand is important in this matter and should be paid attention to. The most famous manufacturers: Rehau, Tece, KAN, Uponor, Valtec.
- Secondly, the marking of pipes can "tell" a lot, it should be carefully studied and you should not hesitate to ask more questions to the sales assistant.
- Thirdly, the qualification of a sales assistant is very helpful in choosing a pipe. Do not forget to demand certificates of conformity, inquire about the availability and price of fittings, mixing units, manifolds and other equipment. It is necessary to find out in which bays the pipe is sold, by how many meters, in order to take this into account in the future calculations.
- Finally, if a PE-Xa pipe is selected, a small test can be performed. To do this, a small section of the pipe must be broken, and then this place must be heated with a construction hairdryer. High-quality PE-Xa and PE-Xb pipes should also return to their original shape. If this has not happened, then whatever is written in the marking is simply not a PEX pipe.

Underfloor heating design principles
One of the most important stages in the arrangement of warm water floors is their competent calculation. Of course, it is best to entrust this to specialists, but the already accumulated experience suggests that this can be done independently. There are tons of free programs and online calculators on the internet. Most of the well-known manufacturers provide their software for free.
water heated floor

First you need to decide what temperature the warm floor should have.
- In residential areas, where people spend most of the time standing, the floor temperature should be between 21 and 27 ° C. This temperature is most comfortable for the feet.
- For work areas - offices, as well as living rooms, the temperature should be maintained around 29 ° C.
- In hallways, lobbies and corridors, the optimum temperature is 30 ° C.
- For bathrooms and swimming pools, the floor temperature should be higher - about 31-33 ° C.
Heating with warm water floors is low-temperature, therefore, the coolant must be supplied at lower temperatures than radiators. If water can be supplied to the radiators at a temperature of 80-90 ° C, then to the warm floor no more than 60 ° C. In heat engineering there is such an important concept as temperature drop in the heating circuit ... This is nothing more than the difference in temperature between the supply pipe and the return pipe. In systems of warm water floors, the optimal modes are 55/45 ° C, 50/40 ° C, 45/35 ° C and 40/30 ° C.
A very important indicator is (loops) warm water floor. Ideally, they should all be the same length, then there will be no problem with balancing, but in practice this is unlikely to be achieved, therefore it is accepted:
- For a pipe with a diameter of 16 mm, the maximum length is 70-90 m.
- For a pipe with a diameter of 17 mm - 90-100 m.
- For a pipe with a diameter of 20 mm - 120 m.
Moreover, it is advisable to focus not on the upper limit, but on the lower one. It is better to divide the room into more loops than to try to achieve circulation with a more powerful pump. Naturally, all loops must be made with pipes of the same diameter.
Step of laying (laying) pipes of a warm floor - another most important indicator, which is made from 100 mm to 600 mm, depending on the heat load on the warm floor, the purpose of the room, the length of the circuit and other indicators. It is almost impossible to make a step of less than 100 mm with PEX pipes; it is very likely that the pipe will simply break. If the underfloor heating will be equipped only for comfort or additional heating, then a minimum step of 150 mm can be made. So which layout step should you use?

- In rooms where there are external walls, so-called edge zones where the pipes are laid with a step of 100-150 mm. In this case, the number of rows of pipes in these zones should be 5-6.
- In the centers of the premises, as well as in those where there are no external walls, the laying step is made 200-300 mm.
- Bathrooms, baths, paths near the pools are laid with a pipe with a step of 150 mm over the entire area.
Ways of laying the contours of the warm floor
The contours of a water-heated floor can be laid in different ways. And each method has its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's consider them.
- Laying a pipe underfloor heating "snake" easier to install, but its significant disadvantage is that there will be a noticeable temperature difference on the floor at the beginning of the circuit and at the end - up to 5-10 ° C. The coolant, passing from the supply manifold to the reverse in the underfloor heating structure, cools down. Therefore, such a temperature gradient arises, which is well felt by the feet. This installation method is justified to be used in boundary zones, where the floor temperature must decrease from the outer wall to the center of the room.

- Laying a pipe underfloor heating "snail" is more difficult to implement, but with this method, the temperature of the entire floor will be approximately equal, since the supply and return flow pass inside each other, and the difference is leveled by a massive floor screed when the design requirements of the laying step are met. In 90% of cases, this method is used.

- Combined methods of laying pipes for underfloor heating are also used very often. For example, the edge zones are laid with a snake, and the main area with a snail. This can help to correctly divide the room into contours, distribute the pipe coil with a minimum of residues and provide the desired mode.
In each of the methods, variable laying step , when in the edge zones it is 100-150 mm, and in the room itself 200-300 mm. Then it is possible in one room to meet the requirements for more intense heating of the edge zones, without using other methods of laying. Experienced installers often do just that.
 Layout of the heating circuit "snail" with a constant step (left) and with variable nudge (right)
Layout of the heating circuit "snail" with a constant step (left) and with variable nudge (right) To calculate the contours, it is best to use special and very easy-to-learn software. For example, the well-known manufacturer Valtec, which distributes its program for free. There are also simpler programs for calculating the layout of the contours, which calculate the length of the loops, which is very convenient. For example, the "Snail" program, which is also distributed free of charge. For those who are not very computer friendly, you can calculate the contours yourself, using graph paper, on which to draw a floor plan on a scale and already on this sheet with a pencil "expand" the contours and calculate their length.

When dividing the premises into the contours of a water heated floor, the following requirements should be met:
- The contours should not go from room to room - all rooms must be regulated separately. An exception may be bathrooms if they are located nearby. For example, the bathroom is next to the toilet.
- One heating circuit must not heat a room with an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 40 m 2. If necessary, the room is divided into several circuits. The maximum length of either side of the circuit should not exceed 8 meters.
- A special damper tape should be laid along the perimeter of the room, between rooms, as well as between individual circuits, which, after pouring the screed, will compensate for its thermal expansion.

The choice of the type of insulation for the warm floor and its thickness
Insulation for a warm water floor is required, because no one would like to spend their money on heating the earth, the atmosphere or unnecessary building structures, but the floor is exactly the one that should take the lion's share of the heat from the heating circuit. For this, insulation is used. What types of them should be used? Among all their diversity, the authors of the article recommend that you should pay attention to only two of them.
- Extruded polystyrene foam (EPS). This material has low thermal conductivity and high mechanical strength. EPPS is not afraid of moisture, it practically does not absorb it. Its price is quite affordable. This insulation is produced in the form of plates of standard sizes 500 * 1000 mm or 600 * 1250 mm and a thickness of 20, 30, 50. 80 or 100 mm. There are special grooves on the side surfaces for good joining of the plates.
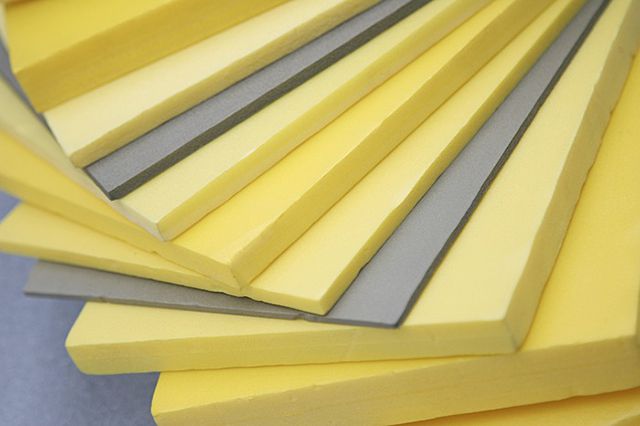

- Profiled heat-insulating high-density polystyrene foam. On their surface there are special round or rectangular bosses, between which it is very convenient to lay the pipe without additional fixation. The pipe fixing pitch is usually 50 mm. It is very convenient for installation, but at a price they are much higher than EPS boards, especially from famous brands. They are produced with a thickness of 1 to 3 cm and dimensions of 500 * 1000 mm or 60 * 1200 mm - it depends on the manufacturer.

EPS boards can have an additional foil layer with additional markings. The marking of the plates is, of course, a useful thing, but the presence of foil only increases the cost of the insulation, and there will be no sense from it for two reasons.
- The reflectivity declared by manufacturers will not work in an opaque environment such as a screed.
- Cement slurry is a strong alkaline medium that will perfectly "eat" an insignificant (several tens of microns) layer of aluminum even before it solidifies. We must realize that foil plates are a marketing ploy and nothing more.
The authors of the article recommend using EPSP plates for insulation. The savings compared to profile mats will be obvious. The difference in cost is enough for fasteners, and there is still a lot of money left. Let's remember the popular wisdom that the money saved is akin to the earned money.
What is the thickness of the insulation in the construction of the warm water floor cake? There are special and complex calculations, but you can do without them. If you learn a few simple rules.
- If underfloor heating will be done on the ground, then the thickness of the insulation should be at least 100 mm. It is best to make two layers of 50 mm each and lay them in mutually perpendicular directions.
- If warm floors are planned in rooms above the basement, then the thickness of the insulation is at least 50 mm.
- If underfloor heating is planned above rooms heated from below, then the thickness of the insulation is at least 30 mm.
Additionally, it is necessary to provide for the fastening of the EPSP plates to the base material, since when pouring the screed they will tend to float. Disc dowels are ideal for this. They need to fasten all the plates at the joints and in the center.

For attaching the pipe to the EPS, special harpoon brackets are used, which securely fix the pipe. They are fastened with an interval of 30-50 cm, and in places where the PEX pipe turns, the step should be 10 cm. It is usually calculated that 500 pieces of harpoon brackets are required for a coil of 200 meters of pipe. When purchasing them, you do not need to chase the brand, as it will cost several times more. There are very high quality and inexpensive staples from Russian manufacturers.

Selection of a collector-mixing unit for a warm floor
The collector of the water floor is the most important element that receives the coolant from the main, distributes it along the contours, regulates the flow and temperature, balances the loops of the contours, and helps to remove air. Not a single warm water floor can do without it.

It is better to entrust the choice of a collector, or more correctly, a collector-mixing unit, to specialists who will select the necessary components. In principle, you can assemble it yourself, but this is a topic for a separate article. Let's just list what elements should be included in order not to make a mistake in the choice.
- Firstly, these are the collectors themselves, which can be equipped with various fittings. They should be equipped with adjusting (balancing) valves with or without flow meters, which are located on the supply manifold, and the return can have thermostatic valves or simply shut-off valves.

- Secondly, any manifold to remove air from the system must be equipped with an automatic air vent.
- Thirdly, both the supply and return collectors must have drain valves for draining the coolant from the collector and removing air when filling the system.
- Fourthly, to connect the pipe to the manifold, fittings should be used, which are selected individually in each specific case.

- Fifthly, special brackets are used to attach the collectors and ensure the required center distance.

- Sixth, if the boiler room is not equipped with a separate riser for underfloor heating, then a mixing unit, including a pump, thermostatic valve, bypass, should be responsible for the preparation of the heat carrier. The design of this node has many implementations, so this issue will be discussed in a separate article.

- Finally, the entire manifold-mixing unit must be located in a manifold cabinet, which is installed either in a niche or openly.

The collector-mixing unit is located in such a place that all the lengths of the lines from it to the loops of the heated floor are approximately equal and the main pipes are in close proximity. The collector cabinet is often hidden in a niche, then it can be placed not only in cabins and boiler rooms, but in dressing rooms, corridors and even living rooms.
Video: What calculations are needed before installing a warm floor
DIY water floor heating installation
After calculations and the purchase of all the necessary components, you can gradually implement a warm water floor. First, it is necessary to outline the places where the collector cabinets will be placed, hollow out, if necessary, niches, and also make passages through building structures. All slotting and drilling work must be completed before the next step.
Installation of insulation
Before this stage, it is necessary to prepare the premises for this - to take out all unnecessary, remove all construction waste, sweep and vacuum the floors. The room must be absolutely clean. When installing the plates, it is necessary to wear flat-soled shoes, as the heels can damage the surface. We list the sequence of actions when installing insulation.
- First of all, the level of the clean floor is beaten off on the walls using a laser or water. All unevenness of the base is measured using a long rule and level.
- If the irregularities exceed 10 mm, then they can be completely leveled with sprinkled clean and dry sand, which should subsequently be leveled.

- If the underfloor heating is done on the ground or above the basement, then a waterproofing film is spread with an overlap of adjacent strips of at least 10 cm and with an approach to the wall. The joints are glued with tape. A polyethylene film of 150-200 microns is quite suitable as waterproofing.
- Starting from the far corner of the room, the process of laying the EPS boards begins. They are stacked against the walls with the marked surface up.
- EPSP plates should be tightly joined together using the grooves that are on their side surfaces. When laying each slab, it must fit snugly to the base and be in a horizontal plane, which is checked by the building level. If necessary, sand is poured under the slab.

- If along the way of laying there are obstacles in the form of protrusions, columns and other elements, then after preliminary marking the plate is cut with a construction knife along a metal ruler. In this case, the EPS must be placed on some non-solid base so that the knife does not become dull, for example, a piece of plywood or OSB.
- When laying the next row, it should be borne in mind that the joints of the slabs should not coincide, but go apart, like brickwork. If at least 1/3 of its length remains with the last EPS plate in the row, then the next row should be laid with it.
- If you plan to lay the second layer of EPS, then it should be carried out in a mutually perpendicular direction with the first layer.
- After installing the thermal insulation, using a perforator with a long drill and a hammer, fix the disc dowels at each joint - at each joint and in the center of each EPSP board. The joints between the EPSPs are sealed with construction tape.

- If after the installation of the insulation there are cavities or cracks, then they can be clogged with EPPS scraps and blown out with polyurethane foam, but this can be done later, after the pipes have been installed.
After that, we can say that the installation of the insulation has been completed. Although EPS boards are dense enough to support the weight of an adult, you still need to take precautions when moving around them. It is best to use wide boards or pieces of plywood or OSB.
Installation of a pipe for a warm water floor
The most important and difficult moment has come - the installation of floor heating pipes. At this stage, you need to be especially careful and accurate, and here you cannot do without an assistant. It is also desirable to have a special device for unwinding the pipe, since it is strictly forbidden to remove the pipe from the coil with rings, since then there will be very strong stresses in it, which will complicate or make installation impossible. The main rule is that the bay must be twisted, and not removed from the stationary bay. In principle, this can be done manually, but with a device it is much easier.

If there are markings on the upper side of the EPSP plates, then this is just great, then the pipe laying will be greatly simplified. And if not, then you should not "be led" on the purchase of foil-clad thin insulation made of foamed polyethylene with applied markings. There will be no sense from him. You can apply the markup yourself. To do this, markers are made on the upper side of the plates with a marker at the distance of the required contour step, and then the lines are beaten off with a paint thread - this way you can make a marking in a short time. After that, you can draw the traces of the contours of the warm floor.
underfloor heating screed

In the designated place, a collector cabinet is attached and a collector is mounted in it, while without a pump-mixing group, it will be needed later. At the entrance to the collector, at the exit from it, as well as at the entrance to, each pipe must be protected by a special corrugation. However, corrugation from renowned manufacturers costs mind-boggling money, so it is quite acceptable to replace it with thermal insulation of the appropriate diameter. Also, pipes must be protected during transitions from room to room and from circuit to circuit.
Installation of underfloor heating pipes should be started from the areas farthest from the collectors, and all transit pipes should be covered with foam polyethylene insulation, which will ensure maximum energy conservation to the point of destination, and will not "lose" heat along the way. Further, the pipe "emerges" from the EPSP plates, already "bare" bypasses its entire heating circuit and "dives" back and already in the thermal insulation follows to the collector. The transit pipes themselves are placed inside the EPSP plates; for this, the passage routes are pre-cut in them with a knife.

If the thermal insulation consists of two layers of EPSP boards, then first the first layer is laid, then all communications are laid, including the transit pipes of the underfloor heating, and then the second layer is adjusted and cut in place.
In addition, in the area of \u200b\u200b\\ u200b \\ u200bthe heated floor, pipes can go to radiators, as well as hot and cold water supply lines. If there are several pipes, then they can be fixed in the bundle either with disc dowels, or with a perforated metal strip and dowels. In any case, they should not protrude beyond the upper surface of the EPSP boards, so that the underfloor heating contour can be easily laid on top. All cavities are blown out with polyurethane foam, which, after hardening, is cut flush from the surface of the insulation plates.
A damper tape is glued to the walls along the perimeter of the room, where there will be warm floors, which is designed to compensate for the thermal expansion of the screed. The tape is available with or without an adhesive layer. When purchasing it, you do not need to chase the brand and overpay several times more. Nowadays a damping tape of Russian production, worthy in every sense, is being produced. If there is no tape at all, then - this is also not a problem - it can be replaced by foam plastic 1 or 2 cm thick, glued to the wall with liquid nails or mounting foam.

The damper tape must also be installed between rooms and different circuits. For this, a special tape with a T-shaped profile is produced. And in this case, it can be replaced by thin foam, glued with polyurethane foam or glue.

Installation of pipes is done as follows:
- 10-15 m of pipe is unwound from the bay, thermal insulation and a corresponding fitting for connection to the collector are put on at its end.
- The pipe is connected to the supply of the corresponding collector outlet.
- The pipe is laid along the previously marked routes and fastened with harpoon brackets on straight sections after 30-40 cm, and at turns after 10-15 cm. The pipe must be bent carefully, without kinks.

- When laying, you do not need to try to fix the pipe immediately, but you should first expand it approximately along the routes by 5-10 m, and only then fix it with brackets. The pipe should lie on the insulation without tension, there should be no effort that tries to pull the staples out of the EPS.
- If for some reason the bracket flew out of its place, then it is mounted in another, at a distance of at least 5 cm.
- After bypassing the entire underfloor heating circuit, the return pipe returns to its supply and next to it follows to the collector. If necessary, thermal insulation is put on it.
- Upon arrival to the collector, the pipe is connected to it with the appropriate fitting.

- Near the corresponding loop of the warm floor on the wall, as well as on paper, the length of the contour must be recorded. These data are required for further balancing.
All contours are laid in the same way. It will be difficult at first, but then, after one laid "snail" everything will be clear and the work will go without problems. When moving along the already laid contours, it is necessary to underlay boards, plywood or OSB under the legs or knees.
 It is not recommended to walk in pipes in shoes. It is better to organize such "paths"
It is not recommended to walk in pipes in shoes. It is better to organize such "paths" Video: Laying floor heating pipes
Installation of reinforcing mesh
Disputes about the appropriateness of the reinforcing mesh are ongoing. Someone says that she is needed, others say the opposite. There are many examples of a successful implementation of a warm floor without a reinforcing mesh and, at the same time, there are examples of an unsuccessful implementation of a warm floor with reinforcement. The authors of the article argue that reinforcement will never be superfluous, but only correctly performed.
The Internet is replete with examples when a metal mesh is laid and fixed on the insulation, and only then a heated floor pipe is attached to it with the help of plastic ties. It seems to be convenient, but this is not reinforcement, but simply placing an absolutely useless mesh under the screed, on which money was spent. Reinforcement is when the mesh is inside the screed, not under it. That is why the authors recommend placing the mesh on top of the pipe.

To reinforce the screed, a metal mesh made of wire 3 mm in diameter with a cell size of 100 * 100 mm is suitable - this is quite enough. It is not recommended to use reinforcement meshes due to the fact that the reinforcement has a corrugated surface and during installation can damage the smooth surface of the pipe. And it is not worth spending extra money on the excessive strength of the screed, because it is assumed that the warm floor is already mounted on a fairly solid foundation. The mesh is laid with an overlap on one cell and tied either with a knitting wire or with plastic clips. The sharp protruding ends must be bitten off so that they do not damage the pipe. Additionally, the mesh is attached to the pipe in several places with plastic clamps.
Instead of a metal mesh, a plastic mesh may well be used, which will perfectly reinforce the screed and save it from cracking. It is more convenient to lay the plastic mesh as it comes in rolls. The use of plastic mesh virtually eliminates pipe damage, and its cost is significantly lower.

After laying the mesh, the question of protecting the pipes again arises, because moving in shoes on a metal mesh can easily damage both it and the pipe.Therefore, it is again recommended to move only on boards, plywood or OSB. But there is still a very competent solution that will avoid damage to the pipes when pouring the screed.
A cement mortar is prepared - the same as it will be when laying the screed (1 part of M400 cement and 3 parts of sand) and during the laying process, "blobs" are made from the solution, which protrude slightly beyond the surface of the mesh - 2 cm is enough. These "blobs" are made with such a frequency (30-50 cm), which will allow you to put boards or plywood on them in the future and move safely. Another plus of this approach is the fixation of the mesh, because when walking on it, it tends to bend, and this can damage the welded seams.
 The mortar “blobs” will fix the mesh and help you move safely
The mortar “blobs” will fix the mesh and help you move safely Filling the contours. Hydraulic tests
This operation should definitely be carried out even before the screed is poured, since in case of a hidden malfunction, it is easier to fix it immediately than after the floors are poured. To do this, a hose is connected to the drain pipe on the collector and is discharged into the sewer, since a lot of water will be spilled through the heating circuits. It is best if the hose is transparent - so it will be easy to track the release of air bubbles.
The inlet of the supply manifold, which must be equipped with a shut-off ball valve, is connected to tap water through a hose or pipe. If the quality of the tap water is poor, then it is worth filling the system through a mechanical filter. A pressure pump is connected to any other outlet connected to the underfloor heating circuits. This can be a free outlet of the supply manifold, the outlet of the return from the manifold and other places - it all depends on the specific implementation of the manifold assembly. In the end, a tee can be screwed into the ball shut-off valve of the supply manifold and through it both filling the system and pressure testing can be done. After testing, the tee can be removed and the manifold can be connected to the supply line.
The system is filled as follows:
- On the collector, all the contours of the warm floor are overlapped, except for one. Automatic air vents must be open.
- Water is supplied and its purity and air outlet are controlled through the drain hose. On the inner surface of pipes during production, technological grease and chips may remain, which must be washed off with running water.
- After all the air has left, and the water flows absolutely clean, the drain valve is closed, and then the already washed and filled circuit is closed.
- All these operations are performed with all contours.
- After flushing, venting and filling all circuits, the water supply valve is closed.
If leaks are found at the filling stage, they are eliminated immediately after the pressure is released. As a result, you should get a system of warm water floors filled with a clean coolant and de-aerated.
To test the system, you will need a special tool - a pressure pump, which you can rent or invite an experienced craftsman who has such a device. Let's describe the sequence of actions for crimping.

- All underfloor heating circuits connected to the collector are fully opened.
- Clean water is poured into the tank of the pressure pump, the pump feed valve opens.
- The pump builds up pressure in the system twice as much as the operating pressure - 6 atmospheres, it is controlled by the pump pressure gauge and on the manifold (if there is a pressure gauge on it).
- After raising the pressure, a visual inspection of all pipes and connections is carried out, which, in principle, should only be on the manifold. The pressure is also controlled by the manometer.
- After 30 minutes, the pressure is again raised to 6 bar and all pipes and connections are inspected again. Then, after 30 minutes, these steps are repeated. If leaks are found, then they are immediately eliminated after the pressure is released.
- If no leaks are detected, then the pressure is again raised to 6 bar and the system is left for a day.
- If after a day the pressure in the system has dropped by no more than 1.5 bar and no leaks are detected, then the underfloor heating system can be considered correctly assembled and sealed.
When the pressure in the system rises, the pipe, according to all the laws of physics, will try to straighten, therefore, it is possible to “shoot” some brackets in those places where they were “greedy” with them. Therefore, the "blobs" from the solution will greatly help keep the pipe in place. Later, when the screed is poured, the pipe will be securely fixed, but during pressure testing, a poorly fixed pipe can present unpleasant surprises.
Video: Filling the system with a coolant
Video: Pressing the underfloor heating system
Installation of beacons
The underfloor heating screed must be poured through pipes under operating pressure. Considering that in most closed heating systems, the operating pressure should be in the range of 1-3 bar, you can take an average value and leave a pressure of 2 bar in the circuits.
As beacons, it is best to use guiding plasterboard profiles PN 28 * 27 / UD 28 * 27. They have sufficient rigidity and a smooth top surface, which is very useful when leveling the screed.

Lighthouses should be installed at the level of the finished floor minus the thickness of the finishing floor covering. To fix them, very often they simply use mortar pillows, on which a guide profile is laid, and then it is sunk in level. But this approach has the disadvantage that if the beacon falls below the required level, it has to be taken out, put in a fresh solution and set up again.
It is best if the beacons from the guide profile have a rigid support under them, and concrete dowels and a screw of the appropriate length can serve as it. It is preferable to use special screws for concrete - pins, which do not require the installation of a dowel, which means that the drilling diameter will be smaller. If you need to drill a hole with a diameter of 10-12 mm for the dowel, then 6 mm is enough for the dowel. The upper surface of the screw head should be level with the surface of the future screed.
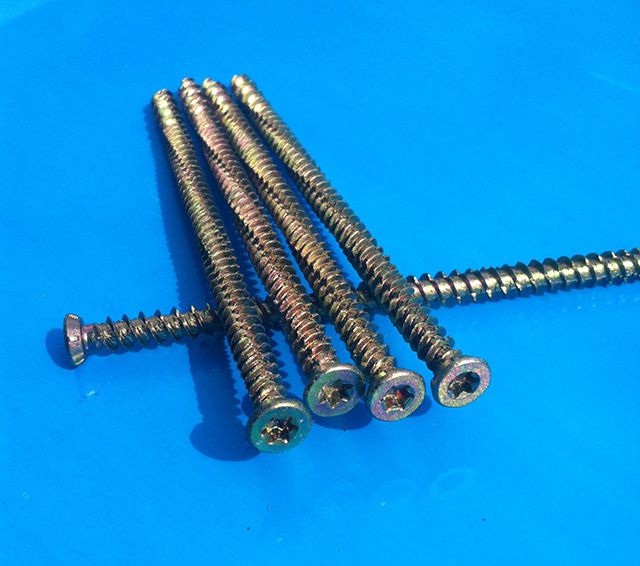 Concrete screws - pins
Concrete screws - pins Lighthouses should be located no more than 30 cm from the walls. There should not be a long distance between the lighthouses, since the solution tends to settle and a pit may form on the already finished screed. Optimally - 1.5 m, then the building rule of 2 m is used to level the screed.When installing beacons, do the following:
- Two lines are drawn from the walls to the left and right of the entrance, at a distance of 30 cm - this will be the position of the extreme beacons.
- The distance between these two lines is divided into equal parts so that it does not exceed 150 cm. It is desirable that one of the strips falls directly at the entrance to the room. If necessary, the strip at the entrance can be smaller.
- Lines of the position of future beacons are drawn on the floor. Marks of the location of the pins are made on them with a step of 40-50 cm.
- Holes are drilled to a given depth with a perforator with a drill corresponding to the dowel.
It is best to use a laser level to set the heads of the pins in one plane. If it is not in the arsenal of a home craftsman, then it does not matter, now this very useful tool can be rented, especially since it will only be required for one day.
 The laser level is an indispensable assistant when marking and installing beacons
The laser level is an indispensable assistant when marking and installing beacons The position of the lighthouses is marked on the wall. To do this, the thickness of the finishing floor covering is subtracted from the level of the clean floor previously drawn on the wall. The laser level is set at this mark, and then, by screwing or unscrewing the pins, their hats are set at the same level. If you use the usual building level for this operation, then it will take much more time, and the error will be higher.
Further, guide profiles are laid on the heads of the dowels, the correct installation is checked by the building level. To fix the lighthouses in their places, use a cement mortar of the same recipe as for the floor screed (1 part cement + 3 parts sand).
The lighthouses are removed from the heads of the pins, and then slides are made from the prepared solution slightly higher than the height of the screed. It is enough to do them after 1 meter, since the lighthouse will already be securely fixed on the heads of the dowels. Further, the profile is laid down and pressed into the solution, and its excess from above is immediately removed with a spatula. At the end, the level checks the correct installation of all beacons.
At the same time, you can check the correct installation of all damper tapes separating the rooms and circuits and, if necessary, reinforce their position with mortar.
water heated floor
Video: Installing beacons for underfloor heating
Pouring underfloor heating screed
Increased requirements are imposed on the screed of a warm water floor, because in addition to the mechanical loads it carries, it also experiences thermal deformations. And usually a cement-sand mortar will not work here, the concrete mixture must be modified with a plasticizer and fiber.
The plasticizer is designed to reduce the water-cement ratio, increase the mobility of the mixture and increase its strength during drying. Mobility when laying underfloor heating screed is extremely important, since the mortar should "grip" the pipes tightly and easily release air bubbles outside. Without the use of a plasticizer, the only way to increase the fluidity of the mixture is to add water to it. But then only part of the water will react with the cement, and the rest will evaporate for a long time, which will increase the setting and hardening time and reduce the strength of the screed. The water-cement ratio must be exactly that which will allow the screed to grab. Typically, 1 kg of cement requires 0.45-0.55 kg of water.

The plasticizer is available in liquid and dry form. It should be applied exactly as the manufacturer recommends, and nothing else. Any "substitutes" in the form of liquid soap, washing powder, PVA glue are unacceptable.
Fiber is intended for dispersed reinforcement of concrete mix, which allows to reduce or practically eliminate the formation of cracks, increase strength and abrasion resistance, increase bending and compressive strength. This is achieved by the fact that the microfibers of the fiber are distributed and hold the screed throughout the entire volume of the concrete mixture.

Fiber can be metal, polypropylene and basalt. It is recommended to use polypropylene or basalt fiber for underfloor heating screed. Add it according to the manufacturer's recommendations, but it is recommended to use at least 500 grams of polypropylene fiber per 1 m 3 of the finished solution. To obtain a mixture with the best properties, add 800 or more grams per 1 m 3.
On sale you can find ready-made mixtures for pouring underfloor heating screed from well-known and not so famous manufacturers. The composition of these mixtures already includes a plasticizer, and fiber, and other components. With the undoubted ease of use and high quality, the cost of the finished screed will be significantly higher than the solution prepared independently.
Before pouring the screed, it is necessary to remove all unnecessary objects from the floor, vacuum the surfaces if necessary. It is also necessary to prepare all the tools and utensils for mixing and transporting the solution. All work on pouring the underfloor heating screed in the room should be done at one time, so it is advisable to have two assistants: one prepares the solution, the second carries it, and the main contractor lays and levels the screed. All windows in the room must be closed, the screed must be limited from exposure to drafts and direct sunlight.
Self-preparation of mortar for screed floor heating should be done only mechanically - the quality of the mortar must be high. A concrete mixer or a construction mixer can be used as auxiliary mechanisms. No drill or hammer attachments will work here, no matter what various "truthful" sources say.

The basis of the solution is made up of Portland cement grade not lower than M400, which must be dry and with a storage time of no more than 6 months after the date of issue. The sand should also be dry, washed and sieved. River sand will not work - it is too regular in shape. For a screed, the ratio of cement to sand should be 1: 3 by weight, but in practice, few people weigh sand and cement, and a universal measurement method is taken - a bucket. Considering that the density of building sand is in the range of 1.3-1.8 t / m 3, and cement during transportation is 1.5-1.6 t / m 3, you can not be afraid to measure cement and sand with buckets, since the quality the mixture will be perfectly acceptable.
The water in the composition of the solution should be about a third of the mass of cement, that is, for 1 bag of 50 kg of cement, approximately 15 liters of water are needed. However, the use of a plasticizer reduces the water-cement ratio, therefore, when preparing a solution with water, you need to be very careful - it is better to underfill a little and then add than pour.
The technology for preparing a solution with a mixer and a concrete mixer is slightly different. With a mixer, it is necessary to stir dry cement, sand and fluffed polypropylene or basalt fiber at low speeds and then gradually add water with a plasticizer dissolved in it. In gravity-type concrete mixers, of which the absolute majority, it is difficult to stir dry cement and sand (dry cement sticks to wet blades and a drum), therefore part of the water with a plasticizer is first poured into it, and then cement is gradually added first, then sand, then another portion of cement and the remaining water. The fiber is added gradually. One part with water, the other with sand. In this case, the fiber should not be thrown into the drum of the concrete mixer in a lump, but must be divided into portions and fluffed before laying.

The time for preparing the solution in a concrete mixer is usually 3-4 minutes, and with a mixer a little more - 5-7 minutes. The readiness of the solution is determined by its uniform color and consistency. If you take a lump of solution in your hands and squeeze, then water should not come out of it, but at the same time the solution should be plastic. If you place the solution in a slide on the floor, then it should not spread much, but only settle slightly under its own weight. If cuts are made in it with a spatula, they should not blur, but should keep their shape.
Laying the screed begins from the far corners of the room and is carried out in strips along the beacons. Only after the completion of one strip, the next one is laid and leveled, the process should end at the entrance to the room. In the process of leveling, it is not necessary to immediately try to perfectly align the screed surface with the beacons. The main thing is that there are no failures in the screed, and small influxes and traces of the rule are easily corrected later.

After 1-2 days (it all depends on external conditions), when it is already possible to walk on the screed, it is necessary to clean its surface. First, it is trimmed with a construction knife and the damper tape protruding from the screed is removed, and then the construction rule is taken and the sharp end is pressed against the plane of the beacons. In the direction away from you, with short but energetic movements, a sweep is performed until the beacons are completely exposed. Then the resulting debris is removed, the screed is moistened with a spray bottle and covered with plastic wrap.

The next day, the lighthouses are carefully removed, you can also unscrew the pins, and the resulting grooves are rubbed with a solution or tile glue. The screed is re-moistened and covered, it is recommended to do this daily for the first 10 days after pouring.
Balancing the contours of the warm floor. Commissioning
After the screed has fully matured, and this is at least 28 days, you can start balancing the contours of the warm floor. And in this process flow meters on the manifold will be very helpful. That is why it is necessary to purchase a manifold with balancing valves and flow meters.
The fact is that underfloor heating loops have different lengths, respectively, they have different hydraulic resistance. It is obvious that the "lion's share" of the coolant will always follow the path of least resistance - that is, along the shortest circuit, while others will get much less. At the same time, in the longest circuit, the circulation will be so sluggish that there can be no talk of any heat removal. In a well-designed project of underfloor heating, the flow rate in each circuit and the position of the control valves are always indicated, but if the underfloor heating is done on its own, then a simplified but valid technique will do.

- If the pump-mixing unit has not yet been connected, then it is being installed. The underfloor heating collector is connected to the supply and return lines.
- All the contours of the underfloor heating are fully opened, the collectors open at the inlet and the ball valves for supply and return. The valves of the automatic air vents must be open.
- Circulation turns on. The maximum temperature is set on the head of the mixing unit, but the boiler does not turn on yet, the coolant must circulate at room temperature.
- The pressure in the entire heating system is brought to operating pressure (1-3 bar).
- All contours of the warm floor are closed, except for the longest one. The position of the flow meter on this circuit is noted and recorded.
- The second longest contour opens completely. If the flow rate in it is greater, then the balancing valve is twisted until the flow rate is equal to the longest one.

- Further, all circuits are sequentially opened in descending order of their length, the flow is regulated by balancing valves.
- As a result, the flow rate in all circuits should be the same. If this is not the case, then you can correct the adjustment on the contours without touching the longest loop.
All of the above operations were performed correctly and the flow meters show that there is circulation in the circuits, then you can start testing a warm floor with a heated coolant. It is necessary to start with low temperatures - from 25 ° С, and then every day gradually increase the temperature by 5 ° С, until the coolant is supplied to the circuits with its operating temperature. What is the sequence of actions at this stage.
- The temperature of 25 ° C is set on the thermostatic valve of the mixing unit, the circulation pump is turned on at the first speed and in this mode the system is allowed to operate for a day. In this case, the circulation through the flow meters is monitored and adjusted.
- After a day, the temperature rises to 30 ° C, and again the underfloor heating system is left for a day. Flow rate and temperature of supply and return are controlled.
- The next day, the temperature rises by another 5 ° C, up to 35 ° C. This is already much closer to the operating mode of the warm floor, so it is already worth adjusting the temperature difference between the supply and return collectors. If it is in the range of 5-10 ° C, then this is normal, and if it is more, then the speed of the circulation pump should be increased by one stage.
- The maximum temperature to which you can raise the temperature in the underfloor heating supply collector is 50 ° C, but it is better not to do this, but check it in operating modes - 45 ° C or 40 ° C. Similarly, the temperature difference between the supply and return is checked. The pump must run at the lowest possible speed so that the temperature difference is up to 10 ° C.
The correctness of the underfloor heating adjustment cannot be assessed immediately, since such a heating system is very inertial. It takes several hours to feel the change in temperature. Therefore, everyone who has made a warm floor on their own should arm themselves with patience and gradually bring the system to such a mode that would provide the desired floor temperature, taking into account the coating. To do this, you will need to "play around" with the settings of the balancing valves, thermal heads (if the collector is equipped with them) and the speed of the circulation pump. The main thing is that a self-made water floor heating system works.
Find out how, having studied the instructions with the photo, in a special article on our portal.
Conclusion
Stubborn statistics indicate that the system of warm water floors, in addition to the obvious comfort, also provides significant energy savings. The same statistics indicate that the number of successful independent implementations of such heating is growing every year. All technologies have already been worked out, the market is flooded with any components, for every taste, color and wallet. The necessary information is always in open sources, you can always ask the experts for advice. The team of authors hope that this article has dispelled the initial fear and made it clear to the readers that it is quite possible to make a water-heated floor with your own hands.
Video: How to calculate and make a water-heated floor with your own hands
One of the options for heating a private house is to arrange underfloor heating. The key advantage of such a heating system is the heating of living quarters from the lowest level, as a result of which the most comfortable microclimate is created in the house. The construction of a warm floor cannot be called complicated, but its installation has certain nuances that you need to know about. This article will answer the question of how to make a warm floor in a private house with your own hands.
Advantages and disadvantages
Warm floors are quite popular today and are used by many owners of private houses. Heat transfer in these systems is carried out by pipes located under the floor covering, through which a heated coolant circulates, or by means of electric heating elements.
As a result, the floor heats up and becomes warm to the touch, which in itself significantly increases the level of comfort in the house.
Among the positive qualities of a warm floor, the following stand out most clearly:
- High level of comfort... The floor heated to a certain temperature allows you to walk on it barefoot, without fear of any discomfort.
- Profitability... Saving in the use of warm floors is achieved due to the efficient distribution of energy - it moves from the bottom up and heats only the volume of the room in which heat is needed, i.e. there are no unnecessary expenses.
- Possibility of setting the temperature regime... It is highly recommended to equip the warm floor with an electronic control unit, which will allow the system to monitor the current temperature in the room and keep it within user-specified limits.
- Ease of installation... Arrangement of warm floors is a fairly simple task, especially when it comes to the electrical version of the system. It is more difficult to lay a water circuit, but even if you wish, you can easily install it yourself.

There are also disadvantages:
- High cost... Installation of a warm floor will require a lot of materials, and some tools will have to fork out. There is only one way to reduce the cost level - to do all the work on arranging the heating yourself.
- Reducing the volume of the room... The thickness of the warm floor can vary from 7 to 12 cm - and it is to this height that the entire floor rises. If the ceilings are high, then there will be no special problems because of this (unless you have to redo the thresholds).
- Demanding flooring... It is possible to cover a warm floor only with coverings that transmit heat well. It is best to purchase specialized materials designed to be used in combination with warm floors. An inappropriate coating will prevent the system from operating efficiently, and in the case of electric heaters, there is also the possibility of damage due to overheating.
The advantages of underfloor heating are significant, but the disadvantages are not critical, therefore such heating systems can be used for heating, both as the main and as an additional source of heat.
Substrate preparation for all types and variants of underfloor heating
One of the most important elements is the basis for underfloor heating in a private house, which must be prepared even before arranging the heating system itself. A number of requirements are imposed on the base - it must be strong enough, even and heat-resistant. Each requirement is important, but it is thermal insulation that requires special attention - without it, the generated heat will simply go under the floor. Various insulation is used for pipes, which must be selected for specific conditions.
The technology for preparing a base with expanded clay insulation includes the following stages:
- Dismantling... The first step is to remove the old coating, under which there may be concrete, soil or wooden supports. All dirt and unnecessary elements must be removed.
- Markup... With the help of a building level along the entire perimeter of the walls, it is necessary to mark a line along which the base will be leveled. In the case of expanded clay, more free space must be left so that the thickness of the insulating layer is sufficient to effectively retain heat.
- Bedding... The base is covered with a layer of sand, the thickness of which should be about 10 cm. After filling, the sand cushion must be compacted.
- Waterproofing... A waterproofing material is laid on the compacted sand layer (polyethylene is the cheapest, but a waterproofing membrane is a more reliable option).
- Placement of beacons... Now you need to install the supports along which the beacon profiles will be located. Beacons need to be aligned very accurately.
- Installation of thermal insulation... All free space between the beacons is covered with expanded clay. For greater reliability and efficiency, it is worth mixing expanded clay with liquid cement mortar.
- Filling the screed... Actually, after laying the thermal insulation layer, you can start pouring the screed, which should reach the previously measured level. The screed is leveled along the profiles.
- Alignment... When the screed grabs a little, the beacons need to be removed and the holes obtained should be repaired. The seams are rubbed, after which the floor must be left until the solution has completely solidified.

In addition to expanded clay, a number of other materials can be used as thermal insulation:
- Polystyrene plates, which are usually reinforced with a reinforcing mesh to increase strength and are attached to the base with anchors;
- Roll foil materials, excellent for use in combination with electric heating elements;
- Polymer mats designed specifically for laying a water-heated floor, for which there are special protrusions in the material, between which pipes are laid.
Diy water floor heating device
There are different options for underfloor heating in a private house, but the most popular type is water. Structurally, such heating is a system of pipelines laid under the floor covering, through which a hot coolant passes. The pipes are connected either to an existing heating system, or directly to a heat source.

Water heat-insulated floor includes the following elements:
- Pipes... For arranging a warm floor, metal-plastic or polyethylene pipes are most often used. Both materials have good thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion.
- Collector... This element is necessary for the formation of a proper wiring - each heating circuit must have separate leads. In inexpensive manifolds, there are only shut-off ball valves, while good devices are equipped with a valve that allows you to regulate the temperature in each individual circuit.
- Circulation pump... The pump ensures normal circulation of the coolant in the warm floors. If the heating equipment has a built-in circulation pump, then there is no need for a separate device.
- Damper tape... This tape is laid along the entire perimeter of the room and allows you to compensate for the expansion of the screed when heated. Standard damper tapes are made of foamed polymers.
- Fasteners... If laying is carried out on mats, then they will perform the function of fasteners for pipes. In all other cases, you will need special brackets equipped with locks and anchoring.
Laying pipes in a private house
In order for the underfloor heating to work efficiently and be sufficiently reliable, the pipes must be laid at a certain distance from each other. Usually, the step value varies from 15 to 35 cm and is determined depending on the required heat transfer - for more efficient heating, the step must be reduced. It is not worth saving on pipes - too large a step will lead to uneven heating of the floor sections, which will lead to a noticeable decrease in comfort.

The total length of pipes for one room is calculated using the following formula:
- D \u003d S / M * k, where
- D - total pipe length,
- S - room area,
- M - laying step,
- k - safety factor, varies from 1.1 to 1.4.
Usually for 1 sq.m. the area of \u200b\u200bthe room requires about 1.5-3.5 m of pipes.

An important point is the layout of the pipeline, which can be performed according to one of the following schemes:
- "Snake"... A good option for small spaces. Since the area is small, the temperature in the pipes practically does not decrease throughout the entire circuit.
- "Snail" and "double snake"... These layouts are suitable for medium-sized rooms. Due to the close arrangement of the supply and return circuits, the floor will warm up evenly.
- Multiple circuit diagram... For full and efficient heating of large rooms, it is most advisable to equip several separate circuits, which will provide good heat transfer and will be quite reliable.
Installation of a water heated floor
A water-heated floor in a private house is laid using the following technology:
- Collector installation... The collector is installed in a collector cabinet or a niche in the wall intended for it, after which it is connected to the heating equipment.
- Installing a damper tape... The tape is laid around the entire perimeter of the building or around the area where the heating circuit will be located. The presence of the tape not only compensates for thermal expansion, but also reduces heat loss.
- Reinforcement... Reinforcement mesh should be laid on the layer of thermal insulation, which is fixed with anchors and connected to each other with ordinary wire.
- Pipe installation... The pipes of the water circuit are unwound, and care must be taken that they do not unscrew along their axis. The pipeline is laid in accordance with the chosen scheme and fixed with brackets or clamps.
- Manifold connection... All circuits are connected to the corresponding terminals, after which the system can be filled with coolant. The water circuit must be left in working order for two days to check for leaks.
- Filling the screed... A conventional cement screed is poured over the water-filled system, which must be left until it hardens completely (this usually takes about a month). When the solution is completely dry, it will be possible to start heating in operating mode. Premature start-up of the system is likely to damage the concrete layer.
The device and types of electric warm floors
If it is necessary to lay underfloor heating in a separate room, then the electric heating system will be more relevant. Most often, electric underfloor heating is used as an auxiliary or local heating. Such a system must be connected to a thermostat, which turns the system on and off as needed.

There are the following types of electric underfloor heating:
- Film... The most popular type of heaters, the main advantage of which is their small thickness. Structurally, film heaters are carbon fiber plates, fastened to each other with conductive tracks and insulated with a polymer material.
- Cable... This type of heater is based on a cable with a high resistance, due to which, when current passes, the product generates thermal energy. The pitch of cable heaters can be varied, thereby influencing the intensity of heating the room.
- Rod... The main structural element are carbon rods connected by wires to form a one-piece structure. The most powerful and reliable, but very expensive type of electric heaters. See also: "How to make an electric warm floor with your own hands - types of warm floors, installation rules."
Installation of a film warm floor
Film warm floor is the most common system, which is largely due to the simplicity of its installation.
An electric underfloor heating in a private house is equipped from scratch using the following technology:
- Laying reflective material... It is highly recommended to install heat-reflecting foil material under the film warm floor, which will prevent the passage of heat into the underfloor space.
- Cut film... It is advisable to cut the film as little as possible in order to reduce the number of wires used. Cutting of the film can only be carried out along the cut lines drawn on it - this avoids damage to the internal elements of the material.
- Film laying... The prepared heating elements are laid out on the base and aligned. You can fasten the strips of film with tape, but it is better not to fasten the edges to make it easier to connect them to the network.
- Connecting stripes... In the areas where the conductive track is located, you need to open the film and attach a clip to it.
- Contact isolation... Each contact and the area where the strips have been cut must be carefully insulated. Butyl plates are a good option for insulation, usually included with the rest of the underfloor heating. Contacts are simply crimped with such plates.
- Thermostat connection... The film leads must be connected to the thermostat, guided by the instructions on its case or in the instructions. It is imperative to turn on the system and make sure that all lanes are working.
- Installation of flooring... If the heating elements function normally, then you can safely cover them with the selected floor covering.

Conclusion
It is very easy to equip a warm floor - all types of warm floors in a private house are assembled without problems with their own hands. The ready-made system will provide full heating of the room and the proper degree of comfort.
As an additional or main source of heating for a private house, water heated floors are often used, which allow you to effectively heat the building. However, there are some peculiarities associated with the installation of the heating circuit and the subsequent operation of the system.
The device of a water-heated floor in a private house has both positive and negative sides, which are important to consider.
Is it possible to heat a country house with a water floor
Water underfloor heating in a private house can be used as a primary or additional heating source. A feature of the system is heating the room from bottom to top. This method is the most effective, as it allows you to achieve the complete absence of cold unheated areas. The advantage of water floors also lies in the fact that the heating of the room is carried out faster and with less energy consumption.
The advantage of water floors also lies in the fact that the heating of the room is carried out faster and with less energy consumption.
There are certain restrictions associated with the use of warm floors. So, for example, the maximum heating intensity depends on the selected flooring.
Laminate and parquet boards can be heated up to a temperature of 30 ° C, after which the material begins to emit harmful and toxic fumes. It will be optimal to install heating systems in country houses using ceramic tiles as a topcoat. Ceramic is resistant to temperature extremes, heats up well and retains heat on the surface for a long time.
There is a manifold for automatic floor control. The mixing block allows you to turn on the heating system in the absence of the owners, as well as control the degree and intensity of heating the room.
How to make a water floor correctly
The design of the system is so simple that it is allowed to lay water floors in a private house with your own hands. At the same time, it is extremely important to observe certain nuances associated with the phased installation and operation of heating.The work is carried out in the following order:
- A rough base is made - if you plan to lay on the ground, first carry out the powder, using sand and crushed stone, tamping them with a vibrating plate. After laying the waterproofing, a rough reinforced screed is poured.
The device of water floor heating in a private house cannot be carried out without the use of waterproofing material. For using welded materials or mastics. Bituminous material at the joints is treated with a construction hairdryer or blowtorch. A vapor barrier must be placed on top of the screed. - Insulation - the efficiency of heating a private house with warm water floors largely depends on a well-made heat-insulating layer. Thus, a screen is created that reduces heat losses and prevents pipe defrosting. Extruded polystyrene or foam can be used. Mineral insulation in this case is ineffective.
- Laying the pipeline - the scheme of laying a water heated floor in a private house is being preliminarily worked out. You can make the plan yourself or contact a professional. The heating calculation takes into account the number of heating zones, the length of each water circuit and the type of pipe laying.
Independent installation of warm water floors in a private house is carried out as follows. A reinforcing mesh is laid, a pipe is laid out along it and fixed with clamps. If a polystyrene system is used, then the pipeline is laid in special grooves located in mats, or in openings located on heat-reflecting plates.
- Pouring the finished floor - Do-it-yourself laying of a water-heated floor in a country house is coming to an end. At this stage, it is extremely important to make the most even base. Lighthouses are displayed. A plasticizer and additives for concrete strength are added to the solution.
It is strictly forbidden to use ordinary cement composition. If a polystyrene system is used, plywood or gypsum fiber board is laid on top. - Loops are connected - initially attached, water circuits are connected to it. When installing, observe the following installation rules. The coolant supply to the radiators is connected to the lower collector outlet, the return to the upper one. Water circuits are connected in reverse, supply at the top, return at the bottom. The manifold controls the floor temperature and controls the flow rate of the heating medium.
- Laying the topcoat - a warm water floor in the country house is revetted with any of the recommended finishing materials: parquet board, linoleum. Recently, self-leveling floors have also been popular.
- The first start - heating the cottage with water-heated floors can be carried out no earlier than 28 days after the screed is poured. Before the first start-up of the system, the circuits must be serviced: filling with water and.
The installation technology is largely influenced by the chosen method of laying the floors. The polystyrene system is more expensive but takes less time to install. Installation with a concrete screed is less expensive, but it can take about 1.5 months from the start of repair work to commissioning.





What is better to connect the underfloor heating system (heat carrier heating source)
According to the operating instructions, the optimum temperature for continuous operation of underfloor heating is the temperature range from 25-30 ° C.The water in the heating system is of a radiator type, it heats up to 60 -70 ° C. Accordingly, it is possible to simply connect the heating of the cottage using warm water floors directly from the boiler, but not efficiently. It is enough to simply try to hold your hand under a stream of hot water with a temperature of 60 ° C. It will simply be impossible to walk barefoot on the floor with such heating intensity.
Therefore, the design of a heating system with water floors includes the ability to connect to the following heating sources:
- Boiler with an intended circuit for underfloor heating.
- The boiler is connected to the mixing unit.
- Indirect heating boiler.
- Instantaneous water heater.
When connecting, it is important to strictly adhere to the installation instructions provided by the manufacturer. Often, the documentation provides recommendations on how to connect.






Pros and cons of using water floors
As with any heating system, underfloor heating has its advantages and disadvantages. The pluses include:- No radiators required - water heating of floors in a private house will be able to fully meet the heat demand for a residential building. With sufficient thermal insulation of a frame country house or any country house, energy consumption is even lower than that of traditional heating using radiators.
- System automation - the principle of operation of a water heated floor allows the use of programmers and control units that allow you to control the operation of the system remotely.
- No need for additional permits.
- Cost - compared to a heating system by means of radiators, water floor heating for suburban construction will cost a little more. So, according to preliminary calculations for 1 m², it will take about 1000 rubles to complete all repair and finishing work, including the cost of work.
- Versatility - various options for the design of the water floor are possible, allowing to take into account all the structural features of the house. Additionally, it can be noted that not only a traditional coolant (water) can be used, but also special antifreezes.
Sometimes it is the only solution to ensure a comfortable and cozy stay in a private house, especially in the northern regions. In the autumn-spring and winter periods, the base under your feet can cool down rather quickly, and you have to walk in warm socks, otherwise your feet get very cold. It can also be considered a plus in some way additional heating of the building itself from the inside... In objects of individual residential construction, heated floors are often made. Wiring diagrams in a private house can be very different, but the essence is the same - such a heating system was and remains the most often equipped in the house. Let's see what are the features of water floors, how you can make them yourself.
Warm floors are not a novelty for a long time. For several decades they have been used to create comfort and coziness in the house and are especially popular in private houses where there are no neighbors below, but only a basement or foundation. And, of course, in the cold seasons of the year, the floor underfoot will be cool, if not icy (a lot depends on how well the floors were insulated).

Water-based floor heating is often recommended for floor heating in any private house, although there are also electric and. The latter are often settled in apartments, since they do not pose the risk of flooding the premises, and are also easier to install - in particular, they do not need the construction of a cement screed. But water floors are perhaps the ideal option for a private house, especially if there is a heating boiler in it.

On a note! The water heating system cannot be regarded as the only heating system in the house. It can only act as an additional one together with heating radiators and other heaters. But making life in the house comfortable is just her task.

It is easy to understand that, unlike the electrical system, water plays the role of a heater in the water, which enters the pipes laid and filled with a screed. The heat carrier is supplied through a special collector, which is connected to the heating system (central, heating boiler, etc.). Heat flows from the heated water circulating through the pipes to the concrete screed, heats it up, and it, in turn, gives off heat to the room and heats the floor covering. Therefore, walking on such a floor will be pleasant.

Attention! Water systems are used, as a rule, in private homes. The apartment rarely has the ability to connect the system to central heating, and it is also possible to flood the neighbors living below in the event of a system breakdown.
Advantages
The water-based heating system has many advantages. These include:
- achieving the desired level of comfort, since the floors will always be warm, and the air in the room will be heated evenly;

- security, but only in a private house. Such floors will not shock, and the worst thing that can happen is a leak. But in a private house, it is not as critical as in an apartment building. Moreover, even if a leak occurs, then the maximum property of the owner will suffer, but not himself, since there is simply no risk of getting burned with hot water;
- savings - is also one of the advantages. Water floors will save a lot of natural and monetary resources, since the water will be used as a heat carrier the same. You can also warm up the room faster using water floors if the ceiling height is very high;
- compatible with all floor coverings - also a plus. Indeed, it is only in rare cases that certain coatings cannot be laid over the heating system. And then, if you do everything correctly, then any coatings can be laid on top of the water system;

- the cost of the water system is low, which will save a certain amount of money during installation.
But this system also has disadvantages. So, for example, installation is indispensable, and this is quite hard work that requires certain skills. Plus, the screed will have to be dried before use, and this is plus 28 days to the duration of the repair. And during this period, nothing can be done in the repaired room. Another drawback is the complexity of repairing the system itself, if necessary. So it is important to do everything with high quality initially, in order to avoid troubles for a long time later.

Types of water floors and device features
The main element of such a floor heating system is the pipes through which the coolant-water circulates. They can be either metal or made of polymer materials. The former are distinguished by their high price and complexity of the connections, while the latter are much easier to install, and they are cheaper. In addition to pipes, you will need other elements of this system. This is a base in the form of a concrete slab or polystyrene, a waterproofing layer, a layer of thermal insulation, a concrete screed. On top of this cake is laid directly on the finishing coating. In general, the thickness of the entire structure will be about 7-15 cm.

Depending on how the underfloor heating is being arranged, there are several main types of construction.
Table. Types of water floors.
| A type | Description |
|---|---|
| Heavy | This is the most common and highly reliable option. Here it is important to carefully prepare the rough surface (sub-floor or floors), then lay heat and waterproof layers, and then a layer of reinforcing mesh, to which the heating circuit itself from pipes will be attached with clamps. After that, it remains to fill everything with a screed, dry it, and the warm floor is ready for use. Heavy water floors are also called concrete or wet floors. The latter is due to the fact that it is required to carry out work on filling the screed. It is important to understand that the screed layer above the pipes themselves should not be less than 3 cm. |
| Lungs | In this case, a special polystyrene foam plate is used as a base for pipes. It is sold ready-made. During installation, it must be laid on the subfloor and laid along it in accordance with the floor heating pipe diagram. They will not need additional fixation, since there are special protrusions on the plate itself that allow you to securely fix the pipes. Then, special heat-distributing plates are placed on top, on top of which the finishing coating is installed. This is a good option for arranging a water floor in conditions of impossibility of installing it according to a standard scheme due to the heavy weight of a standard screed. |

There is also another option for arranging a warm floor system - on wooden slats. That is, a tree will be used as the basis for such a floor, to which the pipes are attached, and from above they are closed with gypsum fiber and a topcoat. This variant is used extremely rarely and it is not reliable.
Wiring diagrams
It has already been mentioned above that the schemes for laying a warm floor can be different. Depending on the scheme and compliance with the installation rules, the distribution of thermal energy in the room will also occur. There are three main pipe layout schemes, but they are all united by the fact that pipes are necessarily installed from the walls towards the central part.
Table. Installation schemes for the water floor.
| Scheme type | Characteristic |
|---|---|
| In this case, the pipes are laid in a spiral from the wall to the center, and then returned to the starting point. Moreover, the structure gradually narrows towards the center of the room. When calculating the circuit and laying it down, remember to leave free space between the pipes so that you can "take" them back to the power source. It is noted that such a scheme will make it possible to achieve the most uniform heating of the floors, and thanks to it, hydraulic resistance can be reduced. The number of pipes is also used less than in other cases. The main drawback is the difficult installation. |
| In this case, pipes are laid along the walls in loops in one direction, and then in the opposite direction. When looking at such a scheme, one can notice the waviness of the final pattern. It is easy to lay pipes in this way, but due to the frequent step of laying pipes, it is unlikely that it will be possible to achieve uniform heating of floors without temperature jumps. |
| In this case, both pipe laying schemes are combined. This option is used if the walls in the room are cold enough. The pipes are laid in such a way that in some places they lie in the form of loops, and in some places - at right angles. |
Installation features
Before we talk directly about the process of installing a water floor, it is worth talking about some of the features of this process. So, it is important to take into account that in many ways the thermal load of any room will directly depend on what materials the walls are made of, how everything is insulated, how large the window openings are, as well as on a number of other factors. We'll have to try to calculate the heat transfer. If it is more than 100 W / m 2, then water floors cannot be used as the main heating system, but only directly as floor heating.

The length of pipes also cannot be any. It will depend on the size of the room and the installation pattern. You may have to lay two or even more contours in one large room. This applies primarily to rooms with an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 30 m 2. And each circuit will heat independently of the other, although all circuits can be connected to the same manifold. However, the diameter of the pipes, the pitch between them and the length must be the same if the lines are connected to the same system. And the length and pitch of the contour, in turn, depend on the diameter of the pipes. The larger it is, the longer the outline can be.

Advice! If the room has built-in furniture, then the floor area under it does not need to be taken into account in the calculations. There will still be no sense from the warm floor, and pipes can not be laid there.
From each wall you need to make a small indent (about 10-15 cm from the outer and up to 30 cm - for the inner walls). The pitch between the pipes can vary between 20-30 cm if they are used as an additional option for heating the room.

A water floor is an ideal heating option for large rooms with an area of \u200b\u200bmore than 20 m 2. But in a small room, it is better to choose some other option, since it will be very inconvenient to lay water lines. It is also worth dwelling on the heavy version of the warm floor if possible, that is, to mount it using a concrete screed. This is the most reliable, albeit the most durable option, but it is ideal for a private home. By the way, the screed itself very well protects the pipes of the circuit from the risk of damage and by itself is capable of retaining heat for a long time, which means it will help save money.






