Compatibility of herbs in the garden table. Neighborhood and alternation of vegetables
Not only we love beautiful juicy vegetables and fruits. Insects are also waiting for the harvest, often not allowing him to keep up, eat everything that they meet. Many plants also show their character. They need a certain composition of the soil, special irrigation conditions, meticulous care and a complex of useful substances.
Now there is a mass of both chemical and organic fertilizers that can solve all our garden problems in a matter of minutes. But we know the magic word "organic" and are completely unwilling to poison ourselves with non-quality products, especially since our modern world and without us take care of harmful substances that our body receives daily. How to protect the crop from pests and how to protect yourself from excess chemicals? Nature came up with everything before us, the plants themselves know who their friends are and with whom it is better not to sit on the same bed.
Story
For a very long time, gardeners - lovers from around the world choose the quality of the crop, not its quantity. This is the main criterion of organic gardening. The quality of grown vegetables.

It all began in America, even before Columbus discovered it in Europe. On the countertense, where corn was the main cultivated crop, the locals planted it next to pumpkins and beans. In Europe, the method of mixed plantings learn the hard-working monks, who in the Middle Ages, after long observing, planted various flowers and herbs together with vegetables. They knew the healing properties of aromatic plants and thus found out their positive effect on the neighboring vegetables. The latest information about the compatibility of plants made by botanists and gardeners - fans of our time, whose perennial labors already help to get organic vegetables.
The benefits of mixed landings
The most important advantage of mixed plantings is to obtain high-quality fruits and vegetables without the use of chemicals.
Secondly, the rational use of garden area. Proper combination of different ripening speeds and on demand for vegetable crops allows for a higher yield. In some combinations, the yield of vegetables can be up to 20 kg per 1 m2 of land.

Thirdly, the combination of different crops on one bed can allow to get a crop from early spring to late autumn.
Fourth, the correct combination of different plants favorably affects their quality: improves the general condition, taste and nutritional value of fruits.
Fifth, the method of mixed planting allows you to avoid depletion of the soil. Different plants have different nutritional requirements, so alternating certain plants in the garden helps keep the balance of nutrients.
The last advantage is the reduction of time and energy for gardening. When combining different plants, we follow the laws of nature, creating their natural habitat in which plants create communities. Because of this, they are less damaged by diseases and pests. Of course, a person does not completely get rid of garden care. But with the help of a combination of plants, we can regulate the number of harmful insects and their influence on the process of growing vegetables.
Plant compatibility
There are many options for combining plants in the garden. Vegetables are combined with other vegetables, they are diluted with aromatic herbs and decorative flowers, and sometimes even some weeds can be beneficial. Talking about all the combinations for a long time, so I chose the most popular plants with their friends and enemies.
Tomatoes
Many consider tomatoes to be a selfish plant that likes to grow by itself, has a great need for watering and lighting and does not tolerate any neighborhood. But thanks to the experience of German and Swiss gardeners, it is known that tomatoes do not grow badly next to celery, carrots and beets, radishes and radishes. But the best of their companion, of course, basil. Due to its aroma, it repels insects, improves their taste and affects the shelf life of fruits. Basil and tomatoes are not only friendly in the garden, but also in cooking. The perfect combination. Poor dill, fennel and kohlrabi cabbage have a bad effect on tomatoes, and you should also not put cucumbers and potatoes next to tomatoes.
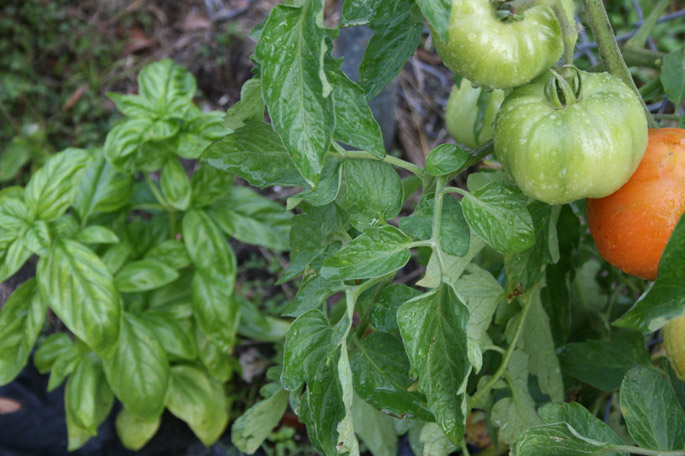

Beet
All kinds of beets are good friends with any cabbage, potatoes, spinach and beans. These five vegetables stimulate each other. Next to the beets, you can plant cucumbers, garlic, strawberries and especially onions. If you respect the distance during planting, beets can be planted next to the carrot, so that its large leaves do not prune carrots. The main enemy of the vegetable is chard, although it belongs to the same botanical family. Also, do not recommend planting beets near the corn.

Pepper
Sweet pepper is quite a friendly plant. Next to it, you can plant not tall varieties of tomatoes, ideally grows next to basil and parsley. Poor tolerance of the neighborhood of fennel and dill.
Cucumbers
The most favorable impact on cucumbers have beans, so it is recommended to plant bush and curling beans around their beds. In addition, you can place beets, cabbage, onions and garlic, radishes, spinach and fennel on the same bed with cucumbers. From herbs, cucumbers grow ideally next to chamomile, dill and cucumber herb. When planting corn next to cucumbers - the corn will be good, and cucumbers as lucky.

Carrot
The biggest pest of carrots is the carrot fly. Therefore, next to the carrot are advised to plant the insect repellent herbs - rosemary, sage, tobacco and onions. But the closest plants for carrots, with which she has a relationship of mutual aid - is a pea and onion. It also grows well next to chard, radish and radish, spinach, salad and garlic. Hostile herbs - dill and anise.
The classic combination is onions and carrots. They have a perfect relationship. Carrots discourage onion fly, and carrot onions. Onions, as an additional culture, grows well next to cucumbers, beets and strawberries. Full contraindication - beans, peas and beans, among the herbs - sage.
Potatoes
With mixed plantings, the potatoes are less sick and fruits well in the same place. His main helpers are the string beans, spinach and beans. These plants scare the Colorado potato beetle and enrich the earth with nitrogen. Good neighbors for potatoes are still cauliflower and corn, especially when blowing with beans, the bad ones are celery and sunflower.
Beans
It is the most friendly plant among the legume family. The relationship of mutual aid and stimulation in beans with all kinds of cabbage, corn, potatoes, beets and spinach. Among the herbs near the beans recommended to plant thyme and oregano, which protect it from black aphids. Absolute incompatibility of beans with onions, garlic, fennel and, attention, peas.
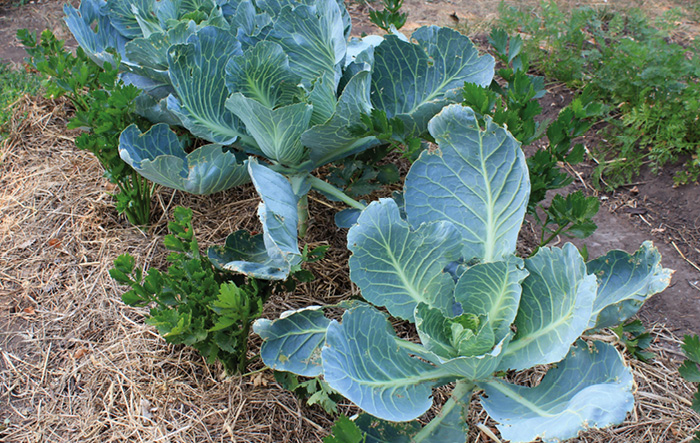
Cabbage
Different types of cabbage react differently to neighbors. But almost everyone is on good terms with celery and cluster beans. Dill, planted between the rows of cabbage, repels caterpillars and aphids, while improving its taste. A good companion for cabbage is the salad of all kinds. To protect the vegetable from butterflies, which like to lay eggs on its leaves, aromatic herbs such as rosemary, thyme, sage and mint are planted around the beds. You can combine planting cabbage with cucumbers, beets, spinach and potatoes. Negative effect on planting adjacent grapes and parsley.

Pumpkins and Zucchini
These plants often suffer from overheating, so they are advised to plant corn next to them, whose foliage protects them from the sun's rays. If you combine a pumpkin with corn, then you must plant a couple of bushes of beans next to it, which will stimulate the growth of corn and saturate the soil with nitrogen. Between the beds with pumpkins and kamochkami parsley grows well.
Let's think together why we need mixed landings? This is when different cultures grow not on separate beds, but on adjacent rows or interspersed.
In nature, there are no large areas occupied by one species. There is always a mixture of herbs in the meadow, in the forest - not only different tree species, but also shrubs, grasses, and mosses. Even in a field where only one crop has been planted after plowing, weeds grow. We can also create a garden in which the plants are adjacent.
Of course, there will be unwanted "aliens" here, but they will not cause much harm. This is because a rich, diverse ecosystem will be in balance! How to do it? The answer is simple - apply the method of mixed plantings. To do this, you need to know which plants are good neighbors, and plan the territory so as to ensure the closest possible proximity of different crops. They should not grow in large arrays, but in adjacent rows or holes.
Better at the border
It has long been noticed that plants grow better on the border of various ecosystems: on the edge of the forest, on the shore of a reservoir, on the edge of the field. To recreate the border effect I use a spiral bed. On it, the border is twisted into a spiral and there is a place for many microclimatic sites: the higher the drier and warmer, there is a shady and sunny side. Usually I plant spicy aromatic plants on a spiral bed. Here is a variant of the sequence of plants: sorrel, valerian, onions, peppermint, clary sage, oak sage, garden thyme, oregano, garden strawberry, sage, cumin, rosemary.
You can simply alternate the rows, referring to the crop compatibility table. However, we must remember that the influence of plants on each other depends on the conditions in which they grow. Sometimes in large quantities they oppress neighbors, and in moderation they are helpers. In general, you need a creative approach and your observations.
Crop compatibility
First select the main crop (for example, tomatoes). Then pick a neighbor who has a positive effect on the main plant. In our case, it can be lettuce or spinach - they will give a harvest before the tomatoes start to bear fruit. High tomato plants will protect the greens from the direct rays of the sun and create a more favorable microclimate for them. Salad after harvesting can be sown again. It is necessary to plant a number of aromatic herbs that deter pests. Just need to ensure that they do not drown out the main culture.
Take into account the time of ripening of the crop. If one culture is removed earlier, it is worthwhile to look for a replacement plant for it. You can not leave the ground naked. It is mulched, green manure is planted.

When choosing crops, one should pay attention to reducing competition between them. Plants with a deep root system will get along better with those whose roots are shallow; species with low nutritional needs will not interfere with those who need a lot of nutrients; high spreading cultures will protect from the sun those that love light penumbra.
Only the water needs of neighbors should be similar.
Plants with deep root system:
Eggplant, legumes (except peas), cabbage, leek, carrots, parsnips, peppers, radishes, beets, celery root, tomatoes, pumpkins.Plants with a small root system:
Lettuce, peas, potatoes, kohlrabi, watercress, corn, onions, cucumbers, parsley, celery, radishes, melons, spinach.
Mixed planting performs several functions: protecting plants from diseases and pests, increasing the yield per unit area, protecting the soil from unilateral depletion, reducing the number of weeds. Fruits and vegetables growing in the community with other species are tastier: mint improves the taste of potatoes, parsley - tomatoes.
If you choose the right plants, they will help each other and please the owner. This is the most effective use of your land.
I have been using crop sealing and joint planting for a long time in my garden. Carrots I sow through a row with onions, plant beds with cabbage with savory, potatoes - beans. And such medicinal plants, like calendula, marigolds and nasturtium, grow throughout the garden.

Cauliflower in marigolds.
Kommunalka for celery
I decided to seal the planting of Brussels sprouts, broccoli and early cabbages, planting root celery among them in the aisle. These cultures combine well. Cabbage stimulates the growth of celery, and he drives away from the cabbage butterflies, butterflies.
At first, everything went like clockwork: both cabbage and celery developed beautifully. But in the second half of the summer, where Brussels sprouts and celery grew, she saw that the first one noticeably overtakes her neighbor in growth. Soon the upper cabbage leaves closed, and my celery was in the lower tier, in thick shadow.
I took care of this "communal" garden bed especially carefully. The cabbage was good, but the celery was “sad” day by day.
I realized that I had made a mistake - it was impossible to plant late-ripening crops near. And if you decided to do this, then you had to leave such a distance between them so that everyone had enough space and light. My celery obviously did not get enough. It did not form powerful rhizomes, it was necessary to be content with only greens.
Another thing celery, planted with early cabbage! Already in July, all the heads of cabbage were cut, and the celery remained on the garden as the rightful owner. The conclusion suggests itself: any plants first need to create optimal conditions for development, namely: adequate nutrition, watering, lighting. And then planted next to the culture can remain friends for a long time.
Who is friends with whom?
Everyone knows that onions and carrots are best friends in the garden. One culture scares off the pests of another, and vice versa. After sprouting carrots, I plant onion seedlings in the discovered gaps.
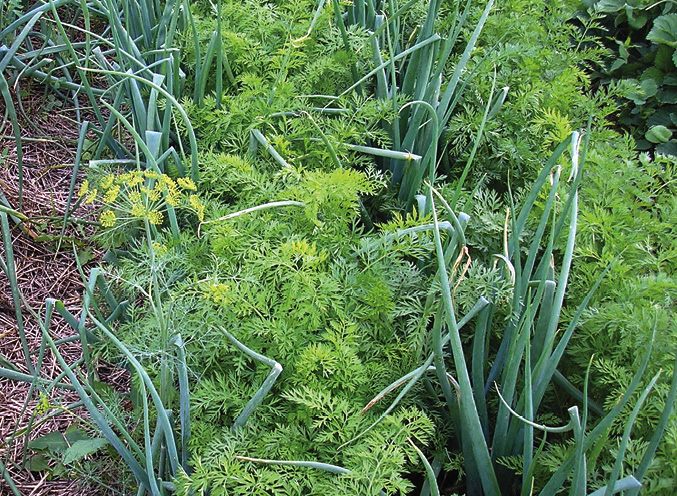

Sweet couple.
The same gaps in the beets fill leaf salad. The beds from under the early radish can be sown with green manure. But it’s more economical to sprinkle radish right into the carrot aisle. Carrots sprout slowly, seedlings remain low for a long time and cannot in any way obscure the fast-growing radish. This way I get a double harvest from one bed. The seeds of early dill are sown in peas: after a while, their antennae will catch on to the stalks of dill.
Along the perimeter of the plot with the potatoes I sow the beans. At first, she is a little depressed in growth, but after digging potatoes grows well and has time to ripen. I add onions to tomatoes - I plant sevok between bushes, but only on greens. After all, tomatoes grow quickly and greatly shade the neighbor.
Otherwise, someone will begin to oppress the neighbor. In general, everything is like in humans. How can you not remember the old saying: "Friendship is friendship, and the tobacco - apart!"
Vegetable beds or why plants satellites?
Gardeners have long noticed that the plants growing alongside influence each other. They release into the environment different substances that "like" or "do not like" their neighbors. For example, early cabbage and tomatoes, late cabbage and early potatoes, tomatoes and celery, beans and potatoes are doing well.

Potatoes and cabbage.
Leaf mustard, marigold, calendula, basil heal the soil and help all crops. They are planted on the edge of the beds, at the entrance to the greenhouse.
There is another big plus in mixed plantings. This is a flight of our imagination. Let's throw out the stereotype that cabbage should sit in even rows! I plant plants arbitrarily (at the corners of the triangle, the contour of the circle), around - nasturtium with marigolds. And the bed looks festive. And the smell of flowers scares away butterflies.

Eggplant and marigold.
Several flowers of phacelia are "hooked" on cucumbers - and they are attracted by the smell of pollinating insects. So just the plot turns into a paradise - a place where you relax with your soul.
Plants satellites placed in between the rows or nests among the main culture. Such mixed plantings create a favorable background, increase disease resistance and even affect the taste of the fruit. When mixed planting does not occur soil fatigue, significantly reduced the number of pests, as the smell of their "food" is interrupted by the smell of other plants. In addition, in these beds creates an ideal refuge for predatory insects that feed on garden pests.
Roman onions with bahchi
I have my own, proven over the years, a method of growing several crops on one bed. For example, onions with melons and watermelons. The harvest turns out excellent! On a bed (2-2.2 m wide), usually in April - early May (on a decreasing Moon) I plant seedlings of onion and turnip in two rows along the edge with a distance of 40-50 cm between them. I place the next two rows from the first 100 cm
At home I sow watermelon and melon seeds for seedlings. Then gently transplant seedlings in open ground, in the center of the beds with onions, at a distance of 70-90 cm from each other. For the prevention of stress and disease, I process onions and melons with microbiological preparations and wood ash extract (200 g per 10 l of water). I water with the help of a drip irrigation system. In the middle of summer I gather a harvest of ripened bulbs. After the appearance of the ovary on the lashes of watermelons and melons, I leave only 2-3 fruits per bush. They will grow large and tasty. By the same technology I add some melon to winter garlic.

Text: garden portalhttp://agraruu.net/
Most often, gardeners and gardeners practice separate beds, that is, tomatoes on one garden, peas on the other, cucumbers on the third, and onions or greens over there. But it has long been no secret to anyone that there is more benefit (and more economical use of the available space, which is important for owners of small plots) when planting some crops together on the same bed. But what and with what is best to plant?
1. Onions and carrots
(By the way, not only carrots are perfectly combined with onions, but also beets, potatoes, etc.). What is the benefit of this neighborhood? For the most part, it is important for carrots, as the onion helps protect it from various pests, because it secretes allicin, which has excellent fungicidal and insecticidal action. This will help you avoid unnecessary additional use of chemistry in the garden.
In addition to onions, carrots can be planted with peas, it fills the soil with nitrogen. But dill, parsley and celery is better to move away from the carrots, they have a depressing effect on it and you will not get a good harvest in such a neighborhood.
2. Basil and tomatoes. This combination is great not only for use in dishes, but also great for planting a flower bed. First, the aroma that basil exudes, repels caterpillars from tomato bushes. Secondly, both of these plants need the same care: watering, loosening the soil, fertilizer, and so on. This means that you will need to make 2 times less effort and spend 2 times less time to care for these plants, if you place them on the same bed. In addition, it is believed that tomatoes grown next to basil are much more fragrant.
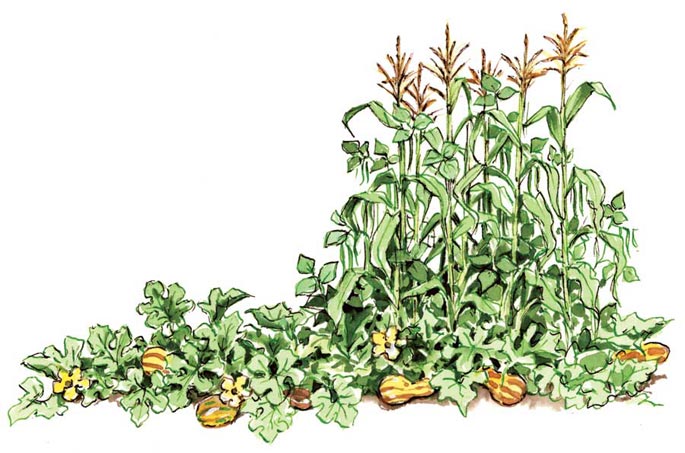
3. Corn, pumpkin and peas.
Another great combination. Corn gives support to peas, which means that you will not need to make or purchase support for peas. Peas, in turn, saturates the soil with nitrogen. This will help avoid additional nitrogen in the soil with chemical fertilizers. A pumpkin "clogs" the weeds, not giving them space to grow. Thus, you will get a harvest of three different types of vegetables, save on pea support, on the introduction of nitrogen into the soil. And, what is most valuable, you will not waste time on weed control.
In my garden I replaced the pumpkin with cucumbers. I did it for several reasons: firstly, no one eats a pumpkin, therefore, there is no need to grow it, secondly, the southern sun burns cucumbers, and the lash dries quickly, and corn gives the necessary shade in the midday heat, and is excellent a support not only for peas, but also for cucumbers.
4. Bulgarian pepper, beans and eggplants. Also a very good neighborhood. Beans will help protect their neighbors from the Colorado potato beetle. In addition, pepper and eggplant need the same care and watering. It is not recommended to plant peppers and eggplants next to potatoes, tomatoes and cucumbers. Potatoes, eggplants and tomatoes have the same pest, and with such an abundance of “nutrition” it will quickly multiply, and you will not have time to process the plants from the Colorado potato beetle.
5. Potatoes and radishes.
Well, a little more from my experience. I planted potatoes and radishes together. First, potatoes are planted, then radish seeds are scattered on the same area on the surface, carefully poured on top with a thin layer of peat or compost (which it used to use). Landing carried out in a moist soil, if not lucky - then watered with a sprinkler. Radishes sprout quickly and by the time of the first weeding or hilling of potatoes (if you spud them), the radish has already been gathered and eaten. By the way, what I liked - because of a sparing planting radish grows large. In addition, the size of the plot allows you to plant several varieties, including the previously untested new items, without fear that the variety will not fit, but takes its place.
Beans.
The most favorable relationship, which can be described as mutual aid, exists between beans and cucumbers. Therefore, it is recommended to plant beans around the beds with cucumbers. They combine well with sweetcorn, potatoes, radishes, radishes, spinach, mustard. Interspersing the beans in planting these crops improves their nitrogen nutrition. Fragrant basil, planted next to the beans, reduces damage to their bean weevil. Other useful herbs for beans: borage, lavender, oregano, rosemary, yarrow. It is not recommended to plant beans with onions, leeks, chives and garlic. The beans are badly affected by the neighborhood of marigolds and wormwood.
Grapes
In Moldova, as mentioned earlier, a large number of cultivated plants were studied for their compatibility with grapes. Corn, beans, rye, potatoes, radishes, and oil radish had a stimulating effect on the growth of grapes. Negative effects were observed when planted with onions, barley, soybeans, cabbage. The incompatibility of grapes and cabbage has been known for a long time. Already in ancient Greece, they knew that cabbage is the enemy of the vine. This may seem surprising, because other plants of the cabbage family are not so hostile to grapes, and radishes and oilseed radishes. on the contrary, they have a beneficial effect on him.
Peas.
Relations of mutual aid are noted at peas with carrots, turnip, cucumbers. It grows well between the rows of these crops, helping them in turn with the fact that, like all legumes, it enriches the soil with nitrogen. Peas can be combined on the same bed with radish, radish, lettuce, kohlrabi, parsley. Unfavorable combination of peas with onion, garlic, tomatoes. Of the herbs on the pea wormwood bad effect of bitter. There are conflicting opinions about the relationship between peas and potatoes and cabbage: some authors consider these combinations to be quite possible, others regard them negatively.
Cabbage.
For different types of cabbage are characterized by fairly similar preferences for accompanying plants.
The relationship of mutual aid is marked in cabbage with bush beans and celery. These species have a positive effect on each other, and celery, in addition, protects the cabbage from earthen fleas. Dill, planted between the rows of cabbage, improves its taste and repels caterpillars, aphids. For cabbage, the neighborhood of borage is also favorable, it has a good effect on cabbage and drives off snails with its hard hairy leaves. Very good accompanying culture for cabbage - all kinds of lettuce. They also protect it from the earthen flea. Cabbage also needs protection from a variety of cabbage butterflies laying eggs on leaves. This role can fulfill aromatic herbs, their strong smell masking the smell of cabbage. Therefore, it is recommended to plant thyme, sage, rosemary, mint, hyssop, wormwood, chamomile around the cabbage plantings. Leek scares caterpillars scoops. Cabbage can be combined on the same bed with cucumbers, tomatoes, spinach, beets, chard, potatoes, chicory. There is no consensus about its compatibility with strawberries and onions. Of all the types of cabbage, kohlrabi is the most suitable partner for beetroot and a bad neighbor for tomatoes. Cabbage does not fit well with parsley and suffers strongly from closely growing grapes. On leafy cabbage tansy does not work well.
Potatoes.
Favorable cultivation of potatoes in a mixed culture. He is less sick and can grow longer in one place without a decrease in yield. The best partners for potatoes are spinach, string beans and beans. Beans planted between the rows, enriches the soil with nitrogen and repels the Colorado potato beetle. Potatoes go well with cabbage, especially cauliflower and kohlrabi, types of lettuce, corn, and radish. Many authors note that a small amount of horseradish plants planted in the corners of a potato plot has a favorable effect on potatoes. Colorado potato beetle scare catnip, coriander, nasturtium, tansy, marigold. It is not recommended to plant potatoes with celery, sunflower and quinoa have a depressing effect on potatoes.
On the relationship of potatoes with tomatoes, beets and peas, there are opposing views.
Strawberry.
Strawberries are favorably influenced by bush beans, spinach, parsley. Parsley is recommended to plant strawberries in between rows to scare slugs. Strawberries can be combined with garlic, cabbage, lettuce, onions, radishes, radishes, beets. Of the herbs, borage (borage) and sage work well on it. Mulching the soil with spruce and pine needles contributes to a significant improvement in the taste of strawberries.
Corn.
It refers to plants that are very demanding to nutrition, therefore it is advised to alternate blocks of corn with blocks of bush beans; she benefits from the neighborhood of this legume plant, a soil improver. Corn is combined with cucumbers, tomatoes, lettuce, beans, early potatoes. These cultures stimulate its growth. Cucumbers are recommended to be planted around corn plots. In terms of allelopathy, corn is a very friendly plant for many crops. It has a positive effect on sunflower, potatoes, grapes. For her, bad neighbors are celery and beetroot.
Bow.
The classic combination is onions and carrots. These two cultures protect each other from pests: carrots drive away an onion fly, and onions drive away a carrot fly. Due to its compact form, the bow is used as an additional crop, which is located in the rows of the main crop. It is combined with beets, lettuce, cucumbers, strawberries, spinach, radishes, and watercress. On the combination of onions and cabbage there is no consensus. Some authors believe that the onion acts well on cabbage and drives off its pests. The edging of the savory is favorable for the growth of onions, chamomile also has a good effect on it, but in small quantities: approximately one plant per 1 st. m beds. Onions are not combined with beans, peas, beans. The sage neighborhood is unfavorable to him.
Leek.
Companion plants for leeks - celery, bush beans, lettuce, carrots, beets. Leek and celery are connected by mutual aid, therefore it is recommended to plant them in alternating rows.
Perennial onions (chives).
It goes well with tomatoes, celery, lettuce, cabbage, carrots, strawberries, endive, it is not recommended to plant next to peas, beans, beets.
Carrot.
Well makes the neighborhood of many crops, grows well next to onions and spinach, and also goes well with tomatoes, radishes, radishes, chard, chives, garlic, lettuce. But the closest plant for carrots, with which it has a relationship of mutual aid, is pea. Carrots are recommended to surround the following crops to scare away carrot flies: rosemary, sage, tobacco, onions. Hostile herbs - dill, anise.
Cucumbers.
For cucumbers, satellite plants are bush and curly beans, celery, beets, lettuce, cabbage, garlic, onions, chives, radishes, spinach, and fennel. The most favorable impact on cucumbers have beans, so they advise planting beans around a plot with cucumbers. Themselves cucumbers planted around the corn, which greatly benefits from such a neighborhood. Herbs favorable for cucumbers are chamomile, dill, and cucumber herb. The question of the compatibility of cucumbers with tomatoes is not clear. Different authors express opposite opinions on this score: some consider that this is a good combination, others - that this is an absolutely impossible combination. So every gardener will have to find out this question in the most experienced way.
Parsley.
It is a companion plant for many crops: asparagus, roses, celery, leek, peas, tomatoes, radishes, strawberries, lettuce. It is recommended to plant on the edges of the beds with tomatoes. Planted next to the roses, it reduces the number of aphids; planted in the aisles of strawberries - drives away slugs.
Pepper.
The satellite plant is basil, the hostile plant is fennel.
Radish.
It tolerates mixed plantings with tomatoes, spinach, parsley, chard, onions, garlic, cabbage, strawberries, peas. Especially favorable for radish, its combination along with leaf and head lettuce, which protect it from earthen flea. Radish, planted between the spray bean, has a particularly delicate taste and large root vegetables. Beans also protect radishes from pests. Since radish seeds germinate quickly, it is recommended to sow them along with slowly germinating crops (beets, spinach, carrots, parsnips) for marking rows. Radish does not like strong heat, so it is often sown in alternating rows with Chervil, which shading it a little and prevents overheating. Nasturtium and watercress, bordering the beds with radish, improve the taste of radish, giving sharpness, and under the influence of leaf lettuce, it gets a more delicate flavor. Unfavorable for radish neighborhood of hyssop. Some gardeners believe that cucumbers are a bad neighbor for him.
Turnip.
Satellite plant - pea. The turnip, mustard and mountaineer (knotweed) are not favorable for turnips.
Salad.
Cabbage and leaf lettuce (chives) goes well with most garden crops. It is a good companion for tomatoes, cucumbers, curling beans and bush, chives, spinach, strawberries, peas. Its neighborhood is especially favorable for cruciferous vegetables - all types of cabbage, radish, radish, as it scares the earthen flea. And for him, the neighborhood of a bow repellent from aphids is helpful. The lettuce does not like overheating and needs partial shading, but only in partial, therefore close proximity of plants with dense foliage, such as carrots, beets, is unfavorable for lettuce. Lettuce bushes can be placed in different parts of the garden, where it will grow under the cover of taller plants. Especially favorable for him is the neighborhood of chrysanthemums.
Beet table.
Khubmani, who has been testing the compatibility of table beet with other vegetables for many years, claims that five types of vegetables - potatoes, tomatoes, sprouts, beets and spinach - stimulate each other. According to his observations, beetroot also has a very good effect on cabbage of all kinds, lettuce, radishes and radishes, for beets the neighborhood of onions, kohlrabi, spinach, lettuce is especially favorable, in addition, it tolerates joint plantings with garlic, cucumbers, strawberries, root celery . Concerning the incompatibility of beets with other cultures there is no consensus. Some gardeners claim that it grows poorly next to chives, corn and potatoes. Regarding chard, which belongs to the same botanical family as beets, there are also differences. One author argues that he favorably affects the beets, the other - that the vegetables of this family do not tolerate root secretions of each other and therefore they cannot be planted next to each other. There are suggestions that beet root secretions have antibiotic properties and, therefore, replanting it to certain crops, in particular to carrots, may have a healing effect on them. But at the same time, one should not forget about keeping a sufficient distance between plants, as the powerful beet leaves shade the neighboring crops.
Celery.
In celery and cabbage, mutual aid relations are noted: cabbage stimulates celery growth, while celery drives cabbage butterflies away from cabbage. Celery goes well with tomatoes, spinach, cucumbers, lettuce, beetroot. Schnitt onions and bush beans are especially beneficial to it. It is not recommended to plant celery next to corn, potatoes, parsley, carrots.
Tomatoes
Some consider tomatoes as “selfish” plants that love to grow on their own, separate from other crops. But the experience of German and Swiss gardeners says that tomatoes tolerate a good neighborhood of other vegetables and are quite suitable for mixed plantings. They go well with celery, endive, radish, radish, corn, lettuce, cabbage, garlic, carrots, beetroot. Mutual auspicious action was noted with chives, spinach, bush beans, parsley, which are often planted as edging of tomato beds. Tomatoes have a hostile relationship with kohlrabi, fennel and dill. As for the relationship of tomatoes with potatoes and cucumbers, opinions differ, perhaps it depends on the method of planting. Favorable for tomatoes, the neighborhood of the following herbs that improve their taste and condition: basil, lemon balm, borage, chives, marigold, mint, sage, savory. Dioecious nettle growing next to tomatoes improves the quality of tomato juice and prolongs the shelf life of the fruit.
Pumpkin.
Pumpkin wells are recommended to be placed between corn plants. Corn shadows the pumpkin in hot weather and saves it from overheating.
Beans.
Spray beans - the most friendly plant of leguminous vegetables. Relations of mutual help and mutual stimulation are marked for beans and radish, all types of cabbage, corn, celery, cucumbers, potatoes, tomatoes, beets, spinach. Nitrogen-rich root secretions, beans help other vegetables growing next to it. In addition, it is compatible with chard, lettuce, strawberries, leek. Beans do not tolerate the neighborhood of onions, garlic, fennel, peas. Herbs for beans recommended savory, which protects it from black aphids.
Garlic.
Apparently, in Western Europe, he is not very popular, so it is rarely used in mixed plantings. It is known that garlic goes well with tomatoes, beetroot, carrots, cucumbers, strawberries and badly affects beans, peas, cabbage.
Spinach.
Spinach is a favorite member of the vegetable community in Germany and Switzerland. He is credited with many positive qualities, including cold resistance, a short period of ripening, compact form. All this makes it a very convenient culture for consistent and combined plantings. In addition, the roots of spinach, a positive effect on soil properties, and saponin, which is part of its root secretions, stimulates the absorption of nutrients by the roots of vegetables growing next to it. The relationship of mutual beneficial effects is marked for spinach and potatoes, tomatoes, beans, and beets. The most common combinations are spinach with kohlrabi, radish, lettuce. It also goes well with carrots, onions, parsley, watercress, celery, cabbage, strawberries. Spinach has no hostile relations with any plant species.
All the above tips regarding the methods of growing vegetables should be taken as recommendations, and not as absolutely firm rules. Each gardener should check them in his plot with the varieties available to him in relation to local conditions.
The methods described provide for the effective use of the entire area of the garden during the entire summer season. With this method of cultivation, an area of 100 m2 (1 hectare) can feed a family of four.
It is necessary to mention another important council of experienced gardeners. This concerns the compilation of the annual landing plan. It is necessary in order, first, to observe the correct alternation of crops by year in accordance with the rotation rules described above, and second, to plan the subsowing and replanting of some crops to others at the beginning of the year. All this is difficult to remember and keep in mind, especially with a large variety of cultures, so the plan-map of the garden is absolutely necessary.
With the onset of spring warm days, gardeners are preparing for the upcoming season. And here the important point is the planning of sites for planting crops. Before you prepare future beds, you need to decide what will be planted on them. In fact, the question is not so simple as it seems at first glance. The fact is that the planting should be done taking into account their compatibility. Cultures can have a positive effect on each other and protect against pests, and can inhibit development and growth. An inexperienced gardener wonders why every year to plan plots if you can do it once and plant the same vegetables on them year after year. Of course, it is convenient. However, you should know that for each plant requires certain trace elements. This means that if the same vegetable has been planted on the same bed for many years, the soil will be either devastated with the necessary elements or oversaturated with those substances planted in several seasons in a row, the type of culture does not need. And there can not do without a crop rotation. Given the fact that most of the sites have a small area, it is not always possible to make a full replacement. Therefore, many people use mixed landings. But, in order to change the location of planting crops, it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the compatibility of vegetables.
What make beds?
Most of the beds look like rectangular areas on which one type of crop is planted. However, there may be many options. And in order to receive as many crops as possible each time, it is necessary to take into account their compatibility in the garden beds. You can create narrow areas on Mittlayderu, which should be made a large percentage of organic and mineral additives. And you can make the beds multi-tiered, which are difficult to equip, but they are great for growing different crops at the same time. And here you should know the compatibility of crops on the same bed, since their proximity affects each other.
Erecting compacted beds with multiple crops at the same time, you save space and get the opportunity to achieve a good result. It should also be aware that the compatibility of vegetable and ornamental crops will be much better than some fruit ones. It is also worth taking into account the difference in the growing season. In fact, flower-fruit beds are constructed not only for beauty. For example, if you plant marigolds near tomatoes, they will protect vegetable crops from harmful insects. There are also varieties of flowers that are tasty traps for many pests. For example, this could be Nasturtium. Having planted it on the beds, the aphid will only fly over it, forgetting about the vegetable crops.
Compatibility of vegetables and herbs
It has long been proven that such plants are well compatible, they do not compete with each other. Having landed them together, you can not only save space, but also diversify the diet of your table. Herbs planted with fruit crops, will protect them from insects and provide vegetables with exquisite taste. Next to the beans is to plant rosemary, which will save it from beetles. Thyme is sown with cabbage, which will protect the crop from harmful insects. Ray and garlic will save vegetable plants from aphids. The marigolds and oregano can become the protection of the fruit plot from pests. Any summer resident, should know about the compatibility of vegetables and greens in the garden.
Early spring vegetables (for example, radishes), as well as fast-growing lettuce should be planted between melons and pumpkin. As long as these crops strengthen and grow, the radish will ripen and will be torn off. Spinach and other shrubs are planted among tall plants (corn and others), which will protect the greens from the scorching sun. Next to the corn, you can also plant sunflowers. These two cultures do not interfere with each other and can freely coexist.
Now about the compatibility of various vegetables in the garden
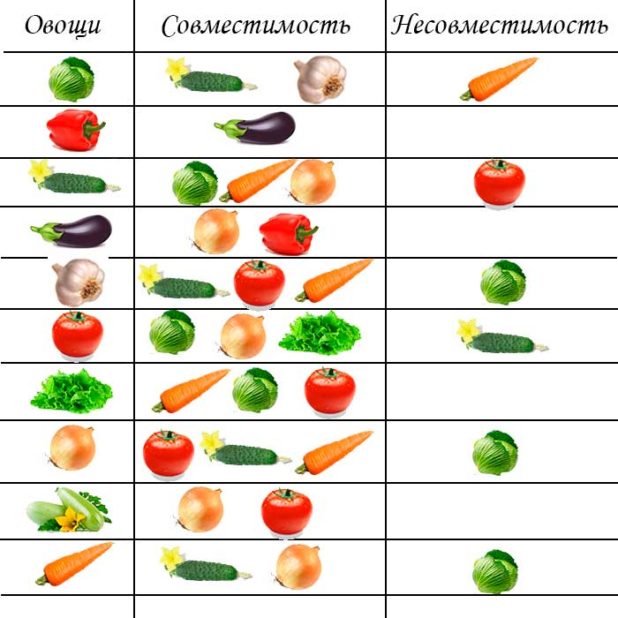 Many gardeners do not like to plant peas for its property to dissolve tendrils that cling to all plants. But, if you plant peas together with corn, the plant will become a good support for powerful trunks, it will not need to be tied up, and you will be able to get two crops from one bed. The bed can also be sown at the same time around the perimeter of carrots or beans, radishes, lettuce, turnips or parsnips. Peas can still be combined with cucumbers. A good neighborhood will be peas with melons and eggplants. Very often it is planted on a potato bed, since the root system of peas is able to provide the soil with essential microelements. Do not plant peas next to garlic and onions.
Many gardeners do not like to plant peas for its property to dissolve tendrils that cling to all plants. But, if you plant peas together with corn, the plant will become a good support for powerful trunks, it will not need to be tied up, and you will be able to get two crops from one bed. The bed can also be sown at the same time around the perimeter of carrots or beans, radishes, lettuce, turnips or parsnips. Peas can still be combined with cucumbers. A good neighborhood will be peas with melons and eggplants. Very often it is planted on a potato bed, since the root system of peas is able to provide the soil with essential microelements. Do not plant peas next to garlic and onions.
Carrots useful to plant on the edge of the plot next to the peas and tomatoes. Also this root can be placed with such herbs as lettuce and sage, rosemary and onions. When making precast beds with greenery and fragrant foliage, you can sow carrots on the edges. You can not plant carrots next to parsley and dill. They will negatively affect the development and growth of root crops.
Onions batun is the first source of vitamins in the spring, so it is grown in their summer cottages, most gardeners. This plant is friendly with many garden crops: bell pepper, beetroot, carrots, tomatoes, broccoli, lettuce. Onions coexist well with cabbage, potatoes, spinach, but do not like being next to sage, beans, peas.
A capricious culture is Bulgarian pepper, which grows much better in the southern regions than in the middle territorial zone. The situation can be corrected if the Bulgarian pepper is planted next to the tomatoes. But together with the beans it can not be grown. To compatibility of vegetable crops in the beds was more suitable, should be planted fragrant herbs and greens. At the same time on the site can grow several different herbs (maximum 10). Pepper will comfortably grow with onions, basil, coriander, spinach.
As a great source of vitamins, lettuce has a beneficial effect on many of the vegetables that grow with it next door. Among them are beets, asparagus, tomatoes, sunflowers and others. Gardeners with experience advise to plant lettuce with carrots, Brussels sprouts and cabbage, cucumbers, corn. Among other things, lettuce can save liquid, as it spreads with a curly low carpet and does not allow moisture to evaporate quickly. This neighborhood is also popular with cucumbers. On one bed you can plant various crops in several ways, taking into account, if you follow some rules. If the bed is a plot on the plane, then in addition to the compatibility of the plants, attention should be paid to the size of the planted crops. In the center it is better to have high plantations (sunflowers, cucumbers, tall tomatoes). Closer to the edge they leave room for eggplants, onions, and peas. You can sow corn, plant peas on it, and place lettuce around it. All cultures are well compatible.
Usually, most of the garden is potato. Before planting, you should think in advance about the plants that you plant next. A good choice will be peas and beans, which are able to enrich the land. You can plant in the neighborhood a family of legumes. Potatoes will be comfortable next to corn, broccoli, white cabbage, eggplants, lettuce, garlic, onions. You should not plant potatoes next to cucumbers, melons, zucchini, tomatoes, sunflowers. The harvest will be better for those who placed these crops further away from each other.
Eggplant gladly coexists with many vegetables. Having no enemies, he is able to be friends with any culture, thereby complementing it. But if you focus on the growth of the plant itself, it is best to plant this plant near potatoes, peas and legumes. Eggplant culture with leafy plants such as lettuce, basil, spinach will be just as comfortable.
It becomes interesting to many, in what sequence should garden crops be planted in order to get the maximum yield from the garden?
The scheme used by German farmers in planting garden crops
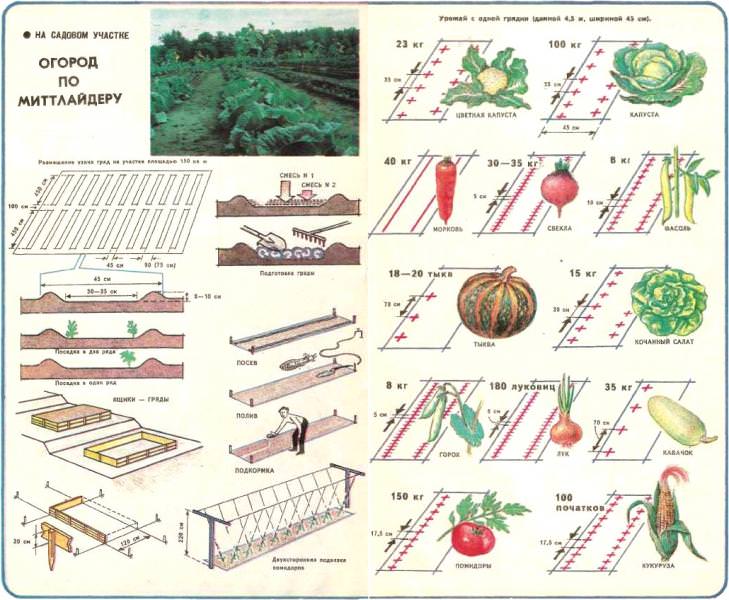 When planting potatoes, they make a wide bed (about a meter), with the roots in the center of the garden. At the same time, late varieties are planted in one row, and early - in two. On one side of the culture, one line is planted with cauliflower, head of lettuce, kohlrabi, on the other - eggplant. You can alternate vegetables in the same row. Spinach is sown in two rows on the edge of the plot. Everything else is free space, which can be filled on the garden bed with radishes and leafy lettuce. Crops are harvested as they ripen, starting with green lettuce. It appears before everyone else, and, pritenyaya other plants, protects them from the scorching sunlight. After you can harvest spinach and then radish. A month later, cauliflower and heading lettuce ripen. Gradually, the bed is released and the potato with eggplant is left with more space for full ripening.
When planting potatoes, they make a wide bed (about a meter), with the roots in the center of the garden. At the same time, late varieties are planted in one row, and early - in two. On one side of the culture, one line is planted with cauliflower, head of lettuce, kohlrabi, on the other - eggplant. You can alternate vegetables in the same row. Spinach is sown in two rows on the edge of the plot. Everything else is free space, which can be filled on the garden bed with radishes and leafy lettuce. Crops are harvested as they ripen, starting with green lettuce. It appears before everyone else, and, pritenyaya other plants, protects them from the scorching sunlight. After you can harvest spinach and then radish. A month later, cauliflower and heading lettuce ripen. Gradually, the bed is released and the potato with eggplant is left with more space for full ripening.
Using this scheme, you can combine different vegetables when planting. Over time, you will gain personal experience, and will begin to plant crops at their discretion.
Planting peanuts
In the gardens of our compatriots rarely be seen such a plant, and in vain. Growing it is not at all difficult, but as a result there will be an opportunity to harvest a nutritious product. It should be said that peanuts in the garden live not with all crops, but it will be good to coexist with cucumbers, corn and any legumes.
Recently, corn is not often planted in gardens. But it is impossible not to notice that the boiled vegetable is endowed with good taste and is enjoyed by adults and children. But this is not all its advantages. Besides the fact that it is endowed with useful microelements, it can be used as a natural support for cucumbers. Considering that this crop is bypassing the aphid, cucumbers will be protected from pests. Along the perimeter of the bed with corn, you can plant curling legumes: peas, beans. Corn also perfectly coexists with potatoes, melons, sunflowers, and zucchini. Do not plant tomatoes next to it.
Growing up, the bushes of tomatoes are trying to pick up all the space next to them, so they are not supportive of the neighborhood of other crops. Planted them in different ways. For example, a high mound is arranged in the center of the garden. On this hill they sow: basil, asparagus, lettuce, dill, parsley, onion, spinach, thyme. Well coexist tomatoes with legumes. Therefore, between the rows should be planted beans. A good option for planting will be melon and carrots, which can be grown in the nearest area. No need to have corn and cabbage next to tomatoes.
Cabbage has many varieties. Everyone grows in his garden a more beloved variety. Most often planted color and white cabbage. An unskilled gardener may think that it will be convenient to plant them side by side and you can first remove the color caput that ripens earlier, and then the white one. However, it is better not to combine these two types of one crop, and when making a common garden bed, plant cucumbers, beans, and celery next to the cabbage. Well I will adjoin around the cabbage aromatic herbs: sage, thyme, spinach, onions, dill. They will save her from harmful insects. Between cabbage heads you can grow radishes and greens. But in this case, it is not necessary to plant cabbage very thickly.
Cauliflower does not approve of the neighborhood with its cousin, but gets along well with beets, beans, cucumbers, celery, sage, thyme. Also, do not plant strawberries and tomatoes next to it. Does not like to be on the same bed with broccoli cauliflower, but goes well with the above cultures.
More friendly is the Brussels sprouts, which may be adjacent to other species. This variety does not tolerate only tomatoes and cruciferous. Often in the garden with Brussels sprouts you can see lettuce, dill, spinach, radishes, sage, turnips.
When planting cucumbers, make sure that their location is far from melons, potatoes, fragrant herbs. For cucumber, you should create a warm high bed, where you can plant beans, peas, lettuce, corn, radishes, lettuce next to them. Planting can be done according to the following scheme: corn is sown in the center, which will support cucumber, as well as peas and beans. They can, by the way, be planted both mixed and in one hole. The edges of the beds can be taken under the radish and lettuce, which quickly ripen.
Combination incompatible
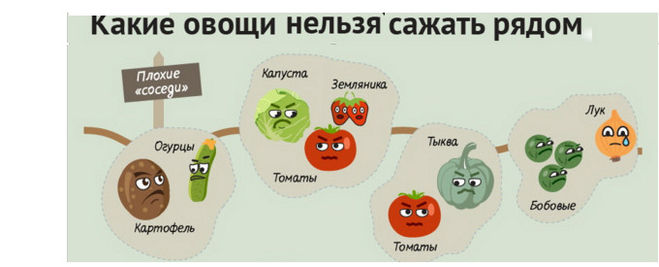 If you are going to plant plants in a greenhouse, where every piece of land is valued, then the issue of crop compatibility will be very relevant for you. For all plants in greenhouse conditions, you need to create a comfortable environment. To place poorly compatible fruit crops in a greenhouse, film curtains are used. With their help, space is divided into sections, thereby creating a peculiar climate for plants.
If you are going to plant plants in a greenhouse, where every piece of land is valued, then the issue of crop compatibility will be very relevant for you. For all plants in greenhouse conditions, you need to create a comfortable environment. To place poorly compatible fruit crops in a greenhouse, film curtains are used. With their help, space is divided into sections, thereby creating a peculiar climate for plants.
In conclusion, it would not be superfluous to note that creating mixed beds can not only save space, but also increase the yield. Just the right location of crops saves resources by spending less fertilizer and water.

