Properties and application of digitalis
Despite the fact that it is easy to recognize digitalis (Digitalis), this genus of the Norichnik family is quite diverse. Currently, there are about 35 species and subspecies of this plant. Four of them grow only in the Caucasus, and two - in Western Siberia. Other types of digitalis are found in Europe, East Asia, and North Africa. There are types of foxglove represented by perennials, only biennial plants are part of the others. And those and others bloom in June and bloom until early September.
According to the International Genetic Resources Network, there are 12 types of digitalis:
1. Nyperyanka rusty (D. ferruginea);
2.Napristum grandiflora (D. grandiflora);
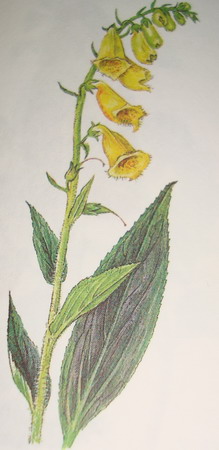
3.Neapolla woolly (D. lanata);
4. Nappetis smooth (D. laevigata);
5.Na pry yellow (D. lutea);
6. Nepristous veins (D. nervosa);
7.Napristina unclear (D. obscura);
8.Naprestyanka small-flowered (D. parviflora);
9.Napristine purpurea (D. purpurea); photo\u003e
10.Napristwort flowers (D. viridiflora);
11. Spanish peasant (D. thapsi);
12.Nepechenian mariana (D. Mariana).
For decorative floriculture, digitalis purpurea with a wide variety of varieties and hybrids is of the greatest interest. A separate page of our site is devoted to the story about it (). And now get to know other significant types of digitalis.
 Plants of this species are perennials. They are distributed almost throughout southern Europe, the Caucasus, Iran and Turkey. The rusty foxglove in nature occupies several belts - from the lower ones, where there are forests and forest-steppe, to alpine meadows located at an altitude of 1600-1800 meters above sea level. The root of her horizontal, which must be considered when landing. Stems erect, with a height of 40 centimeters to one and a half meters. The pubescence of the stems is weak or completely absent. The size of the flower brushes depends on the height of the plant. A half meter brush reaches 60-70 centimeters. They are formed by yellow-brown or red with purple stripes, dots and veins, flowers a little more than 2 centimeters long. They have a lighter bell-shaped top and a darker shovel-like bottom. As a rule, the “spatula” is densely pubescent. It is a kind of landing site for insects, before they crawl into a flower. The foxglove rusty is considered not as aesthetically beautiful flower as foxglove purple, and is valued more than a medicinal plant. But if she takes the right place in the flower arrangement, it will look very impressive. This is best done if the rusty foxglove is planted in the center of the flowerbed, and not singly, but in a group, so that there are many floral “candles”. You can plant sredneroslye and low flowers around. Especially beautiful redheads of reddish rusty look on a blue and white background.
Plants of this species are perennials. They are distributed almost throughout southern Europe, the Caucasus, Iran and Turkey. The rusty foxglove in nature occupies several belts - from the lower ones, where there are forests and forest-steppe, to alpine meadows located at an altitude of 1600-1800 meters above sea level. The root of her horizontal, which must be considered when landing. Stems erect, with a height of 40 centimeters to one and a half meters. The pubescence of the stems is weak or completely absent. The size of the flower brushes depends on the height of the plant. A half meter brush reaches 60-70 centimeters. They are formed by yellow-brown or red with purple stripes, dots and veins, flowers a little more than 2 centimeters long. They have a lighter bell-shaped top and a darker shovel-like bottom. As a rule, the “spatula” is densely pubescent. It is a kind of landing site for insects, before they crawl into a flower. The foxglove rusty is considered not as aesthetically beautiful flower as foxglove purple, and is valued more than a medicinal plant. But if she takes the right place in the flower arrangement, it will look very impressive. This is best done if the rusty foxglove is planted in the center of the flowerbed, and not singly, but in a group, so that there are many floral “candles”. You can plant sredneroslye and low flowers around. Especially beautiful redheads of reddish rusty look on a blue and white background.
Digitalis large-flowered

![]()
This spectacular flower grows in East Asia and in almost all of Europe, with the exception of the most northern regions. Prefers foxglove large-flowered forest edges and felling. Sometimes it can be seen on stony slopes among shrubs. The root of this species is fibrous, strongly branched. Stem height of one and a half meters or a little more, and below, and pubescent above. It is straight in configuration, only slightly branched at the bottom. The leaves of the large-flowered foxglove are lanceolate, at the bottom are large, have fine teeth on the edge and hairs on the underside. The middle leaves are more oval, mostly without denticles, “sitting” on the stem without petioles. The upper leaves are small, also sessile, located near the pedicels. The foxglove large-flowered got its name due to its large beautiful flowers. They look like bells and are somewhat larger in magnitude than all the other foxgloves. So, the length of the petals of its corolla is about 4 centimeters, and the diameter is about 2. Their color ranges from pale yellow to deep yellow with dark dots inside. But the brush inflorescences in this type of digitalis is not very large, only about 25 centimeters. The foxglove grandiflora blooms in the second year after planting. In the first year, it forms only a lush rosette of leaves. This gorgeous flower invariably attracts rave eyes. It looks great in the center of the flower beds, surrounded by more stunted flowers. Also the foxglove large-flowered can decorate the facade of the house, if you plant it near the wall or near the porch. The famous late-flowering hybrid of digitalis, large-flowered and woolly - “John Innes Tetra” 60 cm high with flowers of yellow-orange color, as well as a new  sterile hybrid "Goldcrest" of the same external characteristics.
sterile hybrid "Goldcrest" of the same external characteristics.
The name of the species received for the dense pubescence of the stem, upper leaflets and sepals. Digitalis woolly grows in Moldova, Romania, Hungary, Greece, Turkey, Ukraine, Yugoslavia and Bulgaria. This species is considered endangered and is listed in the Red Book. In many countries, woolly foxglove is grown in specialized farms as a valuable medicinal raw material. In terms of its chemical composition, it practically does not differ from other foxgloves, however, preparations from it are better absorbed and have a less pronounced cumulative (accumulating poisons in the body) effect. Digitalis woolly is a medium high perennial. She grows up to 70-80 sentiments. Its stem and leaves have a dark green or dark purple color. The lower leaves are up to 20 centimeters long, the average is 10-12 centimeters, the upper leaves are up to 4, and the uppermost ones are very small, like all foxgloves, bracts. The foxglove is woolly, just like the foxglove is rusty, it does not have a special aesthetic beauty. The flowers of these two species are slightly similar, both have a “spatula” - a pair of long, fused petals in the lower part of the corolla. Only if the rusty fossil spatula is dark, then woolly is light, much lighter than the other petals. There are individuals with quite  white spatula. Dots and stripes on it are rare, mostly they densely cover the inner surface of the bell-shaped corolla. Its color varies from pink to light yellow or green-yellow. The lower flowers are 3 cm long and the upper ones are about one. The floral brush of the woolly foxglove is not very large, pyramid-shaped, the flowers on it are planted rather thickly. The foxglove woolly blooms in June, July and August.
white spatula. Dots and stripes on it are rare, mostly they densely cover the inner surface of the bell-shaped corolla. Its color varies from pink to light yellow or green-yellow. The lower flowers are 3 cm long and the upper ones are about one. The floral brush of the woolly foxglove is not very large, pyramid-shaped, the flowers on it are planted rather thickly. The foxglove woolly blooms in June, July and August.
This view is appreciated for its beauty. It is rarely mentioned in medical reference books. You can meet the plant in the forests and forest-steppes of Central Europe. Digitalis yellow looks very impressive. Its upright stems - candles are decorated with pyramidal racemes inflorescences with pale yellow or rich yellow flowers, like bells. In some varieties, the corolla has a small pointed tongue in its lower part, and some do not. The leaves of yellow foxglove are smooth, the stem grows up to 1 meter, and the flower brush is up to 50 centimeters long. Currently, breeders bred low-growing varieties of yellow foxglove. They are grown in pots. Low-growing varieties bloom in the first year after planting. Digitalis yellow has been used by gardeners since the late 16th century. In the landscape design with the right selection of a number of growing crops, it looks like a king. This species blooms from early July to late August. The most popular variety is Gelb Janus, which some people call Telb Janus. A wonderful hybrid “Glory of Roundway” with small narrow-bell-shaped flowers of pale pink color was created on the basis of yellow foxglove. Flowers are collected in a dense brush, plant height up to 120 cm.
Digitalis ciliated (Digitalis ciliata)
 This kind of foxglove is not as popular as the others. You can meet him in the lowlands, and at a height of two and a half kilometers above sea level. The stalks of the ciliate foxglove are low, only up to 60 sentiments, but several of them grow from one root, all of about the same height. The leaves of the plant have sharp tips, and at the edges of the notch. The flower brush is small (up to 10 centimeters), the flowers are whitish-pinkish, resembling bells, not large. It is used digitalis ciliated mainly as a honey plant and a medicinal plant. In decorative compositions is very rare.
This kind of foxglove is not as popular as the others. You can meet him in the lowlands, and at a height of two and a half kilometers above sea level. The stalks of the ciliate foxglove are low, only up to 60 sentiments, but several of them grow from one root, all of about the same height. The leaves of the plant have sharp tips, and at the edges of the notch. The flower brush is small (up to 10 centimeters), the flowers are whitish-pinkish, resembling bells, not large. It is used digitalis ciliated mainly as a honey plant and a medicinal plant. In decorative compositions is very rare.
Important! Digitalis grandiflora, rusty, woolly, yellow, ciliary and all other types of digitalis are poisonous. This should be taken into account when contacting the plant.
enters into number of family under the name nornichnikovy, in Latin the name of this plant will sound as follows: Digitalis grandiflora Mill. (D. ambiqua Murr.). As for the family of the large-flowered foxglove, in Latin it will be like this: Scrophulariaceae Juss.
Description of Digitalis grandiflora
The large-flowered foxglove is also known under the following popular names: foxy foto, dzvonchik, styagach, sbanochka, creeping flowers and wine glasses. Digitalis grandiflora is a perennial herb, the height of which can reach one hundred twenty centimeters. Such a plant will be endowed with a fibrous root system, which will form in the first year of the outlet, consisting of large basal leaves. After some time, the stem will appear, which will carry on its top a brush of rather beautiful, large flowers of irregular shape, painted in yellow tones. The leaves, calyx, upper part of the stem, pedicels and the corolla of this plant will be covered with glandular hairs. The leaves of the foxglove large-flowered are elongate-lanceolate and pointed, they are endowed with short broad petioles. The flowers of this plant will be drooping in a small sparse brush. The length of the foxglove of the large-flowered foxglove will be about four to seven millimeters; they will be endowed with sharp and lanceolate lobes. The rim of this plant will be tubular-bell-shaped and large, its length will be about three to four centimeters, it is painted in yellowish tones and from the inside is endowed with brownish veins. The fruit of the foxglove grandiflora is a bilocular ovoid box, the length of which is about eight to fourteen millimeters. The seeds of this plant are tetrahedral and prismatic, and their length will be about one millimeter.Digitalis grandiflora will bloom in July, while seed ripening will occur in August. Under natural conditions, this plant is found on the territory of Western Siberia, the European part of Russia, as well as the northern and western foothills of the Altai. It is noteworthy that the whole plant will be poisonous.
Description of the medicinal properties of digitalis grandiflora
Digitalis grandiflora endowed with very healing properties, with the medicinal purpose of using the leaves of this plant.The presence of such valuable healing properties should be explained by the content of flavonoids, anthraquinones, mineral salts, iridoids, traces of alkaloids, tannins and the following cardiac glycosides: hypoxin, hypotension of digitoxin and purpureoglycoside A, B, C in the leaves of this plant.
Drugs created on the basis of a large-flowered foxglove will contribute to the normalization of biochemical processes and improve the functions of the neuro-muscular system of the heart. As a result, there will be an increase in blood volume, which will flow over a certain period of time from the venous system to the arterial system. Actually, this is how the conditions for the rest of the heart muscle will arise.
Preparations based on this plant are indicated for use in acute and chronic heart failure, and they will most favorably affect the body when the heart rhythm is disturbed.
However, we should not forget that the digitalis grandiflora is a poisonous plant, so long-term use of such drugs can lead to poisoning: it is recommended to use particular caution when handling this plant.
Title: Digitalis grandiflora.
 Latin name: Digitalis grandiflora Mill.
Latin name: Digitalis grandiflora Mill.
Family: Nornichnikovye (Scrophulariaceae)
Lifespan: Perennial.
Type of plant: Herb.
Barrel (stem): Upright.
Height: 30-80 cm
Leaves: Oblong-ovate, pointed, with uneven edges. Length 5–20 cm, width 2–7 cm. Central and lateral pubescent veins protrude from the underside without forming a mesh, green leaves on top, light green on the bottom.
Flowers, inflorescences: Thimble, light yellow.
Fruit: Two-box boxes.
Ripening time: June August.
Smells and tastes: The smell of the plant is weak.
Collection time: Leaves harvest stem (in plants of the second and next years of life) in June-July, and basal (in plants of the first year of life) in August-September.
Features of collection, drying and storage: Immediately after harvesting, the leaves are dried in the shade by a draft or in a dryer at a temperature of 55-60 ° C. The output of dry leaves 19-20%. Ready raw materials should be stored in a dry room without access of sunlight. Shelf life - 2 years.
Spread: In Russia, the large-flowered foxglove is found in the European part (Ladoga-Ilmensky, Upper Volga, Volga-Kama, Volga-Don and Zavolzhsky regions), in the Caucasus and in Western Siberia (Obsky and Upper Tobolsk regions); in Ukraine - in Polesie, in the southern part of the Forest-Steppe and in the Carpathians.
Habitats: Grows in mixed and deciduous forests, among bushes.
Medicinal parts: Leaves.
Useful content: Digitalis leaves contain cardiac glycosides, steroid saponins, flavonoids, choline, organic acids and other substances.
Actions: The main active ingredients of the foxglove are cardiac glycosides, which strengthen and simultaneously reduce the number of contractions of the heart muscle, which contributes to its relaxation and more intensive blood circulation. This causes an increase in the volume of blood pushed into the aorta, the acceleration of blood flow and a decrease in venous pressure.
Due to the normalization of blood flow and dilatation of the renal vessels, urination increases markedly, leading to the disappearance or reduction of edema.
For their physicochemical properties, digitalis glycosides belong to the group of lipophilic glycosides. They are not destroyed in the gastrointestinal tract, are well absorbed and quickly interact with plasma proteins. If the drug is administered rectally, the effect begins to appear after 2-4 hours, reaches a maximum after 8-12 hours, and completely stops after 14-21 days.
Strengthening the excretory function of the kidneys has little effect on the excretion of glycosides, since they are excreted in the urine in small amounts. After absorption in the intestine, a significant amount of them are deposited in the liver and then, secreted along with the bile, re-absorbed. The simultaneous presence of these properties gives the full right to call the digitalis " the king of heart means».
The indications for prescribing digitalis purpurea are chronic heart failure of various origins, paroxysmal tachycardia.
Use Restrictions: PREPARATION PRODUCTS HAVE A HIGH CUMULATIVE ABILITY AND TOXICITY; IT CAN BE TAKEN THEM ONLY ON APPOINTMENT OF DOCTOR . THEIR APPLICATION IS CONTRAINDICATED IN ORGANIC CHANGES IN THE HEART, IN PARTICULAR IN THE CASE OF CARDIUM MUSCLE DIVISION AND EXPRESSED ATHEROSCLEROSIS, AND ALSO ENDOCARDIT WITH STANDING FOR EMBOLISM.
Dosage Forms:
Leaf powder . Take adult patients to 0.05 - 0.1 grams 3-4 times a day. After achieving the desired effect - slowing the pulse, increasing urination, reducing shortness of breath - supportive individual dose is prescribed. For children, the dosage is prescribed by a doctor. In case of impossibility of oral administration, the drug is administered rectally in candles.
Infusion of leaves foxglove : 0.5 - 1 gram of raw material per 180 ml of water. Take 1 tablespoon 3-4 times a day.
Infusion of leaves for children . 0.1 - 0.4 grams of leaves per 100 ml of water. Give 1 teaspoon to 1 dessert spoon 3-4 times a day. In case of impossibility of oral administration, the drug is administered rectally in candles.
Recover!
“Fox gloves”, “fairy house”, “music” and even “bloody fingers” and “dead man's bells” - which only the names for digitalis didn’t tell ordinary people the imagination, supported by ancient folk tales and beliefs.
Perhaps a certain amount of superstition crept into the minds of the scientists who gave the plant the scientific name. The Latin name Digitalis comes from the word digitus - “finger”, and the Russian name comes from the word “thimble”, denoting an item that no one had done in the old days when there were no sewing machines. The foxglove flowers are really the shape and size ideal for so that they can put a finger.
DON'T ANGRY A FAIRY!
“Fairy house” is a name that, obviously, was given to the plant by children. Many of them like to play with these unusual colors. In addition, it was common belief that if you disrupt or damage a foxglove flower in which the fairy hides, left without a house, she can get angry and send misfortunes to the destroyer. In the Middle Ages, the popular rumor assigned another nickname to the plant - “Fox Gloves”. It was believed that the foxglove lends its flowers to foxes - on its paws so that they can sneak up silently on the hen-houses.
FROM WHITE TO PURPLE
In the first year of life, the plant forms a rosette of long basal leaves and only in the second year it accumulates enough strength for the development of the leafy stem and flowering. In the foxglove of the large-flowered flowers, as in all members of this botanical group, horizontally deflected, drooping, are collected in the inflorescence brush; corolla - fused, bell-shaped, slightly irregular in shape. The color of the foxglove flowers varies greatly - from various purple and purple appendages to light gray and pure white. The inner side of the lower lip of the corolla is often decorated with spots and stains of contrasting colors. For the flowers of foxglove large-flowered flowers, lemon-yellow tones and brownish-brown netting of the pharynx are characterized by varying degrees of intensity. The size of flowers of foxglove large-flowered - 3-4 cm in length and 1.5-2 cm in width. The plant blooms in June, numerous small, up to 1 mm in length, prismatic tetrahedral seeds in fruit-boxes are formed in August-September. The foxglove large-flowered mainly reproduces by seeds. It grows singly, does not form thickets. Prefers to settle on acidic soils, under the canopy of deciduous and coniferous-deciduous forests. Included in the regional Red Books of the Altai Territory, Kursk, Kurgan, Novosibirsk, Smolensk, Sverdlovsk, Tver, Tyumen regions, the Republic of Tatarstan, Udmurtia.
HEART AND POISTS
Digitalis refers to poisonous plants, because it contains cardiac glycosides - digitoxin, digitalin, digitonin, and others. They significantly affect the work of the heart, slowing the rhythm of its contractions. The impact of these substances on the human body can lead to dramatic consequences. For this, in Scotland, for example, the plant is called "dead man's bells." However, it is known and especially vividly supported by research in recent years that even toxins of deadly snakes are useful in treating cancer and other diseases, that any poison can be a medicine, and any medicine can become a poison. Everything depends on the quantity and the situation in which these substances are used. The foxglove extract has been known in scientific medicine since the end of the 18th century. It is used in the treatment of severe conditions such as congestive heart failure. This ancient folk remedy received official recognition thanks to the English doctor U. Visinging, who found out: in small doses, the foxglove extract is curative, and only in large doses it is poisonous. In 1896, digitaloxin was isolated from the leaves of digitalis, and in 1930 - digoxin. Subsequently, based on them were created drugs for the treatment of arrhythmias.
RELATIVE PARTIES
The botanical genus Digitalis is not so great: taxonomists have about 20 species, native to Western and South-Western Europe, Western and Central Asia, and North-West Africa. Until recently, the foxglove was attributed to the family of norichnikovyh, and only scrupulous phylogenetic studies conducted ten years ago made adjustments to the definition of the belonging of this plant to this taxonomic rank. Now they are all considered representatives of the plantain family.
A BRIEF DESCRIPTION OF
Kingdom: plants
Department: angiosperms
Class: dicotyledonous
Order: Clear Flowers
Family: plantain
Genus: foxglove
Kind: foxglove large-flowered
Latin name: Digitalis grandiflora
Size: height - 40 - 120 cm
Life form: herbaceous perennial
Lifespan: 3 - 5 years
author Irina Tugay, author photo
Digitalis is distinguished by the unusual beauty of numerous graceful flowers in a long racemose inflorescence.
It is not surprising that they are very popular with gardeners and are often grown in gardens. Moreover, these flowering plants are great for decoration.
Natural foxglove types are generally modest in color. But through the efforts of breeders, varieties of foxgloves with various colors of large flowers were created. This allows you to create a bright elegant curtain of foxgloves of various colors or add foxgloves to fashionable ones.
Another useful quality of digitalis is pronounced medicinal properties. And although all types of digitalis are poisonous, some of them belong to valuable medicinal plants, effectively relieving swelling and heart diseases.
Variants of the names of plants and legends about digitalis
Digitalis was first described in the German herbalist in 1543, where the Latin name of the plant Digitalis (digitalis ("finger")) is given.
Later, this name was rethought as a “thimble”, according to the characteristic shape of flowers.
In English, the foxglove is called Finger-flowerwhich literally translates as "finger flower" as well Yellow foxglove ("yellow fox glove").
Zoski Veras has Belarusian name of foxglove palechnik.
And in the Annenkov dictionary contains local names foxglove: yellow bells, mountain buttercupand stone buttercup (the last names from the Perm province).
There is a German legend about an orphan, who inherited her thimbles from her deceased mother. The evil stepmother took them away from the girl and secretly buried them in the garden, but in the spring, flowers grew in that place, in which the orphan recognized her thimbles. However, the hate-fed stepmother, the flowers of beautiful plants were poisonous.
In Bulgaria, toxic digitalis is impolitably called biasna Treve, bass saw, besnik.
In the language of flowers, foxglove denotes insincerity - apparently, for a dangerous combination of the beauty of a flower and its virulence.
Digitalis grandiflora

Digitalis grandiflora(Digitalis grandiflora) - a large perennial plant of the family n orychnikovyh (Scrophulariaceae).
Attractive varieties of this particular type with large flowers are most often grown in the gardens of the world.
Digitalis large-flowered lubit less flat landscapes than the plains of Belarus, so it grows in abundance in the Urals, in the Carpathians and the foothills of the Caucasus. It is also found in Ciscaucasia, Western Siberia, and Asia Minor.
In our country, the large-flowered foxglove is also confined to a certain hillyness and is more often found on higher elevations (Minsk and Novogrudskaya, on the Mozyr range), along forest meadows and among shrubs. We have the northern boundary of the range of this species. Only recently the large-flowered foxglove is excluded from the local Red Book, but it is on the list of plants requiring preventive protection and rational use.
The foxglove of large-flowered, up to a meter in height, grows up from its rhizome several straight strong stems. Large oblong-elliptic leaves are arranged along a non-branching stalk in the regular order.
There is a pubescence on the plant - more on the stems, less leaves and flowers.
In June, large drooping flowers about 5 cm long, gathered in a one-sided brush, appear in the axils of the upper leaves of the foxglove. They are pale yellow in color and are dotted with attractive maroon and brown spots inside. Amusing spots spell out the spellbound insect path into the depths of the flower, to the nectar. This path is covered with outgrowths, insurmountable for bees, but easily crushed by large bumblebees, which produce pollination.
Here's how it is described in Meterlink in the book "The Mind of Flowers": "... Bumblebees, like bears, burst into the tents of Byzantine princesses, hung with silks and pearls, rudely break under the satin sheets of the corolla of a foxglove ...".
If by the end of the flowering of foxglove, which lasts about one and a half months, pollination did not happen, then self-pollination occurs: the flower halo with stamens attached to it detaches from the receptacle and slides down, brushing at the same time the pistil and waving it out with pollen.
The foxgloves have many seeds, they are small and enclosed in numerous bulky boxes. A plant grown from seed blooms in the second year; in the first year, only a basal rosette of leaves is formed.
Digitalis in landscape design and floristics
In the whole guise of digitalis, a certain breed is felt, captivating the nobility of lines and shapes. The unusual configuration of drooping, bloated tubular foxglove flowers attracts glances, bright spotted flowers surprise and fascinate. Susceptible to beautiful gardeners are widely used many cultural varieties of digitalis with large flowers in landscape design.
The foxglove looks especially good in the garden during a single planting or in small groups.
Planting tall flowering foxglove in the background of a flower garden is an excellent background for any lower plants.
Digitalis frost-resistant and drought-resistant. This unpretentious plant tolerates any garden soil, so it does not cause almost any hassle.
But nevertheless, the largest flowers in digitalis are formed under favorable conditions, on loose and fertile loose soil, p.
Growing seedlings for foxglove is not required, its seeds without any pre-sowing treatment sprout perfectly when sown in the spring right in the garden.
The cultivation features of many varieties of digitalis are associated with a two-year cycle of their development. In the first year, a powerful root system is formed and a large rosette of leaves is built up. In the second year after summer flowering, the plant usually dies, if the root growth is not formed.
It is gratifying that some new attractive varieties of foxglove bloom already in the year of sowing.
In favorable conditions of growth, self-sowing of the foxglove is observed, then worries about the reproduction of these plants disappear.
Florists widely use foxglove inflorescences when creating large compositions. Especially often used new unusual varieties with spectacular buds.
Interesting is the Excelsior group of foxglove purpurea (see the title photo). In this group, especially large flowers (up to 8 cm long) sit almost horizontally, densely and evenly girdling the stem of the plant from all sides. These include varieties with a variety of flower color - white, cream, yellow, pink, red, purple.
Among florists and gardeners, the Apricot Sutton variety of purple foxglove (with a one-sided inflorescence of apricot-pink-cream flowers) and many other varieties are also very popular.
Digitalis in medicine
Digitalis is one of the most important plants used in heart failure. Medicinal raw materials are foxglove leaves and various extracts from them.
Most often for medicinal purposes they use the following types:
- (D. grandiflora);
- digitalis red or purple (D. rurpurea);
- digitalis woolly (D. lanata).
Due to the complex positive effects on the patient, the foxglove is called "the queen of heart remedies." Apparently, it is a unique set of toxic substances digitalis gives such an effective effect. Heart plant glycosides change all the basic functions of the heart - systole, diastole, stroke volume.
The treatment with foxglove preparations is carried out only under medical supervision - after all, the plant is very poisonous, and its glycosides have cumulative properties (they accumulate in the body, their destruction occurs slowly). Therapeutic doses for prolonged use or exceeding the dose can cause toxicosis and cardiac arrest. Therefore, the foxglove is alternated with other cardiac means.
Antidotes in case of digitalis poisoning are caffeine, atropine, potassium chloride.
The amount of glycosides in the foxglove leaves varies depending on various factors (place of growth, time of collection, drying, etc.), which requires constant monitoring of medicinal raw materials. Therefore, for medical purposes, the foxglove is specially cultivated, most often the foxglove is purple.
There is evidence of scientists that digitalis was used as a medicinal plant more than 4 thousand years ago.
In folk medicine in Western Europe, the foxglove was used before the aforementioned herbalist of the 16th century.
The effects of foxglove on heart diseases were studied, among others, by Erasmus Darwin (grandfather of Charles Darwin).
Paul Sedir reported on the preparation of decoction of foxglove leaves used to strengthen and grow hair.
Digitalis preparations act on the body of different people with varying degrees of intensity, having a greater impact on the elderly and men.
Under the influence of foxglove preparations, there have been cases of a change in the color perception of a person: with discoloration of paints and with a shift to a yellow-green-blue range. The latest paintings by the famous artist Van Gogh, who took digitalis at the sunset of life, have just such a prevailing flavor.
Digitalis grandiflora was included in the first edition of the Russian Pharmacopoeia, and to this day continues to be in its list.
Irina Tugay (Republic of Belarus)
fito.of.by
To the website
on site
|
|
Weekly Free Website Digest Site
Every week, for 10 years, for 100,000 of our subscribers, a wonderful selection of relevant materials about flowers and garden, as well as other useful information.
Subscribe and get paid!

