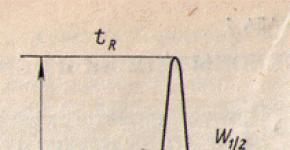Installation of a pump for a warm water floor. Circulation pump for heated floors: calculation, selection, installation
The design of heated floors uses circulation pumps that are not fundamentally different from similar products that are installed in heating systems where radiators are installed as heating devices.
In some cases, a water heated floor is installed without a pump. But this option is discussed in another article.
Determining pump markings
When choosing a circulation pump for a warm water floor, you should know that the markings on it are of great help. It is placed immediately below the model name and looks like two numbers written with a dash. For example: 32 – 60.
The first indicates the connection size, 32 mm (or 1” ¼). Typically, a pump for a warm water floor is supplied complete with union nuts for its installation/disassembly. This is their size.
The second informs about the height to which the pump can supply water. In this case, it is equal to 6.0 m water. Art. (0.6 atm.). There are models that are designed for larger and smaller values of this indicator.
A pump for a water floor is selected taking into account the results of a previously completed hydraulic calculation of CO with heated floors. Information about the load value at specified parameters is applied to the product body.
The pump for a warm water floor is made with three switching modes, differing in performance (i.e., the amount of liquid that the pump is able to pump in an hour).
The third is maximum productivity. In each of the indicated positions, the pump consumes current, the value of which is indicated on the plate.
Types of pump designs
In terms of their design, the circulation pump for a warm water floor of any model is practically no different from each other, with the exception of appearance and control. German pumps produced by Grundpos and Wilo have proven themselves to be the most reliable. The latter are more affordable in price. The above-mentioned pumps belong to a series of household pumps that are installed in residential premises and private houses.
In addition, there is a pump for water floors for industrial use. Their main difference is that they are double and are fixed not with nuts, but with special flanges, the diameter of which exceeds 50 mm.
There are also models such as a pump for warm water floors with a thermostat.
Pumps positioned as products for underfloor heating have a three-way valve. When choosing this option, it should be taken into account that valve designs are not equivalent in performance. Some of them have a specified rate not exceeding 2.5 cubic meters per hour, which does not allow them to work normally if the floors are laid over an area of more than 50 sq.m. Moreover, they are not adjustable. Therefore, you can install them only if you have a small volume pump for a warm water floor.
There are valves with control devices that are controlled manually and by a special servo drive in automatic mode. Their consumption is 4.0 cubic meters/hour and they work on areas up to 150 sq.m.

The pump for a warm water floor has a fairly simple design. The product body and motor (option, rotor) mounted on the body. An impeller is installed on the motor shaft. Once in the housing on one side, the coolant is captured by the rotating impeller and moves to the outlet end on the other side of the pump.
Some models have built-in air vents, but there are very few of them. In the vast majority of designs, air is removed by unscrewing a special nut located in the housing.
The connection diagram for the heated floor pump is similar to that used in systems with installed radiators.
Tips for choosing a device for a heated floor system in your home
How to choose a pump for underfloor heating? Today, the market mainly offers CO pumps with a standard flow rate of about 40 l/min (about 2.5 cubic meters/hour) and a pressure of up to six meters. The flow rate is directly proportional to the pressure value.
When purchasing, you should understand that the flow rate of 40 l/min indicated on the pump will not always correspond to the actual flow rate. Because the latter depends on what the throughput of the floor assembly or the system itself is. A large number of long circuits reduces consumption.
It’s easy to understand this using two graphs: theoretical (for all similar pumps) - No. 1, and real for the 2.5 cubic meter pump considered in the example. with a pressure of six meters - No. 2.
Schedule No. 1. 
Schedule No. 2. 
The higher the throughput capabilities of your system, the weaker the pressure on all connected circuits. That is, the more circuits are closed to one mixing unit, the greater the flow rate.

If you have a parallel connection scheme
The calculation of a pump for a heated floor in this case should begin by calculating the recommended flow rate for each branch and summing up the results.
Calculate the total amount of losses in all circuits (branches). This will help determine the constant flow rate in the mixing unit. As a rule, this value ranges from 40% to 100% of the total flow rates of the circuits. That is, with a total flow rate of the circuits of 15 l/min, the flow rate for incoming heat will be equal to 6 – 15 l/min.
Its value is influenced by:
- The difference between the incoming temperature and the one set by the thermal head;
- Floor heat loss.
Example. The boiler supplies coolant heated to 60 degrees. The mixing unit is set to 40 degrees. We get a consumption of 40%. At the feed 75 degrees, at the node - 40 degrees. Consumption – 25%.
The bypass (if any) should be taken into account in the calculations, because and it has a constant flow rate. Therefore, we add about 6 l/min to it. In long pipes there is more heat loss, which forces the thermal head to increase heat transmission, the flow rate increases and the pressure drops.
If you have a serial connection
The calculation of a pump for a heated floor in this case is performed as follows. The recommended flow rate is calculated for all branches, and the results are summed up.
The resulting value is checked against the existing graph No. 3, which determines the pressure loss.
Schedule No. 3. 
You can create this graph yourself specifically for your pump. The curve is standard for all models. Based on the obtained pressure, the required pipe length is selected from the table.
Conclusion:
The pump pressure according to the third graph must be higher than the pressure loss over the entire length of the laid floor pipes at a known flow rate for each circuit.
The head loss in each circuit is determined from the table below.

The actual pressure of the installed pump is determined using the third graph to determine the total flow rate of the installed mixing unit.
It is important to consider one more information. If instead of water you poured antifreeze or another similar liquid into the system, you should take into account the difference in viscosity, which can reach 30 - 50 percent. Which will lead to an even greater slowdown in the movement of coolant through the pipes. Therefore, other calculations will be required.
In this case, the pump power should be increased by at least 20% (optionally, the pipe should be made shorter by the same 20%). The heat capacity of antifreeze is approximately 20% less than that. Which water has. Accordingly, it will move the same amount of less heat.
Many owners of country houses, having read and heard a lot about the advantages that water “heated floors” provide, are seriously thinking about creating such a room heating system on their own. It should be said right away: this task is extremely difficult, large-scale, requiring the mobilization of all your skills and abilities both in general construction issues and in plumbing installation. It is necessary to take special care in the selection of all components, which, in turn, must meet a number of important requirements.
Apart from the boiler, the pumping and mixing unit acts as the main unit that ensures the required temperature level in the circuits and stable circulation. It can be purchased ready-made, that is, factory assembled, or installed independently. But be that as it may, in any case it must be able to ensure the circulation of the amount of coolant required for the actual system being emitted. How to evaluate this ability? A calculator for calculating the performance of a “warm floor” pumping and mixing unit can help with this.
Prices for heated floors
Circulation pumps are centrifugal type devices. The working bodies are an electric motor and a shaft with an impeller. The cases are made of stainless steel, cast iron, and polymers.
Since absolutely sealed systems do not exist (air accumulates in the pipes), it is not advisable to choose a pump with a cast iron casing; it has low oxidation resistance.
The housing is equipped with two pipes for connecting the supply and return. The pump can also be equipped with an air vent. If not, then there is a nut on the body that can be unscrewed if necessary to bleed off the air.
Pump rotors can be wet or dry. The wet one is in direct contact with water: when electricity is supplied to the device, the shaft with the impeller rotates, draws in the coolant and pushes it further under pressure.
Dry rotors do not come into direct contact with the coolant and therefore require regular maintenance. They are usually not used in private households. This is a powerful equipment suitable for urban homes and industrial complexes.

Selecting parameters
 Calculating a pump for a warm water floor consists of finding the optimal values of two main characteristics, pressure and performance (calculation method for a warm water floor).
Calculating a pump for a warm water floor consists of finding the optimal values of two main characteristics, pressure and performance (calculation method for a warm water floor).
When choosing water as a coolant, productivity is determined by the formula:
A = 0.86 Q / (t1 – t2), where Q is the circuit power in kilowatts, t1 is the temperature in the supply pipe, t2 is the return temperature. For antifreeze, different coefficients are used.
If there are several circuits, the required pump performance is the sum of all A values. For heated floors, delta t is most often taken as 5 degrees, and the power is determined based on the square footage of the heated area. When calculating, ready-made tables are often used.
For the middle lane it will look like this:
- within 120 meters, pump performance is up to 1.5 cubic meters/hour;
- up to 200 – 2.5;
- up to 280 – 4, etc.
As a final value, it is recommended to take the figure with a margin of 20 percent (if the house has poor thermal insulation, then more). When the shaft is positioned vertically, the pump loses up to 40 percent of its power, so the devices are always installed strictly horizontally.
If the cottage is two or three stories high, experts recommend installing a collector unit (a collector for a warm water floor) with its own pump on each floor. A pair of low-power devices will cost no more than one powerful one, and the efficiency will be higher.
How to choose a pump for a warm water floor based on pressure? This characteristic depends on the cross-section of the pipe and the material of manufacture. When calculating, resistance on fittings, mixers, and fittings is taken into account.
In general, the formula looks like this:
B = (RL + K) / 1000, where R is the hydraulic resistance of one meter, L is the length of the longest circuit, K is the safety factor.
In private homes, pumps with a pressure of up to 6 meters of water column (0.6 atmospheres) are used. For a more accurate calculation, you can use a calculator on the Internet. You need to select the pressure according to the average values for the model so that the unit does not work for wear.
The selection of a pump for water heated floors in a store is carried out according to the markings. How to figure it out?
An important function is adjusting the pump speed. It allows you to optimize the temperature regime with the least energy consumption, depending on the weather outside and the temperature in the house.
The simplest model has only one speed, more complex ones have two or three. If there is electronic control of the heating system, the desired speed is selected automatically.

In the classic radiator circuit, the pump is always placed on the return line: high coolant temperatures accelerate wear of the device. The temperature of the heated floor is usually within 40?. If radiators are not provided in the heating system, the pump can be installed on a hot pipe in front of the manifold comb.
This problem is solved by a pump with a thermostat for water heated floors: at temperatures above a certain norm, it turns off automatically.
ks5.ru
Many owners of country houses, having read and heard a lot about the advantages that water “heated floors” provide, are seriously thinking about creating such a room heating system on their own. It should be said right away: this task is extremely difficult, large-scale, requiring the mobilization of all your skills and abilities both in general construction issues and in plumbing installation. It is necessary to take special care in the selection of all components, which, in turn, must meet a number of important requirements.
Apart from the boiler, the pumping and mixing unit acts as the main unit that ensures the required temperature level in the circuits and stable circulation. It can be purchased ready-made, that is, factory assembled, or installed independently. But be that as it may, in any case it must be able to ensure the circulation of the amount of coolant required for the actual system being emitted. How to evaluate this ability? A calculator for calculating the performance of a “warm floor” pumping and mixing unit can help with this.
Calculator for calculating the performance of a "warm floor" pumping and mixing unit
Explanations on the principle and procedure of calculation
First of all, what is performance? Everything is very simple - this is the ability of a device or unit (that is, each of its elements) to pass a certain amount of coolant through itself per unit of time. In the case under consideration, this primarily concerns the pump, which ensures the proper level of circulation throughout all laid out “warm floor” circuits. The throughput capacity is also important for a two- or three-way thermal valve, which provides dosed mixing of hot and cold flows to obtain the required temperature.
It is clear that the pump acts as an “active link”, that is, it must be able to pump the required volume, and the valve must only be able to pass it through itself. Despite this fundamental difference, the performance value must correspond to the parameters of both devices.
- Naturally, in the initial data, the key parameter is the area of the premises in which the “warm floor” circuits are located, connected to this mixing unit. The planned operating principle of such a system is also important - will it act as the only source of heat in winter, or will its operation be necessary only to increase the overall level of comfort in the rooms, and the main load will still fall on the radiators. It is clear that the required thermal power for these two cases will differ.
For rooms such as a bathtub, toilet, hallway, kitchen, it is advisable to take into account the condition that the “warm floor” is the only source of heating.
- Further, the calculations are based on the heat capacity of the coolant, that is, its ability to accumulate thermal energy in the boiler room and release it into the premises. The more fluid of a certain temperature is pumped, the higher the heat transfer. This parameter is already included in the calculation program.
- The temperature difference between the supply and return manifolds is calculated by simply subtracting the values. For water heated floors, with proper balancing and good quality of thermal insulation of the room, the optimal difference is 5 ºС. It may be a little more, but you cannot go beyond 8÷10 ºС. And for a comfortable perception of the “warm floor” surface itself, 25-27, less often – 30 ºС is enough.
- By default, the calculator will calculate for a “warm floor” system filled with water. If a different coolant is used, then allowances can be made for this circumstance. The fact is that not a single antifreeze can compare with water in terms of specific heat capacity, while at the same time differing in its higher density. These data may be indicated on the original packaging of the coolant, or they can be easily found on the Internet specifically for the planned type of non-freezing liquid of one concentration or another.
The result will be shown in several units of measurement - cubic meters per hour, liters per minute and per second. This is so that the user does not have to independently convert from one to another - different component manufacturers often practice different approaches to indicating the performance of their devices.
Water “warm floor” is large-scale and difficult. but a doable task
The whole complex of activities includes many diverse operations - from preparing the base, insulation, laying out contours, pouring screed - to installing control equipment and fine-tuning the system. Appreciate the full scale of the creation do-it-yourself water heated floor A special publication on our portal will help you.
stroyday.ru

Determining pump markings
When choosing a circulation pump for a warm water floor, you should know that the markings on it are of great help. It is placed immediately below the model name and looks like two numbers written with a dash. For example: 32 – 60.
The first indicates the connection size, 32 mm (or 1” ¼). Typically, a pump for a warm water floor is supplied complete with union nuts for its installation/disassembly. This is their size.
The second informs about the height to which the pump can supply water. In this case, it is equal to 6.0 m water. Art. (0.6 atm.). There are models that are designed for larger and smaller values of this indicator.
A pump for a water floor is selected taking into account the results of a previously completed hydraulic calculation of CO with heated floors. Information about the load value at specified parameters is applied to the product body.
The pump for a warm water floor is made with three switching modes, differing in performance (i.e., the amount of liquid that the pump is able to pump in an hour).
The third is maximum productivity. In each of the indicated positions, the pump consumes current, the value of which is indicated on the plate.
Types of pump designs
In terms of their design, the circulation pump for a warm water floor of any model is practically no different from each other, with the exception of appearance and control. German pumps produced by Grundpos and Wilo have proven themselves to be the most reliable. The latter are more affordable in price. The above-mentioned pumps belong to a series of household pumps that are installed in residential premises and private houses.
In addition, there is a pump for water floors for industrial use. Their main difference is that they are double and are fixed not with nuts, but with special flanges, the diameter of which exceeds 50 mm.
There are also models such as a pump for warm water floors with a thermostat.
Pumps positioned as products for underfloor heating have a three-way valve. When choosing this option, it should be taken into account that valve designs are not equivalent in performance. Some of them have a specified rate not exceeding 2.5 cubic meters per hour, which does not allow them to work normally if the floors are laid over an area of more than 50 sq.m. Moreover, they are not adjustable. Therefore, you can install them only if you have a small volume pump for a warm water floor.
There are valves with control devices that are controlled manually and by a special servo drive in automatic mode. Their consumption is 4.0 cubic meters/hour and they work on areas up to 150 sq.m.

The pump for a warm water floor has a fairly simple design. The product body and motor (option, rotor) mounted on the body. An impeller is installed on the motor shaft. Once in the housing on one side, the coolant is captured by the rotating impeller and moves to the outlet end on the other side of the pump.
Some models have built-in air vents, but there are very few of them. In the vast majority of designs, air is removed by unscrewing a special nut located in the housing.
The connection diagram for the heated floor pump is similar to that used in systems with installed radiators.
Tips for choosing a device for a heated floor system in your home
How to choose a pump for underfloor heating? Today, the market mainly offers CO pumps with a standard flow rate of about 40 l/min (about 2.5 cubic meters/hour) and a pressure of up to six meters. The flow rate is directly proportional to the pressure value.
When purchasing, you should understand that the flow rate of 40 l/min indicated on the pump will not always correspond to the actual flow rate. Because the latter depends on what the throughput of the floor assembly or the system itself is. A large number of long circuits reduces consumption.
It’s easy to understand this using two graphs: theoretical (for all similar pumps) - No. 1, and real for the 2.5 cubic meter pump considered in the example. with a pressure of six meters - No. 2.
Schedule No. 1. 
Schedule No. 2. 
The higher the throughput capabilities of your system, the weaker the pressure on all connected circuits. That is, the more circuits are closed to one mixing unit, the greater the flow rate.

If you have a parallel connection scheme
The calculation of a pump for a heated floor in this case should begin by calculating the recommended flow rate for each branch and summing up the results.
Calculate the total amount of losses in all circuits (branches). This will help determine the constant flow rate in the mixing unit. As a rule, this value ranges from 40% to 100% of the total flow rates of the circuits. That is, with a total flow rate of the circuits of 15 l/min, the flow rate for incoming heat will be equal to 6 – 15 l/min.
Its value is influenced by:
- The difference between the incoming temperature and the one set by the thermal head;
- Floor heat loss.
Example. The boiler supplies coolant heated to 60 degrees. The mixing unit is set to 40 degrees. We get a consumption of 40%. At the feed 75 degrees, at the node - 40 degrees. Consumption – 25%.
The bypass (if any) should be taken into account in the calculations, because and it has a constant flow rate. Therefore, we add about 6 l/min to it. In long pipes there is more heat loss, which forces the thermal head to increase heat transmission, the flow rate increases and the pressure drops.
If you have a serial connection
The calculation of a pump for a heated floor in this case is performed as follows. The recommended flow rate is calculated for all branches, and the results are summed up.
The resulting value is checked against the existing graph No. 3, which determines the pressure loss.
Schedule No. 3. 
You can create this graph yourself specifically for your pump. The curve is standard for all models. Based on the obtained pressure, the required pipe length is selected from the table.
Conclusion:
The pump pressure according to the third graph must be higher than the pressure loss over the entire length of the laid floor pipes at a known flow rate for each circuit.
The head loss in each circuit is determined from the table below.

The actual pressure of the installed pump is determined using the third graph to determine the total flow rate of the installed mixing unit.
It is important to consider one more information. If instead of water you poured antifreeze or another similar liquid into the system, you should take into account the difference in viscosity, which can reach 30 - 50 percent. Which will lead to an even greater slowdown in the movement of coolant through the pipes. Therefore, other calculations will be required.
In this case, the pump power should be increased by at least 20% (optionally, the pipe should be made shorter by the same 20%). The heat capacity of antifreeze is approximately 20% less than that. Which water has. Accordingly, it will move the same amount of less heat.
vse-otoplenie.ru
Consideration of the main types of systems
Heat transfer to the floor covering can be carried out due to electrical action or a coolant heated to a certain temperature. In this regard, there are two main categories of systems. Classification is also sometimes made depending on the elements used.
Water structures
Warm floors of this type are mainly installed in private buildings, since in apartments it is quite problematic to connect to central heating. However, when installing a separate boiler, this option is still possible, although it is quite expensive.
A coolant system requires the presence of pipelines and a mixing point for the working fluid. The basic elements are polyethylene or metal-plastic pipes. They can be laid between the joists of a wooden floor or built into a cement-sand screed.
The advantages of such designs:
Note! It is prohibited to create intermediate connections in the circuit. There should be two docking points in total. One of them should be located on the coolant supply, and the other on the return.
Electrical analogues
The operation of the system is based on the principle of heat transfer through an electric current conductor or infrared radiation. It includes a thermostat with a sensor that turns the equipment on and off according to a given program.
There are the following types of basic elements:
Helpful information! If necessary, the systems can be equipped with remote control for more comfortable operation. Many manufacturers have developed special modules for these purposes.
Competent calculation of the heat of a water-type underfloor heating
The quality of heating will depend on the correct calculations of the heat transfer of the heated floor, so calculations must be made without fail. The constants will be:
Efficient underfloor heating: calculation of system power
When calculating water heated floors with your own hands at the preparatory stage, you should determine the basic parameters and purpose of the room, as well as the characteristics of barrier structures. In this case, the heat loss coefficients of the materials used should be well known.
To calculate the thermal load on each loop of the circuit, pressure loss, as well as the speed of movement of the working fluid, you will need to find out a large number of coefficients directly in exact form. To simplify the calculations, it is proposed to take the system power equal to the maximum heat loss.
You can use the following formula:
Q = (V* Pt* K)/860 , Where:
Q – heat losses;
V – volume of the room;
Pt – difference between outside and inside temperatures;
K – coefficient that determines heat resistance (usually its value varies between 1.5-2).
Note! When calculating the heat of a heated floor, which acts as an additional source of heating, minor errors are unlikely to lead to serious consequences, which cannot be said about a system that performs the functions of the main heating.
Competent calculation of pipes for heated floors in a room
After calculating the power, it is necessary to decide on the calculation of the water heated floor pipe. The length of the pipelines will depend on the laying pattern and the distance between the main elements.
When calculating length, the following formula applies:
L = S/N*1.1 , Where:
S – square footage of the room;
N – distance between contours;
1,1 - reserve for turns.
Note! The laying pitch largely depends on the diameter of the pipe used. Most often, it varies between 15-30 cm. When carrying out work, it is not recommended to go beyond this range.
Calculations for pumping equipment
Having made the calculation of the heat of the heated floor, you can begin the calculations necessary to select a pump that can ensure optimal movement of the coolant. You can calculate the basic parameters yourself using a special formula:
Q = 0.86*Ph/Th , Where:
Q – volume of working fluid (cubic m/h);
0,86 – conversion factor;
Ph – power of one circuit;
Th – temperature difference at the inlet and outlet.
Related article:
What types of underfloor heating are there? What are the advantages of each type? Which one is right for you? Read!
The most suitable floor coverings
Warm floors can be installed using various floor coverings. However, for each room the choice should be made after familiarization with the operational features.
Ceramic tiles are more suitable for bathrooms as they can withstand wet environments. Most often, a screed is poured into which the pipelines or cables of the system are embedded, and tiles are laid on top. With additional heating, the tile loses its main disadvantage - its cold surface.
For the kitchen, linoleum can be a good option for finishing the floor. It is often chosen together with a film floor that emits infrared radiation. The elements in this case are placed on top of the screed. Plywood, chipboard or OSB are laid on them. Linoleum is spread on top.
In the same way, a heating system is created in combination with laminate. However, no additional base is required. The panels can be mounted on top of the film.
If necessary, additional heating can be installed directly under the carpet. However, it is better to use it in the bedroom to increase the thermal effect. The main disadvantage of the coating is the difficulty in removing contaminants.
What does the price consist of?
The cost of heated floors varies significantly, since there are many options for their installation. However, it is necessary to understand what the final price consists of.
For your information! The cost of electrical system kits, as a rule, ranges from 2-5 thousand rubles per square meter.
Summarizing
Only the correct calculation of the heat of a heated floor will allow you to create a truly effective and functional floor heating system in an apartment or private house. Errors in calculations can make a design of little use or too energy-consuming.
homemyhome.ru
Pump selection according to technical specifications
Typically, circulation pumps, such as in the photo, are used for floor heating designs. The characteristics of these units best meet the requirements for them.
Calculations are made according to the formula:
Q = 0.86×Pн/(t°flow t – t°rev.t), where
Q – liquid consumption in cubic meters per hour;
Pn – maximum circuit power (kW);
t°pr. t – value of water temperature in the supply pipe;
t°rev. t is the temperature of the liquid at the outlet.
If, when laying a structure, the installation of several circuits is planned, then you need to find out the total value taking into account each of them.

According to experts, it is better to equip a separate room with an autonomous heating system for the floor surface, as a result of which it becomes possible to use thermal energy economically. It will be possible to regulate the state of the microclimate depending on the purpose of a particular room, and make the operation of the structure more reliable.
The difference between the temperature of water in the heating circuit at its inlet and outlet depends on a number of parameters:
- Pipeline length. The longer the circuit, the larger the area it must heat. This means a significant consumption of thermal energy, and the inlet and outlet temperatures will be very different;
- Quality of thermal insulation. If the technology was violated during the creation of the system, then heat losses during the operation of the heated floor will reach high figures. This is especially true for rooms located on the ground floor, since improperly made thermal insulation will contribute to the consumption of a significant amount of energy for heating the ground. Excessive heat loss leads to an increase in the load placed on the circulation pump for the heated floor.
- Climate in the area where the house is located. The further north the region, the greater the power reserve the heating system and circulation unit should have. Manufacturers advise choosing them with an indicator of 20–25%.
Another important value for determining how to choose a circulation pump for a heated floor is the pressure of the coolant flow. It should be enough to overcome the hydraulic resistance of the water in the system. The hydraulic resistance indicator depends on the length of the circuit, the cross-section of the water pipes, and the speed of movement of the liquid.

When purchasing a pump, you should pay attention to the fact that the above parameters are indicated in the accompanying documents.
When independently arranging the system, the formula is used to calculate the coolant pressure:
H= (П×L + ΣК) /(1000), where
H is the desired value;
P – hydraulic resistance per meter of circuit;
L – length of the longest of the circuits together with control systems;
After all the data becomes known, they move on to choosing the optimal pump model.
Types of circulation units
The design features of circular pumps designed for water floors depend on the power parameter.
Household consumers can use the following models of units:
- with a “wet” rotor;
- with a “dry” rotor.
Pumps equipped with a “wet” rotor
The external dimensions of such devices are minimized due to the location of the impeller close to the pump rotor; sometimes it is located in the same housing. To prevent liquid from entering the electric motor, a reliable oil seal made of wear-resistant and heavy-duty rubber is installed on the drive shaft.
Sometimes double water protection is provided for the circulation pump. Since the unit is compact in size, it can be installed directly in the room that will be heated. Manufacturers guarantee power that is enough to operate a heating structure over an area of up to 400 square meters. Read also: “How to calculate the power of a heated floor - theory and practice.”

To operate devices with a “wet” rotor, a single-phase network with a voltage of 220 V is required. The units are characterized by low noise, high performance, and minimal electricity consumption. The completely sealed pump housing is lightweight.
All of the above characteristics make it possible to install circulation units directly on the pipeline. In this case, there is no need for additional fastening on load-bearing surfaces. To eliminate the possibility of electric shock, elements such as the housing, electrical wiring and winding are provided with increased protection. To prevent overheating of the rotor and starter windings as a result of prolonged operation of the unit at critical power levels, a thermal relay is installed.
Pumps equipped with a dry rotor
For such devices, all elements are located in a separate housing. Sufficiently powerful hydraulic units are capable of serving large apartments or several at the same time. To accommodate devices with a “dry” rotor, it is necessary to allocate a technological room. They are installed on a separate frame.
Such pumps have significant weight, and the high levels of noise emitted do not allow them to be placed in living rooms. They are rarely used for private households. Water pumps with a dry rotor are used for large areas - industrial and commercial.
They are driven by a three-phase motor. The pumps are equipped with a complete protective kit for electrical components.
Information on the pump body
The standard markings applied to the body must contain all the technical parameters of the unit. The first number on top indicates the mounting diameter of the pipes for the coolant, the second indicates the pressure (meaning the maximum rise of the liquid to a height), the third number indicates the length of the pump in operating condition.

The following indicators indicate the voltage and frequency of oscillations in the network. Then comes information regarding the magnitude of the phase shift coefficient. The body may contain data on the height of liquid rise depending on the cross-section of the pipes.
Some of the units are equipped with two engines. This design feature allows you to overcome peak loads without overheating the windings. The second of them is put into operation, which is also capable of replacing the failed first engine. As a result, the possibility of the structure freezing in severe frosts is eliminated.
Electric pump installation options
Circulation units are allowed to be installed both at the inlet and outlet of liquid from the pipeline. The installation location is usually selected based on the characteristics of the circuit.
At the water outlet, its temperature is much lower than at the inlet, which is preferable for pumps. But installation at the end of the circuit is not mandatory, since all units are manufactured with a certain margin of safety relative to the maximum operating temperature conditions.
Selecting a pump for a water floor system
Many owners of private households planning to install a floor heating system are interested in the question: “How to choose a circulation pump for a heated floor?”
Experts advise purchasing pumps at the same time as the structural elements of the “warm” floor. Attempts to independently purchase a unit may result in a decrease in the efficiency of the system or its rapid failure. As for the repair of the “warm” floor, it will cost a significant amount.
However, if this is not possible, then knowing how to calculate a pump for a heated floor and how to choose it wisely, you can choose the right model. Read also: “How to calculate a water heated floor - advice from a specialist.”

Before purchasing, you should pay attention to certain parameters:
- Capacity in cubic meters or in the number of liters of liquid that is pumped per unit of time. To ensure sufficient heating of the room, the unit must pass three times the volume of coolant per hour that may be in the heating circuit.
- Maximum possible pressure. It is selected taking into account the diameter, length and material of the pipes for the circuit.
- Dimensions. The smaller the size of the unit, the easier it is to find a mounting location for it. But small pumps are not capable of high performance.
- Current phase. For residential buildings, pumps with a single-phase motor will be sufficient. For large buildings, for example, industrial ones, you should purchase units driven by a three-phase motor.

Knowing how to choose the right pump for a heated floor will help you purchase a model that will ensure the required efficiency of the system, its reliability and long service life.
To extend the life of the pump, you must remember the following rules:
- The unit must be installed in a place where, if necessary, repair work or warranty service can be carried out without problems.
- Despite the fact that imported pumps are of high quality, before the start of the heating season it is necessary to check their technical condition due to the low quality of water and the peculiarities of operating conditions. Particular care should be taken to inspect the condition of the oil seal, which ensures waterproofing of the device shaft from the rotor.
On the eve of the start-up of the floor heating system, it is necessary to remove any air pockets in it. For this purpose, the water is changed several times and a special valve is installed. The presence of air pockets will become an obstacle to the movement of liquid, and the automation will constantly begin to turn on the circulation.
The question of whether a pump is necessary for a warm water floor is decided at the design stage. The desire to reduce the cost of the installed system by abandoning this equipment significantly reduces the efficiency of the water circuit, even if the need to install pipes with a calculated slope is taken into account.
This is due to the rather large total length of the installed pipeline, as well as the frequent occurrence of air locks. For this reason, experts recommend equipping the water heating system with a pump.
Functional purpose
The main functional role of the pump is to create optimal pressure in the heating system, facilitating the unhindered circulation of the coolant. This eliminates the risk of malfunctions in the functioning of the water floor due to airing of the system.

Such a solution becomes especially relevant if the length of the pipes to be laid is significant, and when they are laid, a large number of turns are formed that slow down the movement of the liquid. Equipping a water floor system with a pump that has several speeds increases the heating efficiency, since it becomes possible to maintain a stable design temperature in the system.
Type of equipment
A circulation pump for a heated floor will provide effective heating, supplying liquid at a constant set speed without the formation of destructive excess pressure. It belongs to the centrifugal type. The working parts are an electric motor and a shaft equipped with an impeller.
How to choose a circulation pump
On the body, made of cast iron, stainless steel or durable, corrosion-resistant polymers, there are two pipes used to connect the return and supply. Some models are equipped with an air vent, and in its absence, the function of bleeding air is performed by a special nut, which you simply need to unscrew.
There are two types of circulation pumps.

Determination of performance, power
To choose the right type of circulation pump, you should find out the required productivity (kg/h), taking into account the power of the installed heated floor.
G = Q / 1.16 (t p. - t arr.),
where Q is the required power of the water circuit, W;
1.16 – specific heat capacity of water, W h/kg °C;
tp – supply water temperature, °C;
t arr. – return temperature, °C.
The required heating power is approximately equal to 100 W times the heated area of the room.
To determine the performance of the selected pump in m 3 / h (which is often indicated in the passport), you need to divide the result in kg / h by the density of water, determined from reference tables at the desired coolant temperature. For example, for 80°C the density will be 971.8 kg/m 3.

If you plan to lay several water circuits, then the calculations are carried out for each separately, and the results are summed up. Typically, to avoid problems, the calculated performance indicator is increased by 15-20% so that the system can provide heat to the home when severe cold occurs.
Learning to select a pump
Pressure
Another indicator to be calculated is the amount of pressure created by the pump (N, m), which ensures the normatively established circulation of heated water in the system. The following formula is used to determine:
Н = (R L + Z) / p g,
where R is the hydraulic resistance indicated in the technical documentation of the water circuit, a straight pipe section (depending on the cross-sectional size and material), Pa/m;
L – length of the pipeline to be laid, m;
Z – resistance of various factors that interfere with water movement (bends, turns, fittings, shut-off valves, etc.), Pa;
р – density of water at the temperature required for calculation, kg/m3;
g – gravitational acceleration, ≈ 9.8 m/s 2 .
For country houses, using graphical characteristics that can be found in reference literature, pump models with an average pressure of up to 6 m (0.6 atm.) are usually selected.
Criterias of choice
In order for the circulation pump to ensure the uninterrupted and efficient functioning of the water heated floor, when selecting it, in addition to performance and pressure, you should pay attention to several more indicators.
- Multiple speeds available. Usually three are enough, allowing you to quickly regulate the degree of heating of the coolant.
- Electricity consumption. The most economical are the improved pump models, equipped with a module for automatic control of work intensity depending on the degree of heating of the coolant.
- Noise background. For residential premises this indicator is important. Small-sized types of pumps with a wet rotor practically do not cause any problems.
An important criterion is the manufacturer. Among the large companies that have the image of reliable partners producing high-quality pumps, the following well-known brands can be noted:
- Grundfos (Denmark);
- Ebara (Japan);
- DAB (Italy);
- Halm (Germany);
- Lowara (Italy);
- AlfaStar (Poland);
- Pedrollo (Italy);
- Wilo (Germany).
Circulation pumps of the Wester brand (China) are in demand, which are of good quality at a relatively low cost.
Among the positive consumer reviews, one can highlight a large number directed to the Grundfos brand (Denmark). The pumps of this company, with their easy maintenance and fairly high price, attract private developers with their long-term, flawless operation.
Installation
When installing the pump, it is advisable to position it so that the rotor is oriented horizontally. In this case, the arrow shown on the body must coincide with the direction of movement of the coolant. After installation is completed, water is allowed into the pump, then the screw is opened to remove air. In the vertical direction, performance does not decrease, but there is a risk of power loss of up to 30%.

The circulation pump is mounted depending on the calculated connection diagram in the following positions:
- On the supply pipe. In this case, the pump is located after the mixing unit.
- On the return pipe. Among the recommendations of experts, the prevailing opinion is that the performance of the pump is higher if it is mounted on the return line. This point becomes especially relevant if a solid fuel pump is installed to heat the water, which can bring the coolant to a vapor state, in which the pump simply cannot function.

If the heated area is less than 200 m2, then the difference in water temperature between the supply and return circulation is small. Therefore, the pump can be located in any place convenient for the user. When installing a water heating circuit in mansions with several floors, it is recommended to equip each with a separate pump to make the system easily controllable.
Trouble-shooting
The main factor that negatively affects the functioning of the pump is the quality of the water entering the water heating circuit. If the pump operates continuously, salt deposits reduce its performance to a lesser extent than during periods of shutdown.


Sometimes, after turning off the heated floor for the summer period, the next time it is turned on, the pump stops pumping water due to the fact that the rotor does not turn. You need to carefully turn the impeller several times using available tools. If the pump does not start to function, professional help will be required.
Video: Circulation pump and collector installation
Warm floors have long ceased to be a unique phenomenon; today they are available to everyone; if you have the necessary literature and acquired knowledge, you can install them yourself without involving specialists. This system is gaining popularity: it is now installed not only in private houses, but also in apartments. Water floor heating systems are advantageously economical during operation, but expensive to install. Therefore, it is necessary to select all the components correctly, one of which is the water pump.


The most important thing is to carry out a competent calculation and carry out all installation work in accordance with the instructions.
Peculiarities
Any heating system (especially a floor heating system) must have a pump. It is needed to circulate fluid in the system. In its absence, there will be no exchange of warm and cold liquids. Intense heating will occur at the place where the water is heated, which in the future may lead to overheating of the heating elements, failure of all electrics, and boiling of water in the system.


Pumps for underfloor heating systems are no fundamentally different from other analogues for radiator heating. Such units cannot be used to lift water; they are not designed for this. They are designed to circulate water in the system, preventing it from heating unevenly. Minor rises in the system are possible; the pump must be selected taking this fact into account in advance.

Kinds
Most often, all parts and devices for floor heating are purchased together with the entire underfloor heating system.
When choosing a pump, you need to pay attention to some parameters:
- productivity (it must pump three volumes of liquid from the entire system per hour);
- maximum pressure (it is calculated taking into account the diameter of the pipes and their material);
- dimensions (the smaller the circulation pump, the easier it is to install, but small analogues will not be able to produce sufficiently large power);
- phase of the current (for a private house, a pump motor with a single-phase current will be sufficient, for industrial premises - with a three-phase current).


There are two types of pumps:
- with wet rotor;
- with dry rotor.


Units of the first type do not have enormous power, but for a private house or cottage this option is ideal. The rotor is called “wet” because the impeller itself provides lubrication and cooling of the motor.
The main advantages of this type of rotor are:
- silent operation;
- low energy consumption;
- reliability;
- simple operation and ease of control.

Glanded rotor pumps are often used in industrial settings. They require frequent maintenance such as cleaning and lubrication. At the same time, they work quite noisily.

Principle of operation
The floor heating pump has a simple design. It consists of the body of the product and the rotor or motor attached to the body. An impeller is connected to the motor shaft. It is used to circulate fluid in the pipeline. The use of a separate unit is explained by the fact that it is necessary to create operating pressure in the system for a constant flow of warm water in the pipes.


An additional pump is installed if there is a second circuit or a large pipe laying area.
When installing, remember that the pump shaft must be installed strictly horizontally. With a vertical shaft arrangement, the efficiency will be 35-40% lower. For proper operation, the pump should be installed before the heating element and in front of the manifold. This allows the rotor to operate at lower temperatures, which increases service life. Installing the pump before the heating element avoids airing (the pump will push the water, not allowing the air to remain in one place).


Before starting the system, you must ensure that there are no air pockets.
How to choose?
The correct choice of pump is the key to successful operation of the entire system. There are many parameters that must be taken into account when choosing all parts of the system. You need to know the technical parameters of the system, the area of the room where the heated floor will be, as well as possible heat losses in the circuit itself. Once you know these characteristics, you need to select the right pump.

The first (most important parameter) is the pump performance. It is calculated in cubic meters per hour of pump operation. You should calculate the minimum performance that will be sufficient to operate and circulate water in the system. The main rule is that the pump must move three times more water per hour than is in the system itself.

In this case, it is advisable to add 10-20% to the resulting productivity as a reserve. This will increase the service life of the entire system as a whole. This will make it easier for the pump itself to work, because constant operation at high speeds contributes to rapid wear of the internal elements. The gap in power is needed to increase the power of the system in winter and cold. When calculating pump performance, the area of the room is also taken into account. If the area is large, you can install an additional (less powerful) mini pump so that the load on the main one is not high.

The second important parameter is pressure. To overcome long distances, bends and kinks in pipes, a unit with high pressure is required. The concepts of “pressure” and “performance” are often confused, although they are completely different. The rate of fluid supply to the heating system depends on the pressure. A high-pressure pump will ensure constant circulation of liquid even in the most remote parts of the system.


How to calculate power?
There is a universal formula for calculating the minimum power. It looks like this: G =Q X 0.86/t, where:
- G - system capacity in l/h;
- Q - thermal energy (W);
- 0.86 - coefficient (Kcal/h);
- t is the temperature amplitude during supply and return (C).

Such calculations are often performed by specialists, but if you have free time, you can do them yourself. When making your own calculations, it is necessary to take into account all possible power and heat losses. A standard pump for residential premises has the following indicators: a capacity of 2.6-2.8 cubic meters per hour and a head of 5-6 m. There are features of calculating power for different types of connection diagrams.


With a parallel scheme, it is necessary to start by calculating the costs of the branches and then sum them up. Then the losses in all circuits are calculated. Then you can find out the flow rate in the mixing unit. Its value is influenced by the temperature amplitude and heat loss of the floor. With a sequential connection scheme, the recommended flow rate is calculated. Afterwards, the losses in power and pressure are determined by the amount of flow. Antifreeze has a much higher viscosity than water. Therefore, it is necessary to change the calculations and take a pump with more power.

When choosing sediment and its capacity, consider what you will be pouring into the systems.
Manufacturers
In the market of pumps for heating systems, as in any sales segment, there is a huge selection of companies and manufacturers that create an offer. Among the mass of varieties of goods presented for sale, there are companies with extensive experience, time-tested and with a lot of positive customer reviews.
German company Grundfos has long taken its place in the segment of pumps for heating systems, both radiator and underfloor heating systems. These pumps have few complaints; they are distinguished by their build quality and performance.


German company pumps Wilo are also durable. They are more affordable than Grundfos. The pumps from both companies are almost the same and have the same power and pressure parameters. Both companies produce industrial pumps. They are a double pump. Its operating principle is as follows: if there is insufficient capacity of one pump, the second one is turned on, so the operation of the pump and the entire system is normalized. If one of the pumps breaks down, the second pump will replace it until the broken one is replaced with a new one. This system is extremely convenient and does not create emergency situations.


These two companies are the flagships of the entire industry. The remaining companies are much less known or very expensive. And these two German companies are the best example of a combination of price and quality. Italian pumps are also often used, which are characterized by high power and long service life.