Growing shrub cherries
Among lovers of fruit trees, shrub cherry is becoming more and more popular. This variety is chosen for its unpretentiousness in cultivation and stable yields. Due to the high degree of frost resistance, it is suitable for cultivation in any region of the country. A feature of this species is also a decorative appearance.
Cherry Shrub - unpretentious, high-yielding variety
Features of the variety
Steppe (bush) cherry belongs to the family of pink, to the subgenus of cherries. Variety features:
- frost resistance;
- flower ovaries do not freeze during spring frosts;
- drought resistance.
Due to its characteristics, the steppe cherry is suitable for growing in the Moscow region and the Leningrad region, which are known for their harsh climate.
Description of the steppe cherry tree:
- bush 1.5 heights;
- wide, spherical crown;
- strong rhizome, prone to break through the thickness of the soil;
- young branches have a green color, as they grow older they acquire a brown tint;
- leaves of medium size, light green;
- stem dark brown.
Advantages and disadvantages
Bush cherry has a number of advantages that favorably distinguish it from other varieties. Even a wild steppe cherry, deprived of care, is able to bear fruit perfectly. The yield is up to 8 kg per bush. The advantage is also frost resistance (up to -45 ° C), which allows you to grow a bush even in the conditions of the Siberian climate. Good tolerance to hot, dry days even in the absence of watering.
The variety is suitable for cultivation in order to decorate the landscape. Berry compotes and jams are made from cherries. It is widely used in the preparation of medicines and herbal preparations.
Disadvantages of the variety:
- not adapted to growing in the shade;
- berries have a sour taste, with pronounced astringency;
- for a stable harvest, it is necessary that cherries be planted nearby.
Existing varieties
Bush cherry includes several varieties.
- Generous. Refers to a variety of self-pollinators. A late maturing shrub with excellent frost resistance. It grows up to 2 m tall, fruiting ovaries appear at the 3rd year of life. The fruits are large, bright red. The pulp is juicy, sweet and sour taste.
- Maksimovskaya. The bush reaches 1.5 m in height, has a slightly elongated shape, with an average thickening index. It tolerates heat and drought very well. The variety does not tolerate frost well, has no resistance to coccomycosis. Berries are suitable for transportation due to their dense skin.
- Ruby. Reaches up to 2 m in height, has a spherical crown shape. The culture is late-ripening, the fruiting period falls in August. The fruits are medium in size, have yellowish flesh. Self-infertile shrub, requires planting a number of pollinating varieties.
- Subbotinskaya. It grows up to 2 m in height, has a dense, spherical crown, is susceptible to insect pests. Annually brings a stable harvest of up to 9 kg per bush. The species is self-infertile, ripens late.

Growing Rules
Steppe cherries should be planted on a site that has:
- good illumination;
- lack of drafts, which contribute to the destruction of the crown and the transfer of infectious diseases;
- low occurrence of groundwater, which will avoid flooding of the root system and the development of the fungus;
- a slight elevation to avoid flooding and retaining excess moisture during rain.
Shrub cherries are planted on soil with neutral acidity. If the acid content in the soil exceeds the norm, then the area should first be limed. To do this, prepare lime flour. It is necessary to take 100 kg of quicklime and 4 liters of water. A flat piece of land should be covered with lime and poured with water. After 20 minutes, collect the resulting fluff and repeat the procedure.
The resulting flour is applied to the soil to a depth of 15-25 cm in order to mineralize and reduce the acidity of the soil.
Landing Features
Planting a seedling should be carried out according to a special scheme.
- Preparing the site for planting bush cherries begins with fertilizing the site with manure in the fall. During the winter, the manure will pereperet and forms favorable conditions for rooting and further growth of the crop.
- With the onset of spring, dig a hole: 50 cm deep and 65 cm wide.
- The layer of fertile soil, which is on top, must be mixed with superphosphate fertilizer in the amount of 200 g.
- Fill the hole halfway with the mixture.
- In the center, drive a peg 2 m high, in the future the shrub will rely on it.
- Lower the seedling into the hole, gently straighten the rhizome.
- Fill the hole to the top, tamping well.
- Water the seedling with 20 liters of water.
For planting to be successful, you should choose the right seedling. The plant must necessarily contain a trace from the vaccination, which will confirm the authenticity of the variety. The branches and root system must be intact, without breaking, rot and withered parts.
Features of care
Shrub cherries require regular attention. Care must be correct and timely, then fruit trees will annually produce a bountiful harvest.
Basic rules for caring for bush cherries:
- the implementation of additional watering in the amount of 3 times during the summer period will help provide the plant with moisture, thereby increasing yields;
- loosening and mulching the soil in order to provide oxygen access;
- cleaning wild grass will save the plant from insect invasion;
- removing the undergrowth will increase the supply of nutrients.
Steppe cherry requires care, consisting of the timely application of top dressing. Usually the shrub needs additional nutrition during the period of intensive growth and fruiting. In the spring, after flowering, nitrogen-containing fertilizers are applied. In summer, during the fruit ripening period, the soil is mulched with chicken manure, which allows the soil to be mineralized and stimulates plant growth. Autumn fertilizer in the form of manure will help protect the rhizome from freezing in the winter cold.
pruning
The upper part of the bush cherry should be formed immediately one year after planting the seedling. All branches that are 30 cm from the ground are cut off. Crown care should be regular, then the steppe cherry will have a good appearance and become a decorative decoration of the garden.
In spring and autumn, bush culture requires sanitary pruning, which consists in removing damaged, dry and withered branches. Places of cuts are covered with garden pitch to avoid infection. Old branches that do not bear fruit should also be removed so that young shoots appear in their place.
The steppe culture usually has a spherical crown shape, the formation of which will require timely pruning. The upper part of the main branch is to be cut off, which will contribute to the rapid development of side shoots. The base of the shrub should contain 5 to 10 branches. Multiple shoots depart from them, which are capable of thickening the crown, which has a bad effect on productivity. It is not worth touching the main branches when pruning, it is better to deal with small thickening shoots.
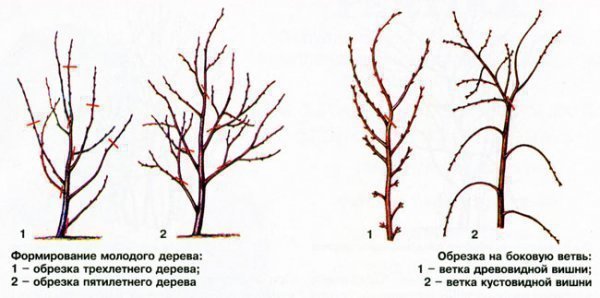
Formation of a young cherry tree
Diseases and pests
Steppe cherries are most susceptible to fungal infections, which can lead to a loss of up to 80% of the crop or to the death of the entire shrub. It is regularly attacked by harmful insects that eat leaves and fruits.
Common diseases
Moniliosis is a type of fungal infection that leads to the withering of the bush. In the advanced stage, it can lead to the death of the plant. It appears as a gray coating on the berries, located in circular patterns. Leads to cracking of the bark, leakage of gum. On flower ovaries and leaves, spots from burns are noticeable, which provokes a fungus.
Disease control:
- elimination of infected areas;
- regular collection of fallen fruits, which will prevent infection from entering the ground and its further transmission;
- seasonal whitewashing of the trunk;
- irrigation with a 1% solution of copper sulfate: 200 g per 10 liters of water.
Coccomycosis also refers to a type of fungal infection that attacks the plant during the hot summer period. Mold spores spread over the leaves, causing red spots and a pink bloom on the underside of the leaf.
In the fight against the disease, the drug "Horus" is used, in a proportion of 2 g per bucket of water. Irrigation of steppe cherries is carried out in three stages: after flowering, and then every 10 days.
Pest and insect control
Fruit mites are microscopic brown bugs that feed on leaf sap. They make egg clutches under the bark of a tree, where the offspring hibernate, and with the advent of heat they attack the plant. To overcome the tick, use the drug "Karbofos", diluting 2 g of the agent in 10 liters of water.
Aphid - an insect reaching 7 mm in length, green in color, feeds on the juice of leaves, flower ovaries and stems. You can notice the presence of aphids on fruit plants by twisted leaves covered with a whitish coating.
Aphid control:
- cleaning the tree from the affected areas manually;
- irrigation with a solution of soap: 300 g of grated laundry soap in a bucket of warm water - treatment is carried out for a week, twice a day.

"Karbofos" is used to combat ticks


