What plant is called water cabbage. Water rose
Winter. Blue predawn twilight, imperceptibly passing into the long dark evening. Black branches of trees sway in the icy wind - and infinitely far from summer, flowers and green foliage. How amazing one of these evenings came home and suddenly feel the strong aroma of jasmine on the doorstep! A glance involuntarily looks for a ghostly piece of summer in the room ... Here it is, our little oasis of heat and greenery - an aquarium! Light shadows play on multi-colored pebbles, bright fish flash in underwater thickets. And on the water, stretching corrugated velvet leaves, are rosettes of amazing plants. That they exude a summer scent. Blooms Pistia stratiotes - “water lettuce”, “water cabbage”, “water rose”, or “velvet rose”, and according to the science - body-cutting pistils - plant from the aroid family ( Araceae), a relative of anthurium, monstera, room calla, wild marsh calla and duckweed.

The leaves of the plant are completely covered with stiff hairs that repel water and trap air bubbles, so the socket does not sink and float, even when submerged in water. The airborne tissue, which develops in the thickness of the leaf, also contributes to the buoyancy of the plant. Flowers (or rather, inflorescences) of typical shape for the family are very similar to calla flowers, only small ones are no more than 1.5–2 cm in size. They open up in the center of the rosettes, among young leaves. Each “flower” consists of two parts - the “veil” covers separately the female flower of the cob — in the lower part of the inflorescence, and separately — the male flowers, reduced to a bunch of accrete stamens, in the upper part.

Such an arrangement of heterosexual flowers within one inflorescence occurs quite often - we recall at least the cattail ( Typha latifolia). If cross-pollination is not possible, self-pollination occurs - pollen from male flowers just crumbles down onto female pistils. The same thing, according to the literature, happens in the pistis. In many publications, including Plant Life, it is argued that the plant “easily self-pollinates and forms fruit.” But in our aquarium for a dozen years, the “cabbage” blossomed regularly, but it didn’t produce fruits either independently or with our obsessive attempts to “help” it.
Pistia blooms as soon as the socket reaches a sufficient size - at least 10 cm in diameter. But the "water rose" is light-requiring, and with a lack of light its sockets become small, and the leaves fall horizontally on the surface of the water - in order to catch more light. Such plants may not bloom for years. If there is very little light, having been tormented for a couple of months, the gun completely turns into organic fertilizer for species that are less demanding of light ...

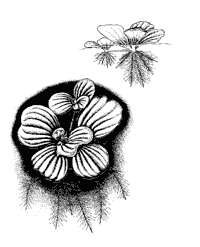
"Giant" pistes from a tropical pond
But if the “rose” is properly illuminated (and warmed up - the heat also loves the gun!) With an incandescent lamp (100 W at a distance of 30 cm from the top of the plant), the leaves will quickly begin to grow, the sockets will fill the entire surface of the water - no longer small and flat, and really look like huge green roses. If the plant feels good, even in the conditions of a room aquarium, the diameter of the sockets can reach 30–40 cm. If you grow a pistol in a usual round aquarium for 20 liters - which is very decorative! - only one copy remains on the water, others simply do not have enough space. Now only the extreme leaves are on the surface, and the central ones have risen beautifully to a height of about 10 cm above the water - this is the first sign that the plant is going to bloom.
If the gun is in the school aquarium, it can serve as a good demonstration object in the lessons of botany. The shape of this plant is a typical rosette (a shortened stem is almost invisible among densely located leaf bases). The leaf position is spiral, which is clearly visible from above. The leaves are quite rare for plant shape - the widest part is the top of the leaf, which is cut off from above. This is a good example for the theme: “Variety of leaf blade shapes”. The venation is parallel (which is typical of most monocotyledonous plants), the veins - the leaf blades pressed in from above and protruding from below - are clearly visible. On the leaves of the gun at high humidity (for example, if it grows under the glass of an aquarium), one can observe the phenomenon of guttation - release of excess water in the form of droplets. The whole plant is densely covered with hairs, which can be examined under a microscope or a strong magnifying glass and make sure that they are multicellular. In pure transparent water, the root system of the pistis is clearly visible. A plant located close to the front wall of the aquarium can measure the rate of root growth by making marks on the glass.

Pistia - a great example of vegetative propagation with the help of affiliated sockets. Its thick pubescent stolons grow quickly, and you can study the dependence of their growth rate on the temperature of the water in the aquarium (if there is an aquarium heater and the temperature can be adjusted). It will be interesting to compare the growth rate of two identical daughter outlets, one of which is separated from the parent plant, and the other continues to be associated with it stolon. Obviously, the more nutrient the environment in the aquarium, the less this difference will be.
In summer, the pistol can be planted in a street pond — to do this, you simply need to throw a few sockets into the water as soon as its temperature rises to 10–15 ° C — from approximately the end of May until the first week of September, cabbage can remain outside. Velvet rosettes are very decorated with a pond, giving it a "tropical flavor."
Interestingly, the leaves of "cabbage" are often used by bees (including domestic bees) as a "raft" for drinking. On pubescent leaves of “cabbage”, unlike, for example, from bare slippery water lilies, it is easier to hold, and besides, bees do not drink water from the edge of the leaf, but from the center of the socket, between the bases of the leaves - conveniently and safely!
In the tropics, “cabbage”, instantly expanding, contributes to waterlogging of water bodies, forming true alloys 1. In some places, this plant is a malicious weed in rice paddies. Recently, largely due to cultivation, the piste has advanced far to the north - there is information about its successful wintering in the water bodies of Denmark. In Russia, this plant is found in the Volga delta. Successful wintering of the gun in the cooling ponds of the CHP plant is not excluded, but we have no reliable information about this.

However, when grown in open freezing waters, there is no chance of surviving the winter. So the ecological catastrophe near Moscow reservoir, into which this plant falls, is not threatened. In this pistea is very similar to another tropical species, which is also a malicious weed in the tropics and has been actively cultivated recently in the middle lane - water hyacinth eichhornia. And just like eihornia, the piste serves as an excellent decorative element of reservoirs.
Nevertheless, when planting “water cabbage” in a very small reservoir we will have to engage in - especially if the summer is hot and there is another aquatic vegetation in the pond that I would like to preserve. Solid carpet outlets for the light is almost impenetrable. Yes, and the normal gas exchange, he begins to interfere.
Those who conduct such an experiment for the first time will face several surprises. Plants will retain the appearance of the usual (fibrous) root system, but the roots themselves and their lateral processes will become significantly longer, stronger, more elastic. The socket will reach an average size larger than in an aquarium (if the water is not very cold), and will get an even more “cabbage” look. The color of the plant will change to a bluish color - the pubescence will become thicker: changes are likely to occur at the tissue level.
And the most curious thing is that with an accidental drying up of a reservoir, the sockets do not dry out immediately, they do not even fade, but continue to grow quietly, if only the soil on which they find themselves remains moist enough 2.
1 In tropical areas, piste is common almost everywhere. It was described from the south of North America in the middle of the 18th century, but there is a hypothesis that it was brought there earlier from Africa. - Approx. ed.
2 We grew a pista in a reservoir with a clay bottom. - Approx. auth.
The publication is sponsored by the Institute of Distance Education and Part-time Education - Humanitarian-Economic and Information-Technological Institute. Having taken advantage of the offer of the State Institute of Architecture and Technical Engineering, you can get a second higher education in Moscow, while being in any part of Russia. Upon graduation, you will receive a state diploma. Your choice of economic areas such as accounting, analysis and audit, finance and credit, taxes and taxation. In order to start distance learning, it is enough to fill in a questionnaire on the site www.GEITI.ru and the institute managers will contact you.
Pterygoid fern or, as it is called, Ceratopteris (Ceratopteris pteridoides) or Water cabbage – family Hornlike (Ceratopteridaceae).
Growing area
Pterygoid fern growing throughout the South American continent, as well as in Central America. Under natural conditions, it can be found in water bodies with slow or standing water.
Appearance
Height Pterygoid fern in nature is about 30 cm, at home it will be limited by size. The broad light green leaves are finger-shaped. The second name is “water cabbage”. The pterygoid fern has received due to the fact that its leaves form a dense rosette resembling a head of cabbage. The fern leaf plate is quite large, like the cuttings, very fragile and fragile. has a fibrous root system - its roots intertwine, forming a thick “beard”, in which fry hide and spawn.
In the aquarium, this fern can take root in the ground, or float freely on the surface of the water. The first option looks spectacularly planted along the back and side walls of the aquarium, and the second - in the form of a beautiful rosette of translucent leaves on the water surface.
The winged fern is a wonderful natural filter, absorbing carbon dioxide and organic matter and actively releasing oxygen. In addition, floating on the surface, it perfectly diffuses the light, creating a comfortable environment for the inhabitants of the aquarium.

Conditions of detention
Contain Pterygoid fern quite difficult, so few people decide to settle it in their underwater garden. The aquarium, where this fern grows, cannot be closed, because the plant is harmed by the condensation that forms on the leaves. Also, he should not be disturbed often, so he should be sedentary. The recommended temperature is 22-28 ° C, the water is neutral, with hardness up to 15 * and a large amount of organic matter. This type of fern needs a lot of light, so the aquarium needs to provide intense lighting. If you do not withstand the listed conditions that are comfortable for the plant, it begins to lose color and slowly dies.


This plant in everyday life is called water cabbage. However, taste has nothing to do with it. Ceratopteris cannot be eaten, but it is possible to keep it in an aquarium.
In nature, this marsh plant is found in a large area of tropical South America (Colombia, Paraguay, Peru, Brazil, northern Argentina) and in some regions of Central America (for example, in Guatemala and Honduras).
Separate small populations are found in the southern states of India, as well as in the countries of the Indochina peninsula (Vietnam, for example).
This type of fern prefers to grow in slow-flowing rivers or in stagnant water of marshes rich in organic matter.
Taxonomy
According to the scientific classification of ceratopteris (Ceratopteris pteridoides in Latin) belongs to the extensive family Hornlike (Ceratopteridaceae). In some sources - Ceratopteris cornuta. Botanists have studied the Ceratopteris pteridoides for a long time and very well.
Appearance and features
 Pterygoid fern is a rather large tropical plant that loves warmth and can exist in turbid, organically saturated water. Capable of firmly rooted in wet ground, but can be on the surface without rooting.
Pterygoid fern is a rather large tropical plant that loves warmth and can exist in turbid, organically saturated water. Capable of firmly rooted in wet ground, but can be on the surface without rooting.
The roots are thin, strongly branched, gray. If the vegetation floats freely in the water, more precisely on its surface, then the hanging root very much resembles a tangled beard.
In natural conditions, specimens of this type of aquatic flora are quite impressive in size:
- the length of a thick stalk ranges from 23 to 30 cm,
- the length of the leaf stalks can reach 18 cm,
- and thickness - up to 2 mm.
And the stem and petioles have a spongy structure. The leaf plate itself is also large: up to 18 cm long and 24 cm wide, dissected in shape.
The light green leaves are fleshy, streaked, fragile, in their structure really resemble cabbage leaves.
The plant has both sterile and fertile (producing shoots) leaves, and they come in both ground and floating specimens.
Along the edges of each fertile leaf there are so-called sporangia, wrapped down. These are special buds in the form of small sacs that contain 32 spores. From them grow new shoots of fern.
It should be noted that such a reproduction mechanism "works" only in natural conditions. There are no cases of natural reproduction of ceratopteris in aquariums.
On the surface of the water, the leaves are folded into a compact "outlet", which resembles in its appearance a small head of cabbage. Hence the name "water cabbage".
Features of the content in aquariums
 Aquarium. Since this type of fern has quite substantial size, an aquarium is also needed for its optimal maintenance, not small, with a capacity of 50 liters or more. However, in the case of aquarium content, the growth (and, accordingly, the size) of the plant will be limited by the existing artificial reservoir.
Aquarium. Since this type of fern has quite substantial size, an aquarium is also needed for its optimal maintenance, not small, with a capacity of 50 liters or more. However, in the case of aquarium content, the growth (and, accordingly, the size) of the plant will be limited by the existing artificial reservoir.
Aqua design. using ceratopteris wins if it is planted in the ground in the background or at the side walls.
Often water cabbage just floats on the surface of the water, being the main element for setting up shading areas, which are very attractive for some species of ornamental fish.
In the thickets of water cabbage, especially in its “beard”, fry like to hide very much.
Aquaparameters. The water in the tank should be sedentary, which is achieved by appropriate adjustment of the compressor and filter pump. The soil should be slightly silted, rich in nutrient organics, which serves as food for the development of the plant.
A tropical aquarium containing Ceratopteris pteridoides should have the following water parameters:
- acid-base balance of 6.5–7.5 units (near the neutral mark);
- temperature in the range from +22 to +28 degrees Celsius;
- rigidity no more than 15 degrees.
Lighting not a very important factor of content, but you should ensure the duration of daylight at least 6 hours Experts strongly recommend the use of lamps only to avoid burning large leaves of fern.
Experts say that with the rejection of the specified conditions of the plant gradually degrades and dies.

But in this case there is a danger that the leaves of the fern will close the entire water surface of a small domestic pond.
- The tank where the ceratopteris is located should be covered with a lid.
Of course, the plant will not jump out, like some species of ornamental fish, but this is necessary in order to prevent the formation of condensation on the surface of large leaves. It can damage the plant.
- She also doesn’t like frequent transplants
If you got the fern out of the ground and left it to float on the surface of the aquarium, then it is not at all a fact that when you re-plant the bush in the aquarium soil it will normally take root.
In general, experts argue that the level of Ceratopteris pteridoides is a complex plant.
The winged fern is appropriate in a medium-sized aquarium (50–100 liters). Let him go to the "swimming", and the decorative qualities of your home pond from this will only increase.
Pistia (Pistia) or Water cabbage is a famous aquarium plant of the Aroid family. Piste well know aquarists. It is also called "water rose", "water salad". This heat-loving tropical plant comes from fresh waters of Africa.
Pisti leaves collected in the outlet, sessile, velvety, light green. The gentle rosettes of its leaves floating on the surface of the water are unusually beautiful. Below, under the leaves, long branched roots are green or almost black in color up to 25-30 cm. The whole plant floats on the surface of the water in the coastal zone, and when the water level drops, it is easily rooted in the ground.
Pistia is considered capricious plant. She does not tolerate cold water, lives only in a warm pond. For full growth of water cabbage you need a lot of light, you also need a sufficient nutrient medium. In favorable conditions, the rosette of leaves can reach a height of 15 cm and a diameter of up to 40 cm.
Flowering is of no interest, even if it produces an inconspicuous inflorescence on a short peduncle. The rosette of leaves itself may look like a green rose or a lush bush of lettuce with corrugated leaves, for which the plant is valued.

In aquariums, the piste does not grow big, its sockets are often 5-7cm. Aquarists know that for the successful cultivation of water cabbage in winter requires a lot of light, otherwise it dries and disappears.
Surprisingly, but transferred to, the pistol grows well, its sockets become large, many children appear. This is just a luxurious floating plant for homestead ponds!
Of course, tropical water cabbage cannot spend the winter in a pond; in the winter it should be stored in an aquarium or a can. If the house has an aquarium and small pistes grow in it, then the planting material for the garden pond will always be in abundance.
Using the gun in garden ponds
Best of all, the piste looks in small ponds, where you can see its exotic beauty well. In bowls filled with water, in small bogs in combination with high shoots of tsiperus or zantedesky, water cabbage will look very impressive. In shallow water, a pista can quickly multiply, forming a floating carpet by the end of summer.
Tips for growing pista (water cabbage, water lettuce)
Location. As well as for, heat-loving pistes are sunny and shallow. Water in them should be warm in the sun. The main requirements for the normal development of water cabbage - heat and bright light.

Temperature. In the pond relocate pisti only when the water warms to a temperature of 10-15 ° C. Air temperature may be slightly lower. If cooling is expected, warm water can be added to the pond.
Nutrition. Water cabbage requires good nutrition. Best of all, it grows in water with a lot of nitrates. For full development requires the presence of fertile soil at the bottom of the reservoir, and even better if the roots reach the silt at the bottom of the pond.
Wintering. Water cabbage winters in an aquarium at a temperature not lower than 16 ° C. In early September, only small outlets from the pond are taken, they are thoroughly washed so as not to introduce pests into the aquarium. It is best to place the plants in a separate aquarium. Pistia needs high humidity, so the aquarium is covered with glass. Be sure to require good lighting, preferably light day 10-12 hours a day.
Beautiful pistis has a number of names: water rose, velvet rose, water salad and water cabbage. The rosettes of its leaves are very elegant and incredibly attractive. This beauty grows in both hemispheres of our huge planet and in fresh tropical and some subtropical waters. The spectacular piste is great for growing in aquariums, as well as in reservoirs of warm greenhouses.
Meet the plant
Pistia is an excellent representative of the Aroid family. It is endowed with numerous floating feathery roots, which serve as an excellent natural filter, and short stalks.The spongy leaves of this plant form rosettes floating on the water surface and are endowed with spaces filled with air. All leaves are blunt-shaped, sessile, slightly narrowed to the bases and widening at the ends, with rounded front edges. The color of the leaves is usually gray-green, they are 8 to 10 cm wide, and 15 to 25 meters long. The leaves appear to be corrugated, since their almost parallel numerous lateral veins are slightly pressed from above. Meanwhile, these veins act as ribs on the lower surfaces of leaflets, incredibly powerful at their bases and less pronounced at their ends. Due to the special structure of the leaves, the pistis is superb on the water. All leaves are densely covered with short grayish hairs, which play the role of a kind of waterproof fabric and protect them from getting wet.

As soon as the diameter of the gun exceeds ten centimeters, it begins to bloom with small white flowers with a rather pleasant aroma. All the flowers are collected in the cob blossoms, located in the middle of the green carpet of leaves.
Pistol use
In addition to the use of warm greenhouses in aquariums and ponds, piste as feed for pigs is cultivated in fish ponds. Yes, and in the culture of this plant was introduced by Chinese pig breeders. Also, an excellent piste serves as a fairly good fertilizer.In China, the young leaves of the piste in boiled are readily eaten. And the Chinese use this plant to cure skin diseases. In India, dysentery is treated with a pistol, and in Malaysia, gonorrhea is treated. In addition, the gun is great for washing greasy dishes and for removing various stains from fabrics.
Not to mention that the piste is considered a malicious weed, capable in the shortest possible time to completely cover the surfaces of small reservoirs, condemning them to a speedy disappearance. In addition, it creates favorable conditions for the life of mosquitoes, thereby contributing to their reproduction.
How to grow
For the cultivation of pistes, the most well suited are sunlit ponds, the depth of which is in the range of ten to forty centimeters. The conditions under which direct contact with the ground at the bottom of the reservoirs will be possible are considered ideal.
Pistia loves heat, so for its full development will require a lot of heat, bright lighting and good food. Light will suit both natural and artificial. In addition, the gun will also need to provide a fairly high humidity.
Plants are launched only after warm weather has been established. This can be done at the beginning of summer, when the temperature of water in reservoirs rises above the mark of ten degrees.
Pistia - a plant quite capricious, I can even say that capricious. It can withstand winter temperatures only if it is at least sixteen degrees. Around the end of August, the pista from open water bodies is transferred to warm rooms. This beauty pretty well transfers winter in home aquariums.

