Albizia
Legume family (Fabaceae).
Deciduous and evergreen trees or shrubs. The leaves are alternate, unpaired twice pinnate, with numerous small leaves. Flowers in axillary petiolate spikelets or spherical heads, with numerous stamens, attract an abundance of butterflies, bees and birds. The fruit is a large flat bean. The genus includes about 25 species growing in tropical and subtropical regions of Asia, Africa and Australia, 1 - in Mexico. In Russia, 1 species grows - Lankaran Albizia. Excellent ornamental plants, some of them are also of industrial and technical importance.
Kinds:
Spreading. Wildly grows in the forests of Lankaran (Republic of Azerbaijan), in Iran. It is widely cultivated in eastern Transcaucasia, found in central Transcaucasia, on the Black Sea coast of the Caucasus - from Dzhubga (north of Tuapse) to Batumi and in the Southern Crimea - from Sevastopol to Alushta.
A deciduous tree 10-15 m high, with a wide spreading umbrella-shaped crown of openwork leaves resembling acacia leaves. Leaves unpaired twice pinnate, up to 20 cm long, with 30-60 leaflets, green above, bluish below. The tree grows 50-100 years.
Flowers in heads, collected in large paniculate inflorescences, fragrant. Stamens numerous, long, pink or whitish-yellow, protruding from small white-yellow flower covers. Its flowering is plentiful and long - it begins in mid-June and lasts until September-October, depending on the weather. In autumn, it retains leaves for a very long time. Albitia remain green until the last moment, and only a frost or a strong wind can destroy them at once. The fruit is a flat, long, membranous, multi-seeded bean.
A very fast growing breed. Albizia is photophilous, it cannot grow in the shade of other trees. Moisture-loving, but mature plants are quite resistant to drought. Handles pruning well.
The root system is superficial, powerful. Grows best in deep, humus-rich, sandy, fresh alluvial soils, but also grows quite satisfactorily in dry, clayey, lime-containing gravelly soils. When planted near the sea, it tolerates salty sea spray well. It also tolerates urban conditions (smoke, soot and dust). It is not frost-resistant enough, without damage it can withstand temperatures as low as -15-16 °, at -18 ° young branches freeze slightly, and at -20-22 ° the main branches of the crown also freeze. Propagated by seeds, layering, cuttings under glass, grafting.
In room conditions blooms very rarely. Location: Light to sunny, protect from strong sun. In winter, the temperature is not higher than 15 °C. In summer, it is advisable to take the plant outside and water it abundantly, in winter - watering is reduced and kept in a cool, well-ventilated area. From April to July, it is necessary to feed once every 2 weeks.
Humidity: uniform. In most cases, the drying of the root ball means the death of the plant.
Fertilizer: from spring to autumn every week, in winter every 3-4 weeks, 0.1%.
Transplantation: first planting at the age of 3-5 years, transplanting every 2-3 years. Handle roots with care. The soil mixture is loose, nutritious.
Formation: young plants are often and strongly shortened, as they themselves branch little. Later pruning activities should be carried out in the spring. Wire pulling is possible, but it is better to use other shaping methods.
Reproduction: seeds, cuttings, root shoots.
In the spring, albizia seeds need stratification. seeds before sowing, soak in warm water until swelling (for 1-2 days) and sown in a moist substrate, lightly sprinkled with soil. Seeds germinate at a temperature of 20-25 "C. When the seedlings grow up, they are planted in pots of 7.5 cm. In winter, Albizia seedlings are kept at a temperature of 5C. When the threat of frost has passed, the plants are planted at a distance of 2 m from each other, protected from the wind, Seeding rate 1.5-2 g per 1 running meter Albizia needs light, rich, well-drained soil, tolerates transplanting well up to 6-8 years.
In warm regions, seeds are sown directly into the ground in autumn, the germination rate is about 80%, and single seeds can sprout in a year. In the first year, albizia seedlings grow slowly and rarely reach a height of 20 cm by autumn. I don’t need to feed them at this time - you can burn the roots of young plants. In addition, with an excess of nitrogen fertilizers, the vegetation of plants is delayed, and the wood of seedlings may not ripen well by winter. Then, in the event of severe frosts, such plants can be severely damaged or even die. Albitia seedlings can be fed from the second year of life, gradually increasing the dosage.
Vegetative propagation of albition is used more often. Some trees produce root shoots that can be separated and transplanted when the plants are dormant.
The Lankaran acacia is being cut satisfactorily; both lignified and green cuttings can be used.
woody cuttings cut from the annual growth of the previous year. They take cuttings with 2-3 buds from the middle of the shoot, treat them with root formation stimulants and plant them in a permanent place in loose fertile soil. After 3-4 months, rooting usually occurs at 70-80%
Green cuttings of albizia are used in July. Cuttings are also taken from the middle of the shoot with 2-3 buds, they are also treated with root formation stimulants, but 2/3 of the leaf blade is removed. They closely monitor soil moisture, and usually by autumn, 70-80% of the cuttings take root.
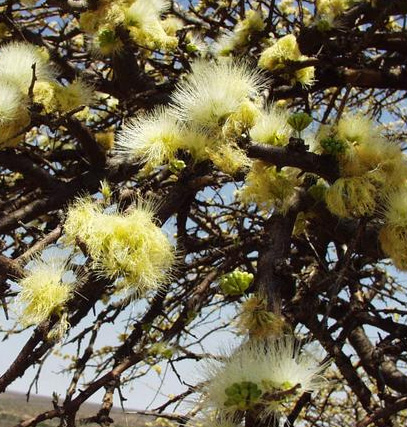 Shrub or tree 3-9 m tall, deciduous with smooth gray or brown bark. The leaves are pinnate, glabrous or shortly pubescent. Feathers 1-2 pairs, leaves 1-4 pairs. Obliquely obovate or almost round, 1-3.6 cm long and 0.6-3 cm wide, pointed. Flowers usually on stalks up to 0.55 cm long. The calyx is light greenish. The corolla is light greenish, up to 1.2 cm long, the stamens are white, about 2 cm long, they protrude from the corolla as a brush. The pods are 7-18 cm long and 1.5-2.9 cm wide.
Shrub or tree 3-9 m tall, deciduous with smooth gray or brown bark. The leaves are pinnate, glabrous or shortly pubescent. Feathers 1-2 pairs, leaves 1-4 pairs. Obliquely obovate or almost round, 1-3.6 cm long and 0.6-3 cm wide, pointed. Flowers usually on stalks up to 0.55 cm long. The calyx is light greenish. The corolla is light greenish, up to 1.2 cm long, the stamens are white, about 2 cm long, they protrude from the corolla as a brush. The pods are 7-18 cm long and 1.5-2.9 cm wide.
 Shrub or small tree 6 m tall, occasionally 12 m with open and round or bell-shaped cover and light gray bark. Shoots pubescent with age, with white lenticels. Leaves with 8-12 pairs of feathers, consisting of 20-40 pairs of leaflets. Leaflets 1 cm long and 0.3 cm wide, sometimes slightly curved, gray-pubescent, shortly pointed. The flowers are round, pinkish in panicles 5 cm long, located in the axils of the petioles. Pods 10-15 cm long.
Shrub or small tree 6 m tall, occasionally 12 m with open and round or bell-shaped cover and light gray bark. Shoots pubescent with age, with white lenticels. Leaves with 8-12 pairs of feathers, consisting of 20-40 pairs of leaflets. Leaflets 1 cm long and 0.3 cm wide, sometimes slightly curved, gray-pubescent, shortly pointed. The flowers are round, pinkish in panicles 5 cm long, located in the axils of the petioles. Pods 10-15 cm long.
 Ceylon, Indochina, S. China, Malaysia Trees up to 20 m tall. Leaves with 4-14 pairs of feathers, leaflets 20-30 pairs, 6-10 mm long, 2-3 mm wide, acute at the apex, stipules up to 1.5 cm long and 3 cm wide. flowers 8-12 mm (central larger), in heads 20-25 mm in diameter (excluding stamens), sometimes reduced to 3-4 peduncles collected in leaf axils, corolla white, stamens up to 30 mm. Pods are flat, 10-17 cm long, 1.7-3.5 cm wide, indehiscent. Seeds elliptical, laterally compressed, about 7 mm long and 4-5 in diameter.
Ceylon, Indochina, S. China, Malaysia Trees up to 20 m tall. Leaves with 4-14 pairs of feathers, leaflets 20-30 pairs, 6-10 mm long, 2-3 mm wide, acute at the apex, stipules up to 1.5 cm long and 3 cm wide. flowers 8-12 mm (central larger), in heads 20-25 mm in diameter (excluding stamens), sometimes reduced to 3-4 peduncles collected in leaf axils, corolla white, stamens up to 30 mm. Pods are flat, 10-17 cm long, 1.7-3.5 cm wide, indehiscent. Seeds elliptical, laterally compressed, about 7 mm long and 4-5 in diameter.
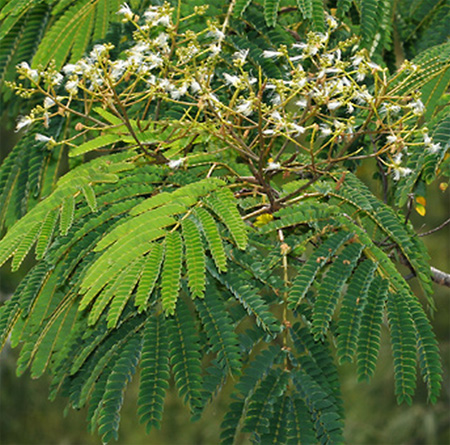 Tree up to 40 m tall with white, gray or greenish bark, smooth or warty. The leaves are pinnate with 8-15, 15-25 pairs of elliptical, crescent-shaped leaflets 1-2 cm long and up to 0.6 cm wide with a strong midrib. Flowers in panicles up to 20 cm in diameter. Calyx up to 0.15 cm long, slightly pubescent. Corolla cream or greenish-yellow, up to 0.45 cm long. Stamens up to 1.7 cm long. Pods 9-12 cm long and up to 2.5 cm wide, densely pubescent or glabrous. This species is the fastest growing in the world.
Tree up to 40 m tall with white, gray or greenish bark, smooth or warty. The leaves are pinnate with 8-15, 15-25 pairs of elliptical, crescent-shaped leaflets 1-2 cm long and up to 0.6 cm wide with a strong midrib. Flowers in panicles up to 20 cm in diameter. Calyx up to 0.15 cm long, slightly pubescent. Corolla cream or greenish-yellow, up to 0.45 cm long. Stamens up to 1.7 cm long. Pods 9-12 cm long and up to 2.5 cm wide, densely pubescent or glabrous. This species is the fastest growing in the world.
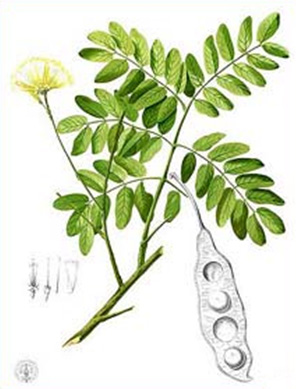 Widespread in India, Burma and the Andaman Islands. Deciduous tree up to 20 m high. Slender straight trunk with wide spreading branches. Fern-like finely divided foliage. Yellow flowers in fluffy inflorescences. Reproduction - seeds.
Widespread in India, Burma and the Andaman Islands. Deciduous tree up to 20 m high. Slender straight trunk with wide spreading branches. Fern-like finely divided foliage. Yellow flowers in fluffy inflorescences. Reproduction - seeds.
Contains: tannins and pseudotannins, melanoxetine, ocanine, flavonoids, albizzigenin, saponin, crystalline calcium, starch, oleanolic and echinocystic acid, sitosterol. The leaves contain campferol, myricitrin, vicenin flavone.
Shirisha is a very famous medicinal plant used in different medical traditions. It has the strongest detoxifying effect on the body, making it one of the most important herbs in Ayurveda's arsenal. It increases metabolism, is effective against poisoning, and has an anti-cancer effect. Has no toxic effect. May have a contraceptive effect. The bark and nectar of flowers are used in the tradition of Ayurveda as a source of tannins, which are used as natural ingredients in the production of creams and balms, as well as a source of aromatic resins. From the nectar of the flowers of the tree, light fragrant honey is obtained.
Albizia bark - astringent, bitter, sweet, has an expectorant effect, increases sexual energy, is useful for ophthalmia, cough, runny nose, skin diseases, diarrhea, neuralgia, epilepsy, all types of poisoning. The stem has sugar-lowering properties. Used as a remedy for bronchitis, leprosy, helminthic lesions. Flowers are used for chronic cough and bronchitis. The seeds are effective against tuberculosis, seminal weakness and poisoning. All parts of the plant are used for snake and scorpion stings. The leaves are useful in night blindness. They are also prepared as an ointment and powder for poultices on ulcers.
 Large tree with gray bark. The leaves are opposite, pinnate with opposite oval leaflets. Flower heads with small flowers similar to acacia flowers. The fruits are oblong pods.
Large tree with gray bark. The leaves are opposite, pinnate with opposite oval leaflets. Flower heads with small flowers similar to acacia flowers. The fruits are oblong pods.
 The species is native to Western Australia. Shrubs or undersized, 2-4 (up to 6) m tall, trees, pubescent shoots. A slender trunk with a soft bark with a wide spreading crown. The leaves are dark green, 15 cm long, doubly pinnate, with 8-10 pairs of first-order leaflets and 20-40 pairs of second-order linear leaflets, 0.6-0.7 cm long, glabrous or pubescent below. Pink, green or cream flowers in brush-like inflorescences 7.5 cm long. The flowers are collected in spikes of a cylindrical shape, 3-6 (8) cm long, yellow. Blooms in March-May. Reproduction - seeds.
The species is native to Western Australia. Shrubs or undersized, 2-4 (up to 6) m tall, trees, pubescent shoots. A slender trunk with a soft bark with a wide spreading crown. The leaves are dark green, 15 cm long, doubly pinnate, with 8-10 pairs of first-order leaflets and 20-40 pairs of second-order linear leaflets, 0.6-0.7 cm long, glabrous or pubescent below. Pink, green or cream flowers in brush-like inflorescences 7.5 cm long. The flowers are collected in spikes of a cylindrical shape, 3-6 (8) cm long, yellow. Blooms in March-May. Reproduction - seeds.
 Sri Lanka. Deciduous tree up to 25 m high. Slender straight branched trunk. Double-pinnate green leaves with oval or lanceolate stipules. Yellow flowers in fluffy long up to 30 cm inflorescences. Mature pods are reddish brown, thin and flat, 13 to 20 cm long and 2 to 4 cm wide, and contain 8 to 12 reddish brown seeds, each weighing about 0.05 grams. The bark is dark gray with horizontal lenticels. Reproduction - seeds.
Sri Lanka. Deciduous tree up to 25 m high. Slender straight branched trunk. Double-pinnate green leaves with oval or lanceolate stipules. Yellow flowers in fluffy long up to 30 cm inflorescences. Mature pods are reddish brown, thin and flat, 13 to 20 cm long and 2 to 4 cm wide, and contain 8 to 12 reddish brown seeds, each weighing about 0.05 grams. The bark is dark gray with horizontal lenticels. Reproduction - seeds.
The usefulness and rapid growth of about a meter in height annually, has led to a wide distribution in the tropics, and sometimes in temperate zones, young plants are susceptible to frost. It has become naturalized over large swathes of tropical Africa, stretching from Tanzania to the east coast through Kenya, Malawi and Zimbabwe, as far south as Mozambique, and is grown in Johannesburg, South Africa. It has also become wild in Central America and Florida in the USA. It is tolerant of a wide range of soil types, but grows best in moist, well-drained, loamy soils, and can grow from sea level to 1800 meters, with an annual rainfall of 600 to 3000 mm.
Albizia fragrant has an attractive dark brown wood with a black heartwood, often striped, strong and dense. In Bangladesh, large areas of tea and coffee plantations are divided by Albizia odoratissima. The leaves are good fodder for livestock.
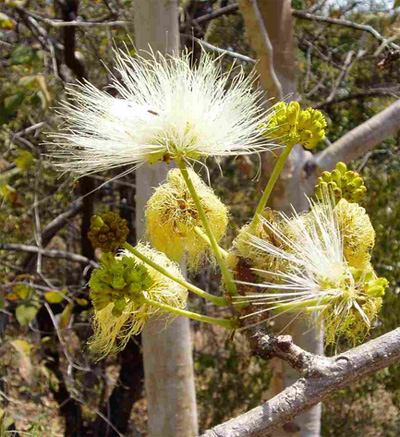 Albizia Tanganyika tends to grow alone, often on sandy soils among rocky areas. It is often found in the hot northwest and slopes.
Albizia Tanganyika tends to grow alone, often on sandy soils among rocky areas. It is often found in the hot northwest and slopes.
The large leaves have prominent glands at the base of the stem leaves. Leaves 2 - 6 pairs of opposite feathers, with 5 - 13 pairs of opposite leaflets (leaf: 250 - 300 mm; leaflet: 12 - 40 mm x 7 x 12 mm). Striking, fragrant flowers appear before the leaves from August - November (50 mm). The broad bean pods are thin, and reddish-brown when ripe, and they split open on the tree (September - December) (up to 300 mm). The wood contains an ingredient that can cause irritation to the nose and throat when handled. The pods are poisonous, and cause nervous breakdowns in animals.
 Africa is a large tree, about 36 m high and 1 m in diameter, with a trunk cleared to 9 - 12 m.
Africa is a large tree, about 36 m high and 1 m in diameter, with a trunk cleared to 9 - 12 m.
Flowers are bisexual, regular, 5-multiple, white or yellow, under which bracts up to 7 mm long are visible; pedicels up to 3 mm long, calyx 3-6 mm long, with a long tube and short lobes, densely pubescent rusty outside, corolla 9-13 mm long, with a 6 mm long tube, rusty hairy outside, numerous stamens, 3-5.5 cm long, united in a tube in the lower half; ovary superior, s. 3 mm long, gradually tapering in to 3 cm long style. Fruit oblong, flat under 15-24 cm x 3-5 cm, glabrous, transversely veined, yellowish-brown, when ripe, opening 2-paper valves, c. 10 seeds. Seeds flattened spherical to ellipsoid, 7-10 mm? 4.5-8 mm.
Flowers produce nectar collected by bees. The bark is used in traditional medicine; The decoction is used to treat dysentery, bronchial passions, and pain caused by fever, and it is applied externally to ulcers, pimples, and other skin conditions. The bark is also used as an anthelmintic. Maceration bark is drunk to treat jaundice. Leaves decoctions are applied externally to treat headaches, and as a wash or steam inhalation against fever (including malaria) and toothache, they are also applied for lice. The maceration leaf is administered as an enema to induce an abortion. The bark is also used in veterinary medicine. In Cameroon, the bark of the root and gums from the trunk of the bark are used in the preparation of poison for arrows. The leaves serve as poison for fish in the Central African Republic.
 widely distributed in tropical Africa, originating from Senegal in the west to Kenya in the east and north to Angola and Tanzania in the south. The tree is medium in size, about 27 m tall and 1 m in diameter. It usually has strongly developed plank roots, but a good shape of the trunk. It is considered useful for soil improvement. The young leaves are eaten cooked or added to soups and sauces. The foliage is rated as poor quality fodder, but usable for goats and sometimes for sheep and cattle. Flowers produce nectar, which is collected by bees. Gum from the bark is used in the food industry (eg as a stabilizer in the preparation of ice cream), the cosmetics industry (eg as a thickener) and the pharmaceutical industry (eg as a drug coating). In traditional medicine, the bark juice is instilled into the eye to treat eye inflammation. A decoction of the bark is used to treat bronchial diseases, fever (including malaria) and female infertility, as well as a laxative, gastric, antidote, anthelmintic and aphrodisiac. The crushed bark is used externally to treat yaws, ulcers, wounds, and toothache. The crushed roots are added to food to treat coughs and as an expectorant. Leaves decoctions are used to treat fever and diarrhea.
widely distributed in tropical Africa, originating from Senegal in the west to Kenya in the east and north to Angola and Tanzania in the south. The tree is medium in size, about 27 m tall and 1 m in diameter. It usually has strongly developed plank roots, but a good shape of the trunk. It is considered useful for soil improvement. The young leaves are eaten cooked or added to soups and sauces. The foliage is rated as poor quality fodder, but usable for goats and sometimes for sheep and cattle. Flowers produce nectar, which is collected by bees. Gum from the bark is used in the food industry (eg as a stabilizer in the preparation of ice cream), the cosmetics industry (eg as a thickener) and the pharmaceutical industry (eg as a drug coating). In traditional medicine, the bark juice is instilled into the eye to treat eye inflammation. A decoction of the bark is used to treat bronchial diseases, fever (including malaria) and female infertility, as well as a laxative, gastric, antidote, anthelmintic and aphrodisiac. The crushed bark is used externally to treat yaws, ulcers, wounds, and toothache. The crushed roots are added to food to treat coughs and as an expectorant. Leaves decoctions are used to treat fever and diarrhea.
 Africa - common in secondary forests. This species is especially fond of tropical conditions and is especially common in the wetter areas of eastern South Africa and Northern Limpopo. The trunk is often serrated (prickly) and twisted. It can reach a height of more than 40 meters. The leaves are very characteristic; 4-8 pairs of bear feathers 6-12 pairs of leaves each. Flowers strike by forming relatively large, hemispherical heads. Petals are white or greenish white. The fruit is a thin pod with a noticeable edge. Seeds flat, brown. The golden yellow wood is light and soft. Sauce is made from the seeds. The resin is used in cosmetics. The bark is used to treat skin diseases and bronchitis. Extracts from the roots are applied to inflamed eyes. The bark also helps in the treatment of human and animal worms or tapeworms, as well as headaches and sinusitis. The tree is also planted in some areas to conserve soil and control erosion.
Africa - common in secondary forests. This species is especially fond of tropical conditions and is especially common in the wetter areas of eastern South Africa and Northern Limpopo. The trunk is often serrated (prickly) and twisted. It can reach a height of more than 40 meters. The leaves are very characteristic; 4-8 pairs of bear feathers 6-12 pairs of leaves each. Flowers strike by forming relatively large, hemispherical heads. Petals are white or greenish white. The fruit is a thin pod with a noticeable edge. Seeds flat, brown. The golden yellow wood is light and soft. Sauce is made from the seeds. The resin is used in cosmetics. The bark is used to treat skin diseases and bronchitis. Extracts from the roots are applied to inflamed eyes. The bark also helps in the treatment of human and animal worms or tapeworms, as well as headaches and sinusitis. The tree is also planted in some areas to conserve soil and control erosion.
Possible difficulties:
Falling buds: the cause may be overdrying of the earthy coma.
Withering leaves: the cause may be overdrying or waterlogging of the earthy coma. Adjust watering. Another reason may be that the substrate is too heavy. Replace the substrate with a more suitable one.
The color of the leaves is lost in the leaves, the leaves turn pale: the reason may be the lack of light. Adjust the lighting. If the plant is in shading for a long period, then it is necessary to accustom it to more light gradually.
Dry brown leaf tips: the cause may be too dry indoor air or lack of watering.
Dark spots appeared on the leaves: the cause may be hypothermia or drafts. Another reason could be illness.
Damaged: at low humidity, it can be damaged by spider mites.
indoor growing
Recommended species: Albizia Leonkaran (Albizia julibrissin) with light pink flowers, collected in heads with stalks, located on the tops of the upper shoots. There are varieties with bright pink flowers. Pinnate leaves of the 2nd order fold at night. Comb-shaped Albizia (Albizia lophanta) grows extremely fast. Yellowish flowers are collected in fleecy panicles.


