Aqueous solution of ammonia formula. Properties, use and storage of aqueous ammonia.
Ammonia water has found quite wide application in, and this is due primarily to its low cost and ease of use. Nowadays, two brands of this substance are produced in chemical plants. Brand "A" is used for various industrial needs, and brand "B" is used as in agriculture. On the latter and will be discussed in this article.
Description and composition
Simply put, ammonia water is a solution of ammonia in water. Externally, it is a clear liquid, which sometimes may have a yellowish tinge. It has a sharp specific aroma resembling the smell of rotten eggs.
Did you know? 10% ammonium solution is widely used in medicine and is called "ammonia".
The chemical formula of this substance is NH4OH
. The percentage of ammonia in this solution, as a rule, is about 30%: 70% is water, and about 24.6%.  In order to obtain such a solution, coke or synthetic ammonia is dissolved under pressure in 2 atmospheres. We also advise you to learn how to properly apply in gardening and horticulture. Ammonia has high volatile properties and is able to erode from the solution, if it is not properly stored. Therefore, under adverse conditions, it may well be unsuitable for use. The density of ammonia water is about 0.9 g per 1 cu. cm.
In order to obtain such a solution, coke or synthetic ammonia is dissolved under pressure in 2 atmospheres. We also advise you to learn how to properly apply in gardening and horticulture. Ammonia has high volatile properties and is able to erode from the solution, if it is not properly stored. Therefore, under adverse conditions, it may well be unsuitable for use. The density of ammonia water is about 0.9 g per 1 cu. cm.
Impact on the garden
Ammonia water is actively used for the kitchen garden, which is associated with its low cost and ease of use. For example, the price of a liter of this solution starts from 10 rubles per kg, while a kilogram of ammonium nitrate costs at least 25 rubles.  The ammonia-based fertilizer is suitable for almost any crop, making it one of the most sought-after and widely used on the market.
The ammonia-based fertilizer is suitable for almost any crop, making it one of the most sought-after and widely used on the market.
On the ground
The use of this fertilizer is important on a variety of soil types. It is always necessary to remember that this substance has an alkaline reaction, and therefore it can change.
The best effect is recorded when applied to well-treated land and, which contains a large amount.  This effect is due to the fact that in such a process the absorption of ammonia takes place much more intensively than on poor and light soils, which, in turn, indicates that plants absorb much greater amount of nitrogen, which is part of ammonia water.
This effect is due to the fact that in such a process the absorption of ammonia takes place much more intensively than on poor and light soils, which, in turn, indicates that plants absorb much greater amount of nitrogen, which is part of ammonia water.
Did you know? Nitrogen, the main component of ammonia,- one of the most common elements on Earth and the main component of air (78.09%).
On dry soil and soil with a light texture, the efficiency of ammonium hydrate will be slightly lower due to its high volatility. Ammonia simply evaporates from the treated area, if you do not close it to a sufficient depth.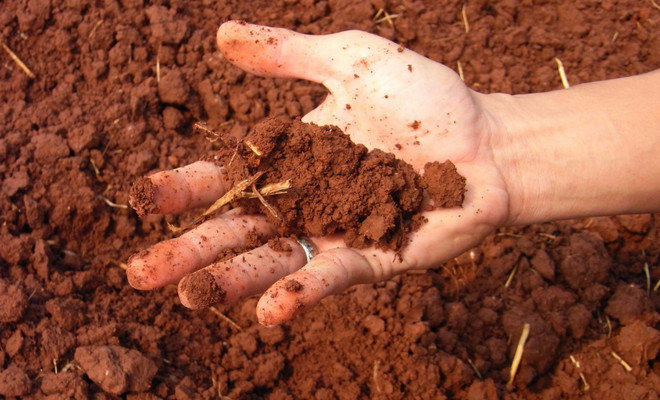  When using ammonia water on bound soils that are highly resistant to erosion and decay of particles (for example, loams), it is worth adhering to a special temperature regime, since high temperatures will contribute to the early decomposition of the substance molecules.
When using ammonia water on bound soils that are highly resistant to erosion and decay of particles (for example, loams), it is worth adhering to a special temperature regime, since high temperatures will contribute to the early decomposition of the substance molecules.
The optimum period of application will be early spring, when the average daily temperature does not exceed 10 ° C. Find out what works best for your plants -.
On culture
The use of ammonium hydrate will be extremely favorable in cultures for which an increased protein content is a positive property, for example, for. This is due to the fact that ammonia increases the concentration of this substance in plants.  Ammonium hydrate, like any other nitrogenous, contributes to the intensification of photosynthesis processes in plants and increases the green mass gain. Find out what are the ways In this regard, it is extremely important to comply with the norms of application, since there is a chance of getting low yields, but at the same time - with a rather intensive stem and leaves.
Ammonium hydrate, like any other nitrogenous, contributes to the intensification of photosynthesis processes in plants and increases the green mass gain. Find out what are the ways In this regard, it is extremely important to comply with the norms of application, since there is a chance of getting low yields, but at the same time - with a rather intensive stem and leaves.
Important! Do not allow the solution to fall on the plants, as this can damage and even completely kill the plant.
Ways and rates of introduction
Self-treatment with ammonia water is not a tricky business. It is enough just to irrigate with a solution of selected land plots at a depth of 10 cm on heavy soils and about 15 cm on light ones. This technique is generally accepted in and has the name "Fertigation".
Important! Fertigation will be extremely ineffective in hot weather due to the abundant evaporation of the active substance.
The best period for such treatment is the autumn period, approximately six months before the start of the active summer season.  But fertilization is not ruled out in the spring as part of complex preparations for sowing.
But fertilization is not ruled out in the spring as part of complex preparations for sowing.
Now it is worth saying a few words about the rates of:
- In case the plants are planted in narrow rows or the land intended for planting crops is fertilized, ammonium hydrate is poured with the help of specialized equipment. Spacing between coulters is about 25–30 cmand the amount of water needed on 1 ha - about 50 kg.
- Processing large areas on which planting of vegetable cultures is planned, fertilizer is brought in row-spacing. Norms - about 60 kg per 1 ha.
- Using ammonia water for industrial crops, it should be remembered that the rates are somewhat increased - up to 70 kg per 1 ha.
 High concentrations of ammonium in the air can cause nausea, dizziness, loss of orientation, abdominal pain, coughing and choking. If you experience these symptoms, you should immediately stop treatment and leave the area saturated with ammonia fumes. The main "competitor" of ammonia water is urea, which contains almost twice as much nitrogen. If it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, it is recommended to rinse them with a large amount of clean boiled water and if complications arise, seek medical help.
High concentrations of ammonium in the air can cause nausea, dizziness, loss of orientation, abdominal pain, coughing and choking. If you experience these symptoms, you should immediately stop treatment and leave the area saturated with ammonia fumes. The main "competitor" of ammonia water is urea, which contains almost twice as much nitrogen. If it comes into contact with the skin or mucous membranes, it is recommended to rinse them with a large amount of clean boiled water and if complications arise, seek medical help. Storage features
Containers for storage of ammonium hydrate can serve as steel tanks with hermetic properties, as well as fuel tanks. Often, ammonia water is delivered by the manufacturer in special tanks, which must be returned after a certain period.  If you intend to store ammonia hydrate in your home, keep in mind its volatile properties and look for a container that has good sealing properties, otherwise the entire potential of this fertilizer will simply evaporate.
If you intend to store ammonia hydrate in your home, keep in mind its volatile properties and look for a container that has good sealing properties, otherwise the entire potential of this fertilizer will simply evaporate.
This fertilizer, despite the small danger it represents, is perfect for any gardener, both with experience and novice.
By observing all precautions, you will undoubtedly benefit greatly from the use of this substance. Good luck to you and your garden!
Was this article helpful?
Well no
And hydrogen. It is a gas without color, but with a pungent odor. The chemical composition reflects the formula of ammonia - NH 3. Increasing the pressure or lowering the temperature of a substance leads to its transformation into a colorless liquid. Gaseous ammonia and its solutions are widely used in industry and agriculture. In medicine, 10% ammonium hydroxide is used - ammonia.
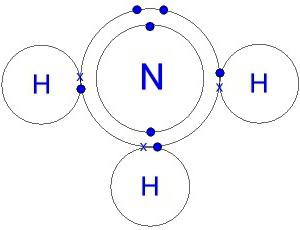
The structure of the molecule. Ammonia Electronic Formula
The hydrogen nitride molecule is shaped like a pyramid, at the base of which is nitrogen bound to three hydrogen atoms. N – H bonds are strongly polarized. Nitrogen strongly attracts the bonding electron pair. Therefore, a negative charge accumulates on N atoms, a positive one is concentrated on hydrogen. An idea of this process is provided by a model of the molecule, electron and ammonia.
Hydrogen nitride is very soluble in water (700: 1 at 20 ° C). The presence of practically free protons leads to the formation of numerous hydrogen "bridges" that connect the molecules to each other. Features of the structure and chemical bonds also lead to the fact that ammonia is easily liquefied with increasing pressure or lowering the temperature (-33 ° C).

origin of name
The term “ammonia” was introduced into scientific use in 1801 at the suggestion of the Russian chemist Y. Zakharov, but the substance of humanity is familiar from deep antiquity. Gas with a pungent odor is released when rotting waste products, many organic compounds, such as proteins and urea, during the decomposition of ammonium salts. Historians of chemistry believe that the substance was named in honor of the ancient Egyptian god Amon. In North Africa there is an oasis of Siwa (Ammon). Surrounded by the ruins of an ancient city and a temple, next to which there are deposits of ammonium chloride. This substance in Europe was called the "salt of Amun." There is a legend that the inhabitants of the Siwa oasis sniffed salt in the temple.

Hydrogen nitride production
The English physicist and chemist R. Boyle burned manure in experiments and observed the formation of white smoke over a stick soaked in hydrochloric acid and introduced into the stream of the resulting gas. In 1774, another British chemist D. Priestley heated ammonium chloride with slaked lime and released a gaseous substance. Priestley called the compound “alkaline air”, because its solution showed properties. Boyle’s experiment in which ammonia interacted with hydrochloric acid was explained. Solid white color occurs when the contact molecules of the reactants in the air.
The chemical formula of ammonia was established in 1875 by the Frenchman K. Berthollet, who conducted an experiment on the decomposition of a substance into its constituent components under the action of an electric discharge. Until now, Priestley, Boyle and Berthollet's experiments have been reproduced in laboratories for the production of hydrogen nitride and ammonium chloride. An industrial method was developed in 1901 by A. Le Chatelier, who received a patent for a method for synthesizing a substance from nitrogen and hydrogen.
Ammonia solution. Formula and properties
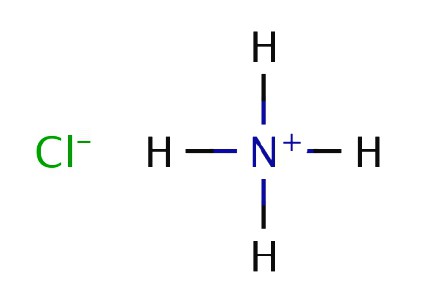
An aqueous solution of ammonia is usually recorded in the form of hydroxide - NH 4 OH. It exhibits the properties of weak alkali:
- dissociates into ions NH 3 + H 2 O = NH 4 OH = NH 4 + + OH -;
- paints phenolphthalein solution in raspberry color;
- interacts with acids to form salt and water;
- precipitates Cu (OH) 2 in the form of a bright blue substance when mixed with soluble copper salts.
The equilibrium in the reaction of the interaction of ammonia with water is shifted towards the original substances. Pre-heated hydrogen nitride burns well in oxygen. Nitrogen is oxidized to diatomic molecules of the simple substance N2. Ammonia also exhibits reducing properties in reaction with copper (II) oxide.

The value of ammonia and its solutions
Hydrogen nitride is used in the production of ammonium salts and nitric acid - one of the most important products of the chemical industry. Ammonia is used as a raw material for soda production (by the nitrate method). The content of hydrogen nitride in an industrial concentrated solution reaches 25%. In agriculture, an aqueous solution of ammonia is used. The formula of liquid fertilizer is NH 4 OH. Substance is directly used in the form of top dressing. Other ways to enrich the soil with nitrogen - the use of salts of chlorides, phosphates. In industrial conditions and agricultural premises it is not recommended to store together mineral fertilizers containing ammonium salts with alkalis. When the integrity of the packaging is compromised, the substances can react with each other to form ammonia and release it into the indoor air. Toxic compound adversely affects the respiratory system, the central nervous system of man. A mixture of ammonia and air is explosive.
Ammonia water
The modern chemical industry offers a large amount of liquid nitrogen fertilizers, the most common of which is ammonia water. The cost of a unit of active substance in ammonia water is 1.5-2 times cheaper than in ammonium nitrate. In addition, as shown by production tests, labor costs for its application are reduced three times, because there is no need to prepare fertilizers for application, and all operations for use (for loading, unloading, application) are fully mechanized. That is why ammonia water is widely used in domestic agricultural enterprises. However, it also has certain features that should not be forgotten. Ammonia water (technical water ammonia) and NH 4 OH is a 25% solution of ammonia in water. Colorless or yellowish liquid with a pungent smell of ammonia contains 20.5% nitrogen (second grade - 16-18%), it can be used for any soil and all crops with a mandatory roll in the soil to a depth of 10-15 cm. In the USSR in 80 -years on the field whether almost 40% of nitrogen fertilizers are applied in the form of ammonia water. In the USA, up to 50% of nitrogenous fertilizers are applied in liquid form. In Ukraine, only about 15% of farms use ammonia water. This is due to the lack of equipment and equipment for storage, transportation and its introduction into the soil.
Ammonia water is used to feed grown crops as nitrogen fertilizer. Before it increases the protein content in plants. Perform situations where plants need excess protein (for example,). Ammonia water (like any nitrogen fertilizer) also stimulates the growth of green mass. Therefore, it is important not to overdo it with the application rate of the drug: with an excess of ammonia water, it is easy to get an excessive amount of green mass and less grain. It is very important that ammonia water gets into the soil, but not into the zone of the root system and not into the zone of seed germination, but deeper than the seeds or away from it, between the rows.
If you just pour the solution with the soil, then there will be large ammonia losses through evaporation and money will be thrown to the wind. So, ammonia water must be earned in the soil. It is desirable that the soil was at the same time wet.
Ammonia water can inhibit the plant, burning its roots for a small temporary space between application and seeding or failure to comply with the application depth. However, if ammonia water was introduced in advance, roughly speaking, six months before sowing, for example, it was brought in October, sown in March, then in principle there can be no negative impact. During the spring application you need to remember several rules: make 1-2 weeks before the crop is sown, just before the crop is sown or at the same time as the crop is sown.
Ammonia water is a very good fertilizer. Due to its liquid form, it can be applied very carefully, evenly, to a certain depth and over large areas.
If we talk about the effects, the ammonia water affects the harmful entomofauna, in particular, suppresses and repels soil insects. If you add ammonia water below the laying of the seed bed, then for a while it scares away the soil pests that destroy the seed that sprouts. Ammonia water is alkaline and may affect soil acidity.
The best way to soil is emphatic, in particular, in the fall. Fertilizer can be applied both for winter plowing, and in spring for presowing cultivation. It is applied to all soils and all crops. Ammonia water is also used to feed tilled crops.
Apply it mainly separately from conventional (dry) fertilizers. According to some data, the effect of ammonia water on winter rye, barley, potatoes, and corn is similar in effect to ammonium nitrate.
With the use of ammonia water arise several difficulties. The concentration of N in ammonia water is about 22%, in urea - 45, in nitrate - 34.6%. It is noticeable that ammonia water has a low ammonium content. Due to the fact that it is still liquid, it occupies a certain volume. In order to introduce ammonia water, households must necessarily have special means, equipment for the transport of aggressive means, which is ammonium. Also in the farm should be a good, high-quality unit for the introduction of ammonia water.
Ammonia water has its price peaks and the period of their fall. When the time of the introduction of nitrogen com- pounds ends, the prices for its derivatives, naturally, decrease. At this moment, and it is desirable to buy ammonia water, the end of which, by the way, is limited. This means that the company needs to have a warehouse where, during the course of 2-3 months, there will be a product. It should be tight, with a stable capacity.
Equipment for the storage of ammonia water requires compliance with a lot of special tolerances: ecology, sanitary facilities, etc .. Accordingly, it is necessary to cooperate with these services. It is necessary to "be friends" with the manufacturer. They buy a tank at the factory, then it is brought, then you need to download the product, transport and save. Rolling stock is the property of either the plant or the railway, so there are deadlines for unloading. It is impossible to keep the tank for a long time, because they will immediately issue fines upon returning the container. Therefore, the housekeeping needs both special transport, and storage, and machines for ammonia water introduction.
Within a radius of more than 30 km from suppliers, the following should be provided for intermediate storage in the riparian and (or) deep-water storage facilities. Freight ammonia water in the near warehouses delivered in railway tanks with lower and upper manholes. Ammonia water is pumped from the rail tank cars to the railroad tank reservoirs. In the absence of the rail train, the motor pump is pumped directly into the car tanks. From railroad trains to deep-well warehouses transported ammonia water by road or tractor transport.
For storage of ammonia water using steel tanks that are sealed. It is allowed to use tanks from under tractor fuel. In the field, ammonia water is more often delivered by tractor trailer tanks (8-10 m 3), equipped for forced filling of cultivators through hermetic, easily replaceable couplings. To reduce the space of vehicles, it is recommended to install field tanks in 25-50 m 3 and fill the cultivators just from these tanks. For making ammonia water using various cultivators.
The competitive analogue is CAS (carbamide-ammonia mixture), where nitrogen is contained in three forms. CAS has buffer properties (the ability to maintain the acidity of the solution, even in the case of adding substances with an acid or alkaline reaction, of course, in certain aisles). Thanks to this property, CAM can be used in tank mixes with pesticides. Regarding the minuses, it is worth noting a higher cost than in ammonia water, as well as the ability to cause corrosion of metals (stainless steel, ceramics, polymers are sustainable).
Everyone who works with ammonia water should be well aware of the main features, safety requirements and strictly adhere to the rules of storage, transportation and incorporation of ammonia water into the soil.
Ammonia water, introduced under spring cultivation in the amount of 90 kg of active ingredient per 1 ha, in the same year provided a harvest of 32.2 centners of stems, 6.5 centners of fibers and 3.4 centners of seeds per hectare. [...]
Ammonium nitrate Ammonium sulfate Urea Ammonia water Liquid ammonia Sodium nitrate Calcium nitrate Ammonium chloride Calcium cyanamide others [...]
Ammonia water is introduced into the peat pile and after that the peat is collected in caravans (piles) of 1000 tons or more each. In these burtae, peat is composted for 2-3 months, during which ammonia nitrogen introduced into peat under the influence of nitrifying microorganisms is partially converted into the nitrate form of nitrogen. The finished peat-mineral ammonia fertilizer according to a given technology of its production due to the introduced mineral fertilizers should have in its composition 0.4 "% of assimilable mineral nitrogen, 0.4% P2O5 and 0.4% CgO. However, the actual content of digestible nitrogen in practice is often This is mainly due to the ammonia loss of ammonia due to its volatilization in the process of ammonization of peat, and the loss of nitrogen compounds from the peat bursts due to their leaching with atmospheric precipitations. Even assuming that no loss of nitrogen and other plant nutrients from TMAU will occur, then, in order to introduce the average commonly used standard of the active elements under such, for example, a culture like potatoes, 60 kg of nitrogen, 60 kg of P2O5 and 60 kg of CgO will require 15 tons of TMAU. These doses of TMAU are usually recommended: for potatoes and other tilled crops (corn, sugar beet) - 15-20 tons, for vegetables - 30 tons and for grains - 10 tons [...]
Ammonia - ammonium sulfate, ammonium chloride, liquid ammonia, ammonia water, ammonia carbonate. [...]
Ammonia sulphite cyanide citrate solution: 30 ml of KS1CH solution, 60 ml of Na23205 solution, 20 ml of ammonium citrate solution are added to 325 ml of ammonia water (20 ml) and the solution is adjusted to 1 l with water. The solution can be stored for several months. [...]
Ammonia water containing impurities of ammonium carbonates is continuously discharged into the collection, from where it is pumped over to the urea plant for the production of liquid fertilizers. In the same absorber for cleaning blown ammonia from the safety valves of the apparatus, from the ammonia evaporator, collections, urea solution and iron ammonium salts. [...]
Ammonia water is a solution of synthetic or coke-chemical ammonia in water; it is produced in two grades. The first grade contains 20.5% nitrogen (25% ammonia), the second 16.4% nitrogen (20% ammonia). Coke chemical ammonia also contains hydrogen sulphide and minor amounts of phenols, rhodium, cyanide and some other compounds. [...]
Ammonia water can be used in the composition of the main fertilizer in the spring, a few days before sowing of spring crops; in the summer in top dressing; before sowing winter crops; in a busy pair and under the autumn plowing. Special machines close up fertilizer on light soils to a depth of 12–16 cm and on heavy ones — 8–12 cm. Applying high doses of aqueous ammonia in autumn on light sandy soils involves the loss of ammonia, because part of the ammonium is not absorbed by the soil. [... ]
Ammonia water is a good fertilizer for potatoes, beets, grain breads and vegetable crops. As an example, one can cite the results of four-year VIUA experiments in which the effect of aqueous ammonia and ammonium nitrate on the potato crop was compared (Table 53). [...]
Ammonium nitrate. . Ammonia water. [...]
Ammonia water was introduced during autumn plowing under spring wheat on an area of 10 hectares. Fertilizer consumption per 1 ha - 280 kg, depth of seal - 25-27 cm (at the bottom of the furrow - trickle). [...]
The effect of ammonia water on cabbage harvest (c / ha). [...]
When ammonia water is introduced into the soil, ammonia is adsorbed by colloids and therefore moves poorly in it. Over time, ammonia nitrogen nitrifies and then becomes more mobile, migrating with the soil solution. Compared to liquid ammonia, the use of ammonia water as a fertilizer is technically simpler and safer, but its major drawback is its low nitrogen content, resulting in increased costs associated with transporting, storing and applying fertilizer to the pulp. Therefore, the use of ammonia water is advisable only in farms located near enterprises producing this fertilizer. [...]
The effectiveness of ammonia water under spring wheat. [...]
Feeding with cannabis ammonia water should be carried out in the phase of formation of three pairs of leaves. Feeding in the later phases of development significantly reduces its effectiveness. [...]
Its solubility in water is greater than that of all other gases: one volume of water absorbs about 700 volumes of ammonia at 20 ° C, 10% ammonia solution is marketed under the name “ammonia”. An 18-20% solution is called ammonia water and is used as a fertilizer. Liquid ammonia is a good solvent for most organic and inorganic compounds. [...]
The data show that ammonia water is an effective nitrogen fertilizer for spring wheat: a yield increase of 2.8 centners per hectare was obtained. [...]
The focus on the use of ammonia water (on average 20.5%\u003e 1) as a liquid nitrogen fertilizer, rather than liquid ammonia (82% S) in our country was associated with the need to maximally facilitate the implementation of safety requirements for storage, transportation and applying these fertilizers to the soil. The use of liquid nitrogen fertilizers allows you to fully mechanize the work on their loading, transportation and introduction into the soil. In this case, loading and unloading operations, transportation and storage are carried out in a closed fully sealed cycle (pump - pipe - tank - storage tanks). At the same time labor productivity in agriculture sharply increases. In addition, the loss of solid fertilizers that occur during their transportation, storage and application to the soil, with the transition to liquid fertilizers is almost eliminated. According to the VIUA, in the transition to the production and use of aqueous ammonia, the total costs are reduced by more than three times compared with the cost of solid fertilizers. [...]
Corrosion in the desorption columns of ammonia from ammonia water, free from acid gas impurities, is negligible, which makes it possible to use steel or cast iron equipment. With a high content of ammonia in the gas being purified, the heat released during absorption starts to have a serious effect on the process. To ensure the isothermal mode of absorption, this heat must be removed. One of the possible solutions is the circulation of ammonia water in the absorber-refrigerator system, although it allows heat to be removed, but does not provide isothermality and, as noted above, leads to significant ammonia losses as a result of violation of the countercurrent principle. [...]
Example 7. To determine the limiting concentration of ammonia water, which can be obtained by passing a gas containing 3% of the mass, ammonia, through a nozzle irrigated with water. Scrubber pressure 2 at. The solubility of ammonia in water under these conditions is characterized by Henry's law: P = 2000 X mm Hg (where X is the molar fraction of ammonia in the solution). [...]
Most of the water used at enterprises is recycled. The main effluents are ammonia water from coking plants, blow-through of working cycles of wet gas cleaning of blast furnaces and oxygen converters, and runoff from the cold rolling shop. [...]
Given that the main raw material for the production of ammonia water is synthetic ammonia, the efficiency of the production of ammonia water is completely dependent on the economy of ammonia production. [...]
The effectiveness of nitrogen fertilizers, especially ammonia water, increases if they are made together with superphosphate. Thus, the yield of maize silage mass from 105.9 centners (the third option) rose to 127.4 centners, or 36.2 centners per hectare. And with the joint introduction of superphosphate with ammonium sulfate yield increase amounted to 26.3 centners per hectare (29.9%). However, it should be noted that the increase in dry matter yield under the action of ammonia water and, in particular, under the influence of ammonium sulfate, was significantly lower compared with the increase in maize silage weight. [...]
Data tab. 3 show that the best way to make ammonia water is a combination of pre-sowing with fertilizing during the growing season. In this case, the yield increase of the silage mass was 106.5 centners per hectare, while at the same rate of aqueous ammonia introduced before planting, the yield increase was 75.5 q / ha. [...]
Adding industrial waste containing molybdenum to ammonia water is not the only way to use it. They can be used for the manufacture of liquid complex fertilizers. Molybdenum wastes are suitable for the production of molybdenum superphosphate and nitrophosphate. [...]
In the experiment of 1862, the effect of urea was compared with the effect of ammonia water (22 ‘\u003e) and ammonium sulfate (21%) on spring wheat. The experience was done on gray forest loam in the 4th field of seed crop rotation. Ammonia Veda under spring wheat was introduced in the fall under the plow, and urea and ammonium sulfate in the spring under the cultivation at the rate of 60 kg of nitrogen per hectare. Plots of 800 square meters. m laid in triple gtov-! Wed. Spring homony has been sown Rmotmyam m L\u003e; April 23, seeding rate of 200 kg per hectare. [...]
For the construction of deep storage facilities for the temporary storage of ammonia water in agricultural conditions, standard designs of 50 m3 warehouses have been developed with the installation of two tanks of 25 m3 each (Project No. 24-117-У1) and a capacity of 100 m3 also with the installation of two tanks of 50 m3 each (No. project 24-117-U). [...]
In recent years, we have studied the action of ammonium chloride (Moss), ammonia water (M), and ammonia carbon No. 4 (compared to standard forms of nitrogenous fertilizers against the background of RK (Table 6). [...]
Ammonium carbonate [(HSH) 2S03] is a crystalline product. It is obtained by saturating ammonia water with carbon dioxide, followed by distilling off ammonium carbonate at a temperature of 70-80 ° or as a result of the interaction of gaseous ammonia and carbon dioxide in the presence of water vapor. Ammonium carbonate is very unstable. In the open air, it decomposes with the release of ammonia and goes into ammonium bicarbonate. The technical product contains 21-24% nitrogen and is a mixture of ammonium carbonate [(N114) 2003], ammonium bicarbonate (] MH4H03) and ammonium carbamate. [...]
Based on the above data, ammonium water and synthetic urea can be recommended for ordinary medium-duty and powerful chernozems along with ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulphate. Ammonia water should be used for feeding corn and in pre-Caucasian chestnut-carbonate soils. [...]
At the Erastov Experimental Station (the author of the article and graduate student F. L. Moskalenko) studied the effect of ammonia water on the growth, development and yield of maize at different periods of application: simultaneously with the sowing, during the autumn soil preparation and under the pre-sowing cultivation of the soil. At the same time, some features of the action of this fertilizer on the germination and field germination of corn seeds were identified. Ammonia water, brought in normally 30 kg of nitrogen per 1 ha in the same row as seeds, to a depth of 10 cm per day of sowing reduced seed germination by 80-90%, and when increasing the nitrogen rate to 60 kg per 1 ha, seedlings died completely. When fertilizer was applied in the same doses, 5-6 cm away from the row of seeds and in a row with seeds, but 6 days after they were sown, there was no negative effect on the germination energy and field germination of seeds. The soil layer of 5-6 cm well protected seedlings of seeds from the poisonous effect of ammonia, and thus created favorable conditions for the absorption of its plants. [...]
Nitrogen fertilizers. The main nitrogenous fertilizer produced in the CMEA member countries is ammonium nitrate. In the GDR, only lime-ammonium nitrate is produced due to the ammonia explosion hazard. Ammonium sulfate in relatively large quantities is produced as a by-product in the coke-chemical production and production of caprolactam in the USSR and the GDR. Recently, the production of urea (urea) as the most concentrated nitrogen fertilizer containing 45-46% N has increased dramatically. Other nitrogen fertilizers (sodium and calcium nitrate) are produced in small quantities. Of the liquid nitrogen fertilizers in the USSR, ammonia water is used in a relatively large volume; it is also used in the GDR and Poland. In the future, a transition to the production of anhydrous ammonia containing 82% N. is planned [...]
When coking coal forms a significant amount of hydrogen sulfide. Purification of gas from hydrogen sulfide by ammonia water makes it possible to obtain valuable products - ammonium sulfide and ammonium polysulfide, which are insect fungicides. [...]
According to the project, especially in the first embodiment, capital costs for the construction of an enterprise producing ammonia water are reduced by one quarter compared to the cost of building a plant for the production of solid nitrogen fertilizers, since much less equipment, metal, pipes, cable products and other materials and simplified plant layout. All equipment for the production of ammonia water, starting from the stage of natural gas conversion and ending with the ammonia synthesis shop, is housed in one unit. According to design developments, the cost of nitrogen contained in ammonia water, compared with nitrogen in solid fertilizers is reduced by about 30-40%. Based on VIUA data, the total cost of 1 ton of nitrogen ex-soil could reach: in ammonia water 77.4%, in ammonium nitrate 100%, in urea 104% - Thus, by total costs, including the scope, ammonia water is more economical solid fertilizers. [...]
In areas of insufficient moisture on black earth soils, common forms of nitrogen fertilizers are ammonium sulphate and ammonium nitrate. Oli are used in small quantities for the main application together with phosphate fertilizers for winter wheat sown on non-steam predecessors, corn and other tilled crops. Experiments conducted on black soil, found a positive impact on the yield of maize new forms of nitrogen fertilizers - ammonia water and a more concentrated form - synthetic urea. [...]
The use of forms of nitrogen fertilizers for grain crops in Bashkiria. The effectiveness of some forms of nitrogen fertilizers and methods of applying ammonia water for corn on black soil. [...]
The effect of liquid nitrogen fertilizers on yields and the quality of vegetable crops — beetroot, tomato, early and late cabbage — was also studied. All experiments confirmed that the use of ammonia water significantly increases the yield of vegetables. Similar results were obtained in experiments with grain crops (spring wheat, oats, barley). At the same time, soil liming improved the effect of fertilizers. [...]
Studies have shown that urea is a good fertilizer, especially when feeding winter rye and sugar beet. Extensive production tests have shown the advantage of using ammonia water as a fertilizer. At the same time, it became clear that there is an urgent need to organize transportation and application of ammonia water without loss of nitrogen. To do this, it is necessary to organize the delivery and introduction of ammonia water on collective and state farms by the combine in special tanks for urgent return, as is done in the United States and other countries. It is also necessary to study the conditions for more efficient use of ammonia water. [...]
Despite the fact that the post: wheat twice fell under heavy rain from hail ?.: and the total harvest was small (11.4 d / ha), the effect of fertilizers was clearly manifested. The yield increase from urea was 2.2 c, from ammonium sulfate - 4.5 c, from ammonia water — 0.8 c per hectare. [...]
The alkaline solution is fed to desalted oil to bind thermally unstable calcium and magnesium chlorides. Neutralize organic acids and hydrogen chloride. Not most refineries practice additional supply of ammonia water in the sludge lines of atmospheric columns to maintain the pH of drainage water at a level of 8-9. [...]
In areas of Eastern Siberia and the Far East, podzolic soils are the most common, on which, as a rule, the use of nitrogen, phosphorus and potash fertilizers is very effective. In broad production tests on the use of ammonia water, carried out in 1957 in the Irkutsk region on areas of several thousand hectares, the increase in the yield of wheat from average doses of nitrogen in ammonia water was usually expressed as close to 10 c / ha. ]
Mineral fertilizers are obtained from mineral substances as a result of mechanical or chemical processing, as well as synthetically. Mineral fertilizers by the nature of the nutrients they contain are divided into five types: 1) nitrogen, 2) phosphorus, 3) potash, 4) lime, and 5) micronutrient fertilizers. Of the nitrogen fertilizers currently the most common are: ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, ammonia water and urea; from phosphate: phosphate rock and superphosphate; from potash; potassium chloride, sylvinite; lime: ground limestone, meadow tuff, marl, defecation mud, gypsum; of micronutrients: manganese, boric, copper and molybdenum. [...]
The flue gases to be cleaned pass through a stage of concentration by electrocyclic gas cleaning. After concentration, the volume of gases is 33.5 thousand m / h with a nitrogen oxide content of 21.4 g / m3 and a temperature of 29 ° C. For the purification of these gases, selective catalytic reduction with ammonia is used. When preparing technical proposals, two options were considered: 1 - using evaporated ammonia water as a reducing agent; 2 - ammonia gas. [...]
At the same time, the regeneration of solutions is complicated not only because of lower ammonia pressures over the solutions, which can be disregarded, since at 95-105 ° C both cyanides, bicarbonate, and ammonium hydrosulfide are completely hydrolyzed. The complication is due to the fact that in these conditions, during desorption of ammonia, absorbed carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide and other acid gases are inevitably desorbed. Therefore, it is impossible to obtain standard ammonia water or ammonia without additional purification of the solution or vapors. [...]
The method of sequential processing of coal with sulfuric acid and ammonia is a universal method of utilization, spent acids, both concentrated and diluted. It consists of the following: Sulfuric acid is processed) crushed tertiary lignite, briquette dust or coal waste in ratios of 1: 1 or in other ratios. The resulting acid mixture (products of coal sulfonation and excess sulfuric acid) is neutralized with gaseous ammonia, ammonia water or ab-gases of nitrogen-fertilizer production containing ammonia. The resulting loose bulk mass can be used as a complex organic-ammonia fertilizer. [...]
When absorbing ammonia from gases containing carbon dioxide, it should be borne in mind that the rate of absorption of the latter is limited by diffusion in the liquid phase. Therefore, it is more expedient to use for absorption apparatuses in which a short contact time is possible “intensive mixing of the gas phase (turbulent diffusion). This reduces the degree of absorption of both components of the gas mixture, but the completeness of absorption of carbon dioxide is particularly small. A short contact time is also used in the selective absorption of hydrogen sulfide by ammonia water from coke oven gas containing large amounts of CO2. [...]
The production of ammonia is a complex set of units, workshops, departments, equipment, interconnected technological chain. At various technological stages of ammonia production, from the synthesis column to the pouring of liquid ammonia into railway tanks for shipment to the consumer, its emissions to the atmosphere are possible. The most significant emissions of ammonia into the atmosphere occur when purging inert gases and tank gases generated during the filling of various capacities with ammonia. In addition, ammonia may be emitted into the atmosphere through various equipment leaks, as well as when filling rail tank cars. One of the possible solutions to the issue of protecting the air from ammonia emissions is the centralized collection and disposal of gas emissions with the production of ammonia water as a commercial product.
There is a chemistry class in every school, every high school and most educational institutions. Water ammonia is one of the substances that need to be equipped with a similar room. Consider in more detail what it is.
Binary compound of nitrogen and hydrogen, the chemical formula of which looks like this: NH3, is the most important of the hydrogen compounds of nitrogen and is called ammonia. In total there are several known compounds of hydrogen with nitrogen.
Aqueous ammonia is a clear liquid, representing nothing more than a solution of ammonia in water, which has a very strong smell of ammonia. Another name for the solution, which can sometimes have a yellowish tint, is ammonia water.
Technical ammonia liquid;
Water technical ammonia;
Water chda.
Chemical properties of ammonia
During chemical reactions in many cases, due to the presence of an indivisible electron pair in the composition, ammonia acts as a complexing agent. In a different way, this is called the Brønsted base. Ammonia belongs to a number of reactive compounds. Due to the presence of the same lone electron pair (at the nitrogen atom N), for ammonia, the addition reactions are especially characteristic. They are also easy to implement.
Receiving aqueous ammonia
A German physicist discovered the physicochemical basis of the method of ammonia production in industry. This method is named after him - the Haber process. This industrial method of producing ammonia is based on the direct reaction of the interaction of two chemical elements: hydrogen and nitrogen. The formula for preparing this compound at high temperature and pressure using a catalyst is as follows:
In order for the process of obtaining ammonia according to the formula to be successful, the following conditions must be met:
Temperature - 500 degrees Celsius;
Pressure - 350 atmospheres;
When using a catalyst, the ammonia yield is 3%.
During the reaction, heat is released and the volume decreases. Under industrial conditions, the principle of circulation is more often used when ammonia is removed, or removed, by cooling. The nitrogen and hydrogen remaining outside the reaction is sent back (to the synthesis column). This process is more economical than a similar one, with a higher yield, using high pressure.
Application
Ammonia water is very widely used in the chemical industry, being one of the important products. Every year the world produces 100 million tons of ammonia. Ammonia water is used to produce nitrogen-based fertilizers: ammonium nitrate and ammonium sulfate, urea. Nitric acid, soda ash and polymers are also produced from it. Used in the production of dyes, manganese, ferroalloys, and other electrolytes. Among other nitrogen fertilizers - ammonium nitrate, ammonium phosphate, carbamide. Ammonia water is also used to produce some explosives and other chemical products in the pharmaceutical and metallurgical industries.
Being a weak base when interacting with acids, ammonia water has a neutralizing effect on them. Aqueous ammonia is widely used for refrigeration and equipment. It is a refrigerant (R 717), can also be used as a solvent.
Ammonia (10% solution of ammonia water) is widely used in the medical field.
Ammonia ChDA on a water basis serves in medicine as a reagent for analysis. It is used both in analytical chemistry and in chemical plants for the production of pure chemical products.
Ammonia water has found quite wide application in agriculture as fertilizer and for ammonization of feed in animal husbandry.
Storage and transportation
It is better to transport ammonia water in glass or steel containers. It can be stored in it for easy transportation. Liquid ammonia is transported in special chemical tanks intended for road freight and rail transport, in steel cylinders and tankers, as well as by movement through a pipeline.
The temperature of liquid ammonia, cooled and ready to be transported, should not exceed - 31.5 degrees Celsius. It is measured on the flange that connects the pipeline of the tanker and the loading line.
Aqueous ammonia is transported in sealed containers on the rail, road and water transport in accordance with the rules of transportation of high-risk goods acting on a specific type of vehicle. Tanks must be filled to 95%, not more. Hatches must be sealed and must be sealed.
Ammonia water is divided into two types. The product of brand A is transported in ammonia trucks and railway tanks. Mark B is transported in tanks with a lower discharge and in ammonia carriers.
Precautionary measures
At normal temperatures and atmospheric pressure, ammonia is gaseous and refers to combustible gases. Ammonia gas can self-ignite at 650 degrees Celsius, the minimum ignition energy is approximately 680 mJ.
A mixture of ammonia and air in a ratio of fractions of 15-28 to 100 is explosive, and liquid ammonia belongs to the class of slow-burning substances.
To extinguish a fire of liquid ammonia or gaseous ammonia, automatic fire extinguishing installations are used, filled with water, non-combustible gas or foam.
Ammonia is a toxic compound with the maximum permissible concentration of the active substance (MAC) in the air of working areas of industrial premises 20 mg / m 3.
Gaseous ammonia can cause tearing and suffocation in a person due to acute irritation of the mucous membranes of the throat, nasal and oral cavity, eyes.
If a jet of gas or a drop of liquid ammonia gets on the skin, it can cause a severe burn. In this case, the affected area should be immediately washed with running cold water and apply lotions (containing 3-5% citric or acetic acid).
If the victim breathed air with a high content of ammonia, he must immediately get out into the fresh air so that the respiratory system is cleansed.
In case of contact with liquid ammonia on the mucous membrane of the eyes, you should quickly flush the eyes with a large amount of water jet.
Precautions when working with liquid ammonia
If your work includes interaction with this substance in any form, you need to follow the rules:
Use personal protective equipment (gas mask, mask, protective apron or suit);
Hands should be protected from frostbite: wear insulated rubber gloves;
To protect the feet in winter, the production is given boots with rubber or felt boots with rubber soles; in the summer, rubber boots or other rubberized shoes are shod.

